前言:Linux 指令 ------ 运维 / 开发的 "效率手术刀"
如果你是 Linux 新手,是不是常对着终端发愁:"想看个日志文件怎么弄?""怎么快速找到某个程序在哪?";如果你是老用户,是不是也偶尔忘了某个指令的实用选项?
其实 Linux 日常工作中,80% 的场景都靠这些基础指令撑起来------ 比如移动文件、查看日志、监控进程、搜索文本...... 本文就把这些高频指令按 "使用场景分类",逐个拆解「功能 + 常用选项 + 实战示例」,看完就能直接复制到终端里用,帮你从 "指令小白" 变成 "终端快手"
一、"一切皆文件"
我们在学习linux系统中要去理解一切皆文件的概念,在我们学习c语言和c++时常用的输入/输出(printf,scanf,cout,cin)的本质都是文件操作(fopen,fstream),我们使用的如此方便只是因为系统已经帮我们打开了。系统打开了extern FILE* stdin/stdout/stderr,我们没有看到这些文件只是因为这些被分装在了printf...里面。系统做这些是因为我们的代码写完了还需要进行编译器的编译,这都是为了方便显示,打开这三个是因为这三个默认已经够用了。
而且我们认为终端也是文件,如果在同时打开多个终端我们可以在一个终端给别的终端上输出信息。
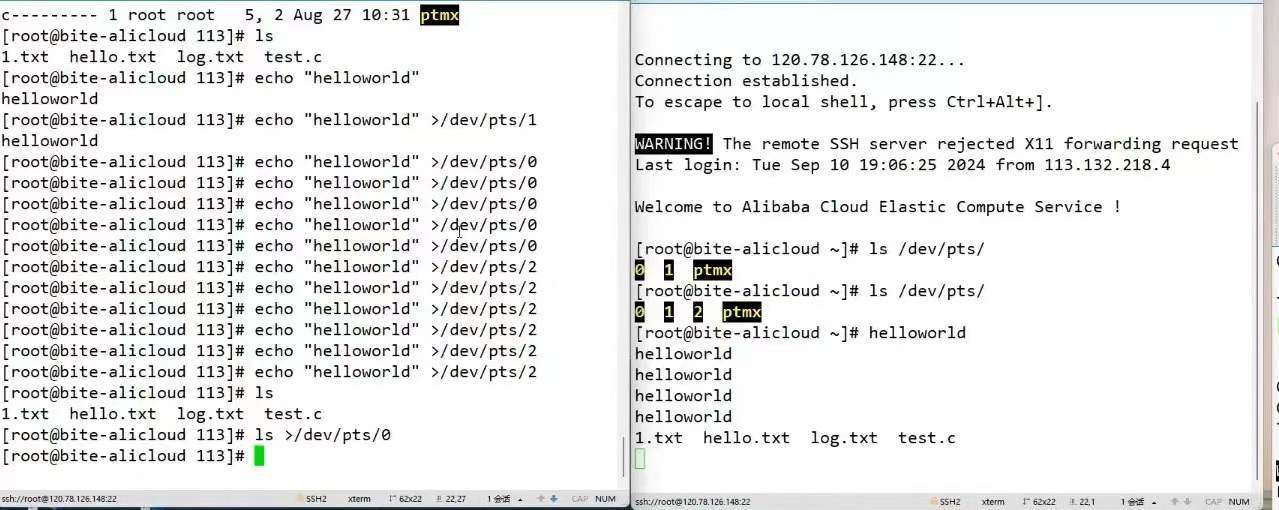
证实:
我们使用echo指令(后面有解释),其实是把字符串写到显示在屏幕上的文件(写入不是打印),当然我们也可以把字符写到别的文件里,如下
[root@VM-0-12-centos ~]# echo "hello world" > hello.txt
[root@VM-0-12-centos ~]# cat hello.txt
hello world关于这个>符号:如果文件不存在就新建,如果存在就清空。所以我们可以用它新建普通文件,清空文件,如果写入的时候不想清空原来的内容可以使用>>
二、文件类型
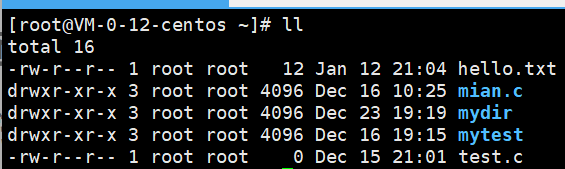
文件类型以开头的那个字符来判断
-:普通文件
d:目录文件
c:字符文件,键盘,显示器,终端,输入的数据具有顺序性
d:块设备文件,磁盘(我们电脑上的c盘,d盘)

l:链接文件
p:管道文件,用来做间接通信
注意:
Linux下不以文件后缀做区别,但这个后缀还是有用的,系统不关心后缀但工具(gcc)关心后缀。
三、文件操作与查看
3.1echo指令/printf指令
echo和printf都是向屏幕打印,echo是以字符串形式打印,printf是用法和c语言中的用法相似。
[root@VM-0-12-centos ~]# echo 'hello world'
hello world
[root@VM-0-12-centos ~]# printf "hello %d,hello %s,hello %f" 520 "cqw" 3.14
hello 520,hello cqw,hello 3.140000[root@VM-0-12-centos ~]# printf "hello %d,hello %s,hello %f\n" 520 "cqw" 3.14
hello 520,hello cqw,hello 3.140000注意:
echo与cat的区别,echo是把echo后面的东西当作字符串打印出来,cat是打印后面指定文件名里的内容。
3.2mv指令
功能说明:移动文件 / 目录,或给文件 / 目录重命名。
常用选项:
i:覆盖文件前先询问(避免误删);
v:显示移动 / 重命名的详细过程。
注意:
我们用它是移动还是重命名取决于后面跟的是目录还是文件名,不是目录就的命名。
[root@VM-0-12-centos mydir]# ll
total 12
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Dec 16 17:36 a
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 17 Dec 18 19:38 hhh.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 45 Dec 23 19:18 other
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 13 08:17 test1.txt
[root@VM-0-12-centos mydir]# mv test1.txt ..
[root@VM-0-12-centos mydir]# ll
total 12
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Dec 16 17:36 a
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 17 Dec 18 19:38 hhh.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 45 Dec 23 19:18 other
[root@VM-0-12-centos mydir]# ls ../
hello.txt mian.c mydir mytest test1.txt test.c
[root@VM-0-12-centos mydir]# mv ../test1.txt .
[root@VM-0-12-centos mydir]# ls ../
hello.txt mian.c mydir mytest test.c
[root@VM-0-12-centos mydir]# ll
total 12
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Dec 16 17:36 a
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 17 Dec 18 19:38 hhh.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 45 Dec 23 19:18 other
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 13 08:17 test1.txt
[root@VM-0-12-centos mydir]# mv test1.txt test2.txt
[root@VM-0-12-centos mydir]# ll
total 12
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Dec 16 17:36 a
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 17 Dec 18 19:38 hhh.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 45 Dec 23 19:18 other
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 13 08:17 test2.txt3.3cat指令
功能:直接输出文件全部内容,适合查看几行的小文件
[root@VM-0-12-centos mydir]# cat hhh.txt
helloworld
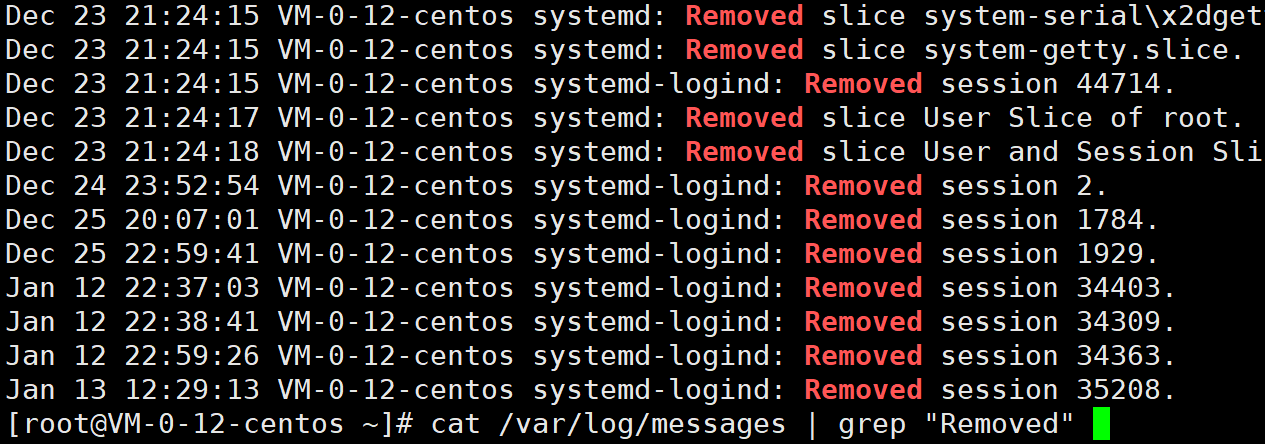
hello**注意:**我们的Linux系统是有日志的概念,用来记录事件(如启动/报错/操作行为),方便排查问题、审计操作和监控状态。
使用指令可以查看到
cat /var/log/messages如果反向打印可以把cat改成tac
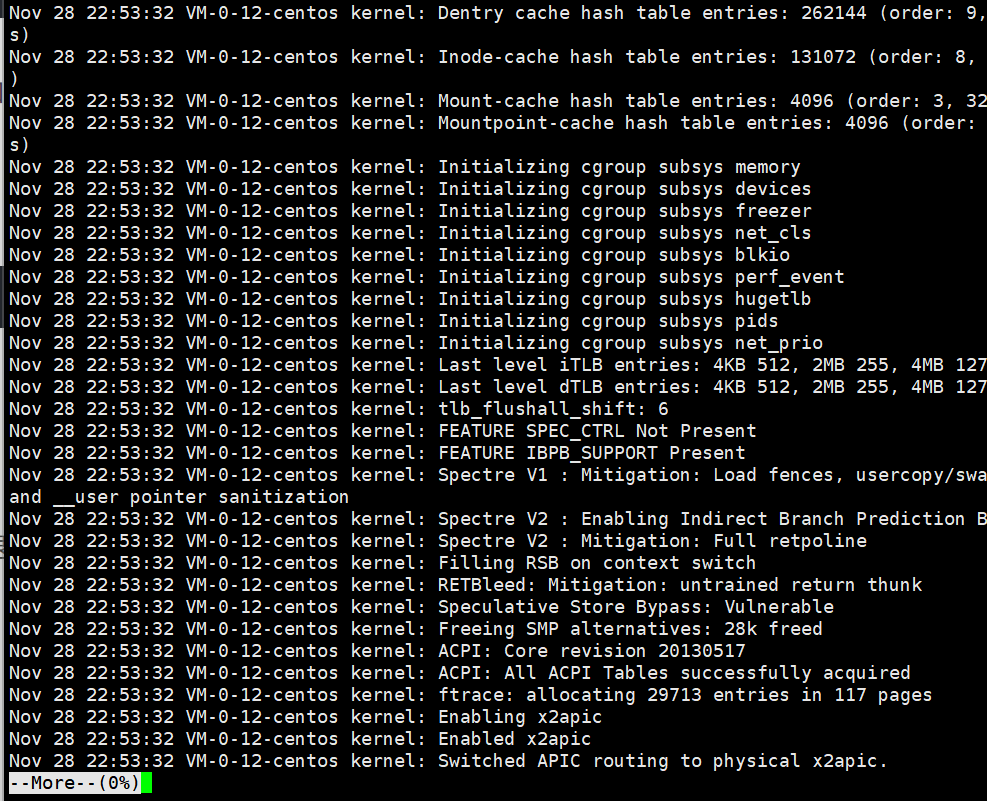
3.4more指令
功能:按页展示文件内容(只能向下翻),按空格翻页,q退出。
注意:由于more有这些功能所以它很适合我们查看日志
3.5less指令
功能:支持上下翻页、搜索文本(按/关键词搜索,n找下一个),比 more 更灵活
**注意:**在我们查看日志的时候更推荐less
3.6head/tail指令
head 指令(看文件开头):
功能:默认显示文件前 10 行,-n指定行数。
tail 指令(看文件结尾 + 实时日志):
功能:默认显示文件后 10 行,-f------ 实时监控文件新增内容。
[root@VM-0-12-centos mydir]# head -3 /var/log/messages
Nov 28 22:53:32 VM-0-12-centos kernel: Initializing cgroup subsys cpuset
Nov 28 22:53:32 VM-0-12-centos kernel: Initializing cgroup subsys cpu
Nov 28 22:53:32 VM-0-12-centos kernel: Initializing cgroup subsys cpuacct
[root@VM-0-12-centos mydir]# tail -3 /var/log/messages
Jan 13 09:01:01 VM-0-12-centos systemd: Started Session 35300 of user root.
Jan 13 09:01:01 VM-0-12-centos systemd: Started Session 35301 of user root.
Jan 13 09:02:01 VM-0-12-centos systemd: Started Session 35302 of user root.**注意:**如果我们想查看中间的内容,比如一共1000条记录,我们想要查看500到510条的,我们可以head -510到一个文件里然后再tail -10就查看到我们想要的部分。
head -510 log.txt | tail -10这条命令把两个指令结合再一起,| 被叫做管道。
四、时间&日历
4.1date指令
功能说明:查看或设置系统时间,支持自定义时间格式。
[root@VM-0-12-centos mydir]# date
Tue Jan 13 09:31:15 CST 2026
[root@VM-0-12-centos mydir]# date +%Y:%m
2026:01我们也可以把时间戳转化为年月日的形式
[root@VM-0-12-centos mydir]# date +%s
1768268926
[root@VM-0-12-centos mydir]# date +%Y_%m_%d_%H_%M_%S -d @1768268926
2026_01_13_09_48_464.2cal指令
功能说明:查看日历(默认显示当月)
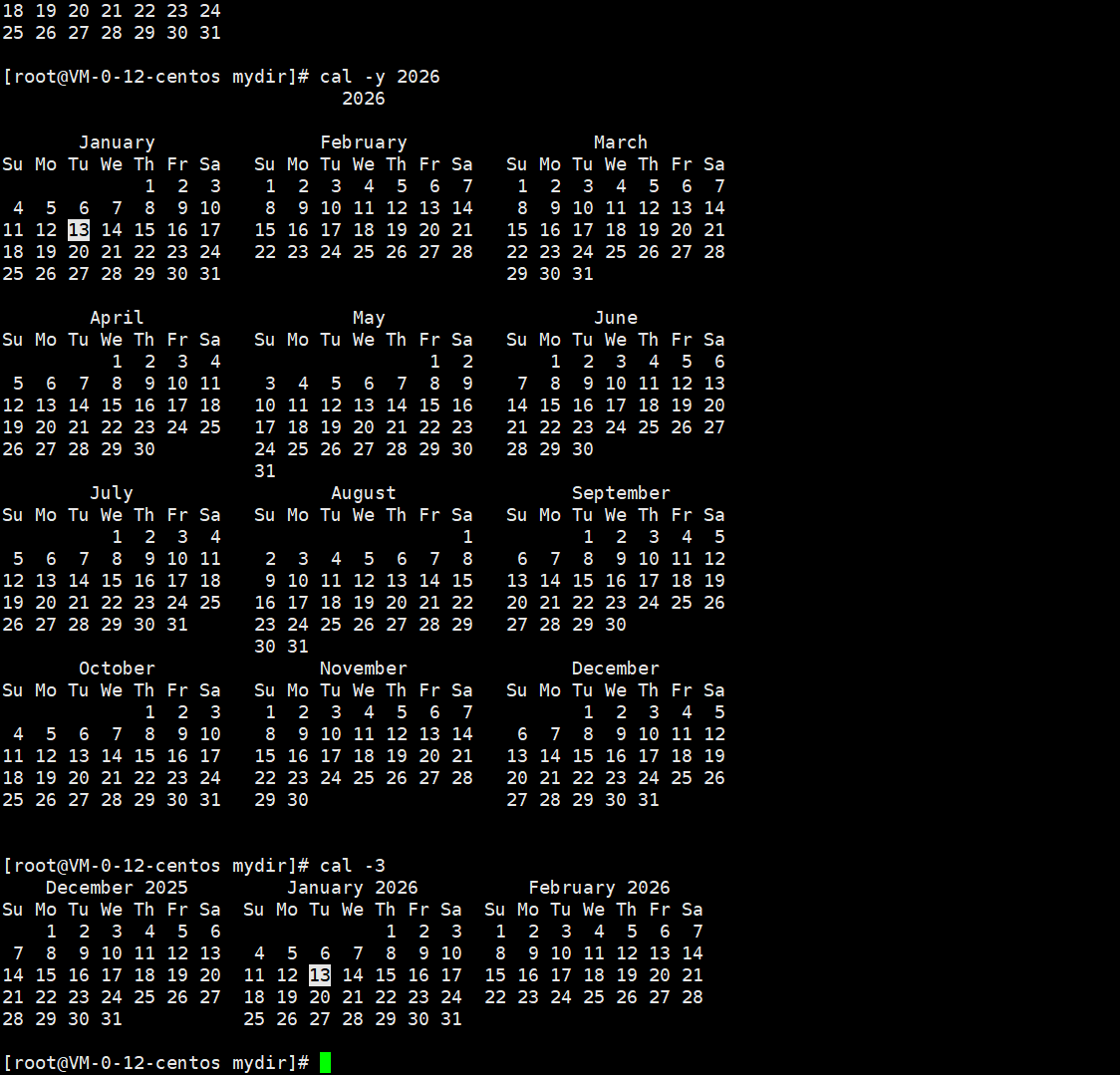
补充:
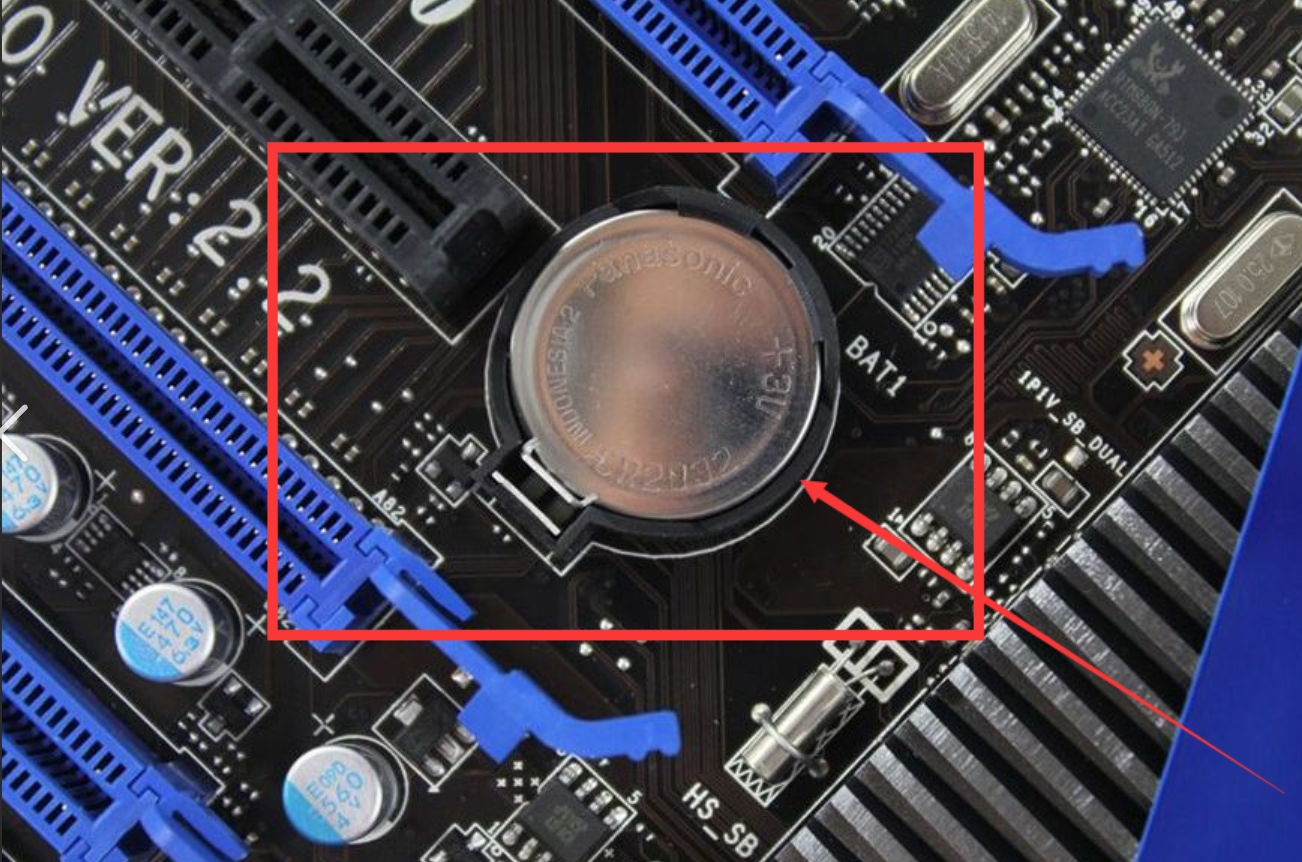
我们的计算机已经关机了,但开机之后为什么它还能记录时间?
我们的主板上有纽扣电池。
五、查找工具
5.1which指令
功能说明:只搜索系统PATH环境变量里的可执行程序,返回其绝对路径。
主要用来查找命令
[root@VM-0-12-centos mydir]# which ls
alias ls='ls --color=auto'
/usr/bin/ls
[root@VM-0-12-centos mydir]# which pwd
/usr/bin/pwd5.2whereis指令
功能说明:搜索程序的二进制文件、源码文件、手册页文件
[root@VM-0-12-centos mydir]# whereis man
man: /usr/bin/man /usr/share/man /usr/share/man/man1/man.1.gz
[root@VM-0-12-centos mydir]# whereis gcc
gcc: /usr/bin/gcc /usr/lib/gcc /usr/libexec/gcc /usr/share/man/man1/gcc.1.gz5.3find指令
功能说明:按 "名称、类型、大小、修改时间" 等条件,在指定目录下搜索文件 / 目录
root@VM-0-12-centos mydir]# find -name "*.txt"
./test2.txt
./hhh.txt六、效率工具
6.1grep指令
功能说明:在文件 / 命令输出中搜索指定文本,常和 "管道(|)" 配合用
常用选项:
-i:忽略大小写;
-v:反向匹配(显示不包含关键词的行);
-n:显示匹配行的行号。
七、打包压缩
打包:文件合并,为了防止文件丢失
压缩:减少体积,节省存储空间,网络传送,可以有效的减少网络传送的时间。
7.1zip指令/unzip指令
[root@VM-0-12-centos mydir]# tree target
target
`-- hhh.txt
0 directories, 1 file
[root@VM-0-12-centos mydir]# zip target.zip target
adding: target/ (stored 0%)
[root@VM-0-12-centos mydir]# ls
a hhh.txt other target target.zip test2.txt
[root@VM-0-12-centos mydir]# ll
total 20
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Dec 16 17:36 a
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 17 Dec 18 19:38 hhh.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 45 Dec 23 19:18 other
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jan 13 17:48 target
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 164 Jan 13 17:50 target.zip
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 13 08:17 test2.txtunzip:-d 指定解压目录
补充:
Linux和window压缩包互传
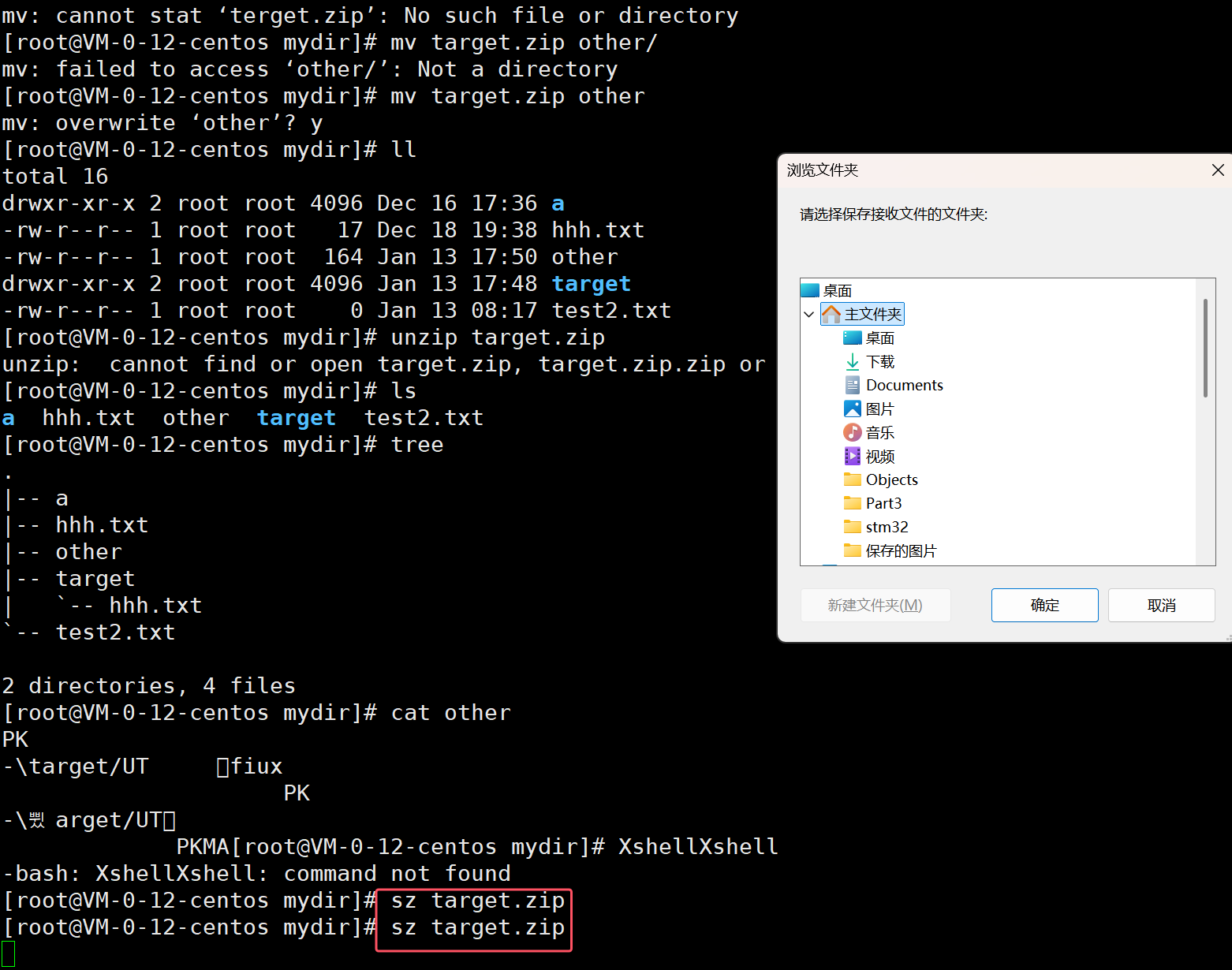
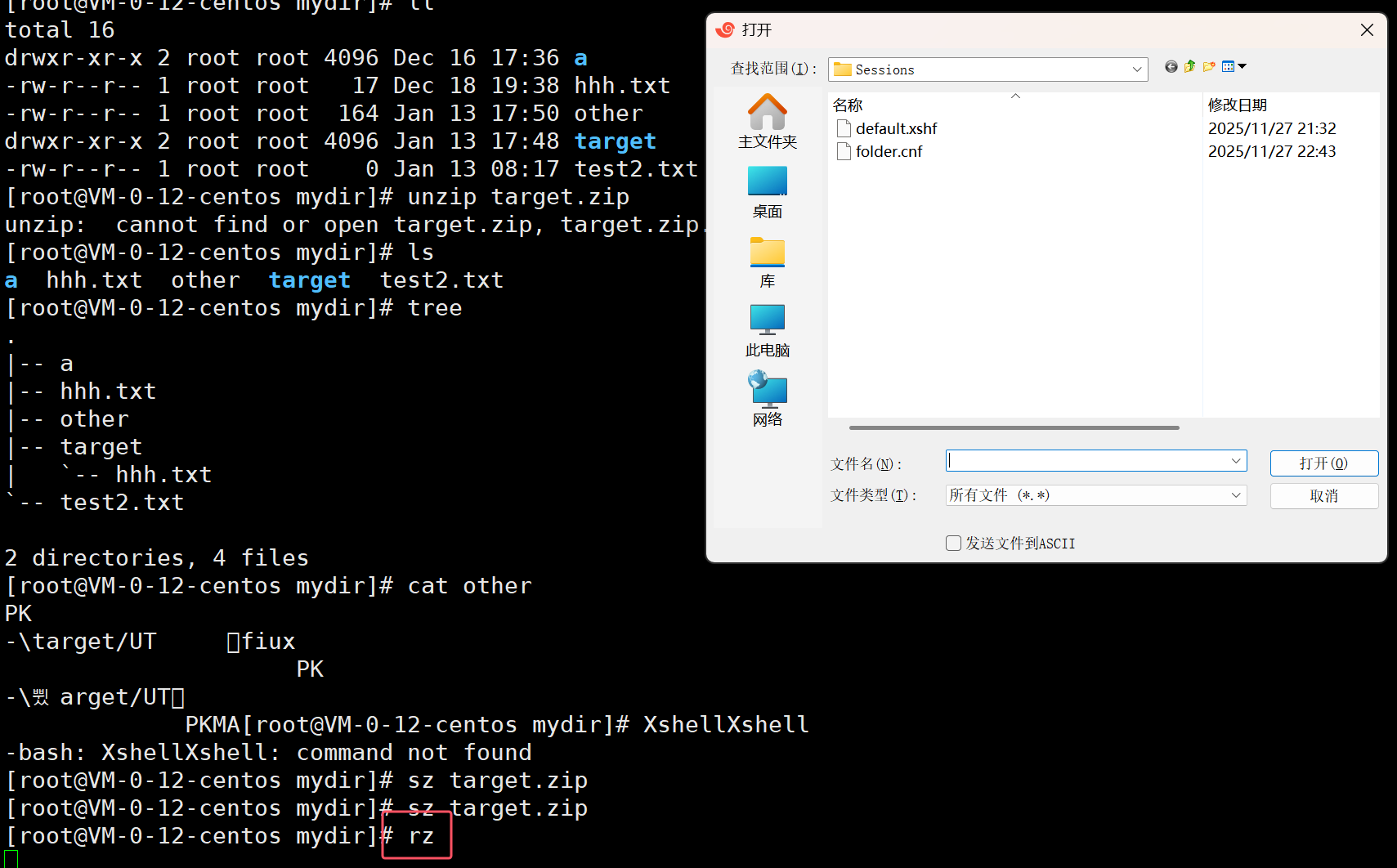
Linux和Linux压缩包互传
scp 压缩包名称.tgz 用户名@你的公网IP:目标机器指定路径7.2tar指令
ar 的选项是 "组合使用" 的,核心选项对应不同功能

八、其他常用指令
8.1bc指令
bc命令可以很方便的进行浮点运算
8.2uname指令
功能:uname用来获取电脑和操作系统的相关信息
问题:怎么在Linux环境下查看你的体系结构和系统
[root@VM-0-12-centos mydir]# uname -a
Linux VM-0-12-centos 3.10.0-1160.119.1.el7.x86_64 #1 SMP Tue Jun 4 14:43:51 UTC 2024 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
[root@VM-0-12-centos mydir]# uname -r
3.10.0-1160.119.1.el7.x86_64