1.list的特点
list的本质就是带头双向链表,可以在常数时间复杂度进行插入删除的容器。
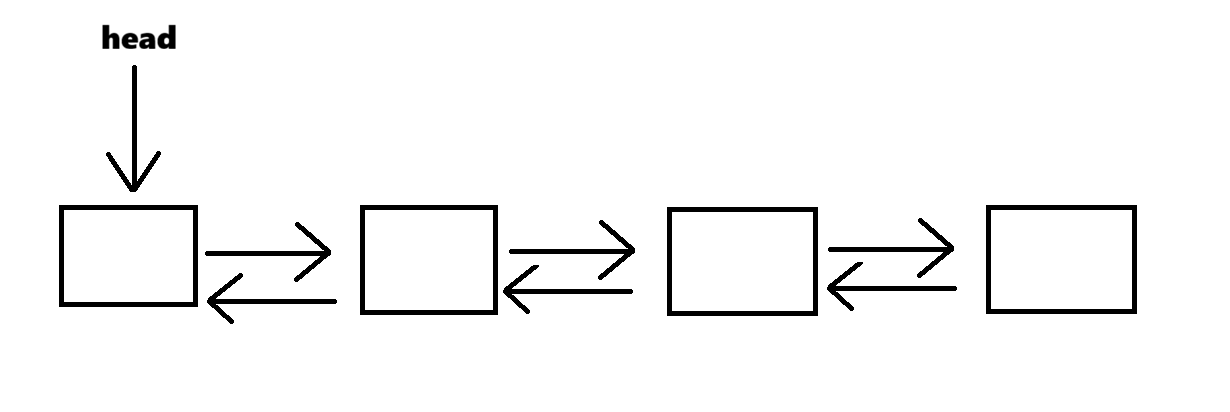
- list和forward_list最主要的区别:forward_list是单链表,只能向前迭代,但list可以双向迭代
- list比其他序列式容器(array,vector,deque)进行插入,移除元素的执行效率更好
- list不支持任意位置的随机访问,要访问中间的元素,需要从头或者尾按序遍历
2.list中的节点
给于_val默认值,前后指针置空(使用struct,默认访问限定符是public)
cpp
//节点
template <class T>
struct ListNode
{
ListNode(const T& val = T())
{
_prev = nullptr;
_next = nullptr;
_val = val;
}
ListNode* _prev;//指向上一个元素
ListNode* _next;//指向下一个元素
T _val; //值
};3.list中的迭代器
迭代器是一种设计模式 ,它在底层指针和用户接口之间增加了一个抽象层。这个抽象层让算法(如 std::sort, std::find)可以统一处理不同容器,而不需要知道容器内部是如何存储数据的。迭代器的实质就是指针,指向每个节点。(注意operator*返回的是T&)
cpp
//迭代器
template<class T>
struct List_Iterator
{
using Node = ListNode<T>;
using self = List_Iterator<T>;
List_Iterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
//不需要析构函数,没有自己开辟空间,用默认构造就行
//++it
self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
//it++
self operator++(int)
{
self tmp(this);
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;
}
//--it
self& operator--()
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}
//it--
self operator--(int)
{
self tmp(this);
_node = _node->_prev;
return tmp;
}
bool operator==(const self& it)
{
return it._node == _node;
}
bool operator!=(const self& it)
{
return it._node != _node;
}
const T& operator*()
{
return _node->_val;
}
Node* _node;
};4.list的构造析构函数
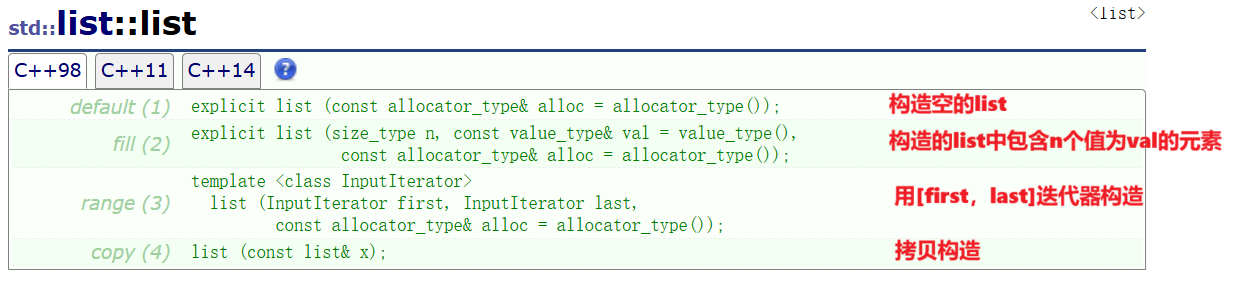
- 默认构造就是先创建一个头节点,让前后指针指向自己
- 拷贝构造就是把一个链表节点的值全部尾插
cpp
template <class T>
class List
{
public:
using Node = ListNode<T>;
using Iterator = List_Iterator<T>;
List()
{
_head = new Node;
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
//前后指针指向自己
}
List(List<T>& list)//拷贝构造
{
_head = new Node;
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
for ( auto e : list)
{
push_back(e);
}
}
~List()//析构函数
{
clear();
assert(_head);
delete _head;
_head = nullptr;
}
void clear()//释放所有节点
{
auto it = begin();
while (it != end())
{
it = erase(it);
}
}
private:
Node* _head;//哨兵节点
};5.list的增删改
insert
在迭代器pos处插入val值。尾插和头插直接复用insert即可

cpp
Iterator insert(Iterator it, const T& val)
{
Node* newnode = new Node(val);
Node* cur = it._node;
Node* prev = it._node->_prev;
//prev newnode cur
prev->_next = newnode;
newnode->_prev = prev;
newnode->_next = cur;
cur->_prev = newnode;
//返回新节点的迭代器
return newnode;
}
//头插
void push_front(const T& val)
{
insert(begin(), val);
}
//尾插
void push_back(const T& val)
{
insert(end(), val);
}erase
删除迭代器pos处的值。对于头删和尾删同理复用

cpp
Iterator erase(Iterator it)
{
assert(it != _head);
Node* cur = it._node;
Node* prev = cur->_prev;
Node* next = cur->_next;
prev->_next = next;
next->_prev = prev;
delete cur;
return next;
}
//头删
void pop_front()
{
erase(begin());
}
//尾删
void pop_back()
{
erase(--end());
}