目录
一.专栏简介
本专栏是我学习《head first》设计模式的笔记。这本书中是用Java语言为基础的,我将用C++语言重写一遍,并且详细讲述其中的设计模式,涉及是什么,为什么,怎么做,自己的心得等等。希望阅读者在读完我的这个专题后,也能在开发中灵活且正确的使用,或者在面对面试官时,能够自信地说自己熟悉常用设计模式。
本章将开始命令模式的学习。
二.前言
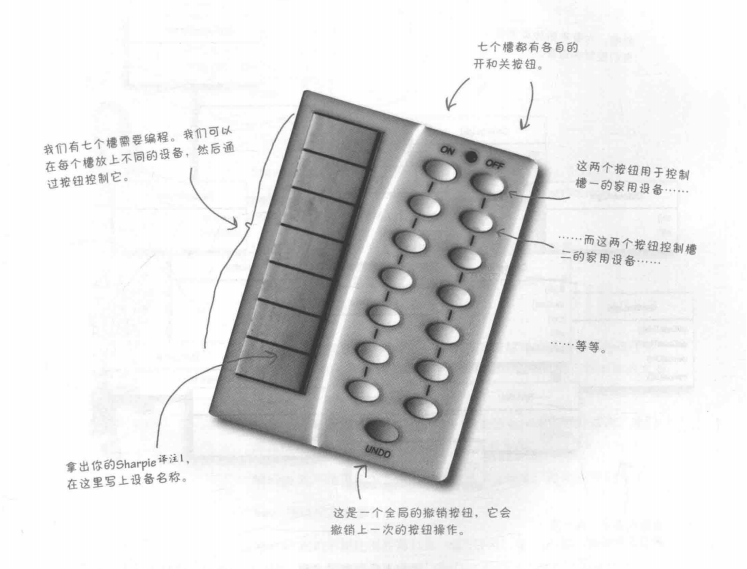
在书中我们需要实现一个遥控器来调用各个家具厂商提供给我们的api,令遥控器可以对这些厂商的家具进行控制,也就是开和关。遥控器的图片如下:
三.看看厂商类
关于我们需要从遥控器控制的对象的接口,这些类应该会给我们带来一些想法。
我用C++写了一下这些类成员函数调用时的输出打印,代码如下:
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class OutdoorLight
{
public:
void on()
{
cout << "OutdoorLight on" << endl;
}
void off()
{
cout << "OutdoorLight off" << endl;
}
};
class CeilingLight
{
public:
void on()
{
cout << "CeilingLight on" << endl;
}
void off()
{
cout << "CeilingLight off" << endl;
}
void dim()
{
cout << "CeilingLight dim" << endl;
}
};
class TV
{
public:
void on()
{
cout << "TV on" << endl;
}
void off()
{
cout << "TV off" << endl;
}
void setInputChannel(int channel)
{
cout << "TV setInputChannel : " << channel << endl;
}
void setVolume(int volume)
{
cout << "TV setVolume : " << volume << endl;
}
};
class Stereo
{
public:
void on()
{
cout << "Stereo on" << endl;
}
void off()
{
cout << "Stereo off" << endl;
}
void setCd(int cd)
{
cout << "Stereo setCd : " << cd << endl;
}
void setDvd(int dvd)
{
cout << "Stereo setDvd : " << dvd << endl;
}
void setRadio(int radio)
{
cout << "Stereo setRadio : " << radio << endl;
}
void setVolume(int volume)
{
cout << "Stereo setVolume : " << volume << endl;
}
};
class ApplianceControl
{
public:
void on()
{
cout << "ApplianceControl on" << endl;
}
void off()
{
cout << "ApplianceControl off" << endl;
}
};
class FaucetControl
{
public:
void openValve()
{
cout << "FaucetControl openValve" << endl;
}
void closeValve()
{
cout << "FaucetControl closeValve" << endl;
}
};
struct Time
{
int hour;
int minute;
int second;
};
class GardenLight
{
public:
void setDuskTime(const Time& t)
{
cout << "setDuskTime : " << t.hour << " h " << t.minute << " m " << t.second << " s" << endl;
}
void setDawnTime(const Time& t)
{
cout << "setDawnTime : " << t.hour << " h " << t.minute << " m " << t.second << " s" << endl;
}
void manualOn()
{
cout << "GardenLight manualOn" << endl;
}
void manualOff()
{
cout << "GardenLight manualOff" << endl;
}
};
class CeilingFan
{
public:
void high()
{
cout << "CeilingFan high" << endl;
_speed = 3;
}
void medium()
{
cout << "CeilingFan medium" << endl;
_speed = 2;
}
void low()
{
cout << "CeilingFan low" << endl;
_speed = 1;
}
void off()
{
cout << "CeilingFan off" << endl;
_speed = 0;
}
int getSpeed()
{
return _speed;
}
private:
int _speed = 0;
};
class GarageDoor
{
public:
void up()
{
cout << "GarageDoor up" << endl;
}
void down()
{
cout << "GarageDoor down" << endl;
}
void stop()
{
cout << "GarageDoor stop" << endl;
}
void lightOn()
{
cout << "GarageDoor lightOn" << endl;
}
void lightOff()
{
cout << "GarageDoor lightOff" << endl;
}
};
class Hottub
{
public:
void circulate()
{
cout << "Hottub circulate" << endl;
}
void jetsOn()
{
cout << "Hottub jetsOn" << endl;
}
void jetsOff()
{
cout << "Hottub jetsOff" << endl;
}
void setTemperature(int temperature)
{
cout << "Hottub setTemperature : " << temperature << endl;
}
};
class Sprinkler
{
public:
void waterOn()
{
cout << "Sprinkler waterOn" << endl;
}
void waterOff()
{
cout << "Sprinkler waterOff" << endl;
}
};
class Light
{
public:
void on()
{
cout << "Light on" << endl;
}
void off()
{
cout << "light off" << endl;
}
};
class SecurityControl
{
public:
void arm()
{
cout << "SecurityControl arm" << endl;
}
void disarm()
{
cout << "SecurityControl disarm" << endl;
}
};
class Thermostat
{
public:
void setTemperature(int temperature)
{
cout << "Hottub setTemperature : " << temperature << endl;
}
};看起来我们有诸多类,而行业中在通用接口上付出的努力并不多。不仅如此,听起来将来还会有更多这样的类。设计一个遥控器API很有意思,我们继续吧。
四.我们的第一个命令对象
实现command接口(抽象类)
代码如下:
cpp
class Command
{
public:
virtual void execute() = 0;
};实现一条开灯命令
现在,假设你要实现一条开灯的命令。根据厂商类,light类有两个方法:on()和off()。
command.h:
cpp
class LightOnCommand : public Command
{
public:
LightOnCommand(Light* light);
void execute();
private:
Light* _light;
};command.cpp:
cpp
LightOnCommand::LightOnCommand(Light* light):
_light(light)
{
}
void LightOnCommand::execute()
{
_light->on();
}这是一条命令,因此需要实现Command接口。构造器被传入命令要控制的特定灯(比如说客厅的灯),并藏在灯实例变量中。当execute被调用时,灯对象成为请求的接收者。接收者也就是最后做事的人。execute()方法调用接收对象上的on()方法,该对象就是我们正在控制的灯。
使用命令对象:
我们来简化一下:假设我们只有一个遥控器,它只有一个按钮以及相应的槽来放置要控制的设备。
command.h:
cpp
class SimpleRemoteControl
{
public:
SimpleRemoteControl();
void setCommand(Command* command);
void buttonWasPressed();
private:
Command* slot;
};command.cpp:
cpp
SimpleRemoteControl::SimpleRemoteControl() :
slot(nullptr)
{
}
void SimpleRemoteControl::setCommand(Command* command)
{
slot = command;
}
void SimpleRemoteControl::buttonWasPressed()
{
slot->execute();
}我们有一个槽 slot持有命令,命令控制一个设备。我们有一个方法setCommand(),用于设置槽的命令,如果这段代码的客户要改变遥控器按钮的行为,可以多次调用这个方法。当按钮被按下,buttonWasPressed()被调用。我们要做的是把当前命令绑定到槽,并调用其execute()方法。
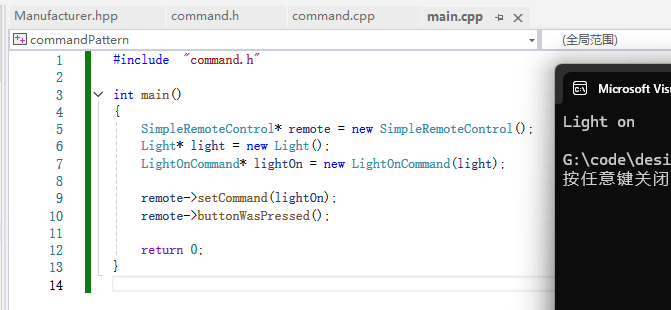
创建一个简单的测试来使用遥控器:
main.cpp:
cpp
#include "command.h"
int main()
{
SimpleRemoteControl* remote = new SimpleRemoteControl();
Light* light = new Light();
LightOnCommand* lightOn = new LightOnCommand(light);
remote->setCommand(lightOn);
remote->buttonWasPressed();
return 0;
}用命令模式的说法,这个main 函数是客户。遥控器是调用者,会被传入一个可以用来做出请求的命令对象。
运行结果:
五.再来定义一个命令对象
这里也就是书中的练习。
代码如下:
command.h:
cpp
class GarageDoorOpenCommand : public Command
{
public:
GarageDoorOpenCommand(GarageDoor* door);
void execute() override;
private:
GarageDoor* _door;
};command.cpp:
cpp
GarageDoorOpenCommand::GarageDoorOpenCommand(GarageDoor* door):
_door(door)
{
}
void GarageDoorOpenCommand::execute()
{
_door->up();
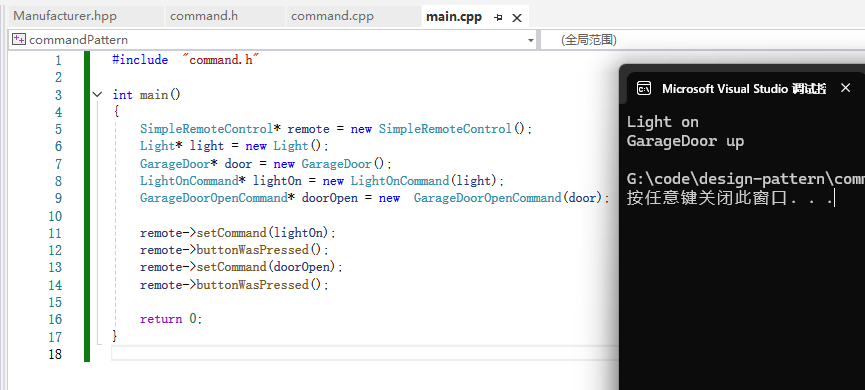
}main.cpp:
cpp
#include "command.h"
int main()
{
SimpleRemoteControl* remote = new SimpleRemoteControl();
Light* light = new Light();
GarageDoor* door = new GarageDoor();
LightOnCommand* lightOn = new LightOnCommand(light);
GarageDoorOpenCommand* doorOpen = new GarageDoorOpenCommand(door);
remote->setCommand(lightOn);
remote->buttonWasPressed();
remote->setCommand(doorOpen);
remote->buttonWasPressed();
return 0;
}运行结果:
六.定义命令模式
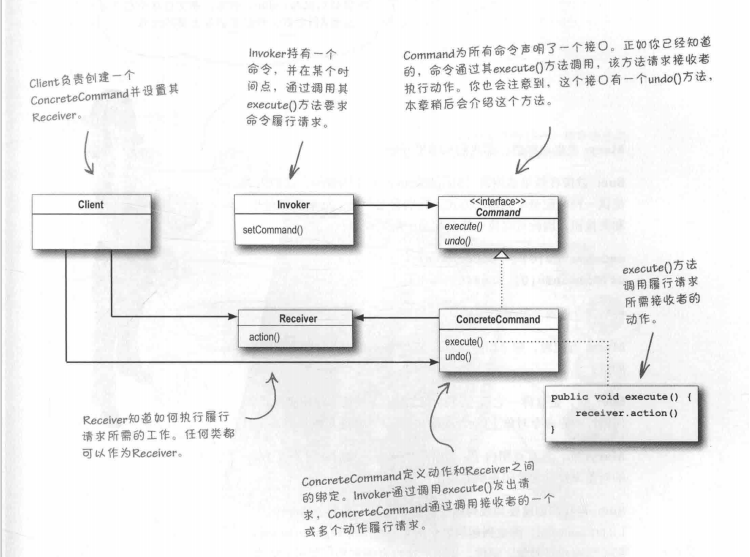
命令模式官方定义:命令模式把请求封装为对象,以便用不同的请求、队列或者日志请求来参数化其他对象,并支持可撤销的操作。
命令模式类图如下:
七.分配命令到槽
我们打算分配命令到遥控器的每个槽,使得遥控器成为调用者。当按钮被按下时,相应命令上的execute()方法会被调用,导致接收者(像灯、吊扇和音响)上的动作被调用。
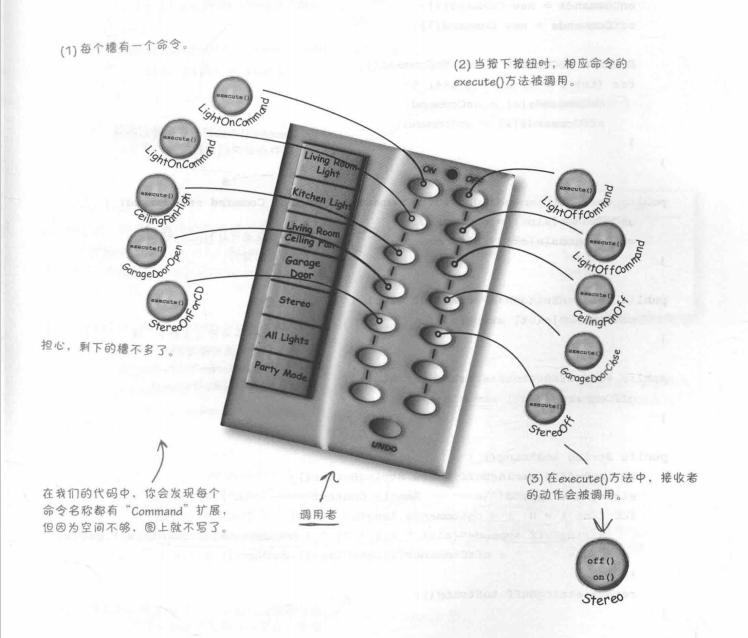
八.实现遥控器和命令并且测试
我们改写了调用者,并且新增了命令,然后测试。
Manufacturer.hpp:
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Light
{
public:
virtual void on() = 0;
virtual void off() = 0;
};
class OutdoorLight : public Light
{
public:
void on() override
{
cout << "OutdoorLight on" << endl;
}
void off() override
{
cout << "OutdoorLight off" << endl;
}
};
class CeilingLight : public Light
{
public:
void on() override
{
cout << "CeilingLight on" << endl;
}
void off() override
{
cout << "CeilingLight off" << endl;
}
void dim()
{
cout << "CeilingLight dim" << endl;
}
};
struct Time
{
int hour;
int minute;
int second;
};
class GardenLight : public Light
{
public:
void setDuskTime(const Time& t)
{
cout << "setDuskTime : " << t.hour << " h " << t.minute << " m " << t.second << " s" << endl;
}
void setDawnTime(const Time& t)
{
cout << "setDawnTime : " << t.hour << " h " << t.minute << " m " << t.second << " s" << endl;
}
void on() override
{
cout << "GardenLight manualOn" << endl;
}
void off() override
{
cout << "GardenLight manualOff" << endl;
}
};
class TV
{
public:
void on()
{
cout << "TV on" << endl;
}
void off()
{
cout << "TV off" << endl;
}
void setInputChannel(int channel)
{
cout << "TV setInputChannel : " << channel << endl;
}
void setVolume(int volume)
{
cout << "TV setVolume : " << volume << endl;
}
};
class Stereo
{
public:
void on()
{
cout << "Stereo on" << endl;
}
void off()
{
cout << "Stereo off" << endl;
}
void setCd(int cd)
{
cout << "Stereo setCd : " << cd << endl;
}
void setDvd(int dvd)
{
cout << "Stereo setDvd : " << dvd << endl;
}
void setRadio(int radio)
{
cout << "Stereo setRadio : " << radio << endl;
}
void setVolume(int volume)
{
cout << "Stereo setVolume : " << volume << endl;
}
};
class ApplianceControl
{
public:
void on()
{
cout << "ApplianceControl on" << endl;
}
void off()
{
cout << "ApplianceControl off" << endl;
}
};
class FaucetControl
{
public:
void openValve()
{
cout << "FaucetControl openValve" << endl;
}
void closeValve()
{
cout << "FaucetControl closeValve" << endl;
}
};
class CeilingFan
{
public:
void high()
{
cout << "CeilingFan high" << endl;
_speed = 3;
}
void medium()
{
cout << "CeilingFan medium" << endl;
_speed = 2;
}
void low()
{
cout << "CeilingFan low" << endl;
_speed = 1;
}
void off()
{
cout << "CeilingFan off" << endl;
_speed = 0;
}
int getSpeed()
{
return _speed;
}
private:
int _speed = 0;
};
class GarageDoor
{
public:
void up()
{
cout << "GarageDoor up" << endl;
}
void down()
{
cout << "GarageDoor down" << endl;
}
void stop()
{
cout << "GarageDoor stop" << endl;
}
void lightOn()
{
cout << "GarageDoor lightOn" << endl;
}
void lightOff()
{
cout << "GarageDoor lightOff" << endl;
}
};
class Hottub
{
public:
void circulate()
{
cout << "Hottub circulate" << endl;
}
void jetsOn()
{
cout << "Hottub jetsOn" << endl;
}
void jetsOff()
{
cout << "Hottub jetsOff" << endl;
}
void setTemperature(int temperature)
{
cout << "Hottub setTemperature : " << temperature << endl;
}
};
class Sprinkler
{
public:
void waterOn()
{
cout << "Sprinkler waterOn" << endl;
}
void waterOff()
{
cout << "Sprinkler waterOff" << endl;
}
};
class SecurityControl
{
public:
void arm()
{
cout << "SecurityControl arm" << endl;
}
void disarm()
{
cout << "SecurityControl disarm" << endl;
}
};
class Thermostat
{
public:
void setTemperature(int temperature)
{
cout << "Hottub setTemperature : " << temperature << endl;
}
};command.h:
cpp
#pragma once
#include "Manufacturer.hpp"
#include <vector>
#define SLOTCOUNT 7
class Command
{
public:
virtual void execute() = 0;
};
class NoCommand : public Command
{
public:
void execute() override;
};
// 调用者
class RemoteControl
{
public:
RemoteControl();
void setCommand(int slot, Command* onCommand, Command* offCommand);
void onButtonWasPressed(int slot);
void offButtonWasPressed(int slot);
void print();
private:
vector<Command*> onCommands;
vector<Command*> offCommands;
};
class LightOnCommand : public Command
{
public:
LightOnCommand(Light* light);
void execute() override;
private:
Light* _light; // 接收者
};
class LightOffCommand : public Command
{
public:
LightOffCommand(Light* light);
void execute() override;
private:
Light* _light;
};
class GarageDoorOpenCommand : public Command
{
public:
GarageDoorOpenCommand(GarageDoor* door);
void execute() override;
private:
GarageDoor* _door; // 接收者
};
class GarageDoorCloseCommand : public Command
{
public:
GarageDoorCloseCommand(GarageDoor* door);
void execute() override;
private:
GarageDoor* _door; // 接收者
};
class StereoOnWithCDCommand : public Command
{
public:
StereoOnWithCDCommand(Stereo* stereo);
void execute();
private:
Stereo* _stereo;
};
class StereoOffWithCDCommand : public Command
{
public:
StereoOffWithCDCommand(Stereo* stereo);
void execute();
private:
Stereo* _stereo;
};
class CeilingFanOnCommand : public Command
{
public:
CeilingFanOnCommand(CeilingFan* ceilingFan);
void execute();
private:
CeilingFan* _ceilingFan;
};
class CeilingFanOffCommand : public Command
{
public:
CeilingFanOffCommand(CeilingFan* ceilingFan);
void execute();
private:
CeilingFan* _ceilingFan;
};command.cpp:
cpp
#include "command.h"
RemoteControl::RemoteControl()
{
onCommands.resize(SLOTCOUNT);
offCommands.resize(SLOTCOUNT);
Command* noCommand = new NoCommand();
for (int pos = 0;pos < SLOTCOUNT;++pos)
{
onCommands[pos] = noCommand;
offCommands[pos] = noCommand;
}
}
void RemoteControl::setCommand(int slot, Command* onCommand, Command* offCommand)
{
onCommands[slot] = onCommand;
offCommands[slot] = offCommand;
}
void RemoteControl::onButtonWasPressed(int slot)
{
onCommands[slot]->execute();
}
void RemoteControl::offButtonWasPressed(int slot)
{
offCommands[slot]->execute();
}
void RemoteControl::print()
{
for (int pos = 0;pos < SLOTCOUNT;++pos)
{
cout << "onCommands[" << pos << "] : " << typeid(*onCommands[pos]).name() << endl;
cout << "offCommands[" << pos << "] : " << typeid(*offCommands[pos]).name() << endl;
}
}
LightOnCommand::LightOnCommand(Light* light) :
_light(light)
{
}
void LightOnCommand::execute()
{
_light->on();
}
GarageDoorOpenCommand::GarageDoorOpenCommand(GarageDoor* door):
_door(door)
{
}
void GarageDoorOpenCommand::execute()
{
_door->up();
}
void NoCommand::execute()
{
cout << "do nothing" << endl;
}
LightOffCommand::LightOffCommand(Light* light):
_light(light)
{
}
void LightOffCommand::execute()
{
_light->off();
}
StereoOnWithCDCommand::StereoOnWithCDCommand(Stereo* stereo):
_stereo(stereo)
{
}
void StereoOnWithCDCommand::execute()
{
_stereo->on();
_stereo->setCd(3);
_stereo->setVolume(11);
}
CeilingFanOnCommand::CeilingFanOnCommand(CeilingFan* ceilingFan):
_ceilingFan(ceilingFan)
{
}
void CeilingFanOnCommand::execute()
{
_ceilingFan->high();
}
CeilingFanOffCommand::CeilingFanOffCommand(CeilingFan* ceilingFan):
_ceilingFan(ceilingFan)
{
}
void CeilingFanOffCommand::execute()
{
_ceilingFan->off();
}
GarageDoorCloseCommand::GarageDoorCloseCommand(GarageDoor* door):
_door(door)
{
}
void GarageDoorCloseCommand::execute()
{
_door->down();
}
StereoOffWithCDCommand::StereoOffWithCDCommand(Stereo* stereo):
_stereo(stereo)
{
}
void StereoOffWithCDCommand::execute()
{
_stereo->off();
}main.cpp:
cpp
#include "command.h"
int main()
{
RemoteControl* remoteControl = new RemoteControl();
Light* outdoorLight = new OutdoorLight();
Light* kitchenLight = new CeilingLight();
CeilingFan* ceilingFan = new CeilingFan();
GarageDoor* garageDoor = new GarageDoor();
Stereo* stereo = new Stereo();
LightOnCommand* outdoorLightOnCommand = new LightOnCommand(outdoorLight);
LightOffCommand* outdoorLightOffCommand = new LightOffCommand(outdoorLight);
LightOnCommand* kitchenLightOnCommand = new LightOnCommand(kitchenLight);
LightOffCommand* kitchenLightOffCommand = new LightOffCommand(kitchenLight);
CeilingFanOnCommand* ceilingFanOnCommand = new CeilingFanOnCommand(ceilingFan);
CeilingFanOffCommand* ceilingFanOffCommand = new CeilingFanOffCommand(ceilingFan);
GarageDoorOpenCommand* garageDoorOpenCommand = new GarageDoorOpenCommand(garageDoor);
GarageDoorCloseCommand* garageDoorCloseCommand = new GarageDoorCloseCommand(garageDoor);
StereoOnWithCDCommand* stereoOnWithCDCommand = new StereoOnWithCDCommand(stereo);
StereoOffWithCDCommand* stereoOffWithCDCommand = new StereoOffWithCDCommand(stereo);
remoteControl->setCommand(0, outdoorLightOnCommand, outdoorLightOffCommand);
remoteControl->setCommand(1, kitchenLightOnCommand, kitchenLightOffCommand);
remoteControl->setCommand(2, ceilingFanOnCommand, ceilingFanOffCommand);
remoteControl->setCommand(3, garageDoorOpenCommand, garageDoorCloseCommand);
remoteControl->setCommand(4, stereoOnWithCDCommand, stereoOffWithCDCommand);
remoteControl->print();
remoteControl->onButtonWasPressed(0);
remoteControl->offButtonWasPressed(0);
remoteControl->onButtonWasPressed(1);
remoteControl->offButtonWasPressed(1);
remoteControl->onButtonWasPressed(2);
remoteControl->offButtonWasPressed(2);
remoteControl->onButtonWasPressed(3);
remoteControl->offButtonWasPressed(3);
remoteControl->onButtonWasPressed(4);
remoteControl->offButtonWasPressed(4);
return 0;
}运行结果:
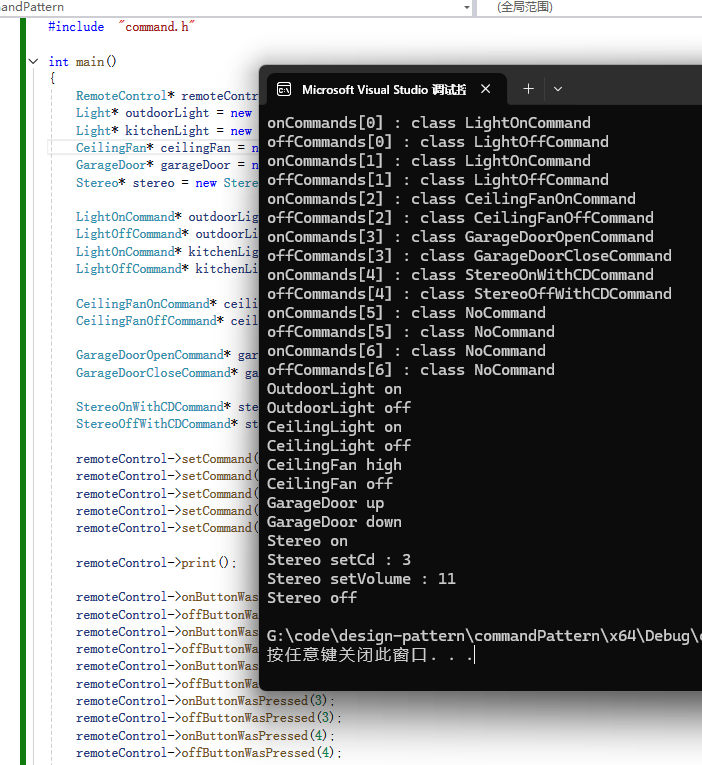
NoCommand对象是一个空对象(null object)的例子。当你不想返回一个有意义的对象时,以及你要把处理null的责任从客户移除时,空对象就很有用。
另外,我们也可以用lambda表达式改写。我们可以用C++的lambda表达式来跳过创建那些具体命令对象的步骤。用了lambda表达式,不用实例化具体命令对象,而是用函数对象代替。换句话说,我们可以用函数对象作为命令。另外,这样做之后,我们也就可以删除所有命令类。我们看看用lambda表达式改写之后的代码:
main.cpp:
main函数中:
cpp
remoteControl->setCommand(5, [outdoorLight]() { outdoorLight->on(); });
// 测试lambda表达式改写
remoteControl->onButtonWasPressed(5);command.h:
cpp
// 调用者
class RemoteControl
{
public:
RemoteControl();
void setCommand(int slot, Command* onCommand, Command* offCommand);
void setCommand(int slot, function<void()>);
void onButtonWasPressed(int slot);
void offButtonWasPressed(int slot);
void print();
private:
vector<Command*> onCommands;
vector<Command*> offCommands;
vector<function<void()>> lambdas;
};command.cpp:
cpp
void RemoteControl::setCommand(int slot, function<void()> onFunc)
{
lambdas[slot] = onFunc;
}一旦我们替换具体命令为lambda表达式,我们可以删除所有具体命令类。如果我们为每个具体命令如此做了,遥控器应用的类总数就会从22减少到9。
九.实现撤销
command.h:
cpp
#pragma once
#include "Manufacturer.hpp"
#include <vector>
#include <functional>
#define SLOTCOUNT 7
class Command
{
public:
virtual void execute() = 0;
virtual void undo() = 0;
};
class NoCommand : public Command
{
public:
void execute() override;
void undo() override;
};
// 调用者
class RemoteControl
{
public:
RemoteControl();
void setCommand(int slot, Command* onCommand, Command* offCommand);
void setCommand(int slot, function<void()>);
void onButtonWasPressed(int slot);
void offButtonWasPressed(int slot);
void undoButtonWasPushed();
void print();
private:
vector<Command*> onCommands;
vector<Command*> offCommands;
vector<function<void()>> lambdas;
Command* undoCommand;
};
class LightOnCommand : public Command
{
public:
LightOnCommand(Light* light);
void execute() override;
void undo() override;
private:
Light* _light; // 接收者
};
class LightOffCommand : public Command
{
public:
LightOffCommand(Light* light);
void execute() override;
void undo() override;
private:
Light* _light;
};
class GarageDoorOpenCommand : public Command
{
public:
GarageDoorOpenCommand(GarageDoor* door);
void execute() override;
void undo() override;
private:
GarageDoor* _door; // 接收者
};
class GarageDoorCloseCommand : public Command
{
public:
GarageDoorCloseCommand(GarageDoor* door);
void execute() override;
void undo() override;
private:
GarageDoor* _door; // 接收者
};
class StereoOnWithCDCommand : public Command
{
public:
StereoOnWithCDCommand(Stereo* stereo);
void execute();
void undo() override;
private:
Stereo* _stereo;
};
class StereoOffWithCDCommand : public Command
{
public:
StereoOffWithCDCommand(Stereo* stereo);
void execute();
void undo() override;
private:
Stereo* _stereo;
};
class CeilingFanOnCommand : public Command
{
public:
CeilingFanOnCommand(CeilingFan* ceilingFan);
void execute();
void undo() override;
private:
CeilingFan* _ceilingFan;
};
class CeilingFanOffCommand : public Command
{
public:
CeilingFanOffCommand(CeilingFan* ceilingFan);
void execute();
void undo() override;
private:
CeilingFan* _ceilingFan;
};command.cpp:
cpp
#include "command.h"
RemoteControl::RemoteControl()
{
onCommands.resize(SLOTCOUNT);
offCommands.resize(SLOTCOUNT);
lambdas.resize(SLOTCOUNT);
Command* noCommand = new NoCommand();
for (int pos = 0;pos < SLOTCOUNT;++pos)
{
onCommands[pos] = noCommand;
offCommands[pos] = noCommand;
//lambdas[pos] = []() { cout << "do nothing" << endl; };
}
undoCommand = noCommand;
}
void RemoteControl::setCommand(int slot, Command* onCommand, Command* offCommand)
{
onCommands[slot] = onCommand;
offCommands[slot] = offCommand;
}
void RemoteControl::setCommand(int slot, function<void()> onFunc)
{
lambdas[slot] = onFunc;
}
void RemoteControl::onButtonWasPressed(int slot)
{
if (slot == 5) lambdas[slot]();
else onCommands[slot]->execute();
undoCommand = onCommands[slot];
}
void RemoteControl::offButtonWasPressed(int slot)
{
offCommands[slot]->execute();
undoCommand = offCommands[slot];
}
void RemoteControl::undoButtonWasPushed()
{
undoCommand->undo();
}
void RemoteControl::print()
{
for (int pos = 0;pos < SLOTCOUNT;++pos)
{
cout << "onCommands[" << pos << "] : " << typeid(*onCommands[pos]).name() << endl;
cout << "offCommands[" << pos << "] : " << typeid(*offCommands[pos]).name() << endl;
}
}
LightOnCommand::LightOnCommand(Light* light) :
_light(light)
{
}
void LightOnCommand::execute()
{
_light->on();
}
void LightOnCommand::undo()
{
_light->off();
}
GarageDoorOpenCommand::GarageDoorOpenCommand(GarageDoor* door):
_door(door)
{
}
void GarageDoorOpenCommand::execute()
{
_door->up();
}
void GarageDoorOpenCommand::undo()
{
_door->down();
}
void NoCommand::execute()
{
cout << "do nothing" << endl;
}
void NoCommand::undo()
{
cout << "do nothing" << endl;
}
LightOffCommand::LightOffCommand(Light* light):
_light(light)
{
}
void LightOffCommand::execute()
{
_light->off();
}
void LightOffCommand::undo()
{
_light->on();
}
StereoOnWithCDCommand::StereoOnWithCDCommand(Stereo* stereo):
_stereo(stereo)
{
}
void StereoOnWithCDCommand::execute()
{
_stereo->on();
_stereo->setCd(3);
_stereo->setVolume(11);
}
void StereoOnWithCDCommand::undo()
{
_stereo->off();
}
CeilingFanOnCommand::CeilingFanOnCommand(CeilingFan* ceilingFan):
_ceilingFan(ceilingFan)
{
}
void CeilingFanOnCommand::execute()
{
_ceilingFan->high();
}
void CeilingFanOnCommand::undo()
{
_ceilingFan->off();
}
CeilingFanOffCommand::CeilingFanOffCommand(CeilingFan* ceilingFan):
_ceilingFan(ceilingFan)
{
}
void CeilingFanOffCommand::execute()
{
_ceilingFan->off();
}
void CeilingFanOffCommand::undo()
{
switch (_ceilingFan->getSpeed())
{
case 1: _ceilingFan->low(); break;
case 2: _ceilingFan->medium(); break;
case 3: _ceilingFan->high(); break;
}
}
GarageDoorCloseCommand::GarageDoorCloseCommand(GarageDoor* door):
_door(door)
{
}
void GarageDoorCloseCommand::execute()
{
_door->down();
}
void GarageDoorCloseCommand::undo()
{
_door->up();
}
StereoOffWithCDCommand::StereoOffWithCDCommand(Stereo* stereo):
_stereo(stereo)
{
}
void StereoOffWithCDCommand::execute()
{
_stereo->off();
}
void StereoOffWithCDCommand::undo()
{
_stereo->on();
_stereo->setCd(3);
_stereo->setVolume(11);
}main.cpp:
cpp
#include "command.h"
int main()
{
RemoteControl* remoteControl = new RemoteControl();
Light* outdoorLight = new OutdoorLight();
Light* kitchenLight = new CeilingLight();
CeilingFan* ceilingFan = new CeilingFan();
GarageDoor* garageDoor = new GarageDoor();
Stereo* stereo = new Stereo();
LightOnCommand* outdoorLightOnCommand = new LightOnCommand(outdoorLight);
LightOffCommand* outdoorLightOffCommand = new LightOffCommand(outdoorLight);
LightOnCommand* kitchenLightOnCommand = new LightOnCommand(kitchenLight);
LightOffCommand* kitchenLightOffCommand = new LightOffCommand(kitchenLight);
CeilingFanOnCommand* ceilingFanOnCommand = new CeilingFanOnCommand(ceilingFan);
CeilingFanOffCommand* ceilingFanOffCommand = new CeilingFanOffCommand(ceilingFan);
GarageDoorOpenCommand* garageDoorOpenCommand = new GarageDoorOpenCommand(garageDoor);
GarageDoorCloseCommand* garageDoorCloseCommand = new GarageDoorCloseCommand(garageDoor);
StereoOnWithCDCommand* stereoOnWithCDCommand = new StereoOnWithCDCommand(stereo);
StereoOffWithCDCommand* stereoOffWithCDCommand = new StereoOffWithCDCommand(stereo);
remoteControl->setCommand(0, outdoorLightOnCommand, outdoorLightOffCommand);
remoteControl->setCommand(1, kitchenLightOnCommand, kitchenLightOffCommand);
remoteControl->setCommand(2, ceilingFanOnCommand, ceilingFanOffCommand);
remoteControl->setCommand(3, garageDoorOpenCommand, garageDoorCloseCommand);
remoteControl->setCommand(4, stereoOnWithCDCommand, stereoOffWithCDCommand);
remoteControl->setCommand(5, [outdoorLight]() { outdoorLight->on(); });
remoteControl->print();
remoteControl->onButtonWasPressed(0);
remoteControl->offButtonWasPressed(0);
remoteControl->undoButtonWasPushed();
remoteControl->onButtonWasPressed(1);
remoteControl->offButtonWasPressed(1);
remoteControl->onButtonWasPressed(2);
remoteControl->offButtonWasPressed(2);
remoteControl->onButtonWasPressed(3);
remoteControl->offButtonWasPressed(3);
remoteControl->onButtonWasPressed(4);
remoteControl->offButtonWasPressed(4);
remoteControl->undoButtonWasPushed();
// 测试lambda表达式改写
remoteControl->onButtonWasPressed(5);
return 0;
}运行结果:
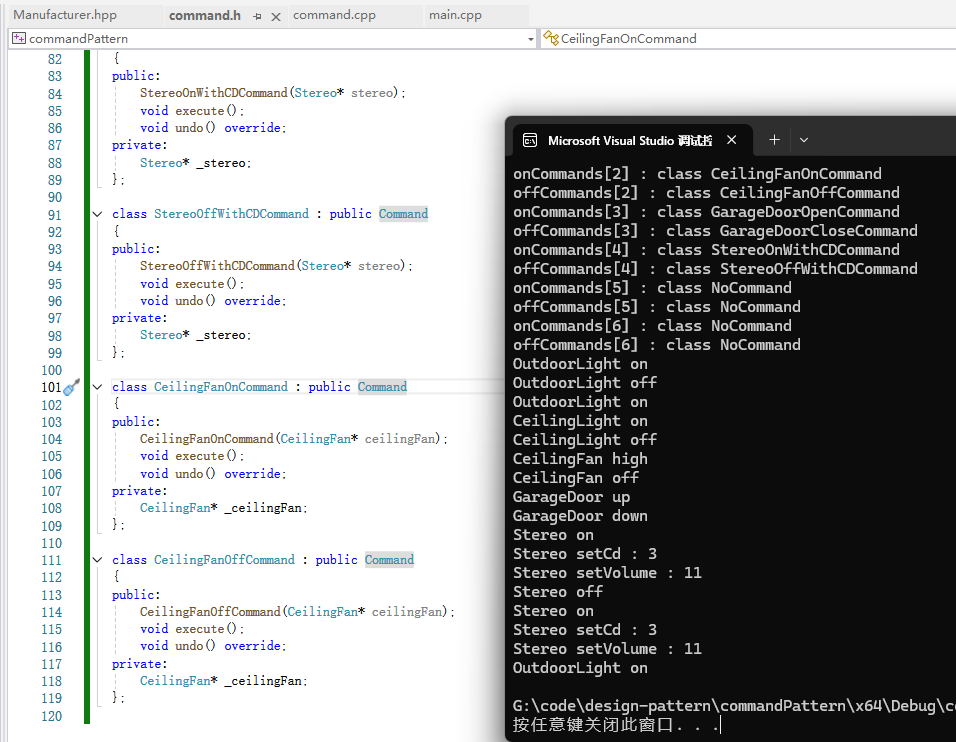
撤销功能成功运行。
十.总结
命令模式中我们还可以实现宏命令,也就是一个命令中组合了一组接收者,这个命令被调用者调用时就会令者一组接收者挨个干活。命令模式还可以运用在请求队列,也就是生产者消费者模型中;还可以运用在日志请求,在Command中加上storage和load方法即可。以下是一些总结:
- 命令模式把做出请求的对象从知道如何执行请求的对象解耦。
- 命令对象处在解耦的中心,封装接收者以及一个(或一组)动作。
- 调用者通过调用命令对象的execute()做出请求,这会使得接收者的动作被调用。
- 调用者可以用命令参数化,甚至可以在运行时动态地进行。
- 通过实现一个undo()方法来把对象重建到最后一次执行execute()前的状态,命令可以支持撤销。
- 宏命令是命令模式的一种简单的延伸。它允许调用多个命令。同样,宏命令很容易支持undo()。
- 在实践中,"聪明"命令对象并不少见。这些对象自己实现请求,而不是委托给接收者。
- 命令也可以用来实现日志和事务系统。