文章目录
- 图论基础
- DFS
- 所有可达路径
- BFS
- 孤岛计数
- 岛屿的最大面积
- 孤岛的总面积
- 沉没孤岛
- 高山流水
- 建造最大岛屿
- 岛屿的周长
- 腐烂的橘子
- 课程表(拓扑排序)
- [实现 Trie (前缀树、字典树)](#实现 Trie (前缀树、字典树))
图论基础
DFS
核心思想:走到底(目标)之后再回溯
代码框架类似于我们前面说的回溯算法的框架:
java
void dfs(参数) {
if (终止条件) {
存放结果;
return;
}
for (选择:本节点所连接的其他节点) {
处理节点;
dfs(图,选择的节点); // 递归
回溯,撤销处理结果
}
}从而我们可以衍生出深搜三要素:
- 确认递归参数
- 确认终止条件
- 处理目前节点出发的路径(通常是for循环且伴有回溯)
所有可达路径
题目链接:98. 可达路径
解题逻辑:
dfs是一个比较广泛的算法,例如我们前面的二叉树的遍历,它属于dfs在二叉树中的应用,以及前面的回溯算法,它也属于dfs的一种。这也就是为什么回溯算法的模板和dfs非常的相似。
代码如下:
java
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = in.nextInt();
int b = in.nextInt();
List<Integer>[] bucket = new LinkedList[a];
for (int i = 0; i < a; i++) bucket[i] = new LinkedList<Integer>();
while (b-- > 0) {
int num1 = in.nextInt();
int num2 = in.nextInt();
bucket[num1 - 1].add(num2);
}
path.add(1);
dfs(bucket, 1, a);
if (result.size() == 0) System.out.println(-1);
for (List<Integer> path : result) {
StringBuffer ss = new StringBuffer();
for (Integer num : path) {
ss.append(num).append(" ");
}
System.out.println(ss.substring(0, ss.length() - 1).toString());
}
}
static List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
static List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
public static void dfs(List<Integer>[] bucket, Integer item, Integer end) {
if (item == end) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (Integer num : bucket[item - 1]) {
path.add(num);
dfs(bucket, num, end);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}BFS
广度优先算法:是一种波纹状的搜索算法,一圈一圈向外递进
在二叉树的遍历中的层序遍历就是bfs在树形结构中的应用。
bfs不需要显式的递归,而是需要借助一个额外的数据结构帮我们存储数据,这个数据结构可以是队列,也可以是栈、数组等线性数据结构。
bfs的代码模板如下:
java
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class BFSExample {
// 表示四个方向:右、下、上、左
private static final int[][] dir = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};
/**
* BFS搜索算法
* @param grid 地图,二维字符数组
* @param visited 标记访问过的节点
* @param x 开始搜索的x坐标
* @param y 开始搜索的y坐标
*/
public static void bfs(char[][] grid, boolean[][] visited, int x, int y) {
// 定义队列,使用LinkedList实现Queue接口
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// 起始节点加入队列
queue.offer(new int[]{x, y});
// 标记为已访问
visited[x][y] = true;
// 队列不为空时继续遍历
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
// 取出队首元素
int[] cur = queue.poll();
int curx = cur[0];
int cury = cur[1];
// 遍历四个方向
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nextx = curx + dir[i][0];
int nexty = cury + dir[i][1];
// 检查坐标是否越界
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.length || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].length) {
continue;
}
// 如果节点未被访问过
if (!visited[nextx][nexty]) {
// 加入队列
queue.offer(new int[]{nextx, nexty});
// 标记为已访问
visited[nextx][nexty] = true;
}
}
}
}
}孤岛计数
题目链接:99. 计数孤岛
同Leetcode:200. 岛屿数量
解题逻辑:遍历整张图,如果该点为陆地且未被搜索过,则岛个数加1,然后将该点及周围的岛全部搜索干净(标记为搜索过),然后继续往下遍历,遇到海洋跳过,遇到搜索了的岛跳过,如此直到遍历完整张图。
DFS版
java
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = in.nextInt();
int b = in.nextInt();
//记录图
int[][] map = new int[a][b];
int[][] record = new int[a][b];
for(int i = 0;i < a;i++){
for(int j = 0;j < b;j++) {
map[i][j] = in.nextInt();
}
}
int count = 0;
//开始遍历
for(int i = 0;i < a;i++){
for(int j = 0;j < b;j++) {
if(map[i][j] == 0 || record[i][j] == 1) continue;
count++;
dfs(map,record,i,j,a,b);
}
}
System.out.println(count);
}
// 表示四个方向:右、下、上、左
private static final int[][] dir = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};
public static void dfs(int[][] map,int[][] record,int x,int y,int limitx,int limity){
if(x < 0 || y < 0 || x >= limitx || y >= limity || record[x][y] == 1 || map[x][y] == 0) return;
record[x][y] = 1;
for(int i = 0;i < dir.length;i++) {
int nextx = x + dir[i][0];
int nexty = y + dir[i][1];
dfs(map,record,nextx,nexty,limitx,limity);
}
}
}BFS版
java
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int m = in.nextInt();
int n = in.nextInt();
boolean[][] record = new boolean[m][n];
int[][] map = new int[m][n];
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) map[i][j] = in.nextInt();
int count = 0;;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if(!record[i][j] && map[i][j] == 1) {
count++;
bfs(map, record, i, j);
}
}
}
System.out.println(count);
}
public static int[][] dire = {{1, 0}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};
public static void bfs(int[][] map, boolean[][] record, int x, int y) {
Deque<int[]> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.offer(new int[]{x,y});
record[x][y] = true;
while(queue.size() > 0) {
int[] pos = queue.poll();
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int curX = pos[0] + dire[i][0];
int curY = pos[1] + dire[i][1];
if(curX < 0 || curY < 0 || curX >= map.length || curY >= map[0].length) continue;
if(!record[curX][curY] && map[curX][curY] == 1) {
queue.offer(new int[]{curX,curY});
record[curX][curY] = true;
}
}
}
}
}岛屿的最大面积
题目链接:100. 最大岛屿的面积
解题逻辑:
本题使用DFS进行解决,BFS可自行探索。
解题代码:
java
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int m = in.nextInt();
int n = in.nextInt();
boolean[][] record = new boolean[m][n];
int[][] map = new int[m][n];
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) map[i][j] = in.nextInt();
int max = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if(!record[i][j] && map[i][j] == 1) {
int area = dfs(map, record, i, j,1);
if(area > max) max = area;
}
}
}
System.out.println(max);
}
public static int[][] dire = {{1, 0}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};
public static int dfs(int[][] map, boolean[][] record, int x, int y,int area) {
if(x < 0 || y < 0 || x >= map.length || y >= map[0].length || record[x][y] || map[x][y] == 0) return area - 1;
record[x][y] = true;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int curX = x + dire[i][0];
int curY = y + dire[i][1];
area = dfs(map, record, curX, curY, area + 1);
}
return area;
}
}孤岛的总面积
题目链接:101. 孤岛的总面积
解题逻辑:
在上一题的基础上加上一个孤岛判断的逻辑(使用类变量),如果不是孤岛,那么不计入到孤岛总面积中。
解题代码:
java
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int m = in.nextInt();
int n = in.nextInt();
boolean[][] record = new boolean[m][n];
int[][] map = new int[m][n];
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) map[i][j] = in.nextInt();
int total = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if(!record[i][j] && map[i][j] == 1) {
flag = true;
int area = dfs(map, record, i, j,1);
if(flag) total += area;
}
}
}
System.out.println(total);
}
public static int[][] dire = {{1, 0}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};
public static boolean flag = true;
public static int dfs(int[][] map, boolean[][] record, int x, int y,int area) {
if(x < 0 || y < 0 || x >= map.length || y >= map[0].length || record[x][y] || map[x][y] == 0) return area - 1;
record[x][y] = true;
if(x == 0 || x == map.length - 1 || y == 0 || y == map[0].length - 1) flag = false;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int curX = x + dire[i][0];
int curY = y + dire[i][1];
area = dfs(map, record, curX, curY, area + 1);
}
return area;
}
}沉没孤岛
题目链接:102. 沉没孤岛
解题逻辑:
在上一题的基础上,将孤岛的坐标收集起来,最后集体沉默就可以了
解题代码:
java
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int m = in.nextInt();
int n = in.nextInt();
boolean[][] record = new boolean[m][n];
int[][] map = new int[m][n];
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) map[i][j] = in.nextInt();
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if(!record[i][j] && map[i][j] == 1) {
flag = true;
dfs(map, record, i, j);
if(flag) allIsland.add(new ArrayList<>(thisIsland));
thisIsland.clear();
}
}
}
for(List<int[]> island : allIsland) {
for(int[] point : island) {
map[point[0]][point[1]] = 0;
}
}
for(int[] row : map) {
for(int narrow : row) {
System.out.print(narrow + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static int[][] dire = {{1, 0}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};
public static boolean flag = true;
public static List<int[]> thisIsland = new ArrayList<>();
public static List<List<int[]>> allIsland = new ArrayList<>();
public static void dfs(int[][] map, boolean[][] record, int x, int y) {
if(x < 0 || y < 0 || x >= map.length || y >= map[0].length || record[x][y] || map[x][y] == 0) return;
record[x][y] = true;
thisIsland.add(new int[]{x, y});
if(x == 0 || x == map.length - 1 || y == 0 || y == map[0].length - 1) flag = false;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int curX = x + dire[i][0];
int curY = y + dire[i][1];
dfs(map, record, curX, curY);
}
}
}高山流水
题目链接:103. 高山流水
解题逻辑:
依旧使用dfs模拟走路,与前面一题的区别在于:
- 走路的逻辑发生变化,下一步还需判断高度是否小于等于当前高度
- 在对起点进行遍历的时候,需要刷新记录,因为每个起点的路径是互不影响的
解题代码:
java
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int m = in.nextInt();
int n = in.nextInt();
boolean[][] record = new boolean[m][n];
int[][] map = new int[m][n];
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) map[i][j] = in.nextInt();
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
flag = new boolean[2];
record = new boolean[m][n];
if(dfs(map, record, i, j)) results.add(new int[]{i, j});
}
}
for(int[] result : results) {
System.out.println(result[0] + " " + result[1]);
}
}
public static int[][] dire = {{1, 0}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};
public static List<int[]> results = new ArrayList<>();
public static boolean[] flag = new boolean[2];
public static boolean dfs(int[][] map, boolean[][] record, int x, int y) {
record[x][y] = true;
if(x == 0 || y == 0) flag[0] = true;
if(x == map.length - 1 || y == map[0].length - 1) flag[1] = true;
if(flag[0] && flag[1]) return true;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int curX = x + dire[i][0];
int curY = y + dire[i][1];
if(curX < 0 || curY < 0 || curX >= map.length || curY >= map[0].length || record[curX][curY]) continue;
if(map[x][y] < map[curX][curY]) continue;
boolean ret = dfs(map, record, curX, curY);
if(ret) return true;
}
return false;
}
}建造最大岛屿
题目链接:104. 建造最大岛屿
解题逻辑:
我们使用搜索(dfs、bfs均可,本题使用bfs)将现有的岛屿做一个染色,同时记录每一个岛屿的大小。然后再遍历每一块水域,如果与岛屿相邻则进行的累加,如此选出最大的岛屿面积。
易错点:在遍历水域的时候,由于水域可能会被岛屿环绕,所以可能会将该岛屿的面积累加多次,所以这里要根据岛屿编号进行去重。
解题代码:
java
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int m = in.nextInt();
int n = in.nextInt();
boolean[][] record = new boolean[m][n];
int[][] map = new int[m][n];
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) map[i][j] = in.nextInt();
Map<Integer,Integer> islands = new HashMap<>();
int islandNum = 2; for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if(record[i][j] || map[i][j] == 0) continue;
int area = bfs(map, record, i, j, islandNum);
islands.put(islandNum, area);
islandNum++;
}
}
int max = 0;
for(Integer val : islands.values()) if(val > max) max = val;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if(map[i][j] == 0) {
int sum = 1;
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
for(int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int curX = i + dire[k][0];
int curY = j + dire[k][1];
if(curX < 0 || curY < 0 || curX >= map.length || curY >= map[0].length || map[curX][curY] == 0 || set.contains(map[curX][curY])) continue;
int area = islands.get(map[curX][curY]);
sum += area;
set.add(map[curX][curY]);
}
if(sum > max) max = sum;
}
}
}
System.out.println(max);
}
public static int[][] dire = {{1, 0}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};
public static int bfs(int[][] map, boolean[][] record, int x, int y, int islandNum) {
Deque<int[]> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.offer(new int[]{x, y});
int area = 0;
record[x][y] = true;
map[x][y] = islandNum;
area++;
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] cur = queue.poll();
x = cur[0];
y = cur[1];
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int curX = x + dire[i][0];
int curY = y + dire[i][1];
if(curX < 0 || curY < 0 || curX >= map.length || curY >= map[0].length || record[curX][curY] || map[curX][curY] == 0) continue;
queue.offer(new int[]{curX, curY});
record[curX][curY] = true;
map[curX][curY] = islandNum;
area++;
}
}
return area;
}
}岛屿的周长
题目链接:106. 海岸线计算
解题思路:
本题转化一下也就是说:岛屿四周靠海的边有多少条?也就是说我们只需要遍历找到岛屿的格子,然后判断他的哪几条边靠海,然后进行累加就可以得到结果。
解题代码:
java
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static int[][] dire = {{1, 0}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int m = in.nextInt();
int n = in.nextInt();
int[][] map = new int[m][n];
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) map[i][j] = in.nextInt();
int result = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if(map[i][j] == 1) {
for(int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int curX = i + dire[k][0];
int curY = j + dire[k][1];
if(curX < 0 || curY < 0 || curX >= map.length || curY >= map[0].length || map[curX][curY] == 0) result++;
}
}
}
}
System.out.println(result);
}
}腐烂的橘子
题目链接:994. 腐烂的橘子
解题逻辑:
这道题的本质就是考察bfs的扩散轮数:每一轮遍历开始前,先获取当前队列的元素总数 size,然后循环 size 次,这 size 个元素就是「当前层的所有节点」,处理完这一层,扩散次数就 +1。
解题代码:
java
class Solution {
public int orangesRotting(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
boolean[][] record = new boolean[m][n];
int result = bfs(grid, record);
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if(grid[i][j] == 1) {
return -1;
}
}
}
return result;
}
public static int[][] dire = {{1, 0}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};
public int bfs(int[][] grid, boolean[][] record) {
Deque<int[]> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
for(int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {
if(grid[i][j] == 2) {
queue.offer(new int[]{i, j});
record[i][j] = true;
}
}
}
int time = 0;
int offset;
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
offset = queue.size();
for (int k = 0; k < offset; k++) {
int[] posi = queue.poll();
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int curX = posi[0] + dire[i][0];
int curY = posi[1] + dire[i][1];
if(curX < 0 || curY < 0 || curX >= grid.length || curY >= grid[0].length || record[curX][curY] || grid[curX][curY] == 0 || grid[curX][curY] == 2) continue;
queue.offer(new int[]{curX, curY});
record[curX][curY] = true;
grid[curX][curY] = 2;
}
}
if(!queue.isEmpty()) time++;
}
return time;
}
}课程表(拓扑排序)
题目链接:207. 课程表
给出一个 有向图,把这个有向图转成线性的排序 就叫拓扑排序
拓扑排序的核心就是不断找入度为0的节点,然后再将这些节点删去,再重新寻找入度为0的节点,如此循环往复即可。
拓扑排序使用广搜(BFS)更加简单常用。如果最终结果集中的元素个数和所给的元素个数不一样,那么就说明有向图成环了!此时拓扑排序是无法完成的。
这之间有两个数据结构发挥了巨大的作用:
- 使用邻接表记录课程之间的关系
- 使用列表存储每个课程的入度
解题代码:
java
class Solution {
public boolean canFinish(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites) {
int[] inDegree = new int[numCourses];
List<List<Integer>> graph = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) graph.add(new ArrayList<>());
for(int[] item : prerequisites) {
inDegree[item[0]]++;
graph.get(item[1]).add(item[0]);
}
int count = 0;
Deque<Integer> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
for(int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) if(inDegree[i] == 0) queue.offer(i);
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
int cur = queue.poll();
count++;
for(int lesson : graph.get(cur)) {
inDegree[lesson]--;
if(inDegree[lesson] == 0) queue.offer(lesson);
}
}
if(count == numCourses) return true;
return false;
}
}实现 Trie (前缀树、字典树)
题目链接:208. 实现 Trie (前缀树)
解题逻辑:
字典树的构造就是将所给字符串拆成单个的字符,依次连接前一个结点形成一棵多叉树。
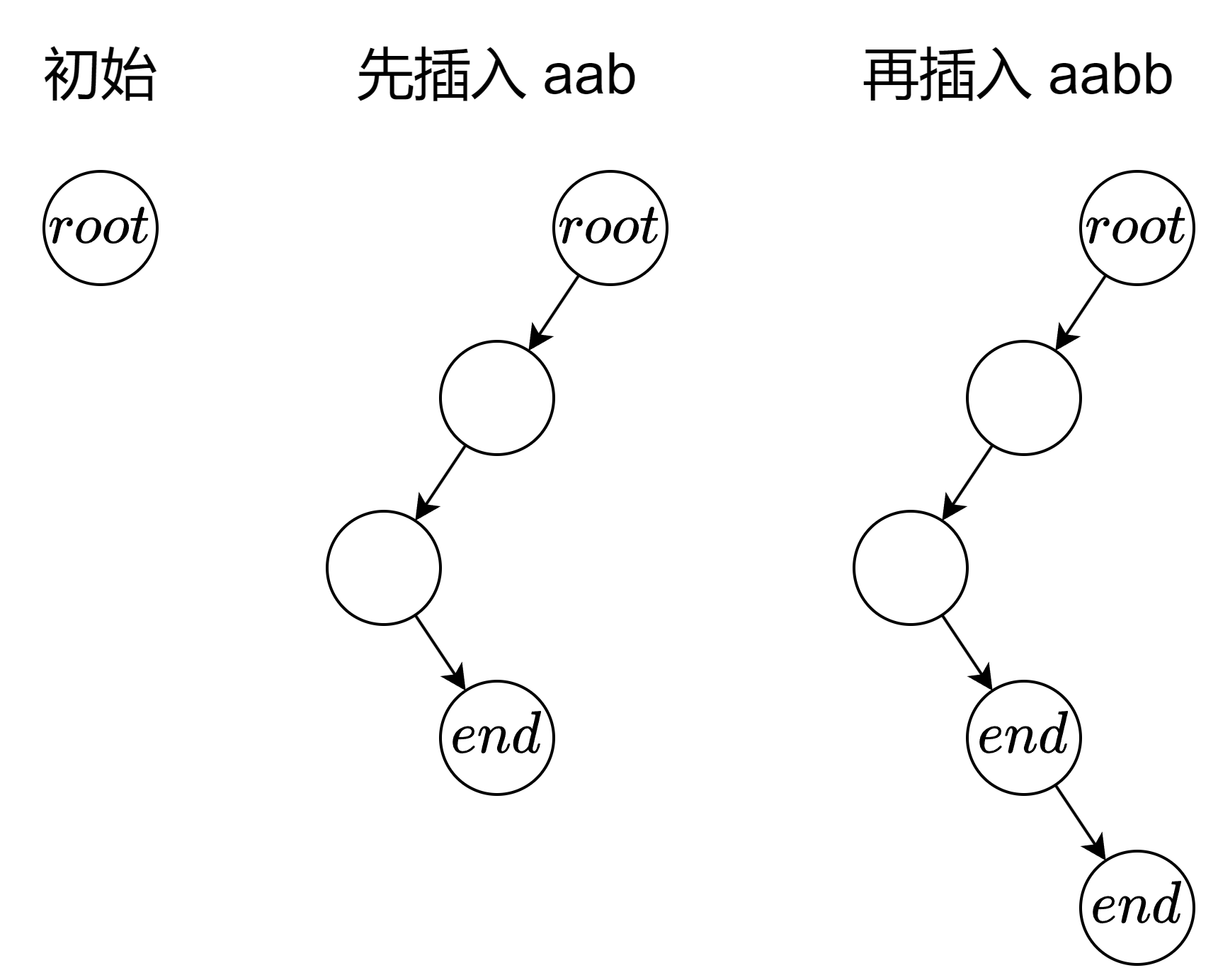
每个节点存储下一个节点的数组以及是否为结尾的标记。
解题代码:
java
class Trie {
class Node{
Node[] nodes = new Node[26];
boolean isEnd = false;
}
private Node root = new Node();
public Trie() {
}
public void insert(String word) {
Node prefix = root;
for(char c : word.toCharArray()) {
if(prefix.nodes[c - 'a'] == null) prefix.nodes[c - 'a'] = new Node();
prefix = prefix.nodes[c - 'a'];
}
prefix.isEnd = true;
}
public boolean search(String word) {
Node prefix = root;
for(char c : word.toCharArray()) {
if(prefix.nodes[c - 'a'] == null) return false;
prefix = prefix.nodes[c - 'a'];
}
return prefix.isEnd;
}
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
Node pre = root;
for(char c : prefix.toCharArray()) {
if(pre.nodes[c - 'a'] == null) return false;
pre = pre.nodes[c - 'a'];
}
return true;
}
}
/**
* Your Trie object will be instantiated and called as such:
* Trie obj = new Trie();
* obj.insert(word);
* boolean param_2 = obj.search(word);
* boolean param_3 = obj.startsWith(prefix);
*/