RT-DETR 简介(Real-Time Detection Transformer)
RT-DETR(Real-Time DEtection TRansformer)是由百度提出的一种面向实时场景的端到端目标检测 Transformer 模型 。与传统基于 CNN 的 YOLO 系列不同,RT-DETR 以 DETR 架构 为基础,通过一系列结构与训练策略优化,实现了 无需 NMS 的实时目标检测能力,在速度与精度之间取得了良好平衡。
1. 模型架构特点
RT-DETR 采用 CNN + Transformer Encoder--Decoder 的混合结构:
-
Backbone(主干网络)
使用高效 CNN(如 ResNet / ConvNeXt / CSP 风格改造)提取多尺度特征,兼顾推理速度与特征表达能力。
-
Hybrid Encoder(混合编码器)
将 CNN 特征映射与 Transformer 编码器结合,通过注意力机制增强全局建模能力,同时引入轻量化设计以降低计算开销。
-
Transformer Decoder(解码器)
使用一组固定数量的 Object Queries,直接预测目标类别和边界框,实现:
-
端到端检测
-
无需 Anchor
-
无需 NMS 后处理
-
2. 核心优势
-
端到端检测
直接输出最终检测结果,避免传统检测器复杂的后处理流程(如 NMS)。
-
实时性能友好
针对实时推理进行了大量工程级优化,相比原始 DETR 系列,大幅降低收敛时间与推理延迟。
-
结构规整,利于部署
模型拓扑清晰,算子类型相对集中,适合进行 ONNX 导出与 NPU 算子映射。
-
精度--速度平衡良好
在 COCO 等数据集上,在同等算力条件下可达到接近 YOLO 系列的速度,同时具备 Transformer 的全局建模优势。
下面在RK3588上完成对RTDETR的部署。
cpp后处理:
#include "DFINE.h"
inline static int clamp(float val, int min, int max) {
return val > min ? (val < max ? val : max) : min;
}
static float sigmoid(float x) { return 1.0 / (1.0 + expf(-x)); }
static float unsigmoid(float y) { return -1.0 * logf((1.0 / y) - 1.0); }
inline static int32_t __clip(float val, float min, float max)
{
float f = val <= min ? min : (val >= max ? max : val);
return f;
}
static int8_t qnt_f32_to_affine(float f32, int32_t zp, float scale)
{
float dst_val = (f32 / scale) + zp;
int8_t res = (int8_t)__clip(dst_val, -128, 127);
return res;
}
static float deqnt_affine_to_f32(int8_t qnt, int32_t zp, float scale) { return ((float)qnt - (float)zp) * scale; }
int DFINE::proprecessDFINE(std::vector<rknn_output> output, std::vector<float> out_scales,
std::vector<int32_t> out_zps,
std::vector<cv::Rect> &boxes,
std::vector<float> &confidences,
std::vector<int> &classids,
std::vector<int> &anchorf,
float confThres)
{
// labels:[1,300,0,0] boxes: [1,300,4,0] scores: [1,300,0,0]
float *labels_data = (float*)output[0].buf;
float *boxes_data = (float*)output[1].buf;
float *scores_data = (float*)output[2].buf;
for (int i = 0; i < 300; ++i) {
std::cout << "scores_data[i]: " << scores_data[i] << std::endl;
if(scores_data[i] < confThres) continue;
int labelsid = static_cast<int>(labels_data[i]);
float x1 = boxes_data[i * 4 + 0] * 640;
float y1 = boxes_data[i * 4 + 1] * 640;
float x2 = boxes_data[i * 4 + 2] * 640;
float y2 = boxes_data[i * 4 + 3] * 640;
std::cout << "x: " << x1 << std::endl;
std::cout << "y: " << y1 << std::endl;
std::cout << "w: " << x2 << std::endl;
std::cout << "h: " << y2 << std::endl;
boxes.push_back(cv::Rect(int(x1), int(y1), (int)(x2 - x1), (int)(y2 -y1)));
float ss = scores_data[i];
confidences.emplace_back(ss);
classids.emplace_back(labelsid);
}
return 0;
}
cv::Mat DFINE::letterboxYolo(cv::Mat src, int &x_pad, int &y_pad, float &scale,int &channel)
{
if(channel == 1)
{
cv::cvtColor(src,src,cv::COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
}
int input_w = modelInputSize.width; // 模型输入的宽
int input_h = modelInputSize.height; // 模型输入的高
int w, h, x, y;
float r_w = static_cast<float>(input_w) / src.cols;
float r_h = static_cast<float>(input_h) / src.rows;
if (r_h > r_w) {
w = input_w;
h = std::round(r_w * src.rows); // 避免浮点数误差
x = 0;
y = (input_h - h) / 2;
scale = r_w;
} else {
w = std::round(r_h * src.cols);
h = input_h;
x = (input_w - w) / 2;
y = 0;
scale = r_h;
}
x_pad = x;
y_pad = y;
cv::Mat re, out;
if (src.channels() == 3) {
re = cv::Mat(h, w, CV_8UC3);
cv::resize(src, re, re.size(), 0, 0, cv::INTER_LINEAR);
out = cv::Mat(input_h, input_w, CV_8UC3, cv::Scalar(114, 114, 114));
} else if (src.channels() == 1) {
re = cv::Mat(h, w, CV_8UC1);
cv::resize(src, re, re.size(), 0, 0, cv::INTER_LINEAR);
out = cv::Mat(input_h, input_w, CV_8UC1, cv::Scalar(114));
} else {
return cv::Mat(); // 返回空矩阵,避免错误
}
// 将缩放后的图像复制到填充后的图像
re.copyTo(out(cv::Rect(x, y, re.cols, re.rows)));
return out;
}
cv::Rect DFINE::get_rect(cv::Mat &img, cv::Rect bbox)
{
float l, r, t, b;
float r_w = modelInputSize.width / (img.cols * 1.0);
float r_h = modelInputSize.height / (img.rows * 1.0);
if (r_h > r_w) {
l = bbox.x;
r = bbox.x + bbox.width;
t = bbox.y - (modelInputSize.height - r_w * img.rows) / 2;
b = bbox.y + bbox.height - (modelInputSize.height - r_w * img.rows) / 2;
l = l / r_w;
r = r / r_w;
t = t / r_w;
b = b / r_w;
} else {
l = bbox.x - (modelInputSize.width - r_h * img.cols) / 2;
r = bbox.x + bbox.width - (modelInputSize.width - r_h * img.cols) / 2;
t = bbox.y;
b = bbox.y + bbox.height;
l = l / r_h;
r = r / r_h;
t = t / r_h;
b = b / r_h;
l = l < 0 ? 0 : l;
t = r < 0 ? 0 : t;
}
return cv::Rect(round(l), round(t), round(r - l), round(b - t));
}
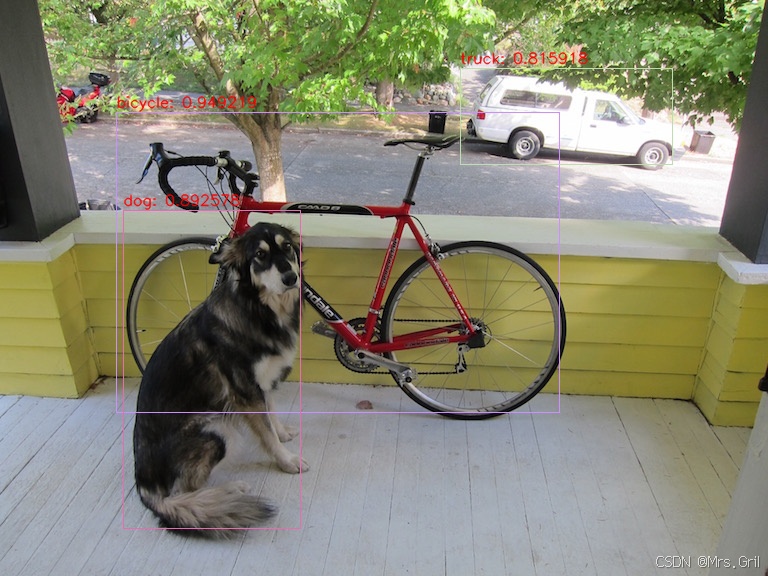
root@lubancat:~/rknn_dfine_demo_Linux# ./rknn_dfine_demo ../rknn_path/rtdetrv2_FP16.rknn ../rknn_path/dog.jpg 10结果展示: