一、岛屿数量
1、题目

2、分析
- 广度/深度优先搜索。广度优先:起始节点入队列,如果水平、垂直方向相邻位置为1切没被访问过(被访问过的1位置,直接改为0),就进队列,重复上述过程,直到队列为空。计数1个岛屿数。
- 遍历图中每个位置为起始,搜索过或者为0的位置直接跳过,直到计数完所有岛屿。
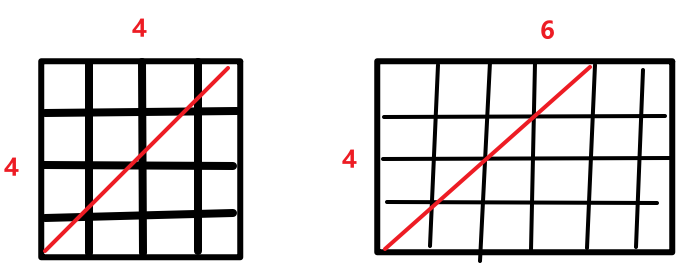
- 时间复杂度:循环遍历起始节点 nm,若需要搜索,图中最多搜索 nm 次。O(2nm)=O(nm)。
- 空间复杂度:队列长度,最长为整个图都是岛屿范围,O(min(n, m))。
红色斜线是最长层:
3、代码
java
class Solution {
public static final int[][] position = {{0, -1}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {1, 0}};
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
int sum = 0; // 计数
int row = grid.length;
if (row == 0) return sum;
int col = grid[0].length;
// 遍历图,尝试以每个位置为起点,开始搜索
for (int i = 0 ; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
// 该位置,没有被访问过且为1,才搜索
if (grid[i][j] == '1') {
bfs(grid, i, j);
sum++;
}
}
}
return sum;
}
public void bfs(char[][] grid, int i, int j) {
int row = grid.length;
int col = grid[0].length;
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(new int[]{i, j}); // 起始位置入队列
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] tmp = queue.poll(); // 队首出栈
// 遍历 tmp 四个方位
for (int[] ints : position) {
int r = ints[0] + tmp[0];
int c = ints[1] + tmp[1];
// 坐标没有超过边界,且没有被遍历过,且为1,才能被纳入队列
if (r >= 0 && r < row && c >= 0 && c < col && grid[r][c] == '1') {
queue.offer(new int[]{r, c});
grid[r][c] = '0';
}
}
}
}
}二、腐烂的橘子
1、题目

2、分析
- 先找到所有腐烂橘子,从他们开始从四周腐烂(广度优先搜索新鲜橘子)。
- 如果没有新鲜橘子,则不用腐烂,返回 0。
- 腐烂结束后,如果还存在新鲜橘子,则返回 -1;否则返回计时。
- 注意:最后一层腐烂橘子,四周已经没有新鲜橘子,但队列不为空,因此会进入循环,导致多计数一次。因此,循环退出条件需要添加:新鲜橘子数 <= 0。
- 时间复杂度:找腐烂橘子、新鲜橘子 O(mn);最坏情况只有一个腐烂橘子,其他都是新鲜橘子,每个新鲜橘子都要入队、出队,O(mn)。最终:O(mn)
- 空间复杂度:最坏情况中间都是腐烂橘子,队列长度,O(min(m, n))。
3、代码
java
class Solution {
public static final int[][] position = {{0, -1}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {1, 0}};
public int orangesRotting(int[][] grid) {
int row = grid.length;
if (row == 0) return 0;
int col = grid[0].length;
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
int freshCount = 0; // 统计新鲜橘子数
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
// 找到初始状态中所有的腐烂橘子,放入队列,作为起始点开始搜索
if (grid[i][j] == 2) queue.offer(new int[]{i, j});
else if (grid[i][j] == 1) freshCount++;
}
}
if (freshCount == 0) return 0; // 不存在新鲜橘子,不需要腐烂
return bfs(grid, queue, freshCount); // 存在新鲜橘子,开始腐烂
}
public int bfs(int[][] grid, Queue<int[]> queue, int freshCount) {
int row = grid.length;
int col = grid[0].length;
int count = 0; // 计分钟数
// freshCount 的作用:最后一层,不会再继续腐烂,不应该计数。此时队列不为空,但 freshCount 为空,就可以结束循环
while(!queue.isEmpty() && freshCount > 0) {
int size = queue.size(); // 该层长度
while (size-- != 0) {
int[] tmp = queue.poll(); // 队首出
// 遍历四个方位上,新鲜的橘子,让它腐烂,并计数
for (int k = 0; k < position.length; k++) {
int r = tmp[0]+position[k][0];
int c = tmp[1]+position[k][1];
if (r >= 0 && r < row && c >= 0 && c < col && grid[r][c] == 1) {
queue.offer(new int[]{r, c});
grid[r][c]=2;
freshCount--;
}
}
}
count++; // 该层腐烂结束后计时
}
return freshCount == 0 ? count : -1; // 新鲜橘子没腐烂完,返回-1
}
}三、课程表
1、题目

2、分析
- 拓扑排序(针对有向无环图进行排序,让先修课程在前):先找到图中没有入度的节点,从他们开始遍历。如果某一个节点的入度边都遍历过了,就可以把该节点在图中删除,入队列,遍历其出度。
- 时间复杂度:初始化图列表 n,构建图 m,找出起始无入度的节点 n,拓扑排序遍历边 m。O(n+m)
- 空间复杂度:构建图的列表(结点数n+边数m)、存储入度计数的数组n、存储没有入度的节点队列n,O(n+m)。
3、代码
java
class Solution {
public boolean canFinish(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites) {
int len = prerequisites.length;
if (len == 0) return true;
// 构建"先修->选修"关系图,如:1->[0,2]。并统计每个节点的入度
List<List<Integer>> map = new ArrayList<>();
int[] preCnt = new int[numCourses];
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) map.add(new ArrayList<>());
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
List<Integer> l ist = map.get(prerequisites[i][1]);
list.add(prerequisites[i][0]);
preCnt[prerequisites[i][0]]++;
}
// 拓扑排序
return bfs(map, preCnt, numCourses);
}
public boolean bfs(List<List<Integer>> map, int[] preCnt, int numCourses) {
int cnt = 0; // 计数已经上过的课
Deque<Integer> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
// 所有入度为 0 的节点入栈
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
if (preCnt[i] == 0) queue.offer(i);
}
// 开始拓扑排序
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int tmp = queue.pop(); // 队首
cnt++;
List<Integer> list = map.get(tmp); // 选修列表
// 选修列表入度减1,并把入度为0的加入队列
for (int value : list) {
preCnt[value]--;
if (preCnt[value] == 0) queue.offer(value);
}
}
if (cnt == numCourses) return true;
return false;
}
}四、实现 Trie 前缀树
1、题目
208. 实现 Trie (前缀树) - 力扣(LeetCode)

2、分析
- 每个树节点,需要存储 26 个子节点的哈希表,若映射值为空则表示没有该子节点。
- Trie:创建树根。
- insert:遍历字母,从根节点开始匹配。若对应字母子节点不存在,则创建节点放入哈希表;若存在,直接移动到子节点。
- search:遍历字母,从根节点开始匹配。存在不匹配,直接返回 false;匹配完了,但是最后一个匹配字母不是最后一个字母,返回 false;其它返回 true。
- startsWith:遍历字母,从根节点开始匹配。存在不匹配,直接返回 false;匹配完了,返回 true。
- 时间复杂度:除了 Trie 是 O(1),其他都是 O(word 长度) 。
- 空间复杂度:总共开销 O(26*所有word长度)。
3、代码
java
class TreeNode {
public TreeNode[] children; // 节点对应 26 个小写字母的分支
public boolean isEnd; // 标记该节点的字母是否是结尾
TreeNode () {
children = new TreeNode[26];
}
}
class Trie {
private TreeNode root;
public Trie() {
root = new TreeNode();
}
public void insert(String word) {
TreeNode cur = root;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
int index = word.charAt(i)-'a';
// 该字母没有创建,则创建节点
if (cur.children[index] == null) cur.children[index] = new TreeNode();
// 创建了,则直接遍历下一个
cur = cur.children[index];
}
cur.isEnd = true; // 标记结尾
}
public boolean search(String word) {
TreeNode cur = root;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
int index = word.charAt(i)-'a';
// 没有匹配字母,返回 false
if (cur.children[index] == null) return false;
cur = cur.children[index];
}
// 如果最后一个字符是结尾节点,返回 true
return cur.isEnd;
}
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
TreeNode cur = root;
for (int i = 0; i < prefix.length(); i++) {
int index = prefix.charAt(i)-'a';
// 没有匹配字母,返回 false
if (cur.children[index] == null) return false;
cur = cur.children[index];
}
return true;
}
}
/**
* Your Trie object will be instantiated and called as such:
* Trie obj = new Trie();
* obj.insert(word);
* boolean param_2 = obj.search(word);
* boolean param_3 = obj.startsWith(prefix);
*/