- YOLO26 on RDK S100P 端侧部署技术报告
- Summary
- Introduction to YOLO26
- Introduction to RDK S100P
- 算法, 工具链, Runtime的权衡
- BenchMark
- Performance
- Accuracy
- 算法层修改参考
- Export程序参考
- OpenExplore步骤参考
- Runtime程序参考
- CPP (CmakeLists.txt)
- CPP (with NMS)
- CPP (without NMS)
- Python (with NMS)
- Python (without NMS)
- Runtime依赖编译参考
Summary
一句话讲清楚YOLO26在NPU平台部署的差异: 基于v8后处理, 删完DFL计算, 删NMS计算, 剩下的就是YOLO26的后处理!
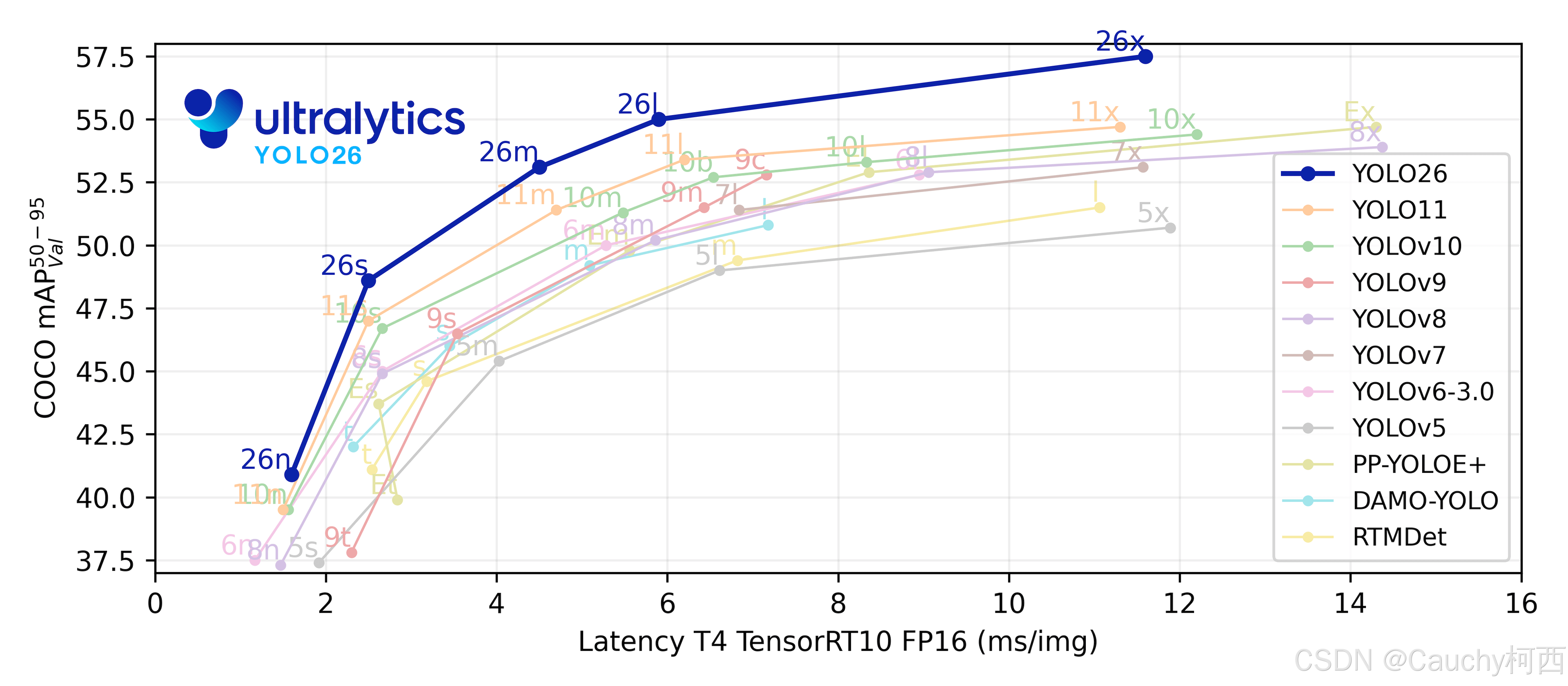
- YOLO26后处理压力更小, v8系的解耦头后处理压力已经是v5的三分之一, 26更是删除了DFL和NMS的计算, 后处理压力进一步减小. 这种改变对密集目标更友好, 更能balance部署方案的BPU吞吐量和算上CPU后处理时间的算法端到端延迟. 这可能是CPU速度提升43%的数据的关键部分, 不过在NPU平台部署体现在了后处理的速度更快.
- 带NMS的后处理精度更高, 无论是ultralytics的GPU上还是端侧NPU上, 由于CPU后处理NMS逻辑为BBox分数预先筛选, 参与NMS的可能只有100个框, 其实NMS时间并不算太长.
- 在RDK S100P上, YOLO26在BPU部分的吞吐量与YOLO11持平, 优于纯Transformer结构的YOLO12. 这符合预期
- 在RDK S100P上, YOLO26精度均好于YOLO12, 尤其是YOLO26小目标检测的定点精度保持断崖领先其他代YOLO. 虽然YOLO12精度比YOLO26略高, 但是纯Transformer的YOLO12计算代价确实太高了.
说明
- 本文类型为post, 技术报告类, 并非入门教程. 文中所有观点仅代表个人, 仅供YOLO爱好者交流.
- 本文所有输入采用HWC-RGB888的输入, 同时带非查表实现的除以255的BPU处理加速, 不使用nv12输入.
- 其他YOLO系列在BPU上的部署参考 RDK YOLO All-in-One: CSDN Link
- 请注意, Ultralytics YOLO采用AGPL-3.0协议, 请遵循相关协议约定使用, 更多请参考: https://www.ultralytics.com/license
Introduction to YOLO26
Ultralytics YOLO26 是 YOLO 系列实时对象检测器的最新演进,从头开始专为边缘和低功耗设备而设计。它引入了简化的设计,消除了不必要的复杂性,同时集成了有针对性的创新,以实现更快、更轻、更易于访问的部署.
YOLO26 的架构遵循的核心原则:
-
简洁性: YOLO26是一个原生的端到端模型,直接生成预测结果,无需非极大值抑制(NMS)。通过消除这一后处理步骤,推理变得更快、更轻量,并且更容易部署到实际系统中。这种突破性方法最初由清华大学的王傲在YOLOv10中开创,并在YOLO26中得到了进一步发展.
-
部署效率: 端到端设计消除了管道的整个阶段,从而大大简化了集成,减少了延迟,并使部署在各种环境中更加稳健.
-
训练创新:YOLO26 引入了MuSGD 优化器,它是 SGD 和 Muon 的混合体------灵感来源于 Moonshot AI 在 LLM 训练中 Kimi K2 的突破。该优化器带来了增强的稳定性和更快的收敛,将语言模型中的优化进展转移到计算机视觉领域.
-
任务特定优化:YOLO26 针对专业任务引入了有针对性的改进,包括用于 Segmentation 的语义分割损失和多尺度原型模块,用于高精度 姿势估计 的残差对数似然估计 (RLE),以及通过角度损失优化解码以解决 旋转框检测 中的边界问题.
这些创新共同提供了一个模型系列,该模型系列在小对象上实现了更高的精度,提供了无缝部署,并且在 CPU 上的运行速度提高了 43% --- 使 YOLO26 成为迄今为止资源受限环境中最实用和可部署的 YOLO 模型之一.
Introduction to RDK S100P

不多介绍了, 我在100TOPs算力的Linux生态位最喜欢的一块开发板: RDK S100P Introduction Link
bash
- RDK S100P
CPU Arch: 6 x Cortex - A78AE @ 2.0 GHz (137K DMIPS)
BPU Arch: 1 x Nash-m @ 1.5 GHz (128 TOPs, int8)
Memory: LPDDR5 @ 24GB
Operating System: >= RDK OS 4.0.4-beta based on Ubuntu 22.04算法, 工具链, Runtime的权衡
DataFlows
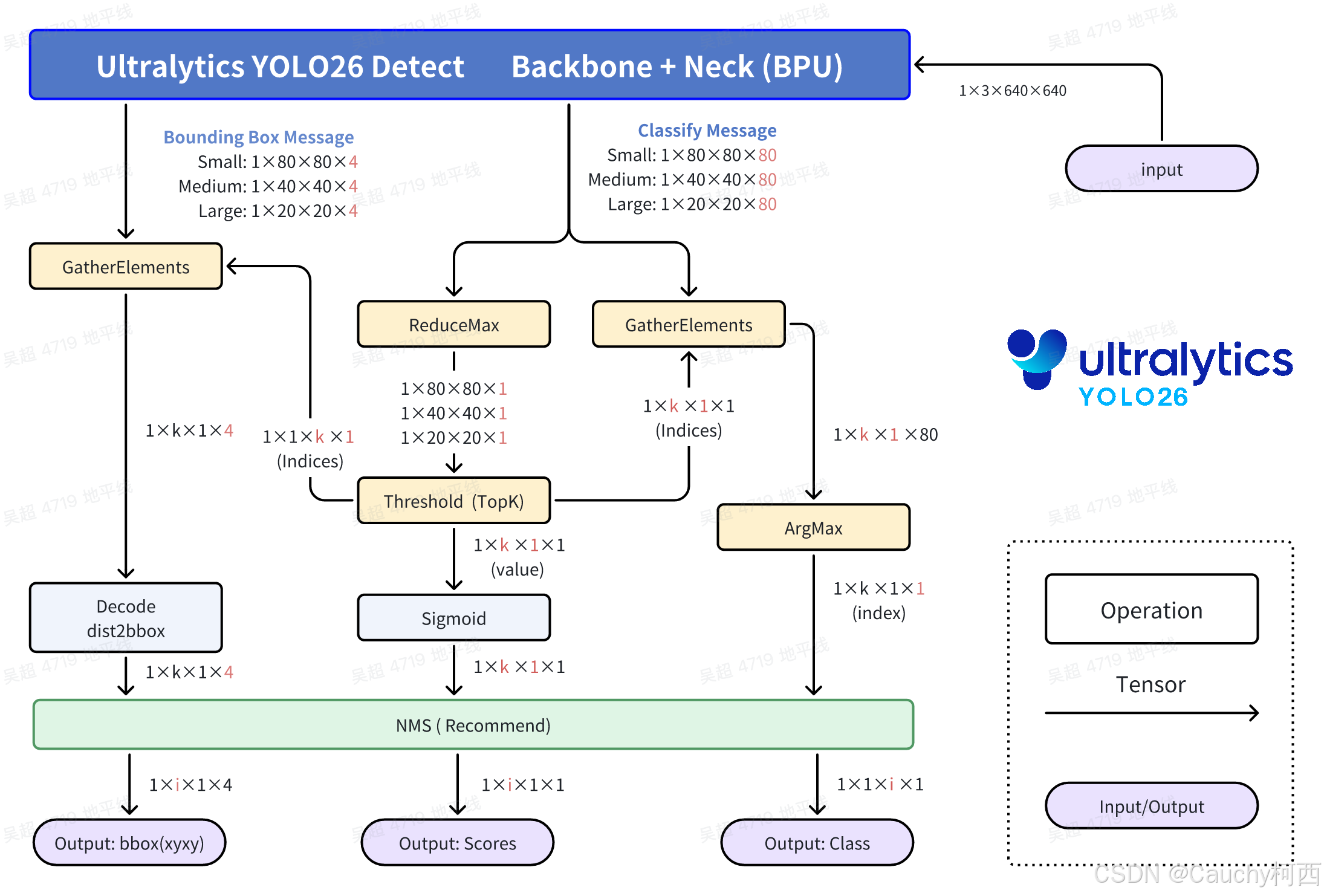
这里对输出头的修改依然是沿用v8系风格, 将bbox和cls的头分开输出, 同时加入NCHW2NHWC的Layout Transpose算子, 使得CPU在沿着C通道做后处理的时候, 每个Grid Cell的数据在内存中是连续的, 提高CPU计算Cache命中率.
classify头: 高性能计算的核心结构与v8系列一致, 首先是利用Sigmoid函数单调性找最大值和比较分数是否合格, 然后分数不合格的Bounding Box直接Contiue或不去Select, 节约Bounding Box的解码计算的计算量.
Bounding Box头: v8从最后一个带实权的卷积算子出来后, ltrb有16个数字, 按照DFL结构规则计算得到ltrb信息, 26从卷积算子出来的数据就直接是ltrb信息了, 这节约了一大部分计算量, 同时也避免了一大部分Vector计算, 是更加纯净的Tensor计算. 往下ltrb通过对应的Grid和stride, 计算得到最终的Bounding Box的xyxy坐标.
关于NMS: 这里可以不使用NMS, 并没有出现那么严重的检测框重复和重叠的现象. 但是从COCO2017数据集验证集的5000张照片的全量精度测试结果来看, 带NMS的计算精度更高.
BenchMark
Performance
| Device | Model | Size(Pixels) | Classes | BPU Task Latency / BPU Throughput (Threads) | CPU Latency (Single Core) | params(M) | FLOPs(B) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S100P | YOLO26n Detect | 640×640 | 80 | 1.31 ms / 727.37 FPS (1 thread ) 2.02 ms / 962.93 FPS (2 threads) | 0.5 ms | 2.4 M | 5.4 M |
| S100P | YOLO26s Detect | 640×640 | 80 | 2.12 ms / 458.86 FPS (1 thread ) 3.58 ms / 549.12 FPS (2 threads) | 0.5 ms | 9.5 M | 20.7 M |
| S100P | YOLO26m Detect | 640×640 | 80 | 4.16 ms / 236.86 FPS (1 thread ) 7.63 ms / 259.35 FPS (2 threads) | 0.5 ms | 20.4 M | 68.2 M |
| S100P | YOLO26l Detect | 640×640 | 80 | 4.95 ms / 199.54 FPS (1 thread ) 9.20 ms / 215.27 FPS (2 threads) | 0.5 ms | 24.8 M | 86.4 M |
| S100P | YOLO26x Detect | 640×640 | 80 | 8.98 ms / 110.47 FPS (1 thread ) 17.19 ms / 115.62 FPS (2 threads) | 0.5 ms | 55.7 M | 193.9 M |
| S100P | YOLO12n Detect | 640×640 | 80 | 1.88 ms / 513.70 FPS (1 thread ) 3.07 ms / 634.97 FPS (2 threads) | 2.0 ms | 2.6 M | 7.7 M |
| S100P | YOLO12s Detect | 640×640 | 80 | 3.10 ms / 315.83 FPS (1 thread ) 5.50 ms / 357.85 FPS (2 threads) | 2.0 ms | 9.3 M | 21.4 M |
| S100P | YOLO12m Detect | 640×640 | 80 | 6.47 ms / 152.80 FPS (1 thread ) 12.18 ms / 162.62 FPS (2 threads) | 2.0 ms | 20.2 M | 67.5 M |
| S100P | YOLO12l Detect | 640×640 | 80 | 10.23 ms / 97.01 FPS (1 thread ) 19.67 ms / 101.04 FPS (2 threads) | 2.0 ms | 26.4 M | 88.9 M |
| S100P | YOLO12x Detect | 640×640 | 80 | 17.05 ms / 58.34 FPS (1 thread ) 33.21 ms / 59.92 FPS (2 threads) | 2.0 ms | 59.1 M | 199.0 M |
| S100P | YOLO11n Detect | 640×640 | 80 | 1.16 ms / 816.50 FPS (1 thread ) 1.66 ms / 1155.65 FPS (2 threads) | 2.0 ms | 2.6 M | 6.5 M |
| S100P | YOLO11s Detect | 640×640 | 80 | 1.81 ms / 533.50 FPS (1 thread ) 2.98 ms / 656.31 FPS (2 threads) | 2.0 ms | 9.4 M | 21.5 M |
| S100P | YOLO11m Detect | 640×640 | 80 | 3.90 ms / 252.02 FPS (1 thread ) 7.10 ms / 278.36 FPS (2 threads) | 2.0 ms | 20.1 M | 68.0 M |
| S100P | YOLO11l Detect | 640×640 | 80 | 4.73 ms / 208.61 FPS (1 thread ) 8.75 ms / 225.99 FPS (2 threads) | 2.0 ms | 25.3 M | 86.9 M |
| S100P | YOLO11x Detect | 640×640 | 80 | 8.84 ms / 112.05 FPS (1 thread ) 16.92 ms / 117.39 FPS (2 threads) | 2.0 ms | 56.9 M | 194.9 M |
- Performance Test Instructions
Device列表示测试的平台, S100P表示RDK S100P, S100表示RDK S100, X5表示RDK X5 (Module).Model列表示测试的模型, 与本文Support Models章节所列模型是对应关系.Size(Pixels)列表示的是模型的算法分辨率, 是导出ONNX模型的输入分辨率, 其他分辨率的图像一般是经过前处理缩放到此分辨率, 再送入网络推理.Classes列表示的是模型的检测目标数量, 这里使用的都是Ultralytics YOLO基于COCO2017数据集或者ImageNet-1k数据集训练出来的权重, 类别数量与对应的数据集的类别数量是一致的.BPU Task Latency / BPU Throughput (Threads)列列举了BPU延迟与BPU吞吐量的情况.
- 单线程延迟为单帧,单线程,单BPU核心的延迟,BPU推理一个任务最理想的情况.
- 多线程帧率为多个线程同时向BPU塞任务, 每个BPU核心可以处理多个线程的任务, 一般工程中2个线程可以控制单帧延迟较小,同时吃满所有BPU到100%,在吞吐量(FPS)和帧延迟间得到一个较好的平衡.
- 表格中一般记录到吞吐量不再随线程数明显增加的数据.
- BPU延迟和BPU吞吐量使用以下命令在板端实验, hrt_model_exec工具由OE包提供, 其源码在OE包的
package/board/hrt_model_exec/src目录下.
bash
hrt_model_exec perf --thread_num 2 --model_file < model.bin / model.hbm >- 由于实验的条件不同, 复现的的结果可能不同, 这里统一参照本文的
Platform Details中的设备状态, 在平台状态最佳时进行实验. - hrt_model_exec工具的性能实验中, 充分考虑了缓存预热, 多线程程序设计等性能测试的内容, 测量的时间为用户程序向BPU提交BPU任务到等待BPU任务结束的时间。
- 在流式数据推理时, 输入输出内存可以开辟一次, 反复使用, 请不要将开辟和回收内存的时间纳入推理时间, 也不要在流式数据推理中反复开辟和回收内存, 这是不科学的程序设计方法.
CPU Latency (Single Core)指的是后处理时间, 目前对后处理有做性能优化, 后处理时间与有效目标的个数正相关, 这里的后处理时间一般是目标图片中有效目标的个数小于100时的性能数据. Python和C/C++的后处理时间会有一点差距, 但是由于Python后处理程序基本也是numpy深度优化了, 所以两者差距并不是很大.params(M)和FLOPs(B)是原始浮点模型的参数量和计算量, 使用Ultralytics YOLO软件包在加载完pt模型后, 使用YOLO.export方法时日志中打印的浮点模型参数量和计算量信息. 由于最终生成的BPU定点模型的参数量和计算量与模型结构优化, 图优化, 编译器优化有关系, 与浮点模型的参数量和计算量正相关但是不一定成正比例, 所以这里统一记录浮点计算量为参考.
Accuracy
| Device | Model | Accuracy bbox-all mAP@.50:.95 FP32 / BPU Python | Accuracy bbox-small mAP@.50:.95 FP32 / BPU Python | Accuracy bbox-medium mAP@.50:.95 FP32 / BPU Python | Accuracy bbox-large mAP@.50:.95 FP32 / BPU Python |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S100P | YOLO26n Detect(e2e) | 0.319 / 0.289 (90.6 %) | 0.107 / 0.087 (81.7 %) | 0.349 / 0.313 (89.6 %) | 0.508 / 0.460 (90.7 %) |
| S100P | YOLO26s Detect(e2e) | 0.395 / 0.363 (92.0 %) | 0.183 / 0.172 (94.1 %) | 0.440 / 0.403 (91.6 %) | 0.583 / 0.525 (90.2 %) |
| S100P | YOLO26m Detect(e2e) | 0.442 / 0.406 (91.8 %) | 0.242 / 0.216 (89.4 %) | 0.489 / 0.442 (90.4 %) | 0.629 / 0.584 (92.8 %) |
| S100P | YOLO26l Detect(e2e) | 0.456 / 0.396 (87.0 %) | 0.260 / 0.225 (86.6 %) | 0.499 / 0.430 (86.3 %) | 0.627 / 0.560 (89.3 %) |
| S100P | YOLO26x Detect(e2e) | 0.484 / 0.441 (91.0 %) | 0.292 / 0.269 (92.2 %) | 0.528 / 0.470 (89.0 %) | 0.669 / 0.630 (94.2 %) |
| S100P | YOLO26n Detect(nms) | 0.319 / 0.290 (91.0 %) | 0.107 / 0.087 (81.7 %) | 0.349 / 0.313 (89.8 %) | 0.508 / 0.463 (91.1 %) |
| S100P | YOLO26s Detect(nms) | 0.395 / 0.367 (93.0 %) | 0.183 / 0.174 (94.8 %) | 0.440 / 0.410 (93.1 %) | 0.583 / 0.530 (91.0 %) |
| S100P | YOLO26m Detect(nms) | 0.442 / 0.421 (95.2 %) | 0.242 / 0.224 (92.6 %) | 0.489 / 0.460 (94.0 %) | 0.629 / 0.603 (95.8 %) |
| S100P | YOLO26l Detect(nms) | 0.456 / 0.437 (96.0 %) | 0.260 / 0.234 (89.8 %) | 0.499 / 0.484 (97.1 %) | 0.627 / 0.609 (97.0 %) |
| S100P | YOLO26x Detect(nms) | 0.484 / 0.466 (96.2 %) | 0.292 / 0.271 (92.8 %) | 0.528 / 0.502 (95.1 %) | 0.669 / 0.654 (97.8 %) |
| S100P | YOLO12n Detect(nv12) | 0.338 / 0.313 (92.4 %) | 0.128 / 0.095 (74.0 %) | 0.374 / 0.342 (91.4 %) | 0.524 / 0.515 (98.3 %) |
| S100P | YOLO12s Detect(nv12) | 0.403 / 0.380 (94.2 %) | 0.201 / 0.152 (75.5 %) | 0.450 / 0.432 (95.9 %) | 0.602 / 0.581 (96.5 %) |
| S100P | YOLO12m Detect(nv12) | 0.452 / 0.423 (93.7 %) | 0.251 / 0.204 (81.3 %) | 0.509 / 0.489 (96.0 %) | 0.638 / 0.616 (96.5 %) |
| S100P | YOLO12l Detect(nv12) | 0.463 / 0.429 (92.8 %) | 0.268 / 0.211 (78.6 %) | 0.522 / 0.492 (94.3 %) | 0.646 / 0.630 (97.7 %) |
| S100P | YOLO12x Detect(nv12) | 0.475 / 0.440 (92.7 %) | 0.276 / 0.222 (80.3 %) | 0.536 / 0.509 (94.9 %) | 0.659 / 0.627 (95.1 %) |
| S100P | YOLO11n Detect(nv12) | 0.327 / 0.306 (93.9 %) | 0.130 / 0.104 (80.0 %) | 0.357 / 0.340 (95.2 %) | 0.511 / 0.500 (97.8 %) |
| S100P | YOLO11s Detect(nv12) | 0.400 / 0.380 (95.0 %) | 0.198 / 0.166 (83.9 %) | 0.445 / 0.427 (96.1 %) | 0.587 / 0.579 (98.6 %) |
| S100P | YOLO11m Detect(nv12) | 0.444 / 0.417 (94.0 %) | 0.247 / 0.214 (87.0 %) | 0.497 / 0.478 (96.1 %) | 0.627 / 0.599 (95.6 %) |
| S100P | YOLO11l Detect(nv12) | 0.460 / 0.434 (94.5 %) | 0.267 / 0.227 (85.2 %) | 0.520 / 0.498 (95.9 %) | 0.638 / 0.611 (95.8 %) |
| S100P | YOLO11x Detect(nv12) | 0.474 / 0.446 (94.0 %) | 0.283 / 0.240 (84.7 %) | 0.529 / 0.506 (95.6 %) | 0.652 / 0.627 (96.1 %) |
- Accuracy Test Instructions
Device列和Model列含义与Performance Test Instructions章节的含义相同.- 精度数据使用微软官方的无修改的
pycocotools库进行计算, 目标检测(Obeject Detection)任务的测评模式为iouType="bbox", 和实例分割(Instance Segmentation)任务的测评模式为iouType="bbox"和iouType="segm", 人体关键点估计的测评模式为iouType="keypoints".
Accuracy bbox-all mAP@.50:.95取自Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets=100 ].Accuracy bbox-small mAP@.50:.95取自Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= small | maxDets=100 ].Accuracy bbox-medium mAP@.50:.95取自Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area=medium | maxDets=100 ].Accuracy bbox-large mAP@.50:.95取自Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= large | maxDets=100 ].
- AP 更关注"质量":既要找到目标(recall), 又要框得准, 类别对(precision), AR 更关注"数量": 只要框住就算,不惩罚误检. 一个模型可以有高 AR 但低 AP, 比如疯狂输出大量低质量框, 找得全但不准. 也可以有高 AP 但低 AR, 比如只输出高置信度结果, 很准但漏很多. 这里取的均为AP指标来衡量模型的精度.
- 测试数据均使用
COCO2017数据集的val验证集的5000张照片, 在板端直接推理, dump保存为json文件, 送入第三方测试工具pycocotools库进行计算, 分数的阈值为0.25, nms的阈值为0.7. - pycocotools计算的精度比ultralytics计算的精度会低一些是正常现象, 主要原因是在计算AP曲线下面积时, pycocotools是取矩形面积, ultralytics是取梯形面积, 我们主要是关注同样的一套计算方式去测试定点模型和浮点模型的精度, 从而来评估量化过程中的精度损失.
- 分类任务使用的数据集为
ImageNet-1k, 使用TOP1和TOP5两个指标来评估量化过程中的精度损失. - BPU模型在量化NCHW-RGB888输入转换为YUV420SP(nv12)输入后, 也会有一部分精度损失, 这是由于色彩空间转化导致的, 在训练时加入这种色彩空间转化的损失可以避免这种精度损失.
- Python接口和C/C++接口的精度结果有细微差异, 主要在于Python和C/C++的一些数据结构进行memcpy和转化的过程中, 对浮点数的处理方式不同, 导致的细微差异.
- 本表格是使用PTQ(训练后量化)使用50张图片进行校准和编译的结果, 用于模拟普通开发者第一次直接编译的精度情况, 并没有进行精度调优或者QAT(量化感知训练), 满足常规使用验证需求, 不代表精度上限.
算法层修改参考
python
# ultralytics/ultralytics/nn/modules/head.py -> Class Detect -> function forward
def forward(self, x):
result = []
for i in range(self.nl):
result.append(self.one2one_cv3[i](x[i]).permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous()) # cls
result.append(self.one2one_cv2[i](x[i]).permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous()) # bbox
return resultExport程序参考
python
from ultralytics import YOLO
YOLO('yolo26n.pt').export(format='onnx', opset=19, simplify=False)OpenExplore步骤参考
yaml
model_parameters:
onnx_model: 'yolo26m.onnx'
march: "nash-m"
working_dir: 'bpu_model_output'
output_model_file_prefix: 'yolo26m_detect_nashm_640x640_hwcrgb888'
input_parameters:
input_type_rt: 'rgb'
input_type_train: 'rgb'
input_layout_rt: 'NCHW'
input_layout_train: 'NCHW'
norm_type: 'data_scale'
mean_value: ''
scale_value: 0.003921568627451
calibration_parameters:
cal_data_dir: '/cal'
calibration_type: 'default'
compiler_parameters:
extra_params: {'input_no_padding': True, 'output_no_padding': True}
jobs: 64
compile_mode: 'latency'
debug: true
optimize_level: 'O2'
bash
hb_compile --config config.yamlRuntime程序参考
注: 这是参考程序, 不承诺一键运行, 如果您发现有可以改进的地方欢迎在文末评论.
CPP (CmakeLists.txt)
c
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.10)
project(yolo26_nashm)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 11)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD_REQUIRED ON)
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -std=c++11 -Wl,-unresolved-symbols=ignore-in-shared-libs")
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS_DEBUG "-Wall -g -O0")
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS_RELEASE "-Wall -O3")
if (NOT CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Release)
endif()
find_package(OpenCV REQUIRED)
set(HOBOT_INCLUDE_PATH "/usr/include")
set(HOBOT_LIB_PATH "/usr/hobot/lib")
include_directories(${HOBOT_INCLUDE_PATH})
include_directories(${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS})
link_directories(${HOBOT_LIB_PATH})
add_executable(yolo26 main.cc)
target_link_libraries(yolo26 ${OpenCV_LIBS} dnn hbucp pthread rt dl m)CPP (with NMS)
cpp
// Copyright (c) 2026, Cauchy - WuChao
#define MODEL_PATH "/root/ssd/YOLO26/detect/yolo26_detect_nashm/yolo26x_detect_nashm_640x640_hwcrgb888.hbm" // D-Robotics *.bin 模型路径
#define TEST_IMG_PATH "/root/ssd/YOLO26/detect/test_imgs/000000132544.jpg" // 推理使用的测试图片路径
#define IMG_SAVE_PATH "cpp_result.jpg" // 推理结果保存路径
#define CLASSES_NUM 80 // 模型的类别数量, 默认80
#define NMS_THRESHOLD 0.25 // NMS的阈值, 默认0.45
#define SCORE_THRESHOLD 0.1 // 分数阈值, 默认0.25
#define NMS_TOP_K 300 // NMS选取的前K个框数, 默认300 // 控制回归部分离散化程度的超参数, 默认16
#define FONT_SIZE 0.5 // 绘制标签的字体尺寸, 默认1.0
#define FONT_THICKNESS 0.5 // 绘制标签的字体粗细, 默认 1.0
#define LINE_SIZE 2.0 // 绘制矩形框的线宽, 默认2.0
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <chrono>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <opencv2/dnn/dnn.hpp>
#include "hobot/dnn/hb_dnn.h"
#include "hobot/hb_ucp.h"
#include "hobot/hb_ucp_sys.h"
#define CHECK_SUCCESS(value, errmsg) \
do \
{ \
auto ret_code = value; \
if (ret_code != 0) \
{ \
std::cerr << "\033[1;31m[ERROR]\033[0m " << __FILE__ << ":" \
<< __LINE__ << " " << errmsg \
<< ", error code: " << ret_code << std::endl; \
return ret_code; \
} \
} while (0)
// COCO Names
std::vector<std::string> object_names = {
"person", "bicycle", "car", "motorcycle", "airplane", "bus", "train", "truck", "boat", "traffic light", "fire hydrant", "stop sign", "parking meter", "bench", "bird", "cat", "dog", "horse", "sheep", "cow", "elephant", "bear", "zebra", "giraffe", "backpack", "umbrella", "handbag", "tie", "suitcase", "frisbee", "skis", "snowboard", "sports ball", "kite", "baseball bat", "baseball glove", "skateboard", "surfboard", "tennis racket", "bottle", "wine glass", "cup", "fork", "knife", "spoon", "bowl", "banana", "apple", "sandwich", "orange", "broccoli", "carrot", "hot dog", "pizza", "donut", "cake", "chair", "couch", "potted plant", "bed", "dining table", "toilet", "tv", "laptop", "mouse", "remote", "keyboard", "cell phone", "microwave", "oven", "toaster", "sink", "refrigerator", "book", "clock", "vase", "scissors", "teddy bear", "hair drier", "toothbrush"};
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
std::string model_path = MODEL_PATH;
std::string img_path = TEST_IMG_PATH;
std::string save_path = IMG_SAVE_PATH;
if (argc >= 2)
model_path = argv[1];
if (argc >= 3)
img_path = argv[2];
if (argc >= 4)
save_path = argv[3];
std::cout << "[INFO] argc: " << argc << std::endl;
std::cout << "[INFO] OpenCV Version: " << CV_VERSION << std::endl;
std::cout << "[INFO] MODEL_PATH: " << model_path << std::endl;
std::cout << "[INFO] IMG PATH: " << img_path << std::endl;
std::cout << "[INFO] IMG SVAE PATH: " << save_path << std::endl;
std::cout << "[INFO] CLASSES_NUM: " << CLASSES_NUM << std::endl;
std::cout << "[INFO] NMS_THRESHOLD: " << NMS_THRESHOLD << std::endl;
std::cout << "[INFO] SCORE_THRESHOLD: " << SCORE_THRESHOLD << std::endl;
float CONF_THRES_RAW = -log(1 / SCORE_THRESHOLD - 1);
int32_t input_H = 640, input_W = 640;
// 加载BPU模型
auto begin_time = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
hbDNNPackedHandle_t packed_handle;
const char *model_fn = model_path.c_str();
CHECK_SUCCESS(hbDNNInitializeFromFiles(&packed_handle, &model_fn, 1), "Init failed");
const char **model_names;
int model_count = 0;
CHECK_SUCCESS(hbDNNGetModelNameList(&model_names, &model_count, packed_handle), "Get name failed");
hbDNNHandle_t dnn_handle;
CHECK_SUCCESS(hbDNNGetModelHandle(&dnn_handle, packed_handle, model_names[0]), "Get handle failed");
int32_t input_count = 0;
CHECK_SUCCESS(hbDNNGetInputCount(&input_count, dnn_handle), "Failed to get input count");
int32_t output_count = 0;
CHECK_SUCCESS(hbDNNGetOutputCount(&output_count, dnn_handle), "Failed to get output count");
std::cout << "[INFO] INPUT COUNT: " << input_count << std::endl;
std::cout << "[INFO] OUTPUT COUNT: " << output_count << std::endl;
std::vector<hbDNNTensor> input_tensors(input_count);
std::vector<hbDNNTensor> output_tensors(output_count);
for (int32_t i = 0; i < input_count; i++)
{
CHECK_SUCCESS(hbDNNGetInputTensorProperties(&input_tensors[i].properties, dnn_handle, i), "Get input props failed");
CHECK_SUCCESS(hbUCPMallocCached(&input_tensors[i].sysMem, input_tensors[i].properties.alignedByteSize, 0), "Malloc input failed");
}
for (int32_t i = 0; i < output_count; i++)
{
CHECK_SUCCESS(hbDNNGetOutputTensorProperties(&output_tensors[i].properties, dnn_handle, i), "Get output props failed");
CHECK_SUCCESS(hbUCPMallocCached(&output_tensors[i].sysMem, output_tensors[i].properties.alignedByteSize, 0), "Malloc output failed");
}
std::cout << "\033[31m Load D-Robotics Quantize model time = " << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::microseconds>(std::chrono::system_clock::now() - begin_time).count() / 1000.0 << " ms\033[0m" << std::endl;
begin_time = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
cv::Mat img = cv::imread(img_path);
std::cout << "\033[31m cv::imread from disk time = " << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::microseconds>(std::chrono::system_clock::now() - begin_time).count() / 1000.0 << " ms\033[0m" << std::endl;
std::cout << "[INFO] cv::imread (cols, rows, channels): (";
std::cout << img.rows << ", ";
std::cout << img.cols << ", ";
std::cout << img.channels() << ")" << std::endl;
// 前处理
begin_time = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
float y_scale = 1.0;
float x_scale = 1.0;
int x_shift = 0;
int y_shift = 0;
cv::Mat resize_img;
x_scale = std::min(1.0 * input_H / img.rows, 1.0 * input_W / img.cols);
y_scale = x_scale;
if (x_scale <= 0 || y_scale <= 0)
throw std::runtime_error("Invalid scale factor.");
int new_w = img.cols * x_scale;
x_shift = (input_W - new_w) / 2;
int x_other = input_W - new_w - x_shift;
int new_h = img.rows * y_scale;
y_shift = (input_H - new_h) / 2;
int y_other = input_H - new_h - y_shift;
cv::Size targetSize(new_w, new_h);
cv::resize(img, resize_img, targetSize);
cv::copyMakeBorder(resize_img, resize_img, y_shift, y_other, x_shift, x_other, cv::BORDER_CONSTANT, cv::Scalar(127, 127, 127));
std::cout << "\033[31m pre process (LetterBox) time = " << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::microseconds>(std::chrono::system_clock::now() - begin_time).count() / 1000.0 << " ms\033[0m" << std::endl;
begin_time = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
uint8_t *data_u8{reinterpret_cast<uint8_t *>(resize_img.ptr<uint8_t>())};
int8_t *data_s8{reinterpret_cast<int8_t *>(input_tensors[0].sysMem.virAddr)};
for (int h = 0; h < input_H; h++)
for (int w = 0; w < input_W; w++) // BGR 到 RGB 的通道顺序转换,同时进行减均值操作 (-128)
{
data_s8[h * input_W * 3 + w * 3 + 2] = static_cast<int8_t>(data_u8[h * input_W * 3 + w * 3 + 0] - 128); // R
data_s8[h * input_W * 3 + w * 3 + 1] = static_cast<int8_t>(data_u8[h * input_W * 3 + w * 3 + 1] - 128); // G
data_s8[h * input_W * 3 + w * 3 + 0] = static_cast<int8_t>(data_u8[h * input_W * 3 + w * 3 + 2] - 128); // B
}
std::cout << "[INFO]\033[31m (u8-128)->s8 time = " << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::microseconds>(std::chrono::system_clock::now() - begin_time).count() / 1000.0 << " ms\033[0m" << std::endl;
// 推理模型
begin_time = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
for (int32_t i = 0; i < input_count; i++)
hbUCPMemFlush(&input_tensors[i].sysMem, HB_SYS_MEM_CACHE_CLEAN);
hbUCPTaskHandle_t task = nullptr;
CHECK_SUCCESS(hbDNNInferV2(&task, output_tensors.data(), input_tensors.data(), dnn_handle), "Infer failed");
hbUCPSchedParam param;
HB_UCP_INITIALIZE_SCHED_PARAM(¶m);
param.backend = HB_UCP_BPU_CORE_ANY;
CHECK_SUCCESS(hbUCPSubmitTask(task, ¶m), "Submit failed");
CHECK_SUCCESS(hbUCPWaitTaskDone(task, 0), "Wait failed");
std::cout << "[INFO]\033[31m forward time = " << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::microseconds>(std::chrono::system_clock::now() - begin_time).count() / 1000.0 << " ms\033[0m" << std::endl;
// 后处理
std::vector<std::vector<cv::Rect2d>> bboxes(CLASSES_NUM);
std::vector<std::vector<float>> scores(CLASSES_NUM);
begin_time = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
std::vector<int32_t> strides = {8, 16, 32};
for (size_t i = 0; i < strides.size(); ++i)
{
int32_t stride = strides[i];
hbUCPMemFlush(&(output_tensors[2 * i + 0].sysMem), HB_SYS_MEM_CACHE_INVALIDATE);
hbUCPMemFlush(&(output_tensors[2 * i + 1].sysMem), HB_SYS_MEM_CACHE_INVALIDATE);
auto *cls_raw = reinterpret_cast<float *>(output_tensors[2 * i + 0].sysMem.virAddr);
auto *bbox_raw = reinterpret_cast<float *>(output_tensors[2 * i + 1].sysMem.virAddr);
int32_t H_Stride = input_H / stride;
int32_t W_Stride = input_W / stride;
for (int h = 0; h < H_Stride; h++)
{
for (int w = 0; w < W_Stride; w++)
{
float *cur_cls_raw = cls_raw;
float *cur_bbox_raw = bbox_raw;
int cls_id = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < CLASSES_NUM; i++)
if (cur_cls_raw[i] > cur_cls_raw[cls_id])
cls_id = i;
if (cur_cls_raw[cls_id] < CONF_THRES_RAW)
{
cls_raw += CLASSES_NUM;
bbox_raw += 4;
continue;
}
float score = 1 / (1 + std::exp(-cur_cls_raw[cls_id]));
if (cur_bbox_raw[2] + cur_bbox_raw[0] <= 0 || cur_bbox_raw[3] + cur_bbox_raw[1] <= 0)
{
cls_raw += CLASSES_NUM;
bbox_raw += 4;
continue;
}
float x1 = (w + 0.5 - cur_bbox_raw[0]) * stride;
float y1 = (h + 0.5 - cur_bbox_raw[1]) * stride;
float x2 = (w + 0.5 + cur_bbox_raw[2]) * stride;
float y2 = (h + 0.5 + cur_bbox_raw[3]) * stride;
bboxes[cls_id].push_back(cv::Rect2d(x1, y1, x2 - x1, y2 - y1));
scores[cls_id].push_back(score);
cls_raw += CLASSES_NUM;
bbox_raw += 4;
}
}
}
std::vector<std::vector<int>> indices(CLASSES_NUM); // 对每一个类别进行NMS
for (int i = 0; i < CLASSES_NUM; i++)
cv::dnn::NMSBoxes(bboxes[i], scores[i], SCORE_THRESHOLD, NMS_THRESHOLD, indices[i]);
std::cout << "[INFO]\033[31m Post Process time = " << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::microseconds>(std::chrono::system_clock::now() - begin_time).count() / 1000.0 << " ms\033[0m" << std::endl;
begin_time = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
for (int cls_id = 0; cls_id < CLASSES_NUM; cls_id++)
{
for (std::vector<int>::iterator it = indices[cls_id].begin(); it != indices[cls_id].end(); ++it)
{
float x1 = (bboxes[cls_id][*it].x - x_shift) / x_scale;
float y1 = (bboxes[cls_id][*it].y - y_shift) / y_scale;
float x2 = x1 + (bboxes[cls_id][*it].width) / x_scale;
float y2 = y1 + (bboxes[cls_id][*it].height) / y_scale;
float score = scores[cls_id][*it];
std::string name = object_names[cls_id % CLASSES_NUM];
cv::rectangle(img, cv::Point(x1, y1), cv::Point(x2, y2), cv::Scalar(255, 0, 0), LINE_SIZE); // 8.3 绘制矩形
std::string text = name + ": " + std::to_string(static_cast<int>(score * 100)) + "%"; // 8.4 绘制字体
cv::putText(img, text, cv::Point(x1, y1 - 5), cv::FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, FONT_SIZE, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 255), FONT_THICKNESS, cv::LINE_AA);
std::cout << "(" << x1 << " " << y1 << " " << x2 << " " << y2 << "): \t" << text << std::endl; // 8.5 打印检测信息
}
}
std::cout << "\033[31m Draw Result time = " << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::microseconds>(std::chrono::system_clock::now() - begin_time).count() / 1000.0 << " ms\033[0m" << std::endl;
cv::imwrite(save_path, img);
hbUCPReleaseTask(task);
for (auto &t : input_tensors)
hbUCPFree(&t.sysMem);
for (auto &t : output_tensors)
hbUCPFree(&t.sysMem);
hbDNNRelease(packed_handle);
return 0;
}CPP (without NMS)
cpp
// Copyright (c) 2026, Cauchy - WuChao
#define MODEL_PATH "/root/ssd/YOLO26/detect/yolo26_detect_nashm/yolo26x_detect_nashm_640x640_hwcrgb888.hbm" // D-Robotics *.bin 模型路径
#define TEST_IMG_PATH "/root/ssd/YOLO26/detect/test_imgs/000000132544.jpg" // 推理使用的测试图片路径
#define IMG_SAVE_PATH "cpp_result.jpg" // 推理结果保存路径
#define CLASSES_NUM 80 // 模型的类别数量, 默认80
#define NMS_THRESHOLD 0.25 // NMS的阈值, 默认0.45
#define SCORE_THRESHOLD 0.1 // 分数阈值, 默认0.25
#define NMS_TOP_K 300 // NMS选取的前K个框数, 默认300 // 控制回归部分离散化程度的超参数, 默认16
#define FONT_SIZE 0.5 // 绘制标签的字体尺寸, 默认1.0
#define FONT_THICKNESS 0.5 // 绘制标签的字体粗细, 默认 1.0
#define LINE_SIZE 2.0 // 绘制矩形框的线宽, 默认2.0
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <chrono>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <opencv2/dnn/dnn.hpp>
#include "hobot/dnn/hb_dnn.h"
#include "hobot/hb_ucp.h"
#include "hobot/hb_ucp_sys.h"
#define CHECK_SUCCESS(value, errmsg) \
do \
{ \
auto ret_code = value; \
if (ret_code != 0) \
{ \
std::cerr << "\033[1;31m[ERROR]\033[0m " << __FILE__ << ":" \
<< __LINE__ << " " << errmsg \
<< ", error code: " << ret_code << std::endl; \
return ret_code; \
} \
} while (0)
// COCO Names
std::vector<std::string> object_names = {
"person", "bicycle", "car", "motorcycle", "airplane", "bus", "train", "truck", "boat", "traffic light", "fire hydrant", "stop sign", "parking meter", "bench", "bird", "cat", "dog", "horse", "sheep", "cow", "elephant", "bear", "zebra", "giraffe", "backpack", "umbrella", "handbag", "tie", "suitcase", "frisbee", "skis", "snowboard", "sports ball", "kite", "baseball bat", "baseball glove", "skateboard", "surfboard", "tennis racket", "bottle", "wine glass", "cup", "fork", "knife", "spoon", "bowl", "banana", "apple", "sandwich", "orange", "broccoli", "carrot", "hot dog", "pizza", "donut", "cake", "chair", "couch", "potted plant", "bed", "dining table", "toilet", "tv", "laptop", "mouse", "remote", "keyboard", "cell phone", "microwave", "oven", "toaster", "sink", "refrigerator", "book", "clock", "vase", "scissors", "teddy bear", "hair drier", "toothbrush"};
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
std::string model_path = MODEL_PATH;
std::string img_path = TEST_IMG_PATH;
std::string save_path = IMG_SAVE_PATH;
if (argc >= 2)
model_path = argv[1];
if (argc >= 3)
img_path = argv[2];
if (argc >= 4)
save_path = argv[3];
std::cout << "[INFO] argc: " << argc << std::endl;
std::cout << "[INFO] OpenCV Version: " << CV_VERSION << std::endl;
std::cout << "[INFO] MODEL_PATH: " << model_path << std::endl;
std::cout << "[INFO] IMG PATH: " << img_path << std::endl;
std::cout << "[INFO] IMG SVAE PATH: " << save_path << std::endl;
std::cout << "[INFO] CLASSES_NUM: " << CLASSES_NUM << std::endl;
std::cout << "[INFO] NMS_THRESHOLD: " << NMS_THRESHOLD << std::endl;
std::cout << "[INFO] SCORE_THRESHOLD: " << SCORE_THRESHOLD << std::endl;
float CONF_THRES_RAW = -log(1 / SCORE_THRESHOLD - 1);
int32_t input_H = 640, input_W = 640;
// 加载BPU模型
auto begin_time = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
hbDNNPackedHandle_t packed_handle;
const char *model_fn = model_path.c_str();
CHECK_SUCCESS(hbDNNInitializeFromFiles(&packed_handle, &model_fn, 1), "Init failed");
const char **model_names;
int model_count = 0;
CHECK_SUCCESS(hbDNNGetModelNameList(&model_names, &model_count, packed_handle), "Get name failed");
hbDNNHandle_t dnn_handle;
CHECK_SUCCESS(hbDNNGetModelHandle(&dnn_handle, packed_handle, model_names[0]), "Get handle failed");
int32_t input_count = 0;
CHECK_SUCCESS(hbDNNGetInputCount(&input_count, dnn_handle), "Failed to get input count");
int32_t output_count = 0;
CHECK_SUCCESS(hbDNNGetOutputCount(&output_count, dnn_handle), "Failed to get output count");
std::cout << "[INFO] INPUT COUNT: " << input_count << std::endl;
std::cout << "[INFO] OUTPUT COUNT: " << output_count << std::endl;
std::vector<hbDNNTensor> input_tensors(input_count);
std::vector<hbDNNTensor> output_tensors(output_count);
for (int32_t i = 0; i < input_count; i++)
{
CHECK_SUCCESS(hbDNNGetInputTensorProperties(&input_tensors[i].properties, dnn_handle, i), "Get input props failed");
CHECK_SUCCESS(hbUCPMallocCached(&input_tensors[i].sysMem, input_tensors[i].properties.alignedByteSize, 0), "Malloc input failed");
}
for (int32_t i = 0; i < output_count; i++)
{
CHECK_SUCCESS(hbDNNGetOutputTensorProperties(&output_tensors[i].properties, dnn_handle, i), "Get output props failed");
CHECK_SUCCESS(hbUCPMallocCached(&output_tensors[i].sysMem, output_tensors[i].properties.alignedByteSize, 0), "Malloc output failed");
}
std::cout << "\033[31m Load D-Robotics Quantize model time = " << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::microseconds>(std::chrono::system_clock::now() - begin_time).count() / 1000.0 << " ms\033[0m" << std::endl;
begin_time = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
cv::Mat img = cv::imread(img_path);
std::cout << "\033[31m cv::imread from disk time = " << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::microseconds>(std::chrono::system_clock::now() - begin_time).count() / 1000.0 << " ms\033[0m" << std::endl;
std::cout << "[INFO] cv::imread (cols, rows, channels): (";
std::cout << img.rows << ", ";
std::cout << img.cols << ", ";
std::cout << img.channels() << ")" << std::endl;
// 前处理
begin_time = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
float y_scale = 1.0;
float x_scale = 1.0;
int x_shift = 0;
int y_shift = 0;
cv::Mat resize_img;
x_scale = std::min(1.0 * input_H / img.rows, 1.0 * input_W / img.cols);
y_scale = x_scale;
if (x_scale <= 0 || y_scale <= 0)
throw std::runtime_error("Invalid scale factor.");
int new_w = img.cols * x_scale;
x_shift = (input_W - new_w) / 2;
int x_other = input_W - new_w - x_shift;
int new_h = img.rows * y_scale;
y_shift = (input_H - new_h) / 2;
int y_other = input_H - new_h - y_shift;
cv::Size targetSize(new_w, new_h);
cv::resize(img, resize_img, targetSize);
cv::copyMakeBorder(resize_img, resize_img, y_shift, y_other, x_shift, x_other, cv::BORDER_CONSTANT, cv::Scalar(127, 127, 127));
std::cout << "\033[31m pre process (LetterBox) time = " << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::microseconds>(std::chrono::system_clock::now() - begin_time).count() / 1000.0 << " ms\033[0m" << std::endl;
begin_time = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
uint8_t *data_u8{reinterpret_cast<uint8_t *>(resize_img.ptr<uint8_t>())};
int8_t *data_s8{reinterpret_cast<int8_t *>(input_tensors[0].sysMem.virAddr)};
for (int h = 0; h < input_H; h++)
for (int w = 0; w < input_W; w++) // BGR 到 RGB 的通道顺序转换,同时进行减均值操作 (-128)
{
data_s8[h * input_W * 3 + w * 3 + 2] = static_cast<int8_t>(data_u8[h * input_W * 3 + w * 3 + 0] - 128); // R
data_s8[h * input_W * 3 + w * 3 + 1] = static_cast<int8_t>(data_u8[h * input_W * 3 + w * 3 + 1] - 128); // G
data_s8[h * input_W * 3 + w * 3 + 0] = static_cast<int8_t>(data_u8[h * input_W * 3 + w * 3 + 2] - 128); // B
}
std::cout << "[INFO]\033[31m (u8-128)->s8 time = " << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::microseconds>(std::chrono::system_clock::now() - begin_time).count() / 1000.0 << " ms\033[0m" << std::endl;
// 推理模型
begin_time = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
for (int32_t i = 0; i < input_count; i++)
hbUCPMemFlush(&input_tensors[i].sysMem, HB_SYS_MEM_CACHE_CLEAN);
hbUCPTaskHandle_t task = nullptr;
CHECK_SUCCESS(hbDNNInferV2(&task, output_tensors.data(), input_tensors.data(), dnn_handle), "Infer failed");
hbUCPSchedParam param;
HB_UCP_INITIALIZE_SCHED_PARAM(¶m);
param.backend = HB_UCP_BPU_CORE_ANY;
CHECK_SUCCESS(hbUCPSubmitTask(task, ¶m), "Submit failed");
CHECK_SUCCESS(hbUCPWaitTaskDone(task, 0), "Wait failed");
std::cout << "[INFO]\033[31m forward time = " << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::microseconds>(std::chrono::system_clock::now() - begin_time).count() / 1000.0 << " ms\033[0m" << std::endl;
std::vector<std::vector<cv::Rect2d>> bboxes(CLASSES_NUM);
std::vector<std::vector<float>> scores(CLASSES_NUM);
begin_time = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
std::vector<int32_t> strides = {8, 16, 32};
for (size_t i = 0; i < strides.size(); ++i)
{
int32_t stride = strides[i];
hbUCPMemFlush(&(output_tensors[2 * i + 0].sysMem), HB_SYS_MEM_CACHE_INVALIDATE);
hbUCPMemFlush(&(output_tensors[2 * i + 1].sysMem), HB_SYS_MEM_CACHE_INVALIDATE);
auto *cls_raw = reinterpret_cast<float *>(output_tensors[2 * i + 0].sysMem.virAddr);
auto *bbox_raw = reinterpret_cast<float *>(output_tensors[2 * i + 1].sysMem.virAddr);
int32_t H_Stride = input_H / stride;
int32_t W_Stride = input_W / stride;
for (int h = 0; h < H_Stride; h++)
{
for (int w = 0; w < W_Stride; w++)
{
float *cur_cls_raw = cls_raw;
float *cur_bbox_raw = bbox_raw;
int cls_id = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < CLASSES_NUM; i++)
if (cur_cls_raw[i] > cur_cls_raw[cls_id])
cls_id = i;
if (cur_cls_raw[cls_id] < CONF_THRES_RAW)
{
cls_raw += CLASSES_NUM;
bbox_raw += 4;
continue;
}
float score = 1 / (1 + std::exp(-cur_cls_raw[cls_id]));
if (cur_bbox_raw[2] + cur_bbox_raw[0] <= 0 || cur_bbox_raw[3] + cur_bbox_raw[1] <= 0)
{
cls_raw += CLASSES_NUM;
bbox_raw += 4;
continue;
}
float x1 = (w + 0.5 - cur_bbox_raw[0]) * stride;
float y1 = (h + 0.5 - cur_bbox_raw[1]) * stride;
float x2 = (w + 0.5 + cur_bbox_raw[2]) * stride;
float y2 = (h + 0.5 + cur_bbox_raw[3]) * stride;
bboxes[cls_id].push_back(cv::Rect2d(x1, y1, x2 - x1, y2 - y1));
scores[cls_id].push_back(score);
cls_raw += CLASSES_NUM;
bbox_raw += 4;
}
}
}
std::cout << "[INFO]\033[31m Post Process time = " << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::microseconds>(std::chrono::system_clock::now() - begin_time).count() / 1000.0 << " ms\033[0m" << std::endl;
begin_time = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
for (int cls_id = 0; cls_id < CLASSES_NUM; cls_id++)
{
for (size_t index = 0; index < bboxes[cls_id].size(); index++)
{
float x1 = (bboxes[cls_id][index].x - x_shift) / x_scale;
float y1 = (bboxes[cls_id][index].y - y_shift) / y_scale;
float x2 = x1 + (bboxes[cls_id][index].width) / x_scale;
float y2 = y1 + (bboxes[cls_id][index].height) / y_scale;
float score = scores[cls_id][index];
std::string name = object_names[cls_id % CLASSES_NUM];
cv::rectangle(img, cv::Point(x1, y1), cv::Point(x2, y2), cv::Scalar(255, 0, 0), LINE_SIZE); // 8.3 绘制矩形
std::string text = name + ": " + std::to_string(static_cast<int>(score * 100)) + "%"; // 8.4 绘制字体
cv::putText(img, text, cv::Point(x1, y1 - 5), cv::FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, FONT_SIZE, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 255), FONT_THICKNESS, cv::LINE_AA);
std::cout << "(" << x1 << " " << y1 << " " << x2 << " " << y2 << "): \t" << text << std::endl; // 8.5 打印检测信息
}
}
std::cout << "\033[31m Draw Result time = " << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::microseconds>(std::chrono::system_clock::now() - begin_time).count() / 1000.0 << " ms\033[0m" << std::endl;
cv::imwrite(save_path, img);
hbUCPReleaseTask(task);
for (auto &t : input_tensors)
hbUCPFree(&t.sysMem);
for (auto &t : output_tensors)
hbUCPFree(&t.sysMem);
hbDNNRelease(packed_handle);
return 0;
}Python (with NMS)
python
# Copyright (c) 2026, Cauchy - WuChao
from pyCauchyKesai import CauchyKesai
import os
import cv2
import numpy as np
from scipy.special import softmax
from time import time
import argparse
import logging
logging.basicConfig(
level = logging.WARN,
format = '[%(name)s] [%(asctime)s.%(msecs)03d] [%(levelname)s] %(message)s',
datefmt='%H:%M:%S')
logger = logging.getLogger("RDK_YOLO")
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--model-path", type=str, default="yolo26n_high_detect_nashm_640x640_hwcrgb888.hbm", help="Path to BPU Model.", )
parser.add_argument("--test-img", type=str, default="test_imgs/000000132544.jpg", help="image file or images path.", )
parser.add_argument("--img-save-path", type=str, default="py_result.jpg", help="image file or images path.", )
parser.add_argument("--classes-num", type=int, default=80, help="Classes Num to Detect.", )
parser.add_argument("--nms-thres", type=float, default=0.7, help="IoU threshold, default 0.7.", )
parser.add_argument("--score-thres", type=float, default=0.25, help="confidence threshold.", )
parser.add_argument("--strides", type=lambda s: list(map(int, s.split(","))), default=[8, 16, 32], help="--strides 8, 16, 32", )
opt = parser.parse_args()
logger.info(opt)
model = Ultralytics_YOLO26_Detect(
model_path=opt.model_path,
classes_num=opt.classes_num, # default: 80
nms_thres=opt.nms_thres, # default: 0.7
score_thres=opt.score_thres, # default: 0.25
strides=opt.strides, # default: [8, 16, 32]
)
img = cv2.imread(opt.test_img)
if img is None:
raise ValueError(f"Load image failed: {opt.test_img}")
exit()
outputs = model.forward(model.letterbox(img))
results = model.postProcess(outputs)
logger.info("\033[1;32m" + "Draw Results: " + "\033[0m")
print(f"{len(results) = }")
for class_id, score, x1, y1, x2, y2 in results:
draw_detection(img, (int(x1), int(y1), int(x2), int(y2)), score, class_id)
cv2.imwrite(opt.img_save_path, img)
logger.info("\033[1;32m" + f"saved in path: \"./{opt.img_save_path}\"" + "\033[0m")
class Ultralytics_YOLO26_Detect():
def __init__(self, model_path, classes_num, nms_thres, score_thres, strides):
self.strides = strides
self.CLASSES_NUM = classes_num
self.SCORE_THRESHOLD = score_thres
self.NMS_THRESHOLD = nms_thres
self.CONF_THRES_RAW = -np.log(1 / self.SCORE_THRESHOLD - 1)
try:
begin_time = time()
self.m = CauchyKesai(model_path)
logger.debug("\033[1;31m" + "Load D-Robotics Quantize model time = %.2f ms"%(1000*(time() - begin_time)) + "\033[0m")
except Exception as e:
logger.error("❌ Failed to load model file: %s"%(model_path))
logger.error("You can download the model file from the following docs: ./models/download.md")
logger.error(e)
exit(1)
self.m.s()
self.input_H, self.input_W = 640, 640
self.grids = []
for stride in self.strides:
assert (self.input_H % stride == 0), f"{stride=}, {self.input_H=}: input_H % stride != 0"
assert (self.input_W % stride == 0), f"{stride=}, {self.input_W=}: input_W % stride != 0"
grid_H, grid_W = self.input_H // stride, self.input_W // stride
self.grids.append(
np.stack(
[
np.tile(np.linspace(0.5, grid_H - 0.5, grid_H), reps=grid_H),
np.repeat(np.arange(0.5, grid_W + 0.5, 1), grid_W),
],
axis=0,
).transpose(1, 0)
)
logger.debug(f"{self.grids[-1].shape = }")
def letterbox(self, img):
begin_time = time()
self.img_h, self.img_w = img.shape[0:2]
self.x_scale = min(1.0 * self.input_H / self.img_h, 1.0 * self.input_W / self.img_w)
self.y_scale = self.x_scale
if self.x_scale <= 0 or self.y_scale <= 0:
raise ValueError("Invalid scale factor.")
new_w = int(self.img_w * self.x_scale)
self.x_shift = (self.input_W - new_w) // 2
x_other = self.input_W - new_w - self.x_shift
new_h = int(self.img_h * self.y_scale)
self.y_shift = (self.input_H - new_h) // 2
y_other = self.input_H - new_h - self.y_shift
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
input_tensor = cv2.resize(img, (new_w, new_h))
input_tensor = cv2.copyMakeBorder(input_tensor, self.y_shift, y_other, self.x_shift, x_other, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=[127, 127, 127])
input_tensor = (input_tensor - 128.0).astype(np.int8)[np.newaxis,:,:,:].copy()
logger.info("\033[1;31m" + f"pre process(letter box) time = {1000*(time() - begin_time):.2f} ms" + "\033[0m")
logger.info(f"y_scale = {self.y_scale:.2f}, x_scale = {self.x_scale:.2f}")
logger.info(f"y_shift = {self.y_shift:.2f}, x_shift = {self.x_shift:.2f}")
return input_tensor
def forward(self, input_tensor):
begin_time = time()
outputs = self.m([input_tensor])
logger.debug("\033[1;31m" + f"forward time = {1000*(time() - begin_time):.2f} ms" + "\033[0m")
return outputs
def postProcess(self, outputs):
begin_time = time()
clses = [outputs[0].reshape(-1, self.CLASSES_NUM), outputs[2].reshape(-1, self.CLASSES_NUM), outputs[4].reshape(-1, self.CLASSES_NUM),]
bboxes = [outputs[1].reshape(-1, 4), outputs[3].reshape(-1, 4), outputs[5].reshape(-1, 4),]
dbboxes, ids, scores = [], [], []
for cls, bbox, stride, grid in zip(clses, bboxes, self.strides, self.grids):
max_scores = np.max(cls, axis=1)
bbox_selected = np.flatnonzero(max_scores >= self.CONF_THRES_RAW)
ids.append(np.argmax(cls[bbox_selected, :], axis=1))
scores.append(1 / (1 + np.exp(-max_scores[bbox_selected])))
ltrb_selected = bbox[bbox_selected, :]
grid_selected = grid[bbox_selected, :]
x1y1 = grid_selected - ltrb_selected[:, 0:2]
x2y2 = grid_selected + ltrb_selected[:, 2:4]
dbboxes.append(np.hstack([x1y1, x2y2]) * stride)
dbboxes = np.concatenate((dbboxes), axis=0)
scores = np.concatenate((scores), axis=0)
ids = np.concatenate((ids), axis=0)
hw = dbboxes[:, 2:4] - dbboxes[:, 0:2]
xyhw2 = np.hstack([dbboxes[:, 0:2], hw])
results = []
for i in range(self.CLASSES_NUM):
id_indices = ids == i
indices = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(
xyhw2[id_indices, :],
scores[id_indices],
self.SCORE_THRESHOLD,
self.NMS_THRESHOLD,
)
if len(indices) == 0:
continue
for indic in indices:
x1, y1, x2, y2 = dbboxes[id_indices, :][indic]
x1 = (x1 - self.x_shift) / self.x_scale
y1 = (y1 - self.y_shift) / self.y_scale
x2 = (x2 - self.x_shift) / self.x_scale
y2 = (y2 - self.y_shift) / self.y_scale
x1 = x1 if x1 > 0 else 0
x2 = x2 if x2 > 0 else 0
y1 = y1 if y1 > 0 else 0
y2 = y2 if y2 > 0 else 0
x1 = x1 if x1 < self.img_w else self.img_w
x2 = x2 if x2 < self.img_w else self.img_w
y1 = y1 if y1 < self.img_h else self.img_h
y2 = y2 if y2 < self.img_h else self.img_h
results.append((i, scores[id_indices][indic], x1, y1, x2, y2))
logger.debug("\033[1;31m" + f"Post Process time = {1000*(time() - begin_time):.2f} ms" + "\033[0m")
return results
coco_names = [
"person", "bicycle", "car", "motorcycle", "airplane", "bus", "train", "truck", "boat", "traffic light",
"fire hydrant", "stop sign", "parking meter", "bench", "bird", "cat", "dog", "horse", "sheep", "cow",
"elephant", "bear", "zebra", "giraffe", "backpack", "umbrella", "handbag", "tie", "suitcase", "frisbee",
"skis", "snowboard", "sports ball", "kite", "baseball bat", "baseball glove", "skateboard", "surfboard", "tennis racket", "bottle",
"wine glass", "cup", "fork", "knife", "spoon", "bowl", "banana", "apple", "sandwich", "orange",
"broccoli", "carrot", "hot dog", "pizza", "donut", "cake", "chair", "couch", "potted plant", "bed",
"dining table", "toilet", "tv", "laptop", "mouse", "remote", "keyboard", "cell phone", "microwave", "oven",
"toaster", "sink", "refrigerator", "book", "clock", "vase", "scissors", "teddy bear", "hair drier", "toothbrush"
]
rdk_colors = [
(56, 56, 255), (151, 157, 255), (31, 112, 255), (29, 178, 255),(49, 210, 207), (10, 249, 72), (23, 204, 146), (134, 219, 61),
(52, 147, 26), (187, 212, 0), (168, 153, 44), (255, 194, 0),(147, 69, 52), (255, 115, 100), (236, 24, 0), (255, 56, 132),
(133, 0, 82), (255, 56, 203), (200, 149, 255), (199, 55, 255)]
def draw_detection(img, bbox, score, class_id) -> None:
x1, y1, x2, y2 = bbox
color = rdk_colors[class_id%20]
cv2.rectangle(img, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), color, 2)
label = f"{coco_names[class_id]}: {score:.2f}"
(label_width, label_height), _ = cv2.getTextSize(label, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1)
label_x, label_y = x1, y1 - 10 if y1 - 10 > label_height else y1 + 10
cv2.rectangle(
img, (label_x, label_y - label_height), (label_x + label_width, label_y + label_height), color, cv2.FILLED
)
cv2.putText(img, label, (label_x, label_y), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 0), 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()Python (without NMS)
python
# Copyright (c) 2026, Cauchy - WuChao
from pyCauchyKesai import CauchyKesai
import os
import cv2
import numpy as np
from scipy.special import softmax
from time import time
import argparse
import logging
logging.basicConfig(
level = logging.WARN,
format = '[%(name)s] [%(asctime)s.%(msecs)03d] [%(levelname)s] %(message)s',
datefmt='%H:%M:%S')
logger = logging.getLogger("RDK_YOLO")
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--model-path", type=str, default="yolo26n_high_detect_nashm_640x640_hwcrgb888.hbm", help="Path to BPU Model.", )
parser.add_argument("--test-img", type=str, default="test_imgs/000000132544.jpg", help="image file or images path.", )
parser.add_argument("--img-save-path", type=str, default="py_result.jpg", help="image file or images path.", )
parser.add_argument("--classes-num", type=int, default=80, help="Classes Num to Detect.", )
parser.add_argument("--nms-thres", type=float, default=0.7, help="IoU threshold, default 0.7.", )
parser.add_argument("--score-thres", type=float, default=0.25, help="confidence threshold.", )
parser.add_argument("--strides", type=lambda s: list(map(int, s.split(","))), default=[8, 16, 32], help="--strides 8, 16, 32", )
opt = parser.parse_args()
logger.info(opt)
model = Ultralytics_YOLO26_Detect(
model_path=opt.model_path,
classes_num=opt.classes_num, # default: 80
nms_thres=opt.nms_thres, # default: 0.7
score_thres=opt.score_thres, # default: 0.25
strides=opt.strides, # default: [8, 16, 32]
)
img = cv2.imread(opt.test_img)
if img is None:
raise ValueError(f"Load image failed: {opt.test_img}")
exit()
results = model.postProcess(model.forward(model.letterbox(img)))
logger.info("\033[1;32m" + "Draw Results: " + "\033[0m")
print(f"{len(results) = }")
for class_id, score, x1, y1, x2, y2 in results:
draw_detection(img, (int(x1), int(y1), int(x2), int(y2)), score, class_id)
cv2.imwrite(opt.img_save_path, img)
logger.info("\033[1;32m" + f"saved in path: \"./{opt.img_save_path}\"" + "\033[0m")
class Ultralytics_YOLO26_Detect():
def __init__(self, model_path, classes_num, nms_thres, score_thres, strides):
self.strides = strides
self.CLASSES_NUM = classes_num
self.SCORE_THRESHOLD = score_thres
self.NMS_THRESHOLD = nms_thres
self.CONF_THRES_RAW = -np.log(1 / self.SCORE_THRESHOLD - 1)
try:
begin_time = time()
self.m = CauchyKesai(model_path)
logger.debug("\033[1;31m" + "Load D-Robotics Quantize model time = %.2f ms"%(1000*(time() - begin_time)) + "\033[0m")
except Exception as e:
logger.error("❌ Failed to load model file: %s"%(model_path))
logger.error("You can download the model file from the following docs: ./models/download.md")
logger.error(e)
exit(1)
self.m.s()
self.input_H, self.input_W = 640, 640
self.grids = []
for stride in self.strides:
assert (self.input_H % stride == 0), f"{stride=}, {self.input_H=}: input_H % stride != 0"
assert (self.input_W % stride == 0), f"{stride=}, {self.input_W=}: input_W % stride != 0"
grid_H, grid_W = self.input_H // stride, self.input_W // stride
self.grids.append(
np.stack(
[
np.tile(np.linspace(0.5, grid_H - 0.5, grid_H), reps=grid_H),
np.repeat(np.arange(0.5, grid_W + 0.5, 1), grid_W),
],
axis=0,
).transpose(1, 0)
)
logger.debug(f"{self.grids[-1].shape = }")
def letterbox(self, img):
begin_time = time()
self.img_h, self.img_w = img.shape[0:2]
self.x_scale = min(1.0 * self.input_H / self.img_h, 1.0 * self.input_W / self.img_w)
self.y_scale = self.x_scale
if self.x_scale <= 0 or self.y_scale <= 0:
raise ValueError("Invalid scale factor.")
new_w = int(self.img_w * self.x_scale)
self.x_shift = (self.input_W - new_w) // 2
x_other = self.input_W - new_w - self.x_shift
new_h = int(self.img_h * self.y_scale)
self.y_shift = (self.input_H - new_h) // 2
y_other = self.input_H - new_h - self.y_shift
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
input_tensor = cv2.resize(img, (new_w, new_h))
input_tensor = cv2.copyMakeBorder(input_tensor, self.y_shift, y_other, self.x_shift, x_other, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=[127, 127, 127])
input_tensor = (input_tensor - 128.0).astype(np.int8)[np.newaxis,:,:,:].copy()
logger.info("\033[1;31m" + f"pre process(letter box) time = {1000*(time() - begin_time):.2f} ms" + "\033[0m")
logger.info(f"y_scale = {self.y_scale:.2f}, x_scale = {self.x_scale:.2f}")
logger.info(f"y_shift = {self.y_shift:.2f}, x_shift = {self.x_shift:.2f}")
return input_tensor
def forward(self, input_tensor):
begin_time = time()
outputs = self.m([input_tensor])
logger.debug("\033[1;31m" + f"forward time = {1000*(time() - begin_time):.2f} ms" + "\033[0m")
return outputs
def postProcess(self, outputs):
begin_time = time()
clses = [outputs[0].reshape(-1, self.CLASSES_NUM), outputs[2].reshape(-1, self.CLASSES_NUM), outputs[4].reshape(-1, self.CLASSES_NUM),]
bboxes = [outputs[1].reshape(-1, 4), outputs[3].reshape(-1, 4), outputs[5].reshape(-1, 4),]
dbboxes, ids, scores = [], [], []
for cls, bbox, stride, grid in zip(clses, bboxes, self.strides, self.grids):
max_scores = np.max(cls, axis=1)
bbox_selected = np.flatnonzero(max_scores >= self.CONF_THRES_RAW)
ids.append(np.argmax(cls[bbox_selected, :], axis=1))
scores.append(1 / (1 + np.exp(-max_scores[bbox_selected])))
ltrb_selected = bbox[bbox_selected, :]
grid_selected = grid[bbox_selected, :]
x1y1 = grid_selected - ltrb_selected[:, 0:2]
x2y2 = grid_selected + ltrb_selected[:, 2:4]
dbboxes.append(np.hstack([x1y1, x2y2]) * stride)
dbboxes = np.concatenate((dbboxes), axis=0)
scores = np.concatenate((scores), axis=0)
ids = np.concatenate((ids), axis=0)
results = []
for bbox, score, class_id in zip(dbboxes, scores, ids):
x1, y1, x2, y2 = bbox
x1 = (x1 - self.x_shift) / self.x_scale
y1 = (y1 - self.y_shift) / self.y_scale
x2 = (x2 - self.x_shift) / self.x_scale
y2 = (y2 - self.y_shift) / self.y_scale
x1 = x1 if x1 > 0 else 0
x2 = x2 if x2 > 0 else 0
y1 = y1 if y1 > 0 else 0
y2 = y2 if y2 > 0 else 0
x1 = x1 if x1 < self.img_w else self.img_w
x2 = x2 if x2 < self.img_w else self.img_w
y1 = y1 if y1 < self.img_h else self.img_h
y2 = y2 if y2 < self.img_h else self.img_h
results.append((class_id, score, x1, y1, x2, y2))
logger.debug("\033[1;31m" + f"Post Process time = {1000*(time() - begin_time):.2f} ms" + "\033[0m")
return results
coco_names = [
"person", "bicycle", "car", "motorcycle", "airplane", "bus", "train", "truck", "boat", "traffic light",
"fire hydrant", "stop sign", "parking meter", "bench", "bird", "cat", "dog", "horse", "sheep", "cow",
"elephant", "bear", "zebra", "giraffe", "backpack", "umbrella", "handbag", "tie", "suitcase", "frisbee",
"skis", "snowboard", "sports ball", "kite", "baseball bat", "baseball glove", "skateboard", "surfboard", "tennis racket", "bottle",
"wine glass", "cup", "fork", "knife", "spoon", "bowl", "banana", "apple", "sandwich", "orange",
"broccoli", "carrot", "hot dog", "pizza", "donut", "cake", "chair", "couch", "potted plant", "bed",
"dining table", "toilet", "tv", "laptop", "mouse", "remote", "keyboard", "cell phone", "microwave", "oven",
"toaster", "sink", "refrigerator", "book", "clock", "vase", "scissors", "teddy bear", "hair drier", "toothbrush"
]
rdk_colors = [
(56, 56, 255), (151, 157, 255), (31, 112, 255), (29, 178, 255),(49, 210, 207), (10, 249, 72), (23, 204, 146), (134, 219, 61),
(52, 147, 26), (187, 212, 0), (168, 153, 44), (255, 194, 0),(147, 69, 52), (255, 115, 100), (236, 24, 0), (255, 56, 132),
(133, 0, 82), (255, 56, 203), (200, 149, 255), (199, 55, 255)]
def draw_detection(img, bbox, score, class_id) -> None:
x1, y1, x2, y2 = bbox
color = rdk_colors[class_id%20]
cv2.rectangle(img, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), color, 2)
label = f"{coco_names[class_id]}: {score:.2f}"
(label_width, label_height), _ = cv2.getTextSize(label, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1)
label_x, label_y = x1, y1 - 10 if y1 - 10 > label_height else y1 + 10
cv2.rectangle(
img, (label_x, label_y - label_height), (label_x + label_width, label_y + label_height), color, cv2.FILLED
)
cv2.putText(img, label, (label_x, label_y), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 0), 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()Runtime依赖编译参考
创建Python 3.12的环境
bash
conda create -n yolo26_runtime python=3.12 -y
conda activate yolo26_runtime
pip install numpy opencv-python scipy源码编译pyCauchyKesai接口
注: 您可以使用任何您喜欢的接口, 但是我喜欢用这个接口.
bash
git clone https://github.com/WuChao-2024/pyCauchyKesai.git
cd pyCauchyKesai/Nash
pip install scikit-build-core pybind11
pip wheel .安装
bash
pip install pycauchykesai-0.0.8-cp312-cp312-linux_aarch64.whl