什么是链表
- 物理存储单元上非连续、非顺序的线性数据结构
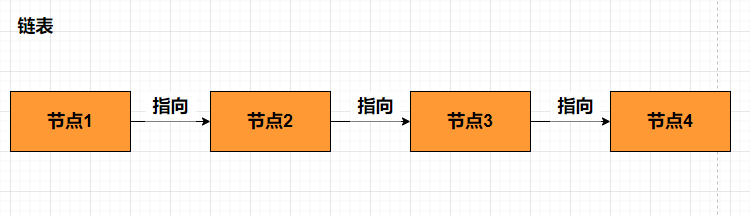
用图形流程来理解(单链表)
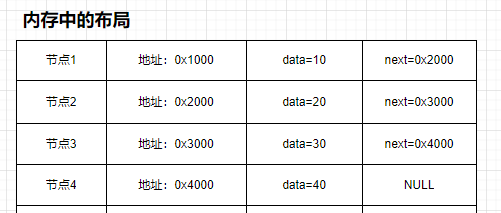
链表的类型
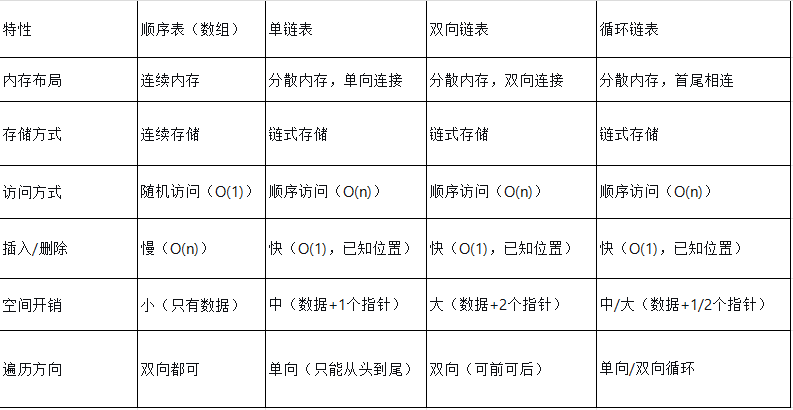
链表差异

那我们为了方便起见,此次的文章就以单链表来学习和理解
为什么要学习链表?
- 内核开发离不开链表
- 驱动开发中的实际应用
- 字符和网络 设备管理离不开链表
单链表创建与应用(最后附源码)
重要参数
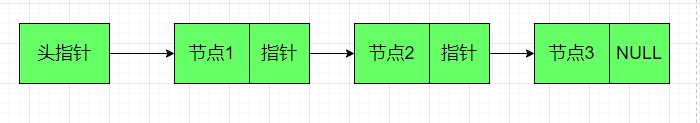
-
定义单链表节点

-
创建一个节点
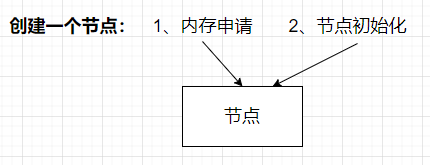

-
创建一个包含多个节点的链表
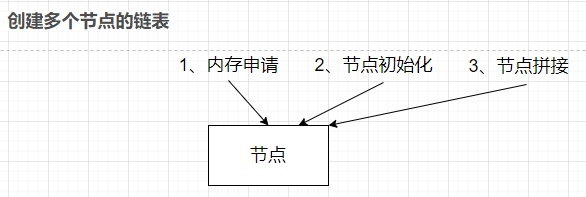

函数调用:
创建结果:
-
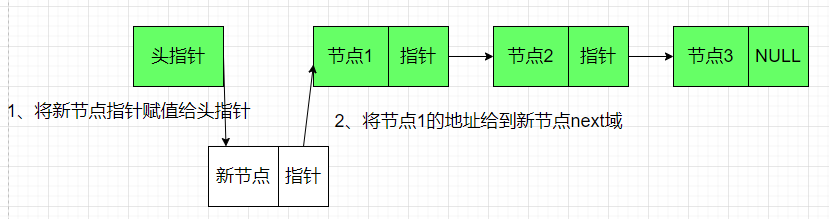
在链表头部插入节点

函数调用:
-
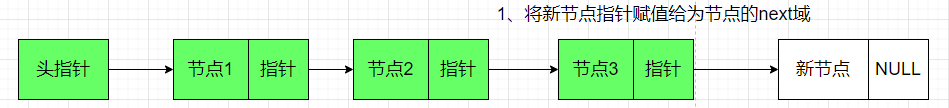
在链表尾部插入节点

函数调用:

-
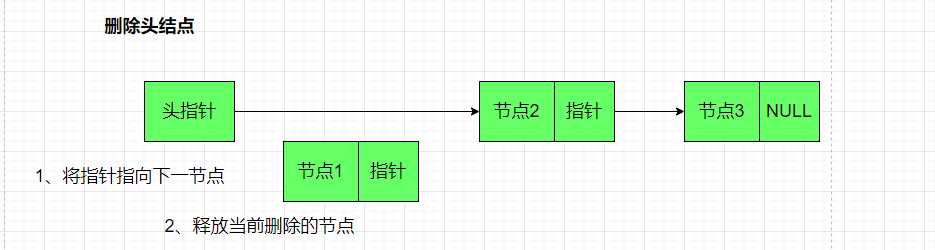
删除链表头部节点

函数调用:

-
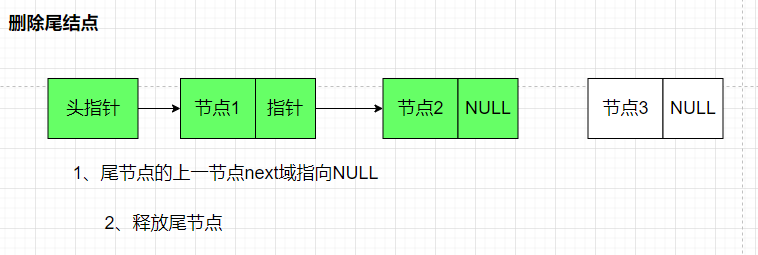
删除链表尾部节点

函数调用:


-
删除指定值(结构体中data的值)的节点(第一个匹配的)
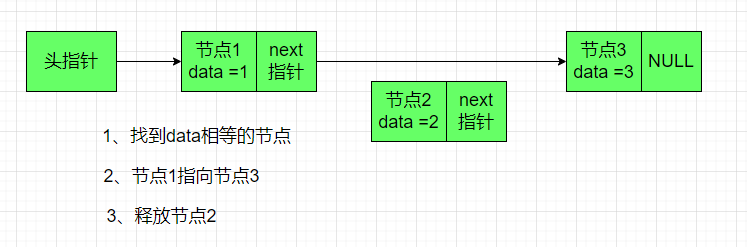

函数调用:

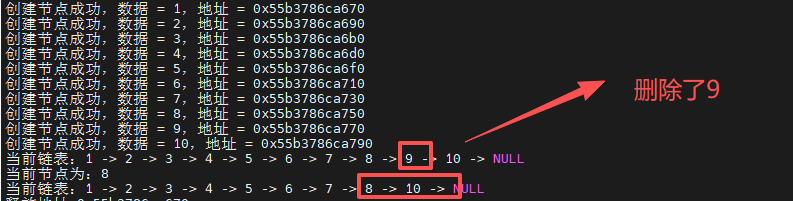
-
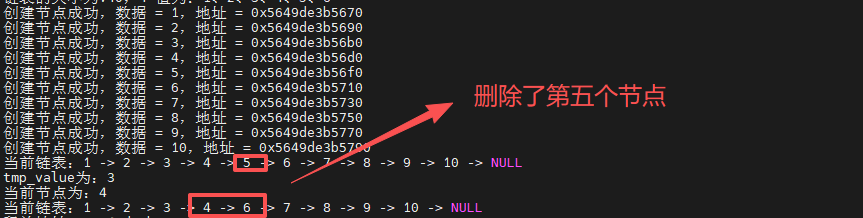
删除指定位置的节点,value 代表删除节点的位置顺序个数
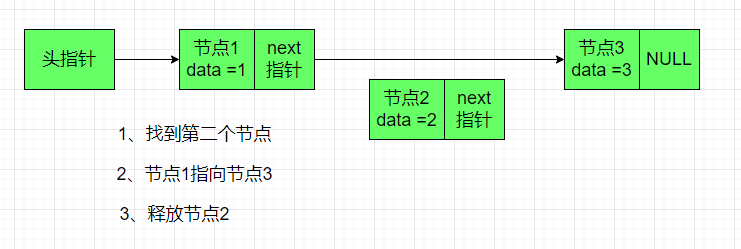

函数调用:
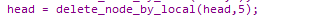
-
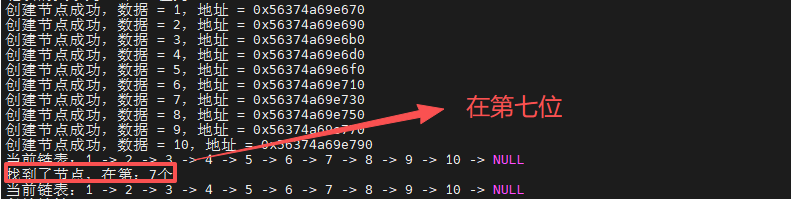
按data值查找节点,返回位置

函数调用:

-
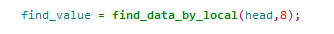
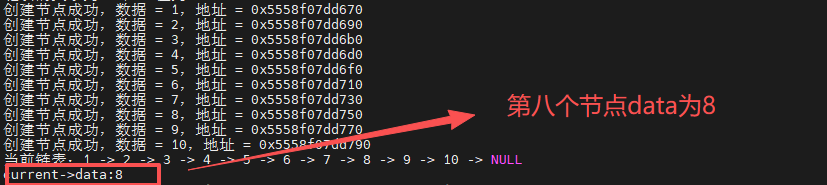
按位置查找节点,返回值

函数调用
-
修改指定位置的节点数据

函数调用:
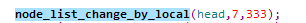
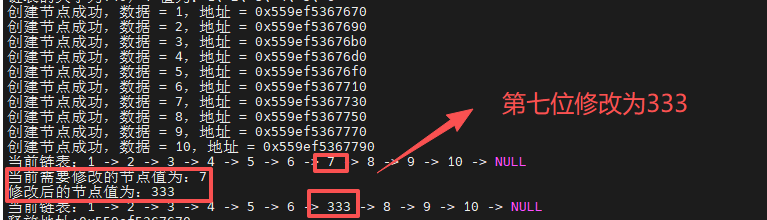
-
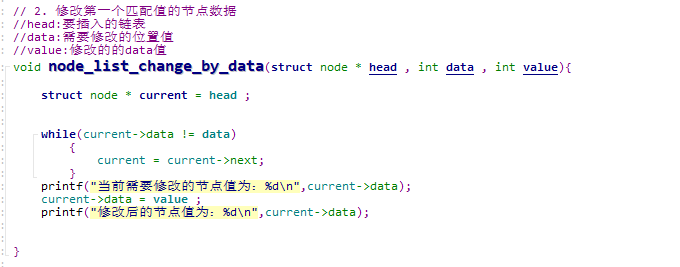
修改第一个匹配值的节点数据
函数调用:

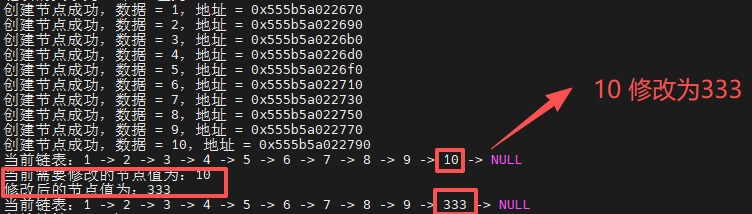
-
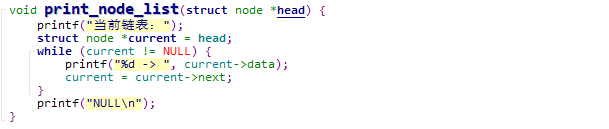
链表信息打印
源码
c
```c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
//定义单链表节点
struct node{
int data;
struct node *next;
};
//创建一个节点
struct node* create_node(int value) {
// 1. 分配内存
struct node *new_node = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
// 2. 检查内存是否分配成功
if (new_node == NULL) {
printf("内存分配失败!\n");
return NULL;
}
// 3. 设置节点数据
new_node->data = value;
new_node->next = NULL; // 重要:新节点默认不连接任何节点
printf("创建节点成功,数据 = %d,地址 = %p\n", new_node->data, new_node);
return new_node;
}
// 创建一个包含多个节点的链表
//value:节点值
//size:节点大小
//return:返回创建的链表
struct node* create_list_node(int *value,int size){
// 头指针:指向链表的第一个节点
// 初始化为NULL,表示空链表
struct node *head = NULL;//头结点
struct node *tail = NULL;//传值的中间节点
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i++)//创建节点并连接
{
struct node *new_node = create_node(value[i]);
if( i == 0)//当为第一个节点时,赋值给头指针
{
head = new_node ;//给头指针赋值
tail = head ;//指向当前链表最后一个,并且当前为第一个节点的地址
}
else
{
tail->next = new_node ;//将新的节点挂载到链表的最后一个节点的指向next域
tail = tail->next ;//继续指向当前链表最后一个,并且当前为下一个节点的地址
}
}
return head ;//返回所创建的链表头指针
}
//删除整个包含多个节点的链表
void delete_list_node(struct node *head){
struct node *current_head = head;
while(current_head != NULL)
{
struct node *tmp_value = current_head;//定义变量保存当前指针值,以便后续释放
current_head = current_head->next ;
printf("释放地址:%p\n",tmp_value);
free(tmp_value);
}
printf("删除当前链表结束\n");
}
// 增操作:添加节点
// 1. 在链表头部插入节点
//head:要插入的链表
//value:插入的data值
//return:返回创建的链表
struct node *insert_node_by_head(struct node *head , int value ){
struct node *new_node = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));//创建新的node节点
if(new_node == NULL)
return NULL;
new_node->data = value ;//新节点赋值
new_node->next = NULL ;
struct node * tmp_head = head ;//将头指针保存
head = new_node ;//将新的节点赋值给头指针
new_node->next = tmp_head ;//将旧头指针指向新节点的next域
return head ;
}
// 2. 在链表尾部插入节点
//head:要插入的链表
//value:插入的data值
//return:返回创建的链表
struct node *insert_node_by_tail(struct node *head , int value ){
struct node *new_node = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));//创建新的node节点
struct node *tmp_node = head ;
new_node->data = value ;//新节点赋值
new_node->next = NULL ;
//从头结点轮训到末尾节点
while(tmp_node->next != NULL)
{
tmp_node = tmp_node->next ;
}
tmp_node->next = new_node; //把新节点给到最后一个节点的空next域
return head ;
}
// ============ 删操作:删除节点 ============
// 1. 删除链表头部节点
//head:插入的链表
//return:返回删除后的链表
struct node *delete_node_by_head(struct node *head){
struct node *tmp_node = head ;//保存头节点,以便方便释放
if(tmp_node == NULL)
return NULL;
head = head->next ;
free(tmp_node);
return head ;
}
// 2. 删除链表尾部节点
//head:插入的链表
//return:返回删除后的链表
struct node *delete_node_by_tail(struct node *head){
struct node *current_node = head ;//保存头节点,以便方便释放
struct node *tmp_node = NULL ;
if(current_node == NULL)
return NULL;
while(current_node->next->next != NULL)//循环到倒数第二个节点
{
current_node = current_node->next ;
}
printf("当前链表节点为:%d",current_node->data);
tmp_node = current_node ;
current_node = current_node->next;
free(current_node);
tmp_node->next = NULL ;
return head ;
}
//删除指定值(结构体中data的值)的节点(第一个匹配的)
//head:要插入的链表
//value:插入的data值
//return:返回删除后的链表
struct node *delete_node_by_data(struct node *head,int value){
struct node * current_node = head ;
struct node * tmp_node = NULL ;
if(head->data == value)//第一个节点是否为删除节点
{
head= head->next ;
free(current_node);
return head ;
}
while(current_node->next->data != value)
{
current_node = current_node->next ;
}
printf("当前节点为:%d\n",current_node->data);
//找到了data相吻合数据
tmp_node = current_node->next;
current_node->next = current_node->next->next ;
free(tmp_node);
return head ;
}
//删除指定位置的节点,value 代表删除节点的位置顺序个数
//head:要插入的链表
//value:插入的data值
//return:返回删除后的链表
struct node *delete_node_by_local(struct node *head,int value){
struct node * current_node = head ;
struct node * tmp_node = NULL ;
int tmp_value = value ;
if(tmp_value == 1)//第一个节点是否为删除节点
{
head= head->next ;
free(current_node);
return head ;
}
tmp_value -= 2;//当位置个数大于1时候,比如2:删除第二个数据,只需要执行一次指针跳跃,所以进行减一,并且需要在到删除节点的前一个节点
printf("tmp_value为:%d\n",tmp_value);
while(tmp_value--)
{
current_node = current_node->next ;
}
printf("当前节点为:%d\n",current_node->data);
//找到了data相吻合数据
tmp_node = current_node->next;
current_node->next = current_node->next->next ;
free(tmp_node);
return head ;
}
// ============ 查操作:查找节点 ============
// 1. 按值查找节点,返回位置
//head:要插入的链表
//value:插入的data值
//return:返回查找的位置
int find_node_by_data(struct node *head,int value){
struct node * current = head ;
int return_value = 1 ;//因为最小值为:1
while(current->data != value)
{
current = current->next ;
return_value++;
}
printf("找到了节点,在第:%d个\n",return_value);
return return_value ;
}
// 2. 按位置查找节点,返回值
//head:要插入的链表
//local:插入的data值
//return:返回查找的位置
int find_data_by_local(struct node *head,int local){
struct node * current = head ;
int tmp_value = local ;
tmp_value -= 1 ;//需要减一处理
while(tmp_value--)
{
current = current->next ;
}
printf("current->data:%d\n",current->data);
return current->data ;
}
// ============ 改操作:修改节点数据 ============
// 1. 修改指定位置的节点数据
//head:要插入的链表
//local:需要修改的位置值
//value:修改的的data值
void node_list_change_by_local(struct node * head , int local , int value){
struct node * current = head ;
local-- ;
while(local--)
{
current = current->next;
}
printf("当前需要修改的节点值为:%d\n",current->data);
current->data = value ;
printf("修改后的节点值为:%d\n",current->data);
}
// 2. 修改第一个匹配值的节点数据
//head:要插入的链表
//data:需要修改的位置值
//value:修改的的data值
void node_list_change_by_data(struct node * head , int data , int value){
struct node * current = head ;
while(current->data != data)
{
current = current->next;
}
printf("当前需要修改的节点值为:%d\n",current->data);
current->data = value ;
printf("修改后的节点值为:%d\n",current->data);
}
//链表信息打印
void print_node_list(struct node *head) {
printf("当前链表:");
struct node *current = head;
while (current != NULL) {
printf("%d -> ", current->data);
current = current->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
int main() {
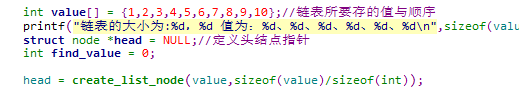
int value[] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};//链表所要存的值与顺序
printf("链表的大小为:%d,%d 值为:%d、%d、%d、%d、%d、%d\n",sizeof(value),sizeof(int),value[0],value[1],value[2],value[3],value[4],value[5]);
struct node *head = NULL;//定义头结点指针
int find_value = 0;
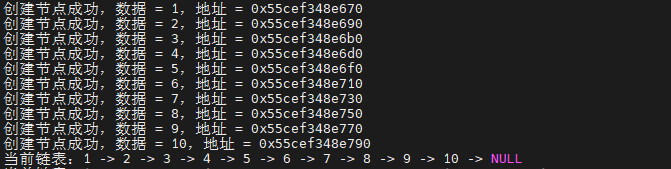
head = create_list_node(value,sizeof(value)/sizeof(int));
print_node_list(head);
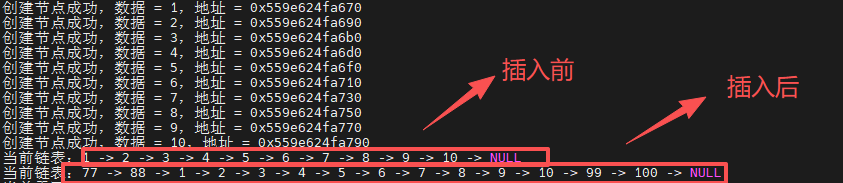
// head = insert_node_by_head(head,88);//链表前段插入节点
//
// head = insert_node_by_head(head,77);//链表前段插入节点
//
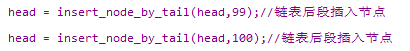
// head = insert_node_by_tail(head,99);//链表后段插入节点
//
// head = insert_node_by_tail(head,100);//链表后段插入节点
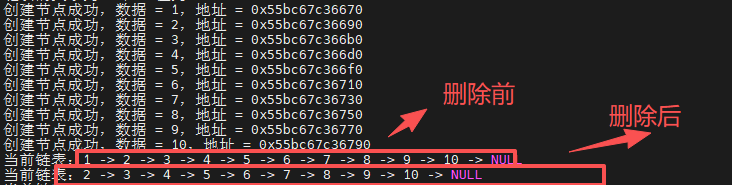
// head = delete_node_by_head(head);//链表前段删除节点
// head = delete_node_by_tail(head);//链表后段删除节点
// print_node_list(head);
// head = delete_node_by_data(head,9);
// head = delete_node_by_local(head,5);
// find_value = find_node_by_data(head,7);
// find_value = find_data_by_local(head,8);
// node_list_change_by_local(head,7,333);
// node_list_change_by_data(head,10,333);
// print_node_list(head);
// delete_list_node(head);
return 0;
}