一:概述
线性探测是计算机编程中用于解决哈希表冲突的一种方案。哈希表是一种数据结构,用于维护键值对集合,并查找与给定键关联的值。
与二次探测和双重哈希一样,线性探测也是一种开放寻址方法。在这些方案中,哈希表的每个单元格存储一个键值对。当哈希函数将新键映射到哈希表中已被其他键占用的单元格时,线性探测会在表中寻找最近的空闲位置,并将新键插入其中。查找操作也以相同的方式进行,从哈希函数给出的位置开始,按顺序搜索表,直到找到匹配的键或空单元格为止。
(引自维基百科)
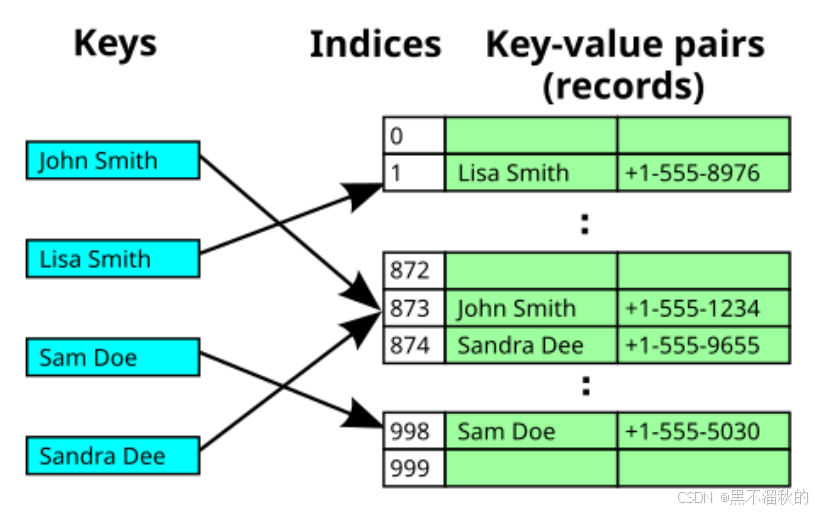
图中John Smith 和 Sandra Dee(两人都哈希到单元格 873)之间的冲突通过将 Sandra Dee 放置在下一个空闲位置(单元格 874)来解决。
二:实现
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <functional>
namespace linear_probing {
class Entry {
public:
int key;
explicit Entry(int k = -999) : key(k) {}
};
class HashTable {
public:
std::vector<Entry> table;
int totalSize;
int size = 0;
const int EMPTY = -999;
const int TOMBSTONE = -1;
explicit HashTable(int initSize = 8)
: totalSize(initSize), table(initSize, Entry(-999)) {
}
void insertKey(int key) {
int idx = probeIndex(key, false);
table[idx].key = key;
++size;
if (size / static_cast<double>(totalSize) >= 0.5) {
rehash();
}
}
void deleteKey(int key) {
int idx = probeIndex(key, true);
if (idx == -1) {
std::cout << "Key " << key << " not found\n";
return;
}
table[idx].key = TOMBSTONE;
--size;
std::cout << "Key " << key << " removed (tombstone left)\n";
}
void searchKey(int key) {
int idx = probeIndex(key, true);
if (idx == -1) {
std::cout << "Key " << key << " not found\n";
}
else {
std::cout << "Key " << key << " found at index " << idx << "\n";
}
}
void displayTable() {
std::cout << "Hash Table: ";
for (const auto& e : table) {
if (e.key == EMPTY) std::cout << " Empty ";
else if (e.key == TOMBSTONE) std::cout << " Tomb ";
else std::cout << " " << e.key << " ";
}
std::cout << "\n";
}
private:
size_t hashFunction(int key) {
return std::hash<int>{}(key);
}
int probeIndex(int key, bool searching) { // 非 const
size_t hash = hashFunction(key);
for (int i = 0; i < totalSize; ++i) {
size_t idx = (hash + i) % static_cast<size_t>(totalSize);
Entry& entry = table[idx];
if (searching) {
if (entry.key == EMPTY) return -1;
if (entry.key == key) return static_cast<int>(idx);
}
else {
if (entry.key == EMPTY || entry.key == TOMBSTONE) return static_cast<int>(idx);
}
}
return -1;
}
void rehash() {
std::vector<Entry> oldTable = table;
int oldSize = totalSize;
totalSize *= 2;
table = std::vector<Entry>(totalSize, Entry(EMPTY));
size = 0;
for (const auto& e : oldTable) {
if (e.key != EMPTY && e.key != TOMBSTONE) {
insertKey(e.key); // 使用 insertKey 保证 size 自增
}
}
std::cout << "Table rehashed. New size: " << totalSize << "\n";
}
};
} // namespace linear_probing
int main() {
using namespace linear_probing;
HashTable ht(8);
// 固定测试数据插入
int keysToInsert[] = { 5, 12, 15, 7 };
for (int k : keysToInsert) {
std::cout << "\nInserting key " << k << "...\n";
ht.insertKey(k);
ht.displayTable();
}
// 删除 key
std::cout << "\nDeleting key 12...\n";
ht.deleteKey(12);
ht.displayTable();
// 查找 key
std::cout << "\nSearching for key 7...\n";
ht.searchKey(7);
std::cout << "\nSearching for key 12...\n";
ht.searchKey(12);
// 最终表状态
std::cout << "\nFinal table:\n";
ht.displayTable();
return 0;
}