背景知识
-
普通的上采样(Upsample)如双线性插值 ,是不可学习的。
-
反卷积(Deconv/ConvTranspose)是可以学习的,但容易产生棋盘格伪影(Checkerboard Artifacts)。
-
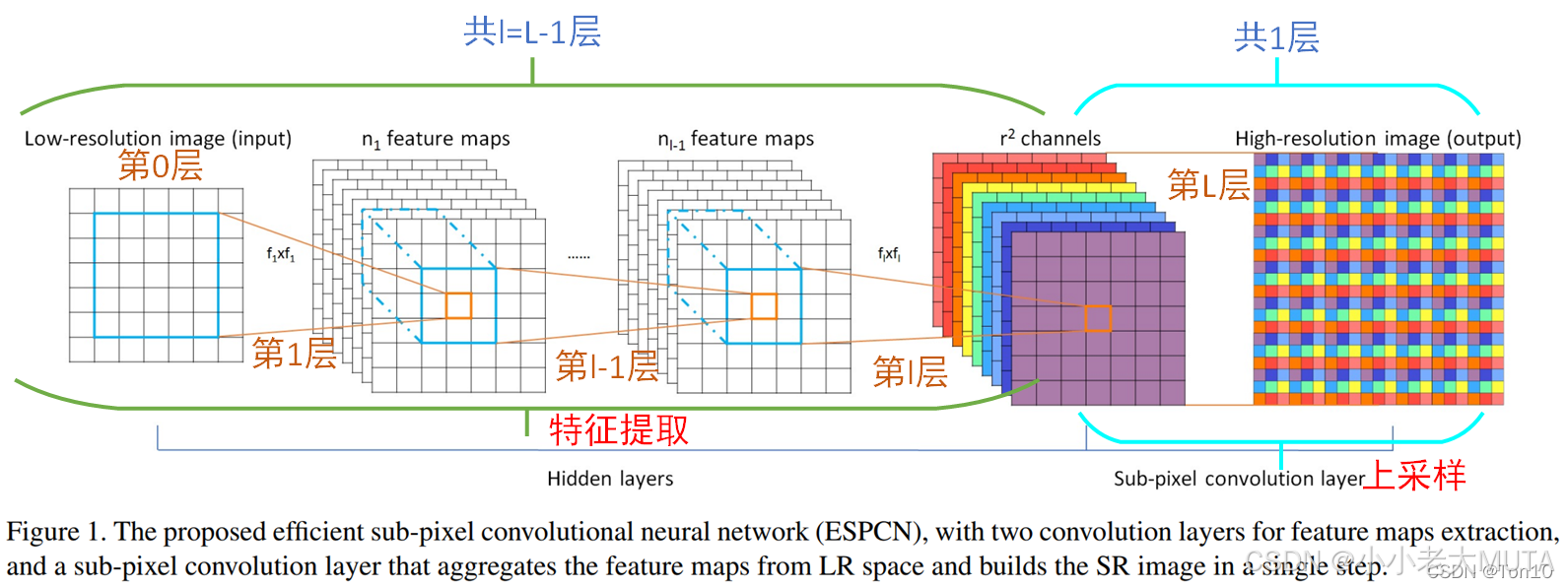
SubPixelConv:出自论文 ESPCN。它的思路是:先在通道维度上把特征变多,然后把多出来的通道"重排"到空间维度上。
亚像素卷积 ( Sub-pixel convolution**)** 就是为了解决上述问题而生的:它既可学习 ,又高效 ,还能减少伪影 。
参考链接;https://blog.csdn.net/MR_kdcon/article/details/123837994
(强推,很详细)
ESPCN:Efficient Sub-Pixel Convolutional Neural Network(超分辨率)
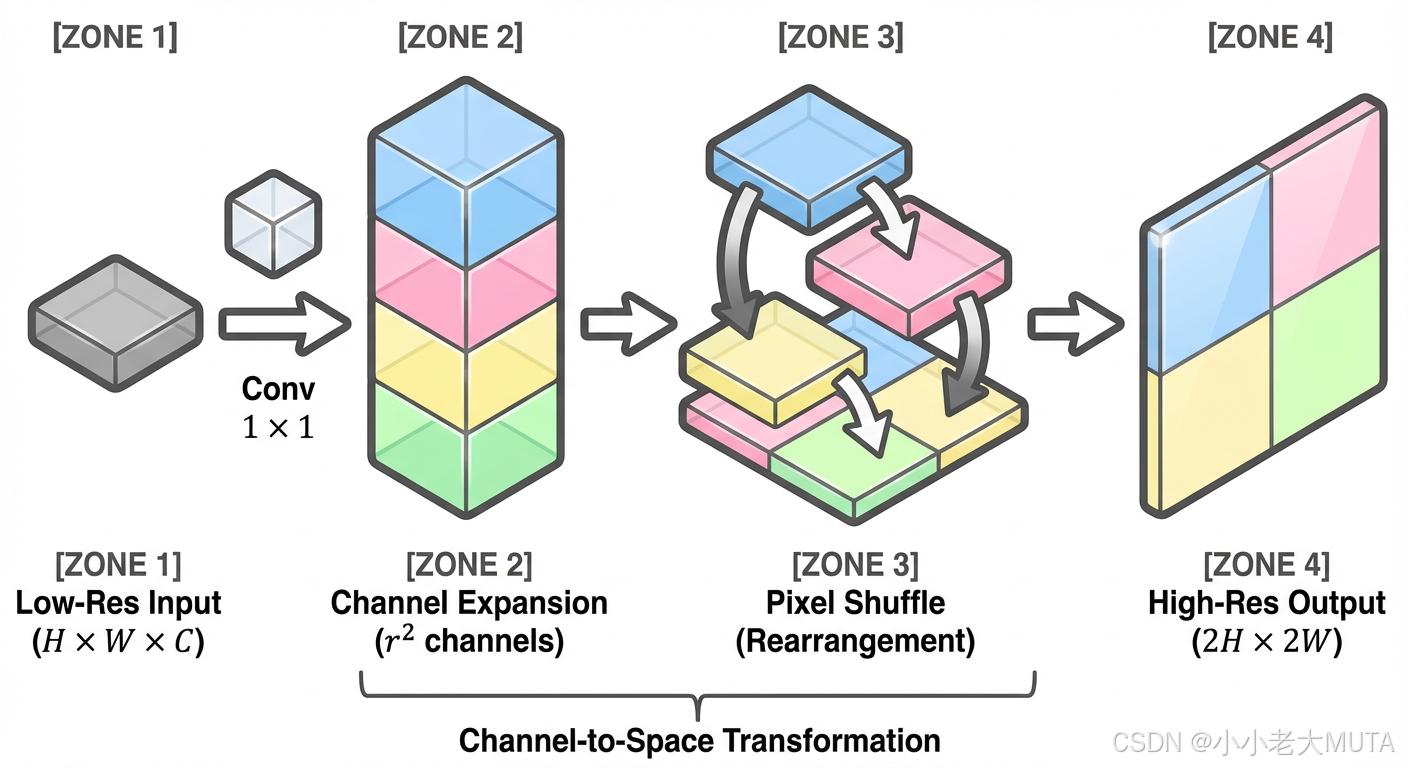
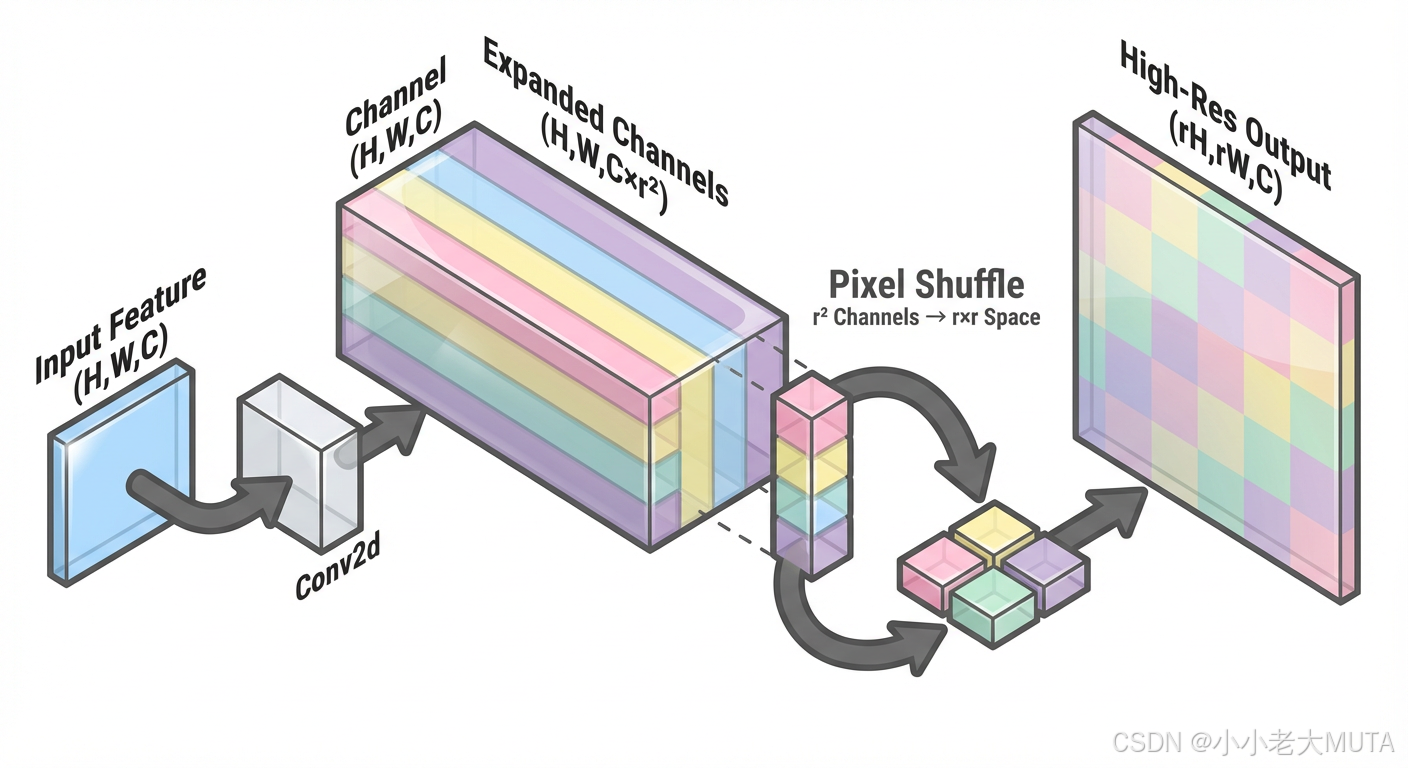
亚像素卷积的核心思想:用通道换空间。
假设我们想把一张特征图的长宽放大 r 倍(r 称为上采样因子,Upscaling Factor)。
1. 输入:一张尺寸为 (H,W),通道数为 C 的特征图。
2. 卷积扩维 (Convolution):
使用一个标准的卷积层(Conv2d),不改变 H 和 W,但是把通道数从 C 变成了
。
现在我们得到了一张"很厚"的特征图:(H,W,
)。
3. 像素重排 (Pixel Shuffle):
这就是核心的"洗牌"操作。
我们将这
个通道里的像素取出来,按照一定的规律排列到空间维度上。
具体来说,对于每个 (h,w) 位置,我们有
个像素值。我们将这
个值填入到一个 r×r 的小方格里。
4. 输出:
空间尺寸变大了:H 变成了 H×r,W 变成了 W×r。
通道数变小了:
变成了 C。
最终得到
的高分辨率图。
python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class SimpleSubPixelConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, scale_factor=2, kernel_size=3):
"""
Args:
in_channels (int): 输入特征图的通道数
out_channels (int): 输出特征图的通道数
scale_factor (int): 上采样倍率 (例如 2 表示长宽各放大 2 倍)
kernel_size (int): 卷积核大小,通常为 3
"""
super().__init__()
self.scale_factor = scale_factor
# 【核心逻辑】
# 为了在 Shuffle 后得到 out_channels 个通道,
# 卷积层必须输出 out_channels * (scale_factor^2) 个通道。
mid_channels = out_channels * (scale_factor ** 2)
# 保持卷积前后 (H, W) 不变所需的 padding
padding = (kernel_size - 1) // 2
# 1. 卷积层:扩充通道
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(
in_channels=in_channels,
out_channels=mid_channels,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
padding=padding
)
# 2. PixelShuffle 层:无需参数,只负责重排
self.pixel_shuffle = nn.PixelShuffle(scale_factor)
# 初始化权重 (ICNR 初始化对 PixelShuffle 效果最好,这里简单用 Kaiming)
self._init_weights()
def _init_weights(self):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(self.conv.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
if self.conv.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(self.conv.bias, 0)
def forward(self, x):
# x shape: (N, C_in, H, W)
x = self.conv(x)
# x shape: (N, C_out * r^2, H, W)
x = self.pixel_shuffle(x)
# x shape: (N, C_out, H*r, W*r)
return x
# 测试一下
if __name__ == "__main__":
layer = SimpleSubPixelConv(in_channels=64, out_channels=32, scale_factor=2)
dummy_input = torch.randn(1, 64, 10, 10)
output = layer(dummy_input)
print(f"Input shape: {dummy_input.shape}") # (1, 64, 10, 10)
print(f"Output shape: {output.shape}") # (1, 32, 20, 20) -> 尺寸翻倍,通道达标