假如现在有这样一个场景,将两个字符串依次进行写入,并对写入完成的字符串进行读取,
如果仍采用之前的方式,第二次的写入值会覆盖第一次的写入值,那要如何解决这一问题呢?
这就要轮到 llseek 出场了。
首先来编写应用测试代码 appllseek.c
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc,char *argv[]){
int fd;//定义 int 类型文件描述符
unsigned int off;//定义读写偏移位置
char readbuf[13] = {0};//定义读取缓冲区 readbuf
char readbuf1[19] = {0};//定义读取缓冲区 readbuf1
fd = open("/dev/test",O_RDWR,666);//打开/dev/test 设备
if(fd < 0 ){
printf("file open error \n");
}
write(fd,"hello world ",13);//向 fd 写入数据 hello world
off = lseek(fd,0,SEEK_CUR);//读取当前位置的偏移量
printf("off is %d\n",off);
off = lseek(fd,0,SEEK_SET);//将偏移量设置为 0
printf("off is %d\n",off);
read(fd,readbuf,sizeof(readbuf));//将写入的数据读取到 readbuf 缓冲区
printf("read is %s\n",readbuf);
off = lseek(fd,0,SEEK_CUR);//读取当前位置的偏移量
printf("off is %d\n",off);
off = lseek(fd,-1,SEEK_CUR);//将当前位置的偏移量向前挪动一位
printf("off is %d\n",off);
write(fd,"Linux",6);//向 fd 写入数据 Linux
off = lseek(fd,0,SEEK_CUR);//读取当前位置的偏移量
printf("off is %d\n",off);
off = lseek(fd,0,SEEK_SET);//将偏移量设置为 0
printf("off is %d\n",off);
read(fd,readbuf1,sizeof(readbuf1));//将写入的数据读取到 readbuf1 缓冲区
printf("read is %s\n",readbuf1);
off = lseek(fd,0,SEEK_CUR);//读取当前位置的偏移量
printf("off is %d\n",off);
close(fd);
return 0;
}驱动程序编写llseek.c
cpp
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/kdev_t.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/atomic.h>
#define BUFSIZE 1024 // 设置最大偏移量为1024
static char mem[BUFSIZE] = {0}; // 设置数据存储数组mem
struct device_test {
dev_t dev_num; // 设备号
int major; // 主设备号
int minor; // 次设备号
struct cdev cdev_test; // cdev结构体
struct class *class; // 类
struct device *device; // 设备
char kbuf[32];
};
static struct device_test dev1;
/* 设备打开函数 */
static int cdev_test_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
file->private_data = &dev1; // 设置私有数据
return 0;
}
/* 从设备读取数据 */
static ssize_t cdev_test_read(struct file *file, char __user *buf,
size_t size, loff_t *off)
{
loff_t p = *off; // 将读取数据的偏移量赋值给loff_t类型变量p
int i;
size_t count = size;
if (p > BUFSIZE) { // 如果当前偏移值比最大偏移量大则返回错误
return -1;
}
if (count > BUFSIZE - p) {
count = BUFSIZE - p; // 如果要读取的偏移值超出剩余的空间,则读取到最后位置
}
if (copy_to_user(buf, mem + p, count)) { // 将mem+p中的值写入buf,并传递到用户空间
printk("copy_to_user error\n");
return -1;
}
for (i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
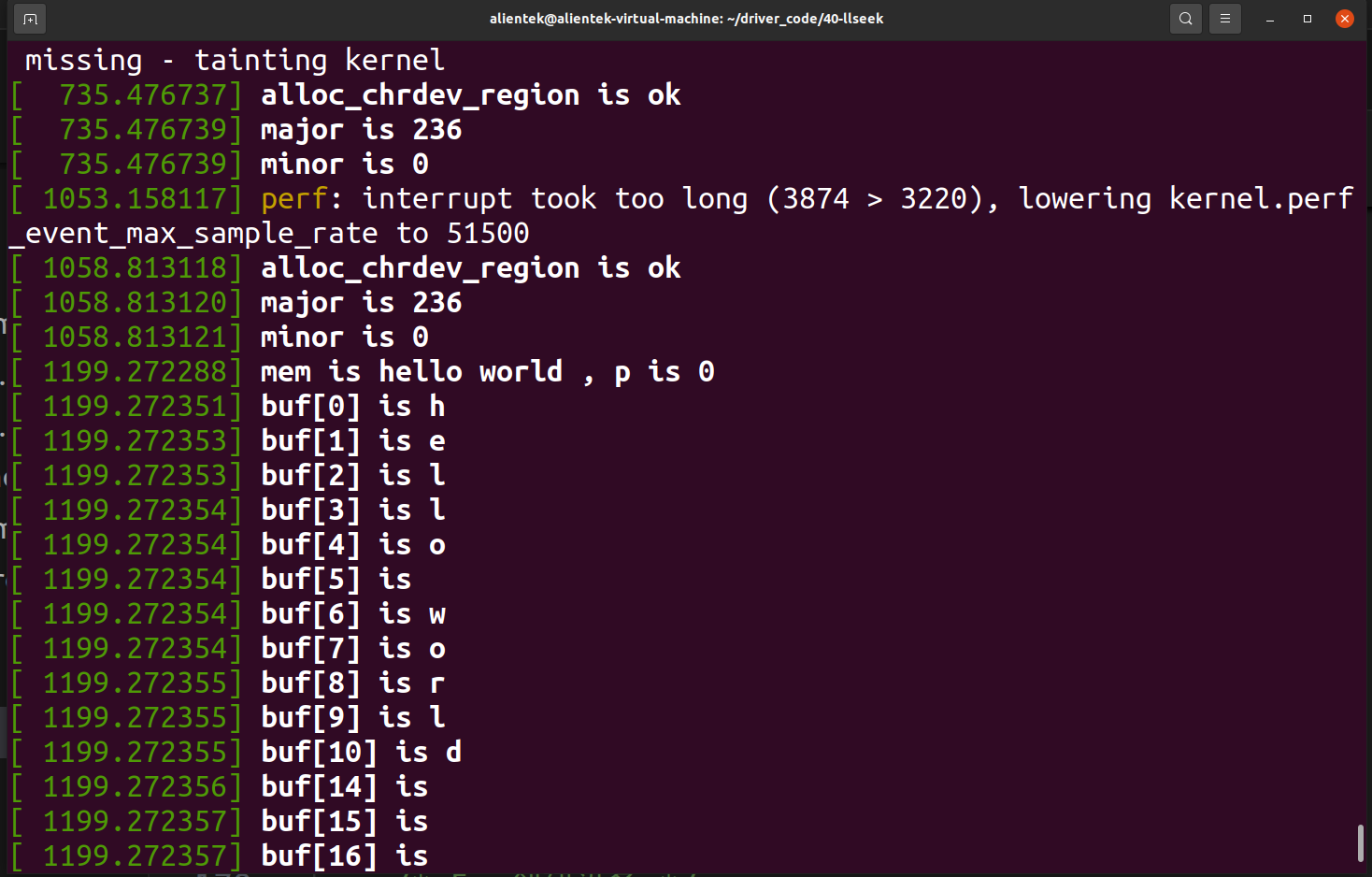
printk("buf[%d] is %c\n", i, mem[i]); // 将mem中的值打印出来
}
printk("mem is %s, p is %llu, count is %d\n", mem + p, p, count);
*off = *off + count; // 更新偏移值
return count;
}
/* 向设备写入数据函数 */
static ssize_t cdev_test_write(struct file *file, const char __user *buf,
size_t size, loff_t *off)
{
loff_t p = *off; // 将写入数据的偏移量赋值给loff_t类型变量p
size_t count = size;
if (p > BUFSIZE) { // 如果当前偏移值比最大偏移量大则返回错误
return 0;
}
if (count > BUFSIZE - p) {
count = BUFSIZE - p; // 如果要写入的偏移值超出剩余的空间,则写入到最后位置
}
if (copy_from_user(mem + p, buf, count)) { // 将buf中的值,从用户空间传递到内核空间
printk("copy_to_user error\n");
return -1;
}
printk("mem is %s, p is %llu\n", mem + p, p); // 打印写入的值
*off = *off + count; // 更新偏移值
return count;
}
/* 设备关闭函数 */
static int cdev_test_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
return 0;
}
/* 设备定位函数 */
static loff_t cdev_test_llseek(struct file *file, loff_t offset, int whence)
{
loff_t new_offset; // 定义loff_t类型的新的偏移值
switch (whence) { // 对lseek函数传递的whence参数进行判断
case SEEK_SET:
if (offset < 0) {
return -EINVAL;
}
if (offset > BUFSIZE) {
return -EINVAL;
}
new_offset = offset; // 如果whence参数为SEEK_SET,则新偏移值为offset
break;
case SEEK_CUR:
if (file->f_pos + offset > BUFSIZE) {
return -EINVAL;
}
if (file->f_pos + offset < 0) {
return -EINVAL;
}
new_offset = file->f_pos + offset; // 如果whence参数为SEEK_CUR,则新偏移值为file->f_pos + offset
break;
case SEEK_END:
if (file->f_pos + offset < 0) {
return -EINVAL;
}
new_offset = BUFSIZE + offset; // 如果whence参数为SEEK_END,则新偏移值为BUFSIZE + offset
break;
default:
break;
}
file->f_pos = new_offset; // 更新file->f_pos偏移值
return new_offset;
}
/* 设备操作函数结构体 */
struct file_operations cdev_test_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE, // 将owner字段指向本模块,可以避免在模块的操作正在被使用时卸载该模块
.open = cdev_test_open, // 将open字段指向cdev_test_open()函数
.read = cdev_test_read, // 将read字段指向cdev_test_read()函数
.write = cdev_test_write, // 将write字段指向cdev_test_write()函数
.release = cdev_test_release, // 将release字段指向cdev_test_release()函数
.llseek = cdev_test_llseek,
};
/* 驱动入口函数 */
static int __init timer_dev_init(void)
{
int ret;
/* 1. 创建设备号 */
ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&dev1.dev_num, 0, 1, "alloc_name"); // 动态分配设备号
if (ret < 0) {
goto err_chrdev;
}
printk("alloc_chrdev_region is ok\n");
dev1.major = MAJOR(dev1.dev_num); // 获取主设备号
dev1.minor = MINOR(dev1.dev_num); // 获取次设备号
printk("major is %d\n", dev1.major); // 打印主设备号
printk("minor is %d\n", dev1.minor); // 打印次设备号
/* 2. 初始化cdev */
dev1.cdev_test.owner = THIS_MODULE;
cdev_init(&dev1.cdev_test, &cdev_test_fops);
/* 3. 添加一个cdev,完成字符设备注册到内核 */
ret = cdev_add(&dev1.cdev_test, dev1.dev_num, 1);
if (ret < 0) {
goto err_chr_add;
}
/* 4. 创建类 */
dev1.class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "test");
if (IS_ERR(dev1.class)) {
ret = PTR_ERR(dev1.class);
goto err_class_create;
}
/* 5. 创建设备 */
dev1.device = device_create(dev1.class, NULL, dev1.dev_num, NULL, "test");
if (IS_ERR(dev1.device)) {
ret = PTR_ERR(dev1.device);
goto err_device_create;
}
return 0;
err_device_create:
class_destroy(dev1.class);
err_class_create:
cdev_del(&dev1.cdev_test); // 删除cdev
err_chr_add:
unregister_chrdev_region(dev1.dev_num, 1); // 注销设备号
err_chrdev:
return ret;
}
/* 驱动出口函数 */
static void __exit timer_dev_exit(void)
{
/* 注销字符设备 */
unregister_chrdev_region(dev1.dev_num, 1); // 注销设备号
cdev_del(&dev1.cdev_test); // 删除cdev
device_destroy(dev1.class, dev1.dev_num); // 删除设备
class_destroy(dev1.class); // 删除类
}
module_init(timer_dev_init);
module_exit(timer_dev_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL v2");
MODULE_AUTHOR("topeet");编译成X86的Makefile
cpp
# 移除ARM64架构和交叉编译器配置,默认使用x86本地编译环境
# export ARCH=arm64 # 注释掉ARM64架构设置
# export CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux-gnu- # 注释掉交叉编译器前缀
obj-m += llseek.o # 驱动源文件名称,保持不变
# 修改内核目录为x86系统的本地内核源码/头文件目录
# 方案1:使用系统当前运行内核的头文件(推荐,无需手动下载内核源码)
KDIR := /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build
# 方案2:如果你有本地下载的x86内核源码,替换成对应的路径,例如:
# KDIR := /home/yourname/linux-x86-kernel # 根据实际路径修改
PWD ?= $(shell pwd)
all:
make -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules # 本地编译x86内核模块
clean:
make -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) clean # 清理编译产物
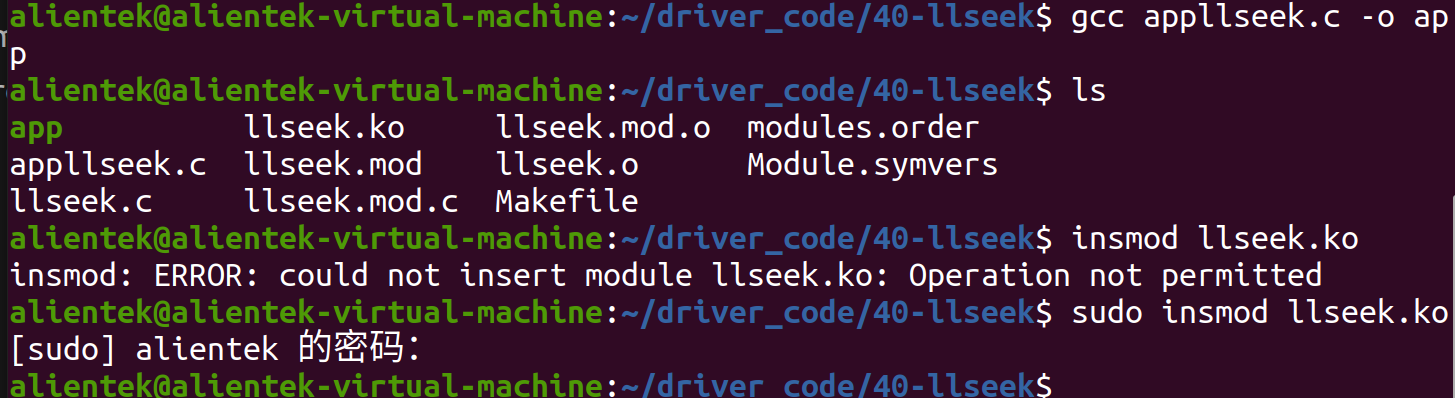
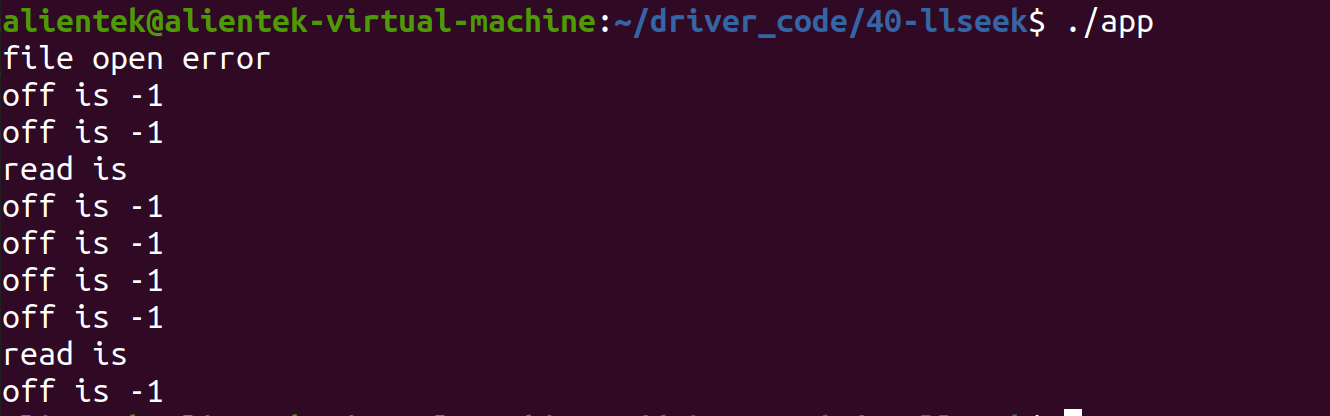
失败

要加上权限
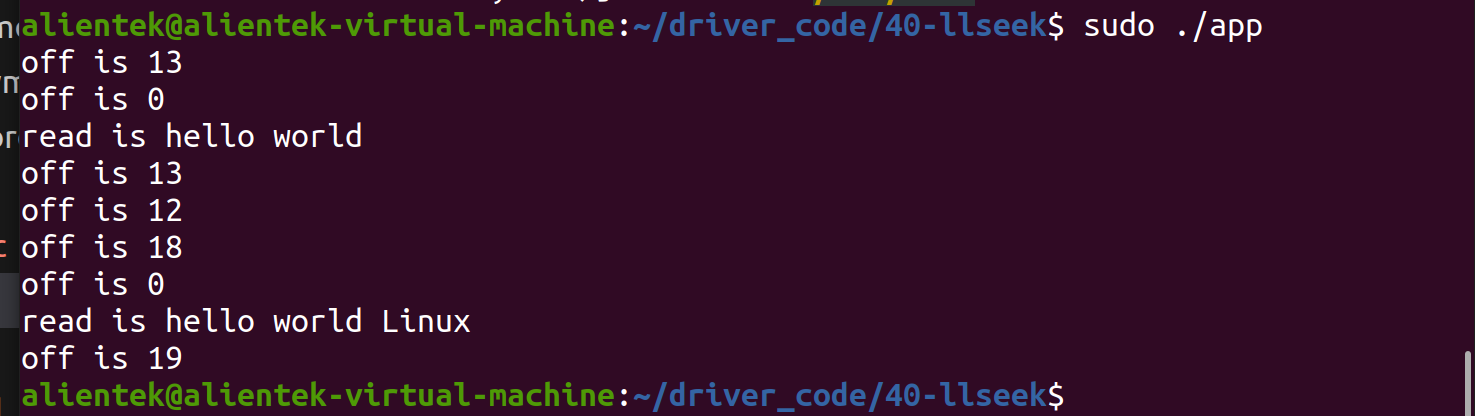
dmesg