其实C++一次重大更新是STL横空出世,由惠普实验室两位大佬编写并进行开源,STL(Standard Template Library,标准模版库)是常见的数据结构和算法的库,是C++标准库的重要组成部分;后续改出很多版本,公众认可度较高且可读性较强的是gcc编译器采用的SGI版本,Linux采用的是gcc编译器。
C strxxx 系列库函数
C++ string 管理字符数组,增删改查+算法
string是STL六大分类容器的一部分,
https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/string/
1.Member functions
1.1 constructor
构造
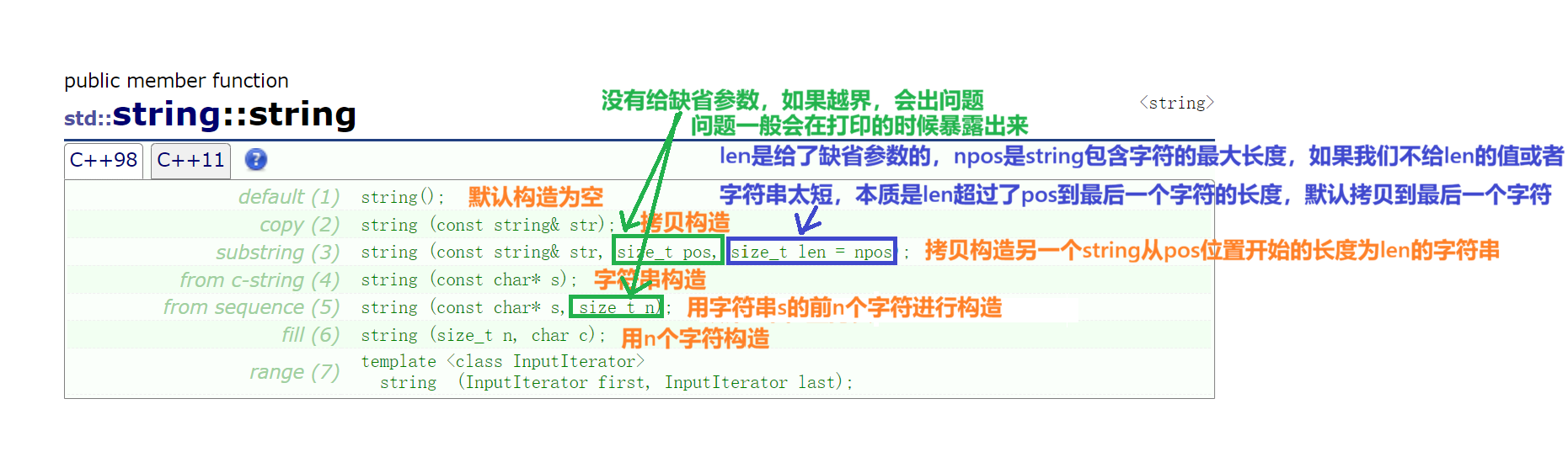
cpp
int main() {
string s1;//默认构造为空
string s2("an apple a day, keep my enemies away");//字符串构造
string s3(s2);//拷贝构造
string s4(s2, 2);//从s2第2个位置拷贝构造
string s5(s2, 80,1000);//从s2第2个位置拷贝构造三个字符
string s6("an apple a day, keep my enemies away",100);//用字符串前n个字符进行构造
string s7(10, 'a');//用10个字符a构造
return 0;
}s1.copy(buffer, pos, len)把s1第pos个位置开始的len长度个字符拷贝给buffer,注意拷贝完的buffer默认没有'\0'
2.Iterators
迭代器的底层不一定完全是指针,有可能是封装的更复杂的数据结构
范围for早期C++和Java不支持,Python等语言支持,后来C++和Java也奉行"拿来主义",把范围for拿过来了;C++的范围for底层就是迭代器
cpp
int main() {
string s1("guchen");
for (auto& ch : s1) {//for (char& ch : s1)
cout << ch <<" ";//查
ch = 'a';//改
}
cout << s1 << endl;
return 0;
}
但是string能用[ ],一般不使用迭代器

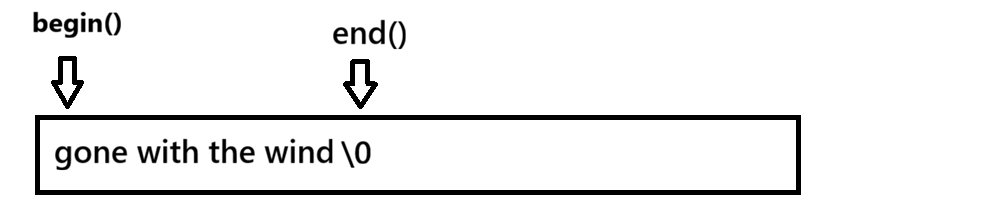
cpp
int main() {
string s("gone with the wind");
string::iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end()) {
(*it)++;//改
cout << *it << " ";//查
it++;//进行迭代
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}输出如下
cpp
h p o f ! x j u i ! u i f ! x j o e迭代器是通用的
cpp
int main() {
vector<int> v = { 1,2,3 };//顺序表
vector<int>::iterator vit = v.begin();
while (vit != v.end()) {
cout << *vit << " ";
vit++;
}
cout << endl;
list<int> l = { 1,2,3 };//链表
l.push_back(10);
list<int>::iterator lit = l.begin();
while (lit != l.end()) {
cout << *lit << " ";
lit++;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}对于max_size这个函数,不同编译器下的测试结果不一定相同
cpp
int main() {
string s("gone with the wind");
cout << s.max_size() << endl;
return 0;
}
cpp
//VS2022测试结果
9223372036854775807
//Linux centos7 测试结果
4611686018427387897

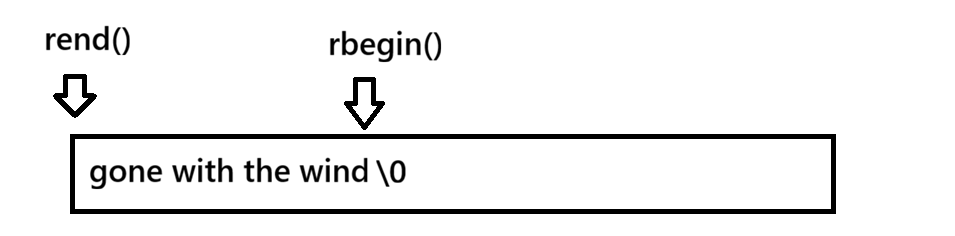
也可以反向迭代
cpp
int main() {
string s("gone with the wind");
auto it = s.rbegin();//等价于string::reverse_iterator it = s.rbegin();
while (it != s.rend()) {
(*it)++;
cout << *it << " ";
it++;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
后来C++11出了c四件套,就是上面四个本来就有的const版本,但是用的一般比较少

cpp
void Func(const string& s) {
string::const_iterator it = s.begin();//此处加了const,权限不能放大
while (it != s.end()) {
cout << *it << " ";
it++;
}
cout << endl;
string::const_reverse_iterator rit = s.rbegin();
while (rit != s.rend()) {
cout << *rit << " ";
rit++;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
string s1("guchen");
Func(s1);
return 0;
}迭代器也可以结合算法使用,因为迭代器提供了统一的访问和修改容器数据的方式,算法可以通过迭代器,处理容器内数据
cpp
int main() {
vector<int> v = { 3,2,1 };
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
reverse(v.begin(), v.end());
list<int> l = { 1,2,3 };
reverse(l.begin(), l.end());
return 0;
}
3.Capacity
3.1 resize

cpp
int main() {
string s("great expectations");
s.resize(10,'a');
return 0;
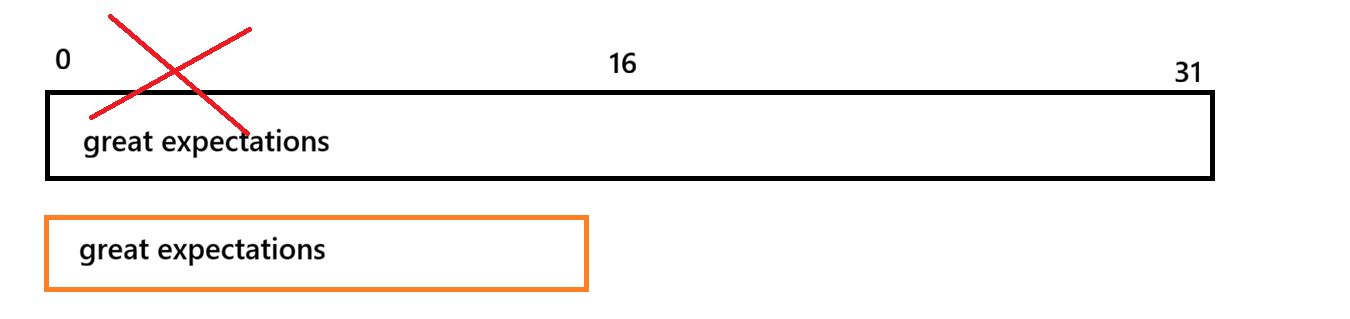
}s的size本来为18,调整为10后,capacity并没有改变,因为缩容也是有代价的,因为C/C++内存管理不支持一段一段进行管理
不是说把16-31还给操作系统
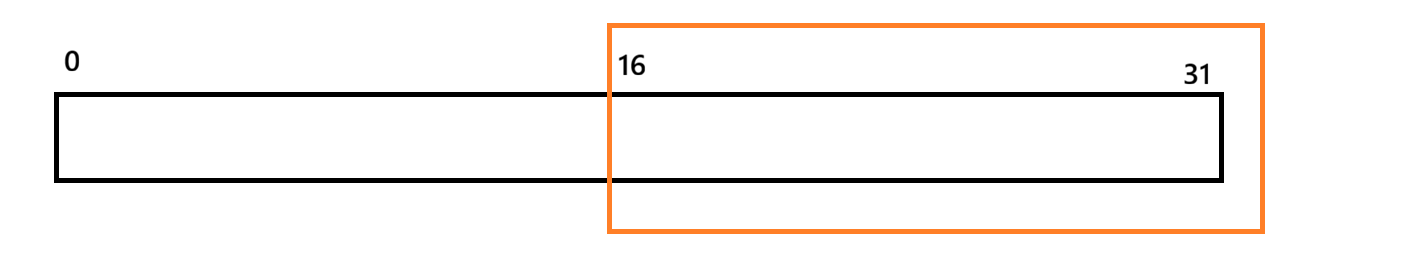
而是重新开一片空间,把原有内容复制到新空间,更新地址,把原有空间释放,本质是时间换空间
cpp
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <string>
3 using namespace std;
4 int main() {
5
6 string s("great expectations");
7
8 cout<<s.size()<<endl;
9 cout<<s.capacity()<<endl;
10 s.resize(35,'a');
11
12 cout<<s.size()<<endl;
13 cout<<s.capacity()<<endl;
14 string s1("great expectations");
15
16 cout<<s1.size()<<endl;
17 cout<<s1.capacity()<<endl;
18 s1.resize(10,'a');
19
20 cout<<s1.size()<<endl;
21 cout<<s1.capacity()<<endl;
22 return 0;
23 }输出如下
cpp
//VS2022
18
31
35
47
18
31
10
31
//g++ centos7
18
18//初始化18个字符,size和capacity都是18
35//resize到35,此时size是35,capacity是36(二倍式的扩容)
36
18
18
10//缩容到10,size是10,capacity还是18
183.2 reserve

cpp
int main() {
string s("great expectations");
cout << s.size() << endl;
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
s.clear();//把size置为0
cout << s.size() << endl;
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
s.reserve(10);
cout << s.size() << endl;
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
return 0;
}输出如下
cpp
//VS2022
18
31//初始化18个字符,size是18,capacity是31
0//clear之后size是0,capacity是31
31
0//此时reserve到10,capacity变成15
15
//g++ centos7
18
18
0
18
0
10
cpp
int main() {
string s("great expectations");
cout << s.size() << endl;
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
s.reserve(10);
cout << s.size() << endl;
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
return 0;
}输出如下
cpp
//VS2022
18
31//初始化18个字符,size是18,capacity是31
18
31//此时reserve到10,capacity还是31
//g++ centos7
18
18
18
183.3 shrink_to_fit

C++11引入的,Linux下编译要加上标准g++ code.cpp -std=c++11
cpp
int main() {
string s("great expectations");
cout << s.size() << endl;
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
s.clear();
cout << s.size() << endl;
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
s.shrink_to_fit();
cout << s.size() << endl;
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
return 0;
}
cpp
//VS2022
18
31
0
31
0
15
//g++ centos7
18
18
0
18
0
04. Element access
4.1 operator[ ]
string重载了运算符[ ],字符对象可以像字符数组一样使用,但是二者原理不同
因为返回的是引用,所以可以修改
cpp
int main() {
string s1("guchen");
for (int i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++) {
s1[i] = 'a';//改
s1[i]++;//增
cout << s1[i] << endl;//查
}
s1.clear();//删,置s1.size()为0
char s[] = "akui";
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(s); i++) {
s[i] = 'b';
cout << s[i] << endl;
}
s1[1];//s1.operator[](1)
s[1];//*(s+1)
return 0;
}我们看到string下有size和length,因为container包括vector(顺序表),list(链表),map(红黑树),顺序表、链表、字符类说length长度还说的过去,但是红黑树说length就不合适了,所以s红黑树用size表征结点个数,而相较于string,STL出现的晚,所以string并没有归在STL中,但如果单单从逻辑上说的话,容器嘛,存储数据的地方,那肯定string也可以算在string的容器里了,所以string也引入了size
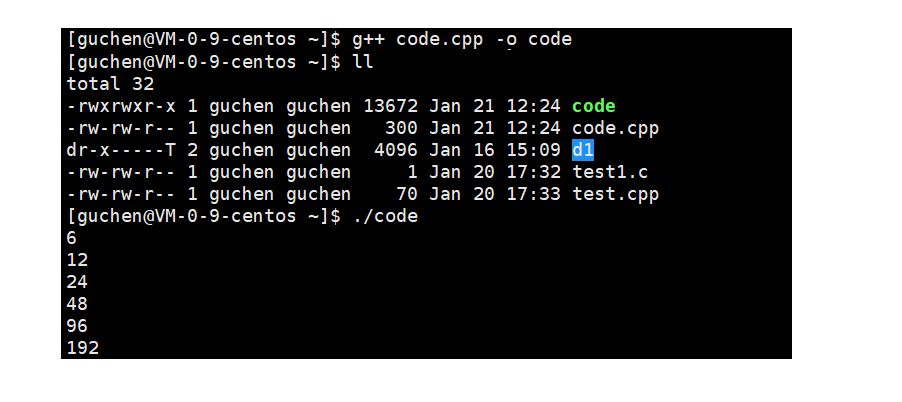
稍微看一下VS2022下的扩容逻辑
cpp
int main() {
string s;
int num = s.capacity();
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
s += '0';
if (num != s.capacity()) {
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
num = s.capacity();
}
}
return 0;
}输出如下
cpp
15
31
47
70
105如果6个字符,capacity是15;24个字符,capacity是31;36个字符,capacity47;54个字符,capacity是63,扩容和开空间不完全是1个逻辑,开空间貌似是以最小的能够容纳数据的16的倍数开;
如果是Linux下g++编译器,是给多少字符,就给多少空间,二倍进行扩容
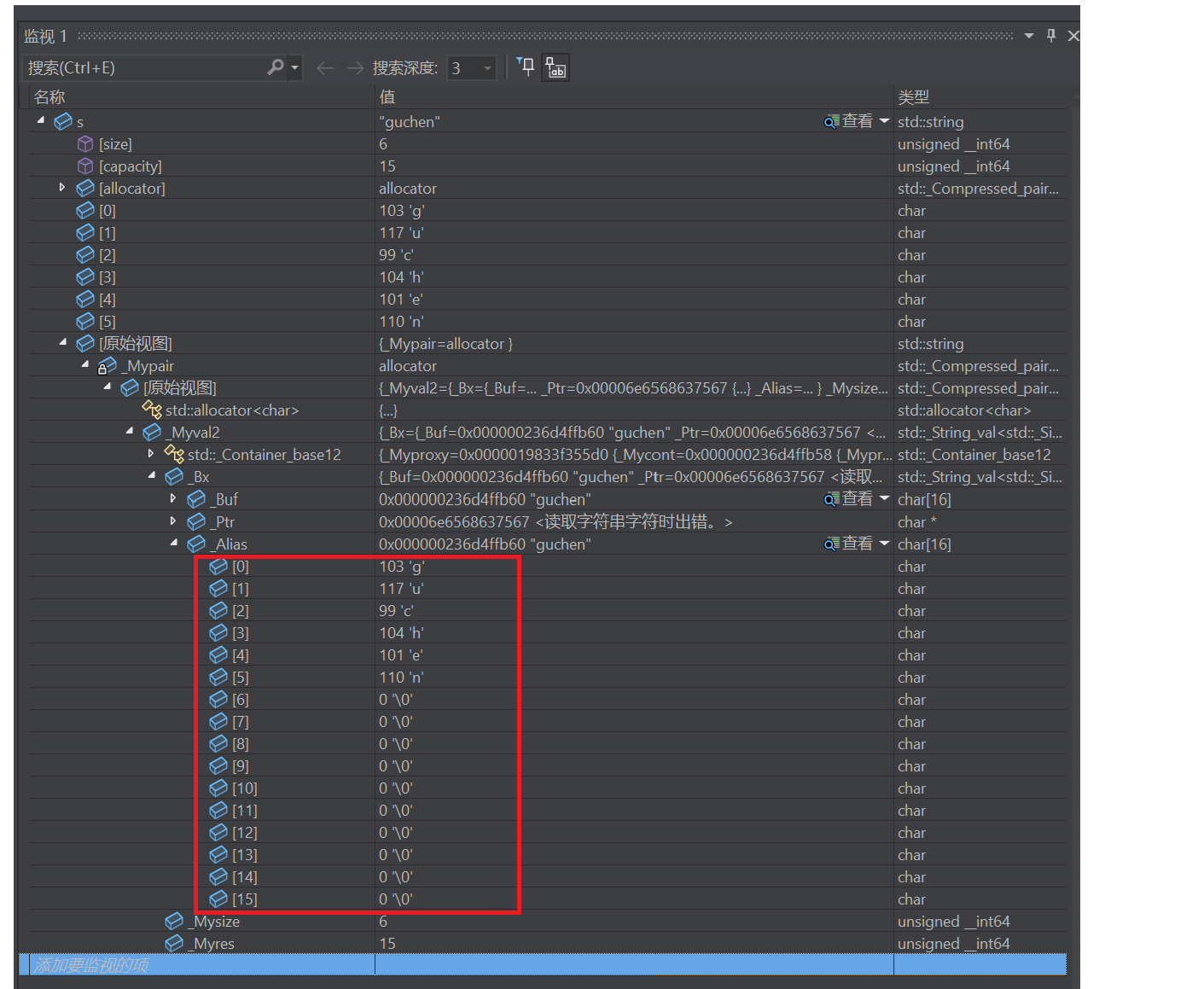
因为STL是一个规范,没有规定怎么实现,但底层实现大同小异
我们看到string s("guchen");初始化字符对象时6个字符开辟了16个空间,除了刚开始的字符剩下的以'\0'初始化,其实底层类似顺序表
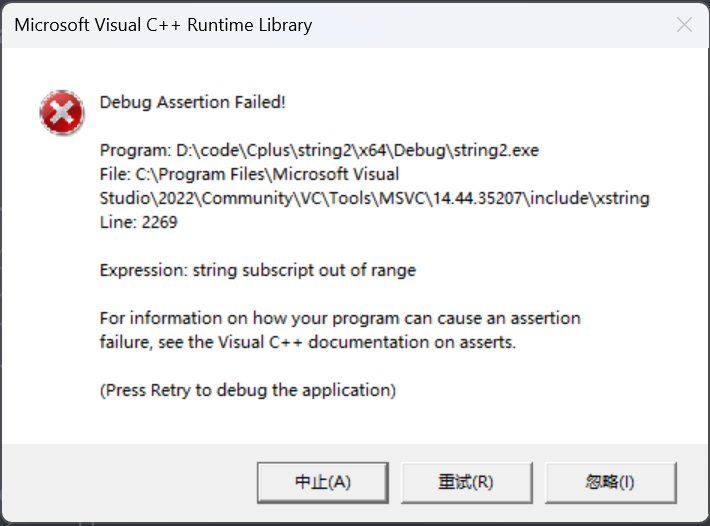
越界会断言
cpp
int main() {
string s("great expectations");
cout << s[40] << endl;
return 0;
}
4.2 at

返回pos指向的字符,如果pos越界,抛异常
cpp
int main() {
string s("great expectations");
cout << s.at(1) << endl;
return 0;
}输出r
cpp
int main() {
string s("great expectations");
cout << s.at(40) << endl;
return 0;
}
越界会抛异常
cpp
int main() {
string s("tara");
try {
cout << s.at(40) << endl;
}
catch (const exception e) {
cout << e.what() << endl;
}
return 0;
}输出如下
cpp
invalid string position5.Modifiers
5.1 push_back
cpp
int main() {
string s1("lemon");
s1.push_back('i');
cout << s1 << endl;//输出lemoni
return 0;
}5.2 append

string一些接口有一些冗余
cpp
int main() {
string s1("lemon ");
string s2("sweet");
s1.append(s2);
s1.append(s2,2,3);
s1.append("nice");
s1.append("nice",2);
s1.append(10, 'a');
cout << s1 << endl;
return 0;
}5.3 operator+=
其实+=就是append更好用
cpp
int main() {
string s1("lemon ");
string s2 = "sweet";//拷贝构造
s1 += "c";
s1 += s2;
s1 += "nice";
return 0;
}也可以直接进行字符串对象比较
cpp
int main() {
string s1("lemon ");
string s2 = "sweet";
cout << (s1 > s2) << endl;
cout << (s1 == s2) << endl;//流插入的优先级比较高
return 0;
}切分为子串
cpp
int main() {
string s1("https://cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/string/");
string sub1(s1, 0, 6);//协议
string sub2(s1, 8, 13);//域名
string sub3(s1, 22);
//string sub4(s1, 22,s1.size()-22);两种写法等价
cout << sub1 << endl;
cout << sub2 << endl;
cout << sub3 << endl;
return 0;
}将输入的整数转成逆置后的字符串对象
cpp
int main() {
size_t x,val;
string strx;
cin >> x;
//假设x不为零
while (x) {
val = x % 10;
strx += ('0' + val);
x /= 10;
}
return 0;
}5.4 assign
用一个新的字符串代替原有内容
cpp
int main() {
string s("great expectations");
s.assign("normal no more");
cout << s << endl;//输出normal no more
return 0;
}5.5 erase
迭代器区间一般都是左闭右开
cpp
int main() {
string s("great expectations");
s.erase(s.begin(), s.begin() + 5);
cout << s << endl;//输出expectations
s.erase(s.begin());//抹掉刚开始的一个字符
s.erase(5, 1);//从下标为5的字符开始,共抹掉一个字符
s.erase(5);//只剩从头开始的5个字符
return 0;
}5.6 repalce
cpp
int main() {
string s("apple peach");
string s1("pear is sweet");
s.replace(6, 4, s1);
cout << s << endl;//输出apple pear is sweeth
return 0;
}5.7 swap

cpp
int main() {
string s("apple peach");
string s1("pear");
s.swap(s1);
return 0;
}5.8 insert
cpp
int main() {
string s("tara");
s.insert(0, 10, 'y');
s.insert(s.begin()+10, 10, 'x');
return 0;
} 6. String operations
6.1 c_str
因为C++是兼容C的,有的时候C++项目需要调用一些数据库,比如MySQL,但这些数据库只提供的C的接口,如果使用C类型的字符串,空间管理会麻烦很多,所以这个时候就需要获取字符串对象的字符串。

cpp
int main() {
string s("apple peach");
string s1("pear");
const char* s2 = s.c_str();
string filename = "test.cpp";
filename += ".zip";
FILE* fout = fopen(filename.c_str(), "r");
return 0;
}6.2 copy
拷贝
cpp
int main() {
string s1("i was served lemons but i made lemonade");
char buffer[20];
s1.copy(buffer, 3, 2);
buffer[3] = '\0';
cout << buffer << endl;//输出was
return 0;
}6.3 find/rfind
从头开始找

从尾开始找
牛刀小试
cpp
class Solution {
public:
int firstUniqChar(string s) {
for(int i=0;i<s.size();i++){
int pos1=s.find(s[i]);//该字符第一次出现的地方
int pos2=s.rfind(s[i]);//该字符最后一次出现的地方
if(pos1==pos2)//如果第一次和最后一次出现的位置相同,说明只出现了一次
return i;
}
return -1;//如果没有找到,返回-1
}
};6.4 find_first_of/find_first_not_of
find_first_of
找到字符串对象中第一个与str/s任何字符(1)(2)(3)或c(4)相同的字符,返回下标
cpp
int main() {
string s("tara testover");
int pos = s.find_first_of("abcde");
while (pos != string::npos) {
s[pos] = '*';
pos = s.find_first_of("abcde",pos+1);
}
cout << s << endl;
return 0;
}输出如下
cpp
t*r* t*stov*rfind_first_not_of
找到字符串对象中第一个与str/s任何字符(1)(2)(3)或c(4)不相同的字符,返回下标
6.5 find_last_of/find_last_not_of
find_last_of
找到字符串对象中最后 一个与str/s任何字符(1)(2)(3)或c(4)相同的字符,返回下标
cpp
int main() {
string s("tara testover");
int pos = s.find_last_of("abcde");
while (pos != string::npos) {
s[pos] = '*';
pos = s.find_last_of("abcde", pos - 1);
}
cout << s << endl;
return 0;
}输出如下
cpp
t*r* t*stov*rfind_last_not_of
找到字符串对象中最后一个与str/s任何字符(1)(2)(3)或c(4)不相同的字符,返回下标
6.6 substr

cpp
//将网址拆分为协议 域名 资源
void Divide(string& url1) {
int pos1 = url1.find("://");
if (pos1 != string::npos) {
string protocol = url1.substr(0, pos1), domain;
int pos2 = url1.find("/", pos1 + 3);
if (pos2 != string::npos)
domain += url1.substr(pos1 + 3, pos2 - (pos1 + 3));
string uri = url1.substr(pos2 + 1);
cout << protocol << endl;
cout << domain << endl;
cout << uri << endl;
}
}
int main(){
string url1 = "https://blog.csdn.net/m0_74328241?spm=1010.2135.3001.5343";
string url2 = "https://leetcode.cn/problems/ba-zi-fu-chuan-zhuan-huan-cheng-zheng-shu-lcof/description/";
string url3 = "https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/erase/";
string url4 = "https://www.doubao.com/chat/36368173941801218";
Divide(url4);
return 0;
}
7.Convert to strings

cpp
int main(){
char str1[] = "abcd";
char str2[2];
str2[0] = 98;//存储的是b
char str3[] = "顾宸";
cout << sizeof(str3) << endl;//输出5,和编码有关,ascii码不足以表示汉字,unicode编码,一个汉字两个字节,2^16-1=66535,足以表示常见的汉字(utf8,还有utf16 ,utf32等,还有gbk编码,很多生僻词包括的比较全,编码表,也就是值和符号的映射对应关系表)
return 0;
}8.牛刀小试
cpp
class Solution {
public:
string addStrings(string num1, string num2) {
string strRet;
int end1=num1.size()-1,end2=num2.size()-1,carry=0,i=0, val1, val2,ret;
while(end1>=0||end2>=0){//只要有一个字符串没处理完就接着处理
val1=(end1>=0)?num1[end1]-'0':0;//0的ascii码值是48,我们要把ascii表示的字符数字转化为值对应的数字,-'0',相对值就是
val2=end2>=0?num2[end2]-'0':0;
ret=val1+val2+carry;
carry=ret/10;
strRet+=ret%10+'0';
end1--;
end2--;
}
//如果两个字符串长度相等,且产生进位,上面的处理逻辑不会处理这种情况,所以单独处理;亦或是两个字符串不相等,处理完最后一个字符串还产生进位
if(carry==1)
strRet+='1';
reverse(strRet.begin(),strRet.end());//属于algorithm,记得包头文件
return strRet;
}
};也可以通过头插的方式
cpp
class Solution {
public:
string addStrings(string num1, string num2) {
string strRet;
int end1=num1.size()-1,end2=num2.size()-1,carry=0,i=0, val1, val2,ret;
while(end1>=0||end2>=0){
val1=(end1>=0)?num1[end1]-'0':0;
val2=end2>=0?num2[end2]-'0':0;
ret=val1+val2+carry;
carry=ret/10;
strRet.insert(strRet.begin(),ret%10+'0');
end1--;
end2--;
}
if(carry==1)
strRet.insert(strRet.begin(), '1');
return strRet;
}
};但是头插的效率会低一些,如果是尾插,每次是O(1),因为一般会维护tail指针,N次就是O(N);如果是头插,移动数据次数分别是1+2+...+N-1,是O(N^2)

cpp
class Solution {
public:
void reverseString(vector<char>& s) {
int left=0,right=s.size()-1;
while(left<right){
swap(s[left],s[right]);
left++;
right--;
}
}
};
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
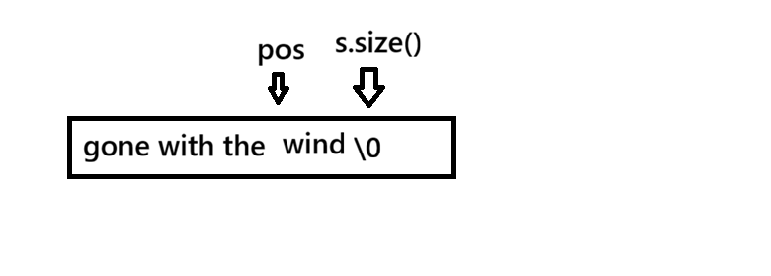
int main() {
string s;
getline(cin,s);//cin是istream类型的全局对象
int pos = s.rfind(" ");
if(pos!=string::npos)//npos是string的静态局部变量,可以通过类域访问,size_t的npos是2^32-1(32位下),int的话是-1
cout<< (s.size()-(pos+1));
else
cout<< s.size();//如果pos是-1,说明不存在空格,只有一个单词,返回字符对象长度
}
流提取存在的问题是,以空格或换行作为输入的分隔符用来处理多组输入,而这个题目输入的字符串是可能包含空格的,而getline是可以手动设置分隔符的,默认是换行;getline不是成员函数,所以可以直接调用
