为什么我们需要"工具调用"?
在开发大模型应用时,我们经常面临两个痛点:
-
数据时效性问题:模型是基于过去的数据训练的,它不知道"现在几点了",也不知道"今天北京的天气如何"。
-
无法执行动作:大模型只是一个"大脑",它只能生成文本,无法直接去发邮件、查数据库或定闹钟。
Spring AI 的工具调用(Function Calling)机制,就是给大模型装上了"手"和"眼睛"。 它允许模型在需要的时候,自主决定调用我们定义好的 Java 方法,从而获取外部信息或执行实际操作,大大增强了模型的能力边界。
工具分类
1.信息检索工具
工具从外部如数据库、网络服务、文件系统或网络搜索引擎)检索信息。其目的是增强模型的知识,使其能够回答原本无法回答的问题。
2.采取行动工具
可用于在软件系统中执行操作,例如发送电子邮件、在数据库中创建新记录、提交表单或触发工作流。其目标是将原本需要人工干预或明确编程的任务实现自动化。
信息检索工具
环境配置
项目根目录pom文件
XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.5.7</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.test</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-parent</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>spring-ai-parent</name>
<description>spring-ai-parent</description>
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
<spring-ai.version>1.0.0</spring-ai.version>
<spring-ai-alibaba.version>1.0.0.2</spring-ai-alibaba.version>
</properties>
<packaging>pom</packaging>
<modules>
<module>Tools</module>
</modules>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-bom</artifactId>
<version>${spring-ai.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-alibaba-bom</artifactId>
<version>${spring-ai-alibaba.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>Tools模块pom文件
XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>com.test</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-parent</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<relativePath /> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.test</groupId>
<artifactId>Tools</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>Tools</name>
<description>Tools</description>
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- 百炼-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-alibaba-starter-dashscope</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>application.yml
XML
server:
port: 8087
spring:
application:
name: ChatMemory
ai:
dashscope:
api-key:
yourkey #换成你自己的apikey
chat:
options:
model: qwen-plusAiConfig配置类
java
package com.test.tools.config;
import com.test.tools.tools.DateTimeTools;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.ai.chat.client.ChatClient;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class AiConfig {
@Resource
private DateTimeTools dateTimeTools;
@Bean
public ChatClient chatClient(ChatClient.Builder builder) {
return builder
.defaultTools(dateTimeTools)
.build();
}
}controller
java
package com.test.tools.controller;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.ai.chat.client.ChatClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class ChatController {
@Resource
private ChatClient chatClient;
@GetMapping("/chat")
public String chat(String question) {
return chatClient.prompt()
.user(question)
.call()
.content();
}
}定义获取用户所在时区的当前日期和时间的工具
java
package com.test.tools.tools;
import org.springframework.ai.tool.annotation.Tool;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
@Component
@Slf4j
public class DateTimeTools {
/*
* @Tool(name="工具名,未提供则使用方法名,类中唯一及特定聊天的工具库中唯一")
* @Tool(description="工具描述,未提供则使用方法名,强烈建议提供详细的描述")
*/
@Tool(name = "current_datetime",description = "获取用户所在时区的当前日期和时间")
public String getCurrentDatetime() {
log.info("获取用户所在时区的当前日期和时间");
return LocalDateTime.now().toString();
}
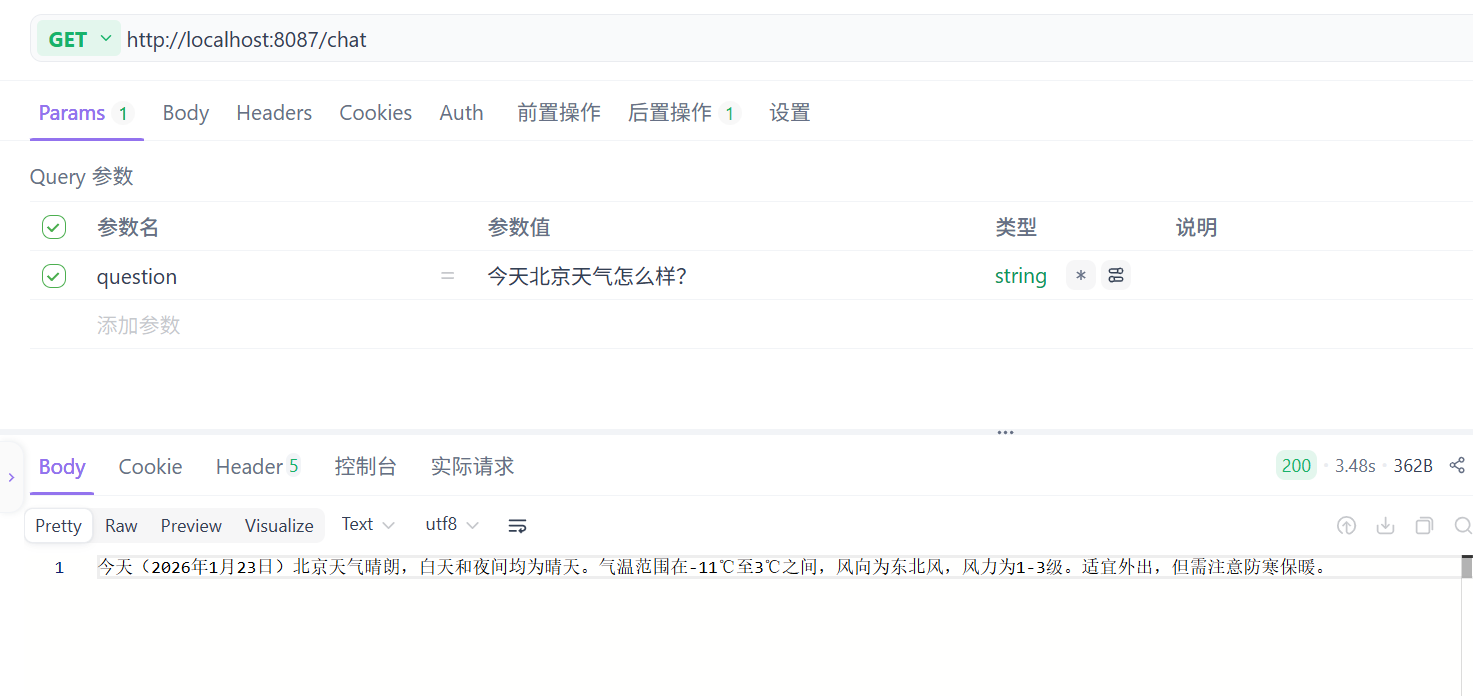
}查看效果
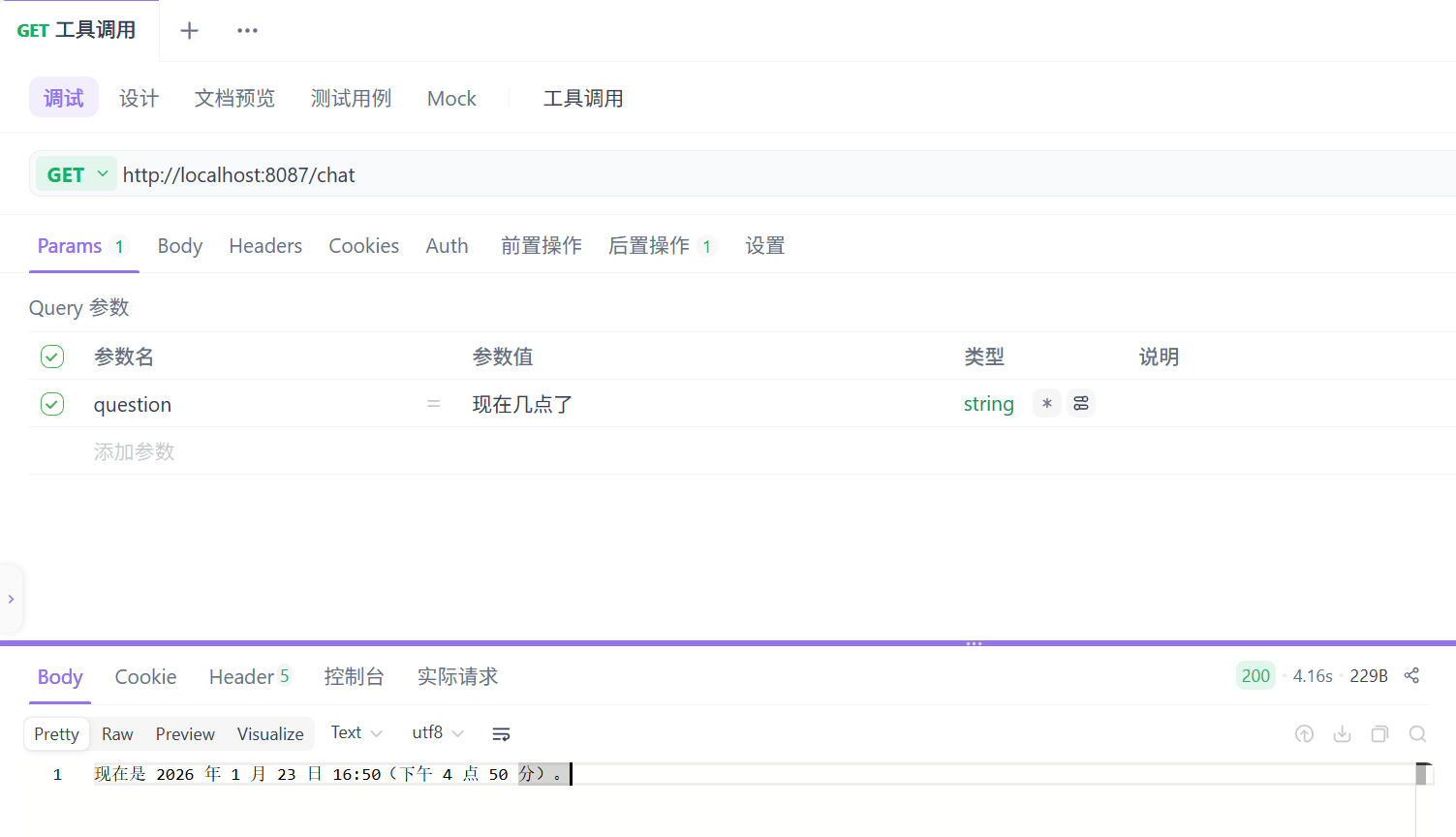
注释掉AiConfig类中.defaultTools(dateTimeTools)这行代码,观察结果
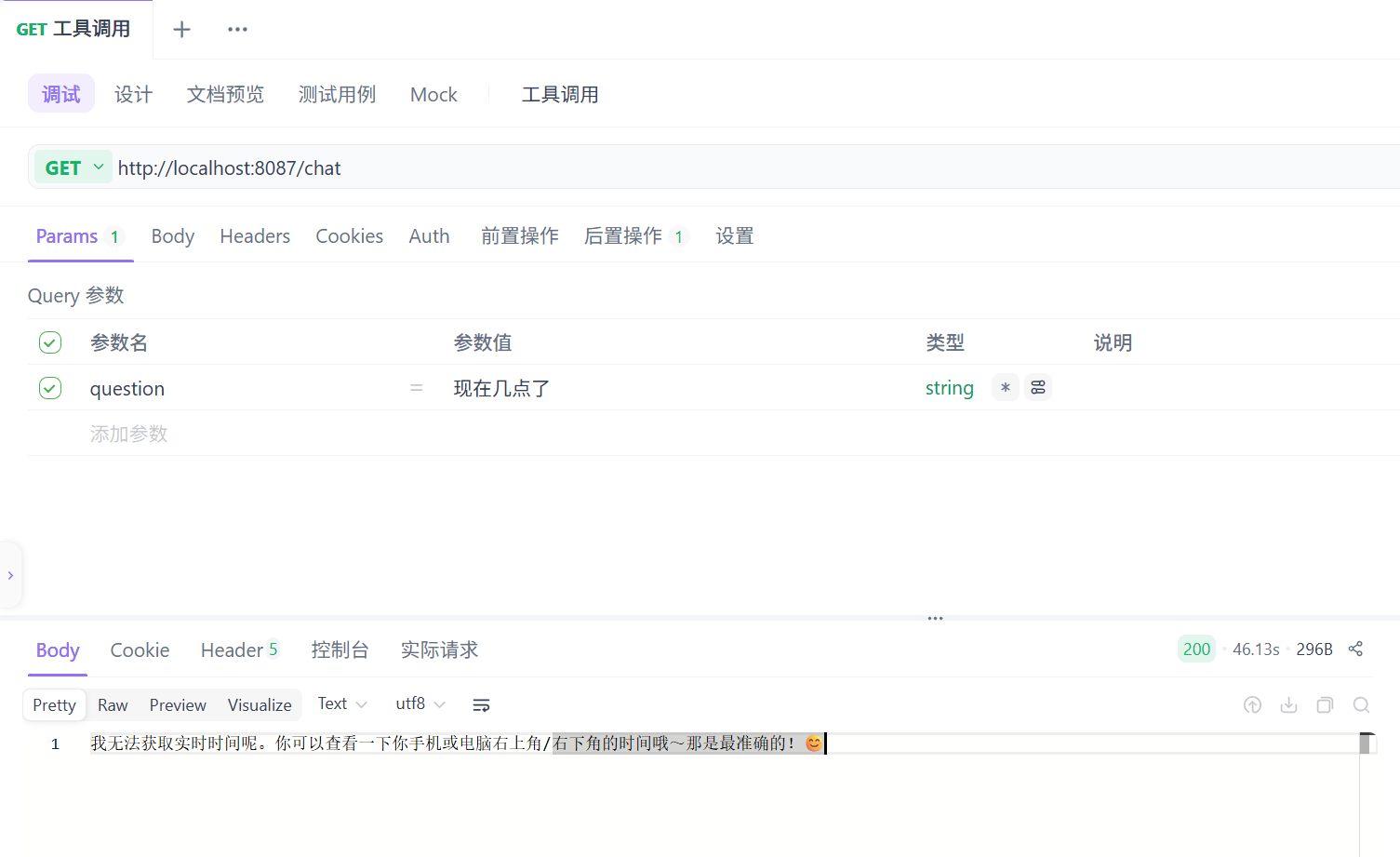
采取行动工具
定义设置闹钟的工具
在DateTimeTools类中添加下面的方法
java
/**
* 设置闹钟
*/
@Tool(description = "为用户设置闹钟,时间以ISO-8601格式提供")
public void setAlarm(String time) {
// 创建一个LocalDateTime对象,并设置时间为用户提供的时间
LocalDateTime alarmTime = LocalDateTime.parse(time, DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE_TIME);
// 异常处理
if (alarmTime.isBefore(LocalDateTime.now())) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("时间不能早于当前时间");
}
log.info("已设置闹钟,时间为:{}", alarmTime);
}查看结果
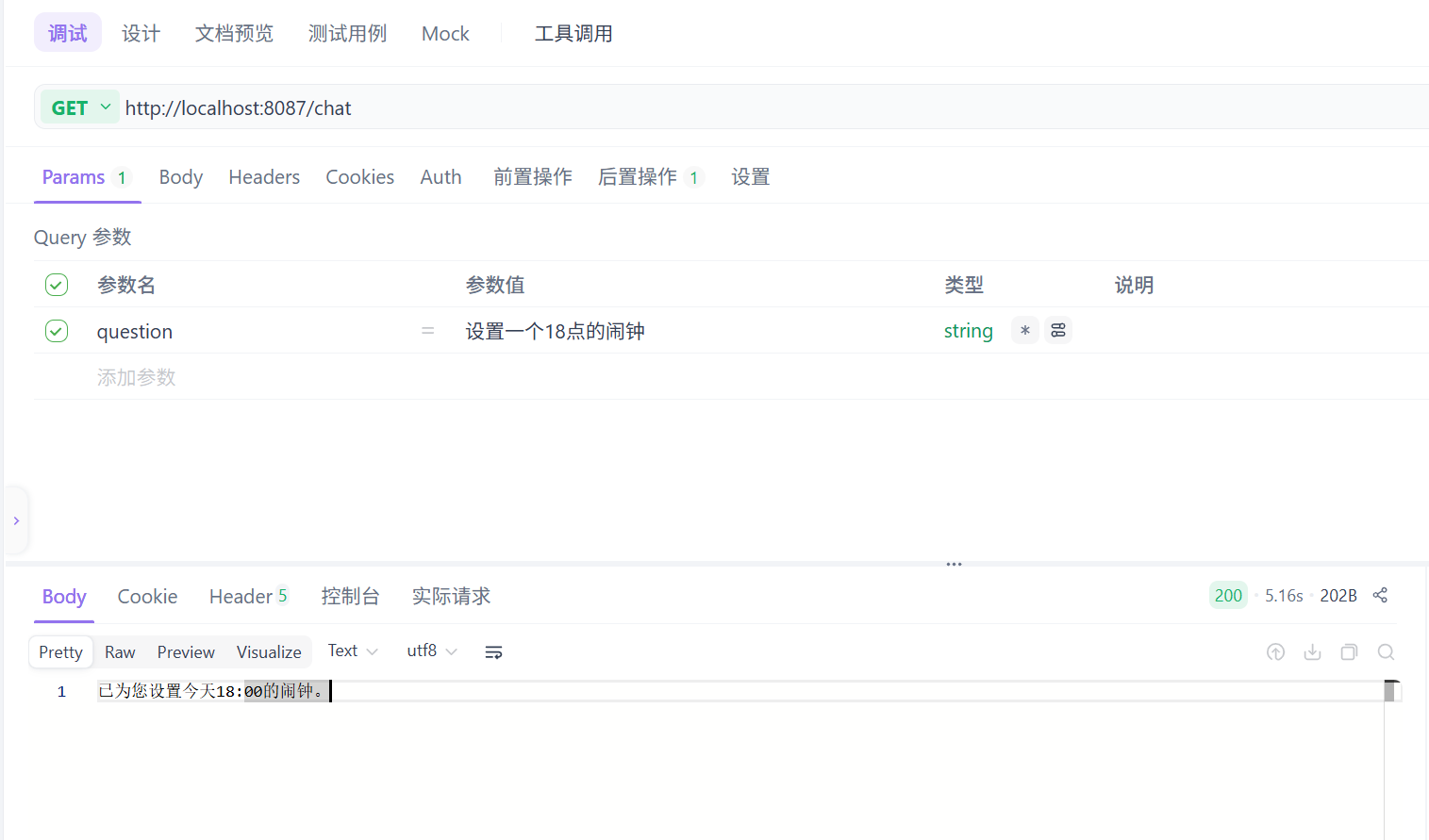
回到控制台查看日志
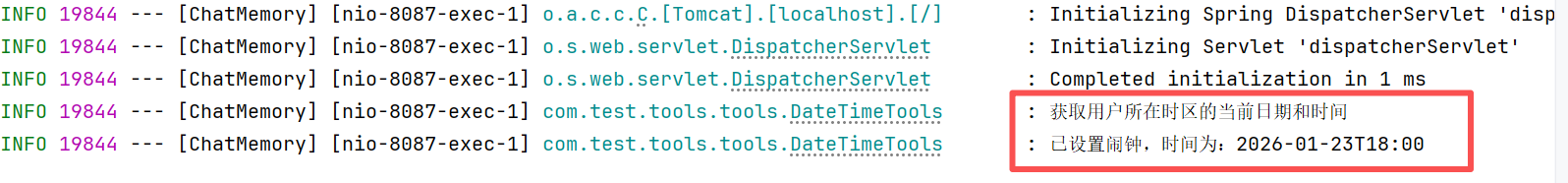
从日志可以看出,模型具备了调用工具的自动编排能力
实战:获取实时天气数据
1.去高德开放平台获取
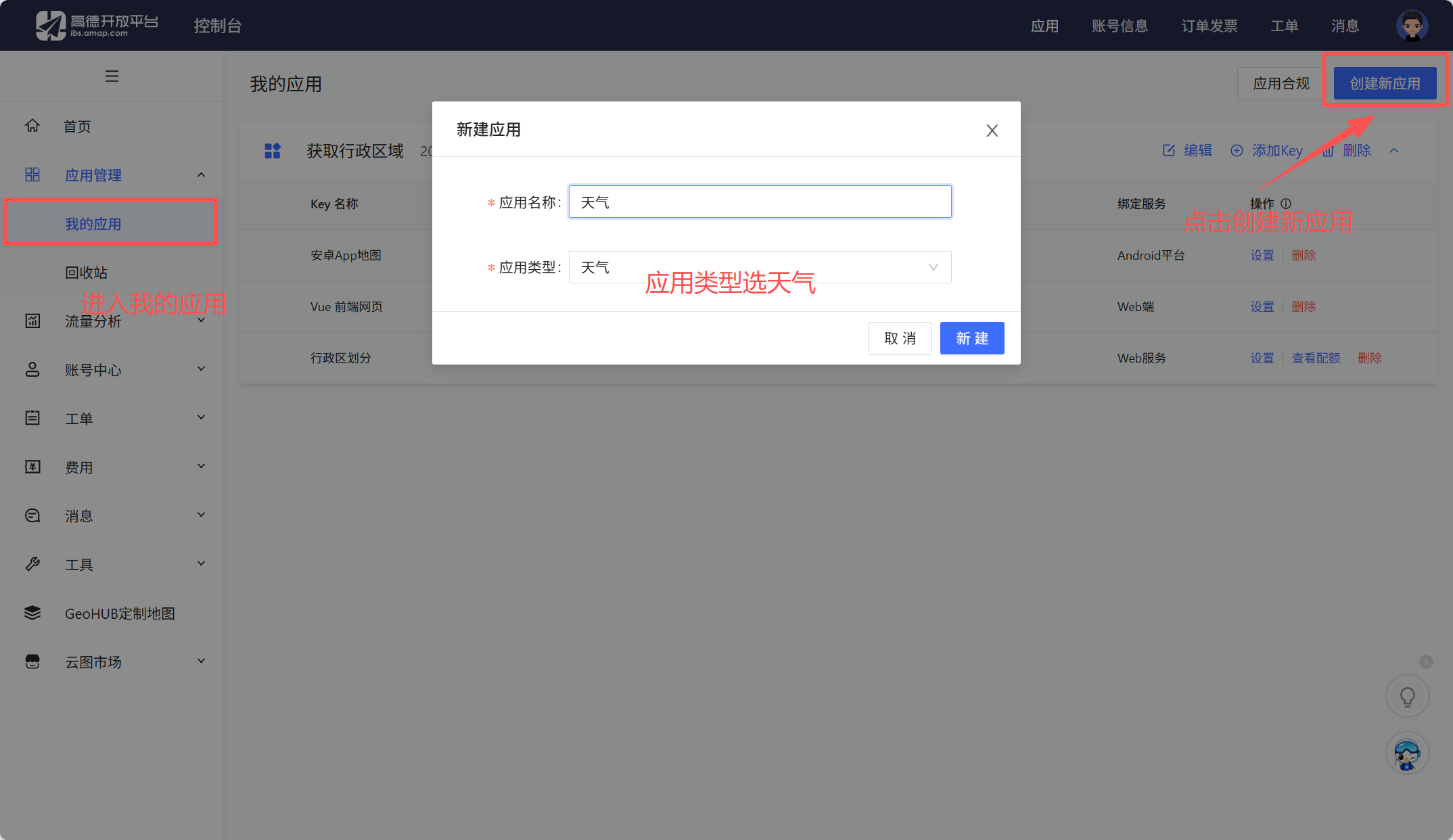
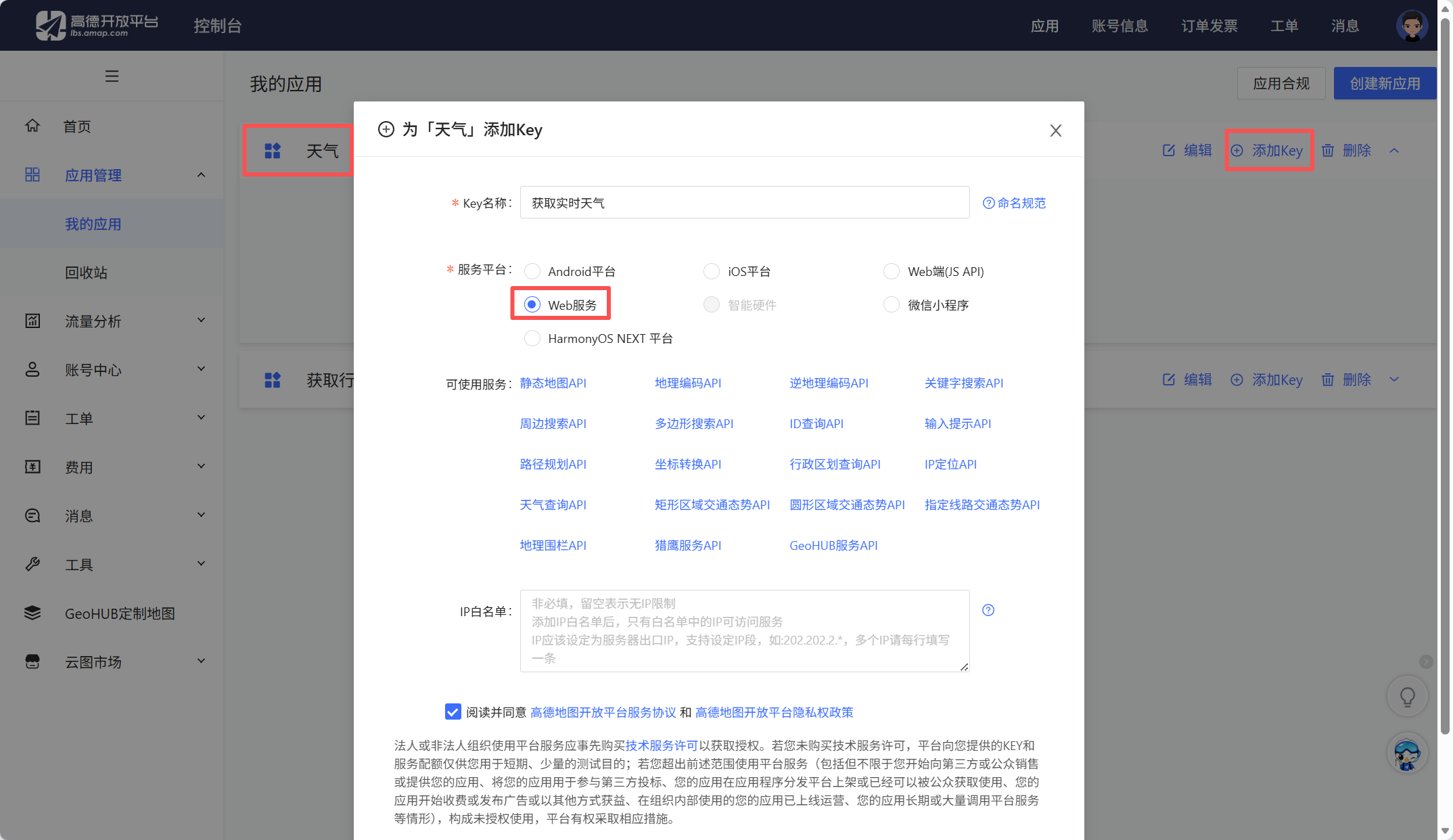
找到刚刚创建的应用,点击添加key
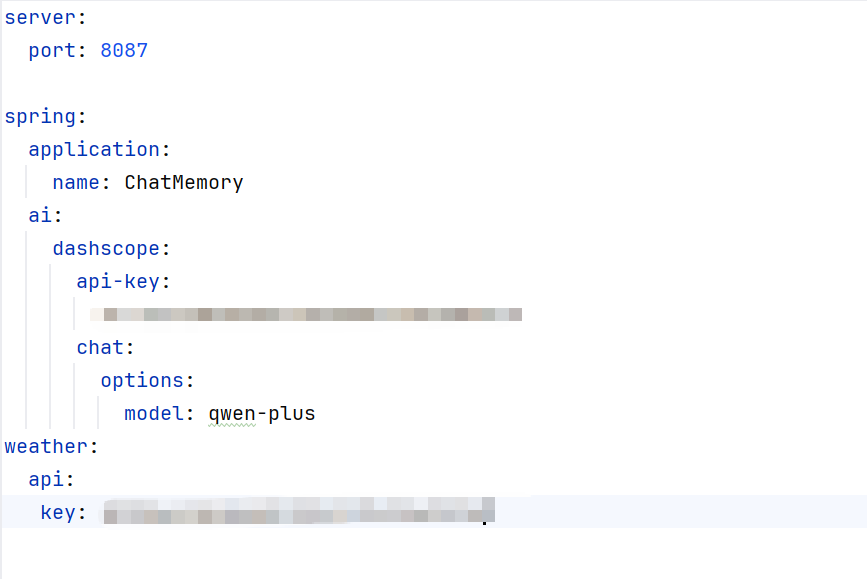
2.在application.yml中配置高德key
3.定义获取实时天气的工具
java
package com.test.tools.tools;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.springframework.ai.tool.annotation.Tool;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestClient;
import java.util.Map;
@Component
public class WeatherTools {
@Value("${weather.api.key}")
private String apiKey;
@Tool(description = "获取指定地区的天气数据")
public String getCurrentWeather(String city) {
// 1.基础服务地址
String baseUrl = "https://restapi.amap.com";
// 2.基于baseUrl构建一个RestClient实例
RestClient client = RestClient.builder().baseUrl(baseUrl).build();
// 3.发起HTTP GET请求,并用Map 存储响应数据
String uri = "/v3/weather/weatherInfo?city={0}&key={1}&extensions=all";
Map<?, ?> result = client.get().uri(uri, city, apiKey)
// 执行HTTP 请求并获取响应数据
.retrieve()
// 将响应的 JSON 解析为 Map
.body(Map.class);
// 4.Jackson 库将 Map 转换为 JSON 字符串后返回给AI模型
try {
return new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(result);
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}修改AiConfig类
java
package com.test.tools.config;
import com.test.tools.tools.DateTimeTools;
import com.test.tools.tools.WeatherTools;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.ai.chat.client.ChatClient;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class AiConfig {
@Resource
private DateTimeTools dateTimeTools;
@Resource
private WeatherTools weatherTools;
@Bean
public ChatClient chatClient(ChatClient.Builder builder) {
return builder
.defaultTools(dateTimeTools, weatherTools)
.build();
}
}4.查看结果