前言
这是一个基于Python的Excel自动化工具,能够根据数据模板批量生成个性化的多工作表Excel文件。能让测试人员告别手动复制粘贴!一键将数据批量填充到模板,自动生成上百份标准化报告。
现成工具分享:
通过网盘分享的文件:TestTool_V3.0.exe
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1y2uoE-c0BaZMW5lIl04Amg?pwd=i5pq 提取码: i5pq
工具介绍:
导入模板文件+信息文件,选择输出文件位置,点击"生成测试用例"按钮,自动生成完整的用例表并自动调整列宽。
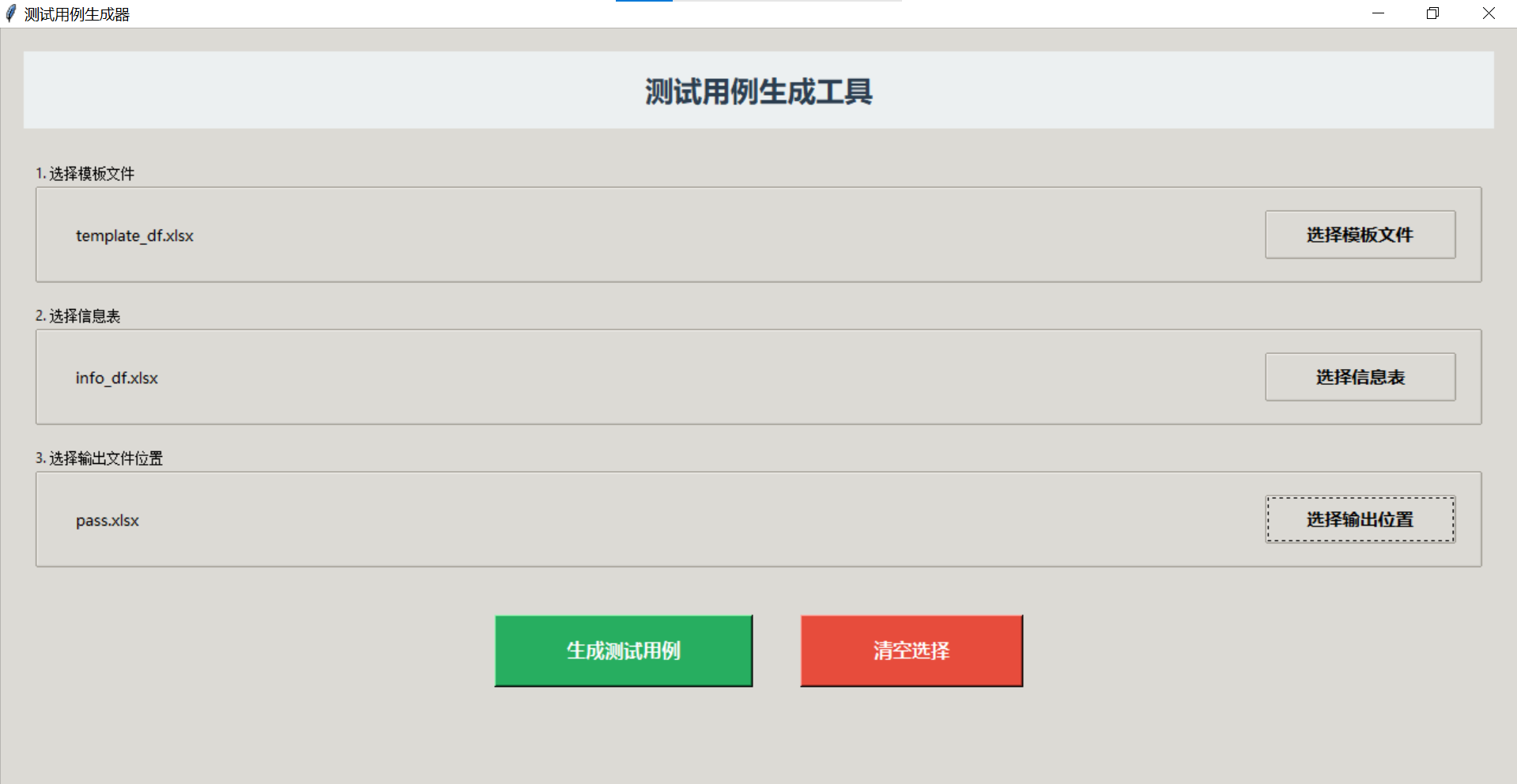
背景
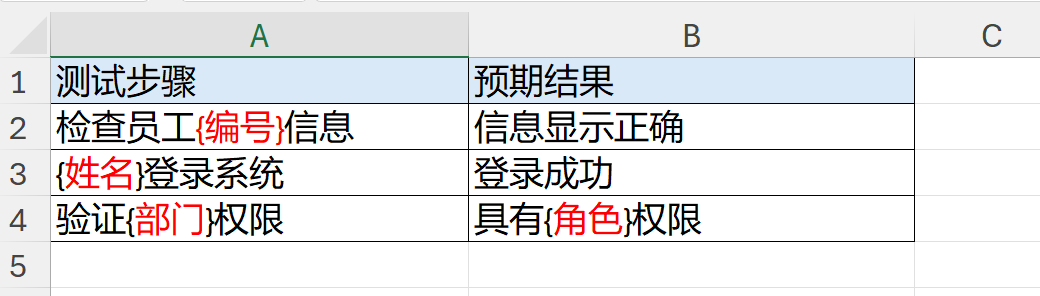
模板表如下:
信息表如下:
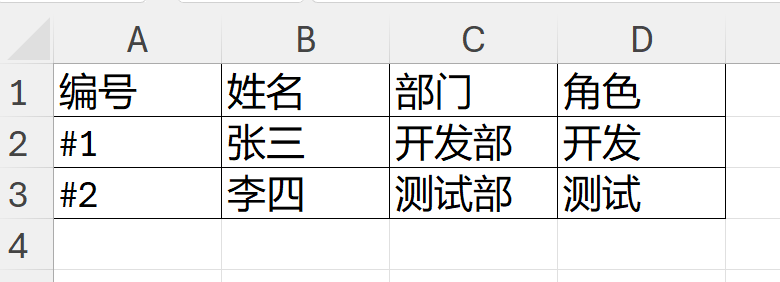
如上:信息表提供了两个人的信息。现在需要在模板表的基础上,分别为2人生成一个sheet,并将模板中{}的内容替换为信息表中对应的数据。
预期效果如下:
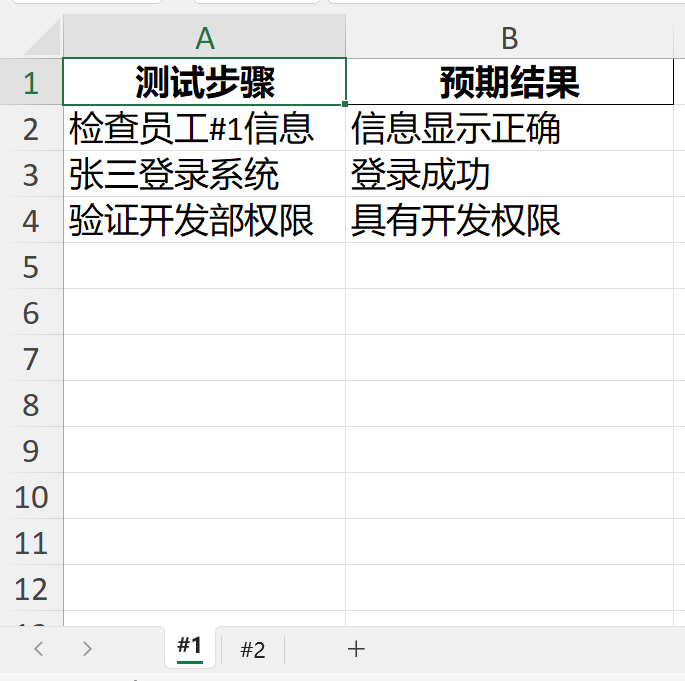
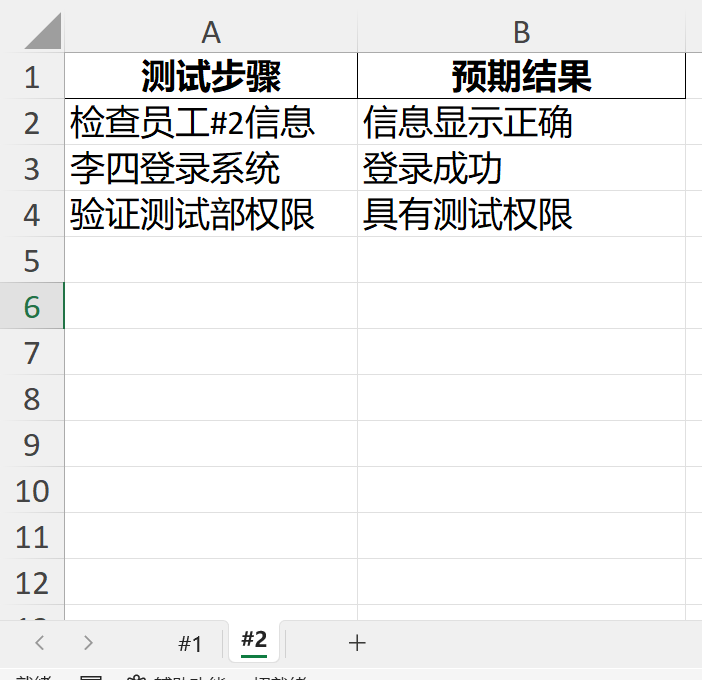
一、clean_sheet_name()
Excel本身有一套针对sheet的命名规则。clean_sheet_name() 函数的作用就是写出命名规则,具体是:
-
预处理:在数据传给 Excel 前,确保名称合规
-
避免错误:防止写入 Excel 时失败
-
保持一致性:确保所有工作表名称都符合规范
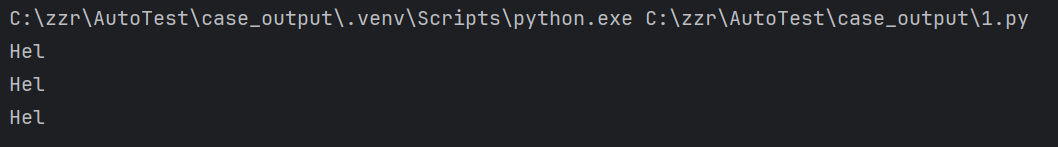
1.1 切片操作
python
name = 'Hello world'
print(name[:3])
print(name[0:3])
print(name[slice(0,3)])结果:
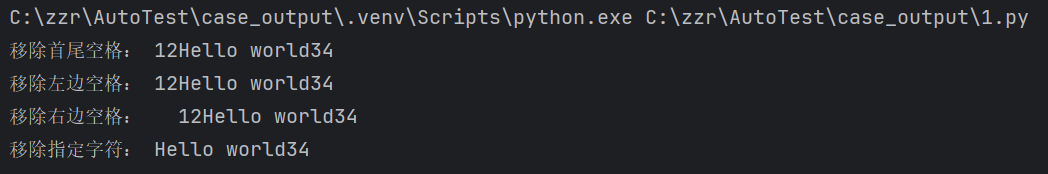
1.2 strip()移除首尾两端的空格
python
name = ' 12Hello world34 '
print(f"移除首尾空格:",name.strip())
print(f"移除左边空格:",name.lstrip())
print(f"移除右边空格:",name.rstrip())
# 先移除首端的空白再移除数字
print(f"移除指定字符:",name.lstrip().strip('12'))结果:
通过strip()检查字符串是否为空:
python
# 确保名称不为空
# 方法1
if not name.strip():
name = "Sheet"
# 方法2
if name.strip() == "":
name = "Sheet"
# 方法3
if len(name.strip()) == 0:
name = "Sheet"(1)not name.strip() 的判断逻辑
在Python中,空字符串 "" 在布尔上下文中被视为 False,非空字符串被视为 True。
所以:
-
name.strip()返回空字符串 →if not ""→True -
name.strip()返回非空字符串 →if not "some_value"→False
(2)Python中可以写 if False,但它没有实际意义,不会执行
python
# 实际上,if 语句会自动进行布尔转换
value = ""
if value: # 这里会自动转换为 if bool(value)
print("非空")
else:
print("空") # 会执行这个
# 所以这些都是等价的:
if not value:
pass
if value == "":
pass
if len(value) == 0:
pass
if bool(value) == False:
pass1.3 clean_sheet_name()修改不合规则的sheet名
pd.isna():专门检测 pandas/Numpy的缺失值(None, np.nan, NaT等)
python
import pandas as pd
def clean_sheet_name(name, max_length=31):
"""
清理sheet名称,确保符合Excel命名规则
参数:
name: 原始sheet名称
max_length: 最大长度限制(Excel限制为31个字符)
"""
if pd.isna(name):
name = "Sheet"
else:
name = str(name)
# 移除非法字符
illegal_chars = [':', '\\', '/', '?', '*', '[', ']']
for char in illegal_chars:
name = name.replace(char, '')
# 截断到最大长度
if len(name) > max_length:
name = name[:max_length]
# 确保名称不为空
if not name.strip():
name = "Sheet"
return name
# 测试各种情况
test_cases = [
None, # 空值
"销售数据:2024年/第一季度", # 包含非法字符
"这是一个非常非常非常长的Excel工作表名称超过了31个字符llll", # 超长
" ", # 只有空白
"正常名称", # 正常情况
]
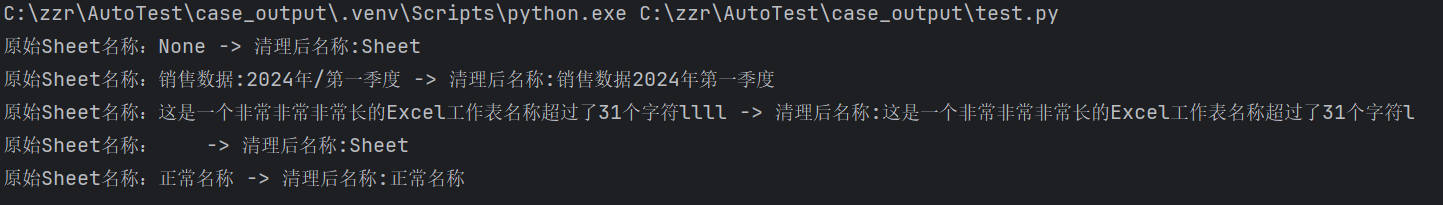
for test in test_cases:
print(f"原始Sheet名称:{test} -> 清理后名称:{clean_sheet_name(test)}")结果:
二、Pandas内置方法
2.1 iterrows()
iterrows() 返回一个迭代器,每次迭代返回一个元组,包含两个值:
-
第一个值:行索引(从0开始的整数)
-
第二个值:该行的数据(pandas Series对象)
python
import pandas as pd
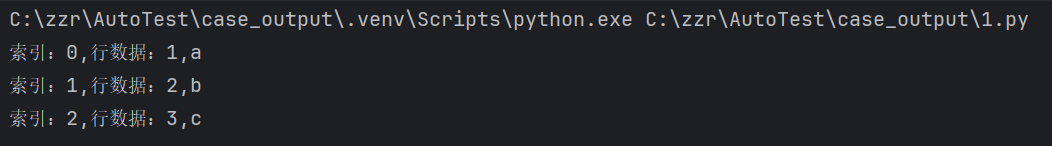
df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 2, 3], 'B': ['a', 'b', 'c']})
for idx,row in df.iterrows():
print(f"索引:{idx},行数据:{row['A']},{row['B']}")结果:
1、可以只接收行数据,不要索引吗?
可以,但需要用下划线 _ 表示不关心的变量:
python
for _,row in df.iterrows():
print(f"行数据:{row['A']},{row['B']}")2.2 read_excel()
read_excel() 是 pandas 的一个内置函数, 是一个顶级函数。
# 读取Excel文件
df = pd.read_excel('文件.xlsx', sheet_name='Sheet1')2.3 .loc()
test_case_df.loc[idx, col] 的作用是:
-
精确定位 :通过行标签
idx和列标签col找到DataFrame中的特定单元格 -
支持CRUD:可用于读取、修改、创建数据
-
标签导向:使用有意义的标签而非容易变化的位置索引
python
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [1, 2, 3],
'B': [4, 5, 6],
'C': [7, 8, 9]
}, index=['row1', 'row2', 'row3'])
# 使用.loc - 基于标签
print(df.loc['row2', 'B']) # 输出: 5
# 使用.iloc - 基于位置(整数索引)
print(df.iloc[1, 1]) # 输出: 5 (第2行第2列)loc()会选择DataFrame中特定行和列的单个值(也就是单元格的值), 这是Pandas中最常用、最推荐的数据选择方法之一。
2.4 columns返回列名
python
import pandas as pd
# 创建一个DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'姓名': ['张三', '李四', '王五'],
'年龄': [25, 30, 28],
'城市': ['北京', '上海', '广州']
})
# .columns 返回列名
print(df.columns)
# 输出: Index(['姓名', '年龄', '城市'], dtype='object')
print(type(df.columns)) # <class 'pandas.core.indexes.base.Index'>2.5 f-string中花括号的转义规则
python
name = "张三"
age = 25
print(f"{name}") # 张三
print(f"{{name}}") # {name}
print(f"{{{name}}}") # {张三}
print(f"{{{{{name}}}}}") # {{张三}}三、主函数
3.1 with pd.ExcelWriter() as writer
这是上下文管理器的使用方式
python
# 等价写法(不推荐,因为需要手动关闭)
writer = pd.ExcelWriter(output_file, engine='openpyxl')
try:
# 写入操作
total_rows = len(info_df)
# ...
finally:
writer.save() # 必须手动保存
writer.close() # 必须手动关闭
# 使用 with 语句(推荐)
# 自动处理资源的打开和关闭,即使出错也会正确关闭
with pd.ExcelWriter(...) as writer:
# 写入操作
pass
# 退出 with 块时自动调用 writer.save() 和 writer.close()(1)参数说明:
-
output_file:输出文件的路径字符串 -
engine='openpyxl':指定使用 openpyxl 引擎处理 Excel 文件
(2) 基本用法
writer 指的是什么?
writer 是 pd.ExcelWriter 创建的一个Excel写入器对象,它代表了名为"output.xlsx"的这个Excel文件。
python
import pandas as pd
# 创建示例数据
info_df = pd.DataFrame({
'姓名': ['张三', '李四', '王五'],
'年龄': [25, 30, 35],
'城市': ['北京', '上海', '广州']
})
output_file = r'C:\Users\uexwcl\Downloads\output.xlsx'
with pd.ExcelWriter(output_file,engine='openpyxl') as writer:
total_rows = len(info_df)
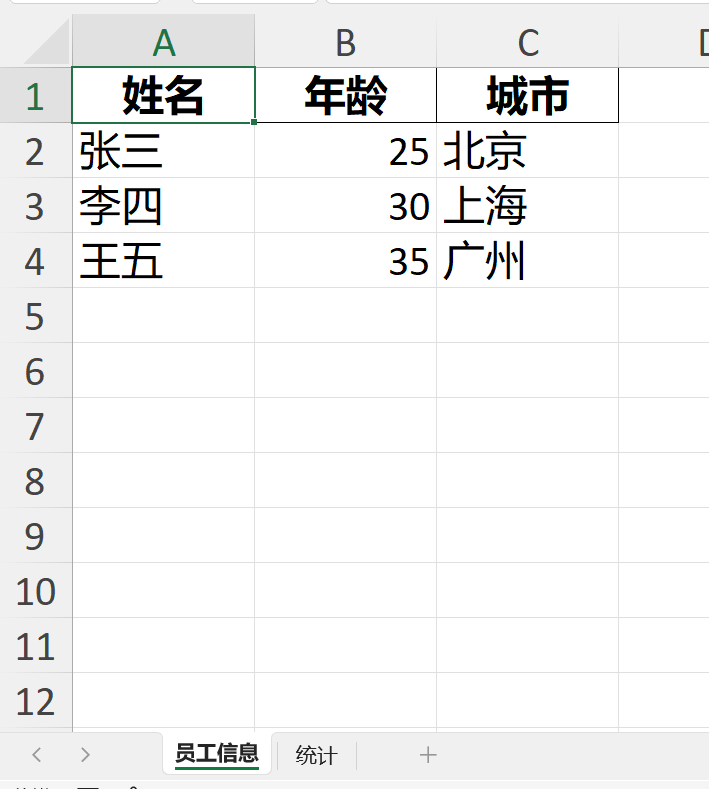
# 1.将DataFrame写入Excel,指定sheet名
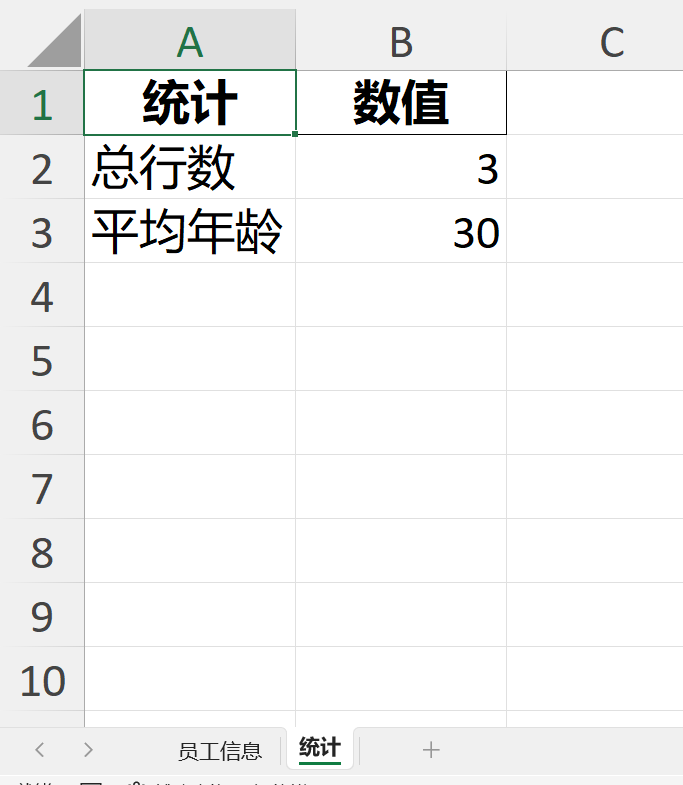
info_df.to_excel(writer, sheet_name='员工信息', index=False)
# 2.写入多个工作表
summary_df = pd.DataFrame({
'统计': ['总行数', '平均年龄'],
'数值': [total_rows, info_df['年龄'].mean()]
})
summary_df.to_excel(writer,sheet_name='统计',index=False)结果:
3.2 替换占位符逻辑(优化)
仍然是4层循环,不过是先提取模板表中每个单元格的占位符,并对占位符进行去重处理,再来和信息表中的列名比对。一致则替换。
算法层通过占位符去重减少计算;数据层使用Pandas向量化操作;内存层采用流式处理和模板复用来控制内存峰值。
python
# 4. 为信息表中的每一行生成一个sheet
for index, row in info_df.iterrows():
# 获取编号(用于sheet名称)
sheet_name = clean_sheet_name(row.get('编号'))
print(f"正在处理第 {index + 1}/{total_rows} 行: {sheet_name}")
# 复制模板
test_case_df = template_df.copy()
# 5. 替换模板中的占位符
for col in test_case_df.columns:
for idx in test_case_df.index:
cell_value = clean_value(test_case_df.loc[idx, col])
# 提取实际存在的占位符-- 非贪婪匹配,匹配 { 和 } 之间的所有内容
placeholders = re.findall(r'\{(.*?)\}', cell_value)
if placeholders: # 只有存在占位符时才处理
for placeholder in set(placeholders): # 去重
if placeholder in info_df.columns:
replacement = clean_value(row.get(placeholder, ""))
cell_value = cell_value.replace(f"{{{placeholder}}}", replacement)
test_case_df.loc[idx, col] = cell_value四、问题记录
1、模板中{}里包含":"、空格,就无法替换成信息表的具体内容
# 提取实际存在的占位符
placeholders = re.findall(r'\{(\w+)\}', cell_value)
python
import re
# 示例1
cell_value = "Hello {name}, your score is {score_2023}"
placeholders = re.findall(r'\{(\w+)\}', cell_value)
# 结果: ['name', 'score_2023']
# 示例2 - 不匹配的情况
cell_value = "No placeholders here"
placeholders = re.findall(r'\{(\w+)\}', cell_value)
# 结果: []使用正则表达式从字符串中提取的占位符特点:
-
只提取花括号
{}内的内容 -
占位符名称只能包含:字母、数字、下划线(
\w的含义) -
区分大小写
-
不支持带空格的占位符名称
-
不支持特殊字符(如
{user-name}不会被匹配)
2、自动调整列宽
python
def auto_adjust_column_width(worksheet, df):
"""
自动调整Excel列的宽度以适应内容
参数:
worksheet: openpyxl的worksheet对象
df: 对应的DataFrame
"""
try:
# 遍历DataFrame的每一列
for column in df:
# 获取列索引(从1开始)
column_letter = openpyxl.utils.get_column_letter(df.columns.get_loc(column) + 1)
# 计算列的最大宽度
# 考虑列名本身的宽度
max_length = max(
len(str(column)), # 列名宽度
df[column].astype(str).map(len).max() # 该列数据最大宽度
)
# 添加一些边距(增加20%的宽度或至少5个字符)
adjusted_width = max_length * 1.2 + 5
# 设置列宽,限制在5到50之间
adjusted_width = max(5, min(adjusted_width, 50))
# 应用列宽
worksheet.column_dimensions[column_letter].width = adjusted_width五、源码
51. CaseOutput.py
python
import pandas as pd
import openpyxl
import warnings
import re # 正则表达式模块,用于提取占位符
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
def clean_sheet_name(name, max_length=31):
"""
清理sheet名称,确保符合Excel命名规则
参数:
name: 原始sheet名称
max_length: 最大长度限制(Excel限制为31个字符)
"""
if pd.isna(name):
name = "Sheet"
else:
name = str(name)
# 移除非法字符
illegal_chars = [':', '\\', '/', '?', '*', '[', ']']
for char in illegal_chars:
name = name.replace(char, '')
# 截断到最大长度
if len(name) > max_length:
name = name[:max_length]
# 确保名称不为空
if not name.strip():
name = "Sheet"
return name
def clean_value(value):
"""
清理单元格值,处理NaN和None
参数:
value: 原始值
返回: 清理后的字符串
"""
if pd.isna(value):
return ""
return str(value)
def auto_adjust_column_width(worksheet, df):
"""
自动调整Excel列的宽度以适应内容
参数:
worksheet: openpyxl的worksheet对象
df: 对应的DataFrame
"""
try:
# 遍历DataFrame的每一列
for column in df:
# 获取列索引(从1开始)
column_letter = openpyxl.utils.get_column_letter(df.columns.get_loc(column) + 1)
# 计算列的最大宽度
# 考虑列名本身的宽度
max_length = max(
len(str(column)), # 列名宽度
df[column].astype(str).map(len).max() # 该列数据最大宽度
)
# 添加一些边距(增加20%的宽度或至少5个字符)
adjusted_width = max_length * 1.2 + 5
# 设置列宽,限制在5到50之间
adjusted_width = max(5, min(adjusted_width, 50))
# 应用列宽
worksheet.column_dimensions[column_letter].width = adjusted_width
except Exception as e:
print(f"自动调整列宽时发生错误: {e}")
# 如果出错,设置默认列宽
for column in df.columns:
column_letter = openpyxl.utils.get_column_letter(df.columns.get_loc(column) + 1)
worksheet.column_dimensions[column_letter].width = 20
def generate_test_cases_from_files(template_file, info_file, output_file):
"""
处理文件生成测试用例
参数:
template_file: 模板文件路径
info_file: 信息表文件路径
output_file: 输出文件路径
返回: 生成的测试用例数量
"""
try:
print("正在读取模板文件...")
# 1. 读取模板文件,保持空单元格为空字符串
template_df = pd.read_excel(
template_file,
dtype=str, # 所有列都读取为字符串类型
keep_default_na=False
)
print("正在读取信息表...")
# 2. 读取信息表,保持空单元格为空字符串
info_df = pd.read_excel(
info_file,
dtype=str,
keep_default_na=False
)
print("正在生成Excel文件...")
# 3. 创建Excel写入对象
with pd.ExcelWriter(output_file, engine='openpyxl') as writer:
total_rows = len(info_df)
# 4. 为信息表中的每一行生成一个sheet
for index, row in info_df.iterrows():
# 获取编号(用于sheet名称)
sheet_name = clean_sheet_name(row.get('编号'))
print(f"正在处理第 {index + 1}/{total_rows} 行: {sheet_name}")
# 复制模板
test_case_df = template_df.copy()
# 5. 替换模板中的占位符
for col in test_case_df.columns:
for idx in test_case_df.index:
cell_value = clean_value(test_case_df.loc[idx, col])
# 提取实际存在的占位符-- 非贪婪匹配,匹配 { 和 } 之间的所有内容
placeholders = re.findall(r'\{(.*?)\}', cell_value)
if placeholders: # 只有存在占位符时才处理
for placeholder in set(placeholders): # 去重
if placeholder in info_df.columns:
replacement = clean_value(row.get(placeholder, ""))
cell_value = cell_value.replace(f"{{{placeholder}}}", replacement)
test_case_df.loc[idx, col] = cell_value
# 6. 将当前指示灯的测试用例保存到sheet
test_case_df.to_excel(
writer,
sheet_name=sheet_name,
index=False
)
# 获取当前sheet的worksheet对象
worksheet = writer.sheets[sheet_name]
# 调用自动调整列宽函数
auto_adjust_column_width(worksheet, test_case_df)
print(f" 已自动调整 {sheet_name} 的列宽")
print(f"Excel文件生成完成,共生成 {total_rows} 个测试用例")
return total_rows
except KeyError as e:
raise Exception(f"Excel文件中缺少必要的列: {e}")
except PermissionError as e:
raise Exception(f"文件访问权限错误,请关闭Excel文件后重试: {e}")
except Exception as e:
raise Exception(f"文件处理错误: {e}")5.2 panel.py
python
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk, filedialog, messagebox
import os
from CaseOutput import generate_test_cases_from_files
class TestCaseGeneratorGUI:
def __init__(self, root):
self.root = root
self.root.title("测试用例生成器")
self.root.geometry("650x350")
# 初始化文件路径
self.template_file = ""
self.info_file = ""
self.output_file = ""
# 设置样式
self.setup_styles()
# 创建界面
self.create_widgets()
def setup_styles(self):
"""设置界面样式"""
style = ttk.Style()
style.theme_use('clam')
# 自定义大按钮样式
style.configure(
'Large.TButton',
font=('Microsoft YaHei', 11, 'bold'),
padding=(10, 8),
anchor='center',
relief='raised',
width=15
)
# 标签样式
style.configure(
'File.TLabel',
font=('Microsoft YaHei', 10),
padding=(5, 2)
)
# 标签框样式
style.configure(
'TLabelframe',
font=('Microsoft YaHei', 11, 'bold'),
padding=10
)
def create_widgets(self):
"""创建界面组件"""
# 主容器
main_container = ttk.Frame(self.root, padding=20)
main_container.pack(fill='both', expand=True)
# 标题
title_label = tk.Label(
main_container,
text="测试用例生成工具",
font=("Microsoft YaHei", 18, "bold"),
fg="#2c3e50",
bg="#ecf0f1",
pady=15
)
title_label.pack(fill='x', pady=(0, 20))
# 创建内容框架
content_frame = ttk.Frame(main_container)
content_frame.pack(fill='both', expand=True)
# 文件选择区域
self.create_file_selection(content_frame)
# 按钮区域
self.create_button_area(content_frame)
def create_file_selection(self, parent):
"""创建文件选择区域"""
# 模板文件选择区域
template_frame = ttk.LabelFrame(parent, text="1. 选择模板文件")
template_frame.pack(fill="x", padx=10, pady=10)
template_inner = ttk.Frame(template_frame)
template_inner.pack(fill='x', padx=5, pady=8)
self.template_label = ttk.Label(
template_inner,
text="未选择文件",
foreground="gray",
style='File.TLabel',
width=50,
anchor='w'
)
self.template_label.pack(side="left", fill='x', expand=True, padx=(10, 5))
template_btn = ttk.Button(
template_inner,
text="选择模板文件",
command=self.select_template_file,
style='Large.TButton'
)
template_btn.pack(side="right", padx=5)
# 信息表文件选择区域
info_frame = ttk.LabelFrame(parent, text="2. 选择信息表")
info_frame.pack(fill="x", padx=10, pady=10)
info_inner = ttk.Frame(info_frame)
info_inner.pack(fill='x', padx=5, pady=8)
self.info_label = ttk.Label(
info_inner,
text="未选择文件",
foreground="gray",
style='File.TLabel',
width=50,
anchor='w'
)
self.info_label.pack(side="left", fill='x', expand=True, padx=(10, 5))
info_btn = ttk.Button(
info_inner,
text="选择信息表",
command=self.select_info_file,
style='Large.TButton'
)
info_btn.pack(side="right", padx=5)
# 输出文件选择区域
output_frame = ttk.LabelFrame(parent, text="3. 选择输出文件位置")
output_frame.pack(fill="x", padx=10, pady=10)
output_inner = ttk.Frame(output_frame)
output_inner.pack(fill='x', padx=5, pady=8)
self.output_label = ttk.Label(
output_inner,
text="未选择位置",
foreground="gray",
style='File.TLabel',
width=50,
anchor='w'
)
self.output_label.pack(side="left", fill='x', expand=True, padx=(10, 5))
output_btn = ttk.Button(
output_inner,
text="选择输出位置",
command=self.select_output_file,
style='Large.TButton'
)
output_btn.pack(side="right", padx=5)
def create_button_area(self, parent):
"""创建按钮区域"""
button_frame = ttk.Frame(parent)
button_frame.pack(pady=30)
# 使用tk.Button获得更多控制
self.generate_btn = tk.Button(
button_frame,
text="生成测试用例",
font=('Microsoft YaHei', 12, 'bold'),
command=self.generate_test_cases,
state="disabled",
bg="#27ae60",
fg="white",
activebackground="#229954",
activeforeground="white",
relief="raised",
bd=2,
padx=30,
pady=12,
cursor="hand2",
width=15
)
self.generate_btn.pack(side="left", padx=20)
self.clear_btn = tk.Button(
button_frame,
text="清空选择",
font=('Microsoft YaHei', 12, 'bold'),
command=self.clear_selection,
bg="#e74c3c",
fg="white",
activebackground="#c0392b",
activeforeground="white",
relief="raised",
bd=2,
padx=30,
pady=12,
cursor="hand2",
width=12
)
self.clear_btn.pack(side="left", padx=20)
def select_template_file(self):
"""选择模板文件"""
file_path = filedialog.askopenfilename(
title="选择模板文件",
filetypes=[("Excel文件", "*.xlsx *.xls"), ("所有文件", "*.*")]
)
if file_path:
self.template_file = file_path
file_name = os.path.basename(file_path)
self.template_label.config(text=file_name, foreground="black")
self.check_generate_button()
def select_info_file(self):
"""选择信息表文件"""
file_path = filedialog.askopenfilename(
title="选择信息表",
filetypes=[("Excel文件", "*.xlsx *.xls"), ("所有文件", "*.*")]
)
if file_path:
self.info_file = file_path
file_name = os.path.basename(file_path)
self.info_label.config(text=file_name, foreground="black")
self.check_generate_button()
def select_output_file(self):
"""选择输出文件位置"""
file_path = filedialog.asksaveasfilename(
title="保存测试用例文件",
defaultextension=".xlsx",
filetypes=[("Excel文件", "*.xlsx"), ("所有文件", "*.*")]
)
if file_path:
self.output_file = file_path
file_name = os.path.basename(file_path)
self.output_label.config(text=file_name, foreground="black")
self.check_generate_button()
def check_generate_button(self):
"""检查是否启用生成按钮"""
if self.template_file and self.info_file and self.output_file:
self.generate_btn.config(state="normal", bg="#27ae60")
else:
self.generate_btn.config(state="disabled", bg="#95a5a6")
def clear_selection(self):
"""清空所有选择"""
self.template_file = ""
self.info_file = ""
self.output_file = ""
self.template_label.config(text="未选择文件", foreground="gray")
self.info_label.config(text="未选择文件", foreground="gray")
self.output_label.config(text="未选择位置", foreground="gray")
self.generate_btn.config(state="disabled", bg="#95a5a6")
def generate_test_cases(self):
"""生成测试用例"""
try:
# 检查文件是否存在
if not os.path.exists(self.template_file):
messagebox.showerror("错误", f"模板文件不存在: {self.template_file}")
return
if not os.path.exists(self.info_file):
messagebox.showerror("错误", f"信息表文件不存在: {self.info_file}")
return
# 调用生成函数
result = generate_test_cases_from_files(
self.template_file,
self.info_file,
self.output_file
)
if result:
messagebox.showinfo(
"生成成功",
f"测试用例生成成功!\n\n"
f"保存位置: {self.output_file}\n"
f"共生成 {result} 个测试用例"
)
else:
messagebox.showerror("错误", "生成失败,请检查文件格式")
except Exception as e:
messagebox.showerror("错误", f"生成过程中发生错误:\n{str(e)}")
def main():
root = tk.Tk()
# 设置窗口居中
window_width = 650
window_height = 400
screen_width = root.winfo_screenwidth()
screen_height = root.winfo_screenheight()
x = (screen_width - window_width) // 2
y = (screen_height - window_height) // 2
root.geometry(f"{window_width}x{window_height}+{x}+{y}")
# 创建应用
app = TestCaseGeneratorGUI(root)
# 运行主循环
root.mainloop()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()六、打包方法
1. 安装 PyInstaller
python
pip install pyinstaller2. 创建打包脚本
在项目根目录创建 build_exe.py:
python
# build_exe.py - 打包脚本
import PyInstaller.__main__
import os
import shutil
import sys
def build_executable():
"""构建可执行文件"""
# 主程序入口文件
main_script = "panel.py" # 假设您的主程序是 panel.py
# PyInstaller 配置参数
args = [
main_script, # 主脚本
'--name=TestCaseGenerator', # 程序名称
'--onefile', # 打包成单个exe文件
'--windowed', # 如果是GUI程序(控制台程序去掉这个)
'--icon=icon.ico', # 图标文件(可选)
'--add-data=templates;templates', # 包含模板文件夹
'--add-data=*.xlsx;.', # 包含Excel文件
'--hidden-import=pandas',
'--hidden-import=openpyxl',
'--hidden-import=numpy',
'--clean', # 清理临时文件
]
# 运行打包
PyInstaller.__main__.run(args)
print("打包完成!可执行文件在 dist/TestCaseGenerator.exe")
if __name__ == "__main__":
build_executable()3. 简单打包命令
python
# 1. 将panel.py修改为可执行入口(如果需要)
# 2. 执行打包命令
pyinstaller --onefile --name=TestTool panel.py- 打包效果