线程(Thread):
是操作系统能够进行运算调度的最小单位。它被包含在进程中,是进程中的实际运作单位。一个进程中可以并发多个线程,每条线程并行执行不同的任务。
进程(Process):
是资源分配的基本单位。所有与该进程有关的资源,都被记录在进程控制块PCB(Process Control Block)中。以表示该进程拥有这些资源或正在使用它们。
Java中线程与进程
-
进程管资源,线程管执行
-
Java是支持多线程运行的编程语言, JVM是支持多线程运行的平台
-
程序在启动之后,我们通常会说某某Java进程,或者某某JVM进程
-
操作系统主要负责将所有的线程调度到可用的CPU上
-
在Hotspot的JVM中,每个线程与操作系统本地线程直接映射的;两者的生命周期也严格保持一致。
Jvm线程及分类
主线程:是产生其他子线程的线程
子线程:被Thread包含的"方法体"或者"委托"均为子线程
用户线程:平时使用到的线程均为用户线程
守护线程:用来服务用户线程的线程,例如垃圾回收线程。
线程的核心方法:
start(): 启动线程,不能被重复调用
run(): 运行线程,可以被重复调用
yield(): 线程让步,线程从RUNNING(运行)状态变成RUNNABLE(就绪)状态
sleep(): 线程休眠,会释放掉CPU资源给其他线程,但锁是不会释放的,线程会由RUNNING状态进入到TIMED_WAITING状态
join(): 方法是进行线程同步的,暂停当前线程,等待子线程的执行,也称之为线程合并
interrupt(): 由对象调用,该对象的线程会进行线程中断(只有RUNNING状态下的线程才能中断[isinterrupt=true], 否则发生中断异常)
setDaemon(): 指定是否为守护线程
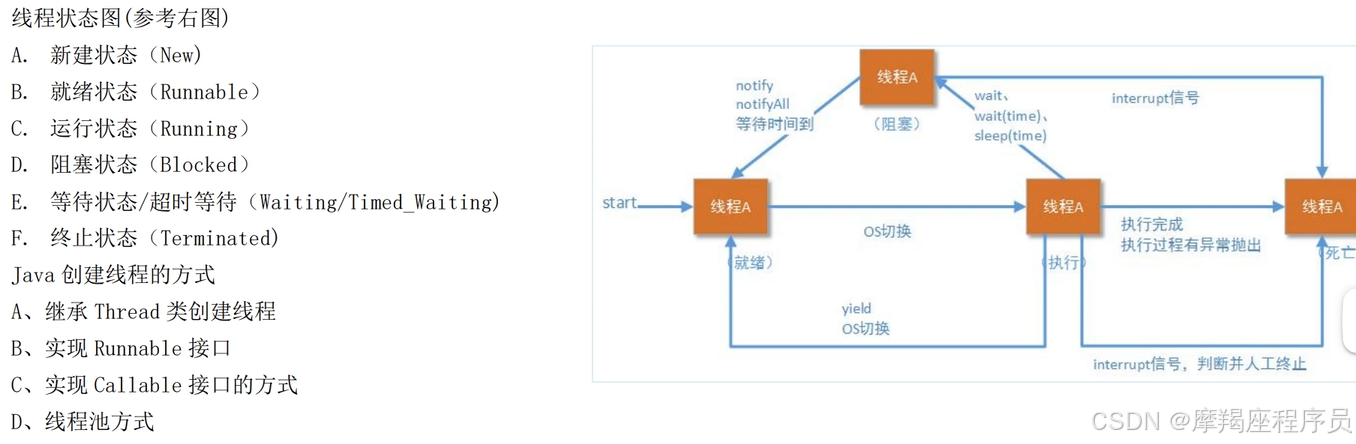
JAVA 创建线程的方式
A. 继承Thread类创建线程
java
package com.coding.threads;
public class CreateThread01 extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
try{
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch (Exception e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println(this.getName() + " thread is running");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
CreateThread01 t1 = new CreateThread01();
t1.setName("test线程-01");
t1.start();
}
}B. 实现Runnable接口
java
package com.coding.threads;
public class CreateThread02 implements Runnable{
private String name;
public void setName(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public String getName(){
return this.name;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
try{
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch (Exception e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println(this.getName() + " thread is running");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
CreateThread02 t1 = new CreateThread02();
t1.setName("test测试02");
Thread thread = new Thread(t1);
thread.start();
}
}C. 实现Callable接口的方式
java
package com.coding.threads;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
public class CreateThread03 implements Callable<Object> {
private String name;
public void setName(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public String getName(){
return name;
}
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
while(true){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch (Exception e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println(this.getName() + " thread is running");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
CreateThread03 t1 = new CreateThread03();
t1.setName("test线程-03");
FutureTask<Object> task = new FutureTask<>(t1);
Thread t = new Thread(task);
t.start();
}
}