- 一句话概括:就是从简单分布建模复杂的分布;

- 这里我就用简单的例子去做一组简单的实验:用高斯分布建模出一个多项式混合分布;
- 代码
python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.stats import multivariate_normal
from tqdm import tqdm
# 设备配置
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
# ====================== 1. 定义目标多项式混合分布(固定参数) ======================
class GaussianMixture:
def __init__(self):
# 固定3个高斯分量的混合分布
self.weights = np.array([0.3, 0.5, 0.2]) # 权重和为1
self.means = np.array([[-2.0, -1.0], [1.0, 3.0], [4.0, -2.0]]) # 各分量均值
self.covs = np.array([
[[0.5, 0.1], [0.1, 0.4]], # 分量1协方差
[[0.6, -0.2], [-0.2, 0.5]], # 分量2协方差
[[0.4, 0.0], [0.0, 0.6]] # 分量3协方差
])
def sample(self, n_samples):
"""采样目标混合分布样本"""
# 选择每个样本所属的分量
component_indices = np.random.choice(3, size=n_samples, p=self.weights)
samples = []
for i in component_indices:
sample = np.random.multivariate_normal(self.means[i], self.covs[i])
samples.append(sample)
return np.array(samples)
def pdf(self, x):
"""计算混合分布的概率密度"""
pdf_vals = 0.0
for w, mu, cov in zip(self.weights, self.means, self.covs):
pdf_vals += w * multivariate_normal.pdf(x, mean=mu, cov=cov)
return pdf_vals
# ====================== 2. Flow Match 向量场预测网络 ======================
class FlowMatchNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim=2, hidden_dim=128):
super().__init__()
self.net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(input_dim + 1, hidden_dim), # 输入:x(2维) + t(1维)
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(hidden_dim, hidden_dim),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(hidden_dim, hidden_dim),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(hidden_dim, input_dim) # 输出:向量场(2维)
)
def forward(self, x, t):
"""
输入:
x: [batch_size, input_dim] 样本
t: [batch_size, 1] 时间步(0~1)
输出:
v: [batch_size, input_dim] 预测的向量场
"""
x_t = torch.cat([x, t], dim=-1)
return self.net(x_t)
# ====================== 3. Flow Match 训练函数 ======================
def train_flow_match(
net,
target_dist,
epochs=10000,
batch_size=256,
lr=1e-4,
device=device
):
optimizer = optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=lr)
loss_fn = nn.MSELoss()
net.train()
pbar = tqdm(range(epochs), desc="Training Flow Match")
for epoch in pbar:
# 1. 采样时间t (0~1)
t = torch.rand(batch_size, 1, device=device)
# 2. 采样源分布样本x0 ~ N(0, I)
x0 = torch.randn(batch_size, 2, device=device)
# 3. 采样目标分布样本x1 ~ 混合分布
x1 = torch.tensor(target_dist.sample(batch_size), dtype=torch.float32, device=device)
# 4. 计算中间状态xt = (1-t)*x0 + t*x1 (Flow Match的核心插值)
xt = (1 - t) * x0 + t * x1
# 5. 计算目标流场:v_t^*(x_t) = x1 - x0 (条件流场)
target_v = x1 - x0
# 6. 模型预测流场
pred_v = net(xt, t)
# 7. 计算损失(匹配预测流场和目标流场)
loss = loss_fn(pred_v, target_v)
# 8. 反向传播
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# 打印进度
if (epoch + 1) % 1000 == 0:
pbar.set_postfix({"Loss": f"{loss.item():.6f}"})
return net
# ====================== 4. 推理采样函数(欧拉法) ======================
def sample_flow_match(
net,
n_samples=10000,
num_steps=100, # 欧拉法步数
device=device
):
"""
从源分布出发,沿着学习到的向量场流动到目标分布
"""
net.eval()
# 1. 采样源分布样本
x = torch.randn(n_samples, 2, device=device)
dt = 1.0 / num_steps # 时间步长
with torch.no_grad():
for step in range(num_steps):
t = torch.ones(n_samples, 1, device=device) * (step / num_steps)
# 欧拉法更新:x_{t+dt} = x_t + dt * v_t(x_t)
v = net(x, t)
x = x + dt * v
return x.cpu().numpy()
# ====================== 5. 绘图函数 ======================
def plot_distributions(target_dist, generated_samples):
"""绘制目标分布、生成样本的对比图"""
# 生成网格用于绘制概率密度等高线
x = np.linspace(-6, 8, 100)
y = np.linspace(-5, 6, 100)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
pos = np.dstack((X, Y))
# 计算目标分布的概率密度
Z = target_dist.pdf(pos)
# 创建子图
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12, 5))
# 子图1:目标混合分布
ax1.contourf(X, Y, Z, cmap="Blues", alpha=0.8)
ax1.set_title("Target Gaussian Mixture Distribution", fontsize=12)
ax1.set_xlabel("x1")
ax1.set_ylabel("x2")
ax1.set_xlim(-6, 8)
ax1.set_ylim(-5, 6)
# 子图2:Flow Match生成的样本
ax2.scatter(generated_samples[:, 0], generated_samples[:, 1], s=1, alpha=0.6, c="orange")
ax2.set_title("Generated Samples (Flow Match)", fontsize=12)
ax2.set_xlabel("x1")
ax2.set_ylabel("x2")
ax2.set_xlim(-6, 8)
ax2.set_ylim(-5, 6)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig("flow_match_distribution.png", dpi=300)
plt.show()
# ====================== 主程序 ======================
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 1. 初始化目标分布
target_dist = GaussianMixture()
# 2. 初始化Flow Match网络
net = FlowMatchNet(input_dim=2, hidden_dim=128).to(device)
# 3. 训练模型
trained_net = train_flow_match(
net=net,
target_dist=target_dist,
epochs=10000,
batch_size=256,
lr=1e-4,
device=device
)
# 4. 推理采样
generated_samples = sample_flow_match(
net=trained_net,
n_samples=10000,
num_steps=100,
device=device
)
# 5. 绘制对比图
plot_distributions(target_dist, generated_samples)
# 保存模型
torch.save(trained_net.state_dict(), "flow_match_model.pth")
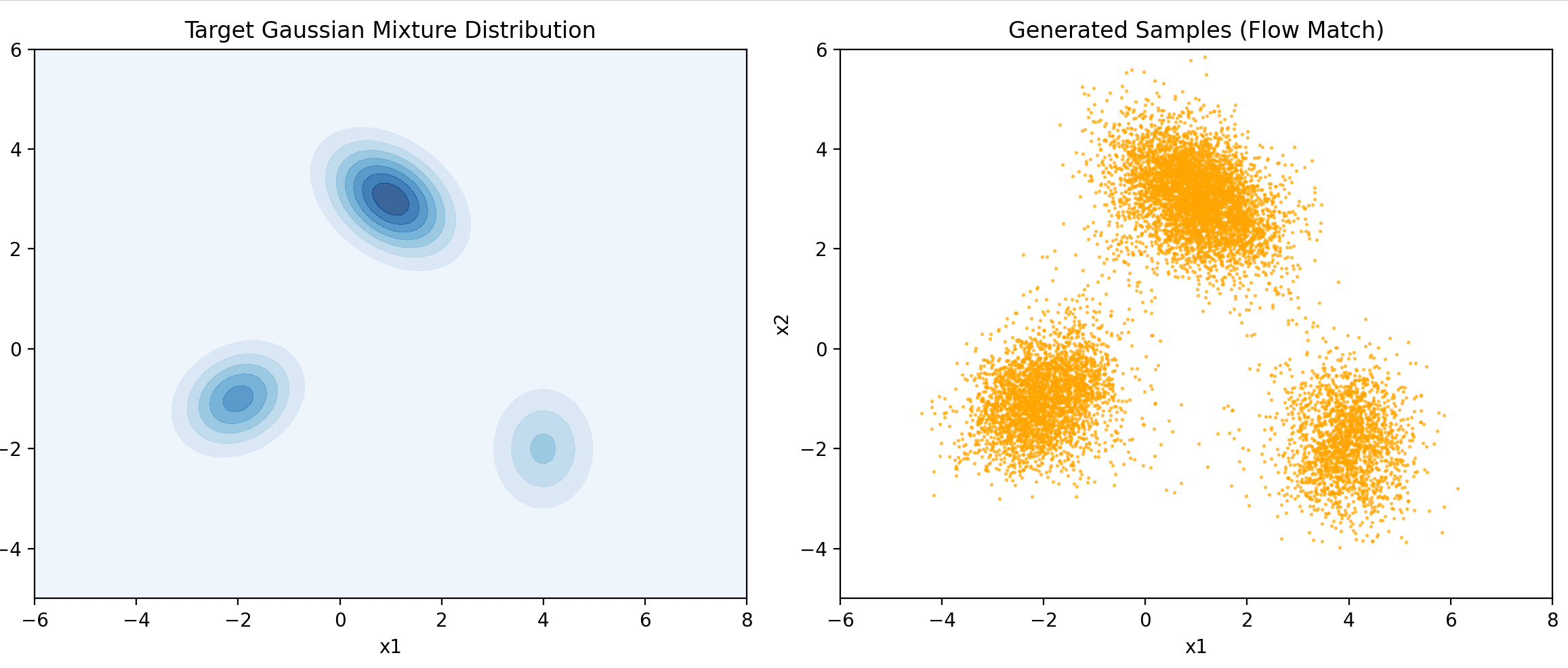
print("模型已保存为 flow_match_model.pth")最后结果图:
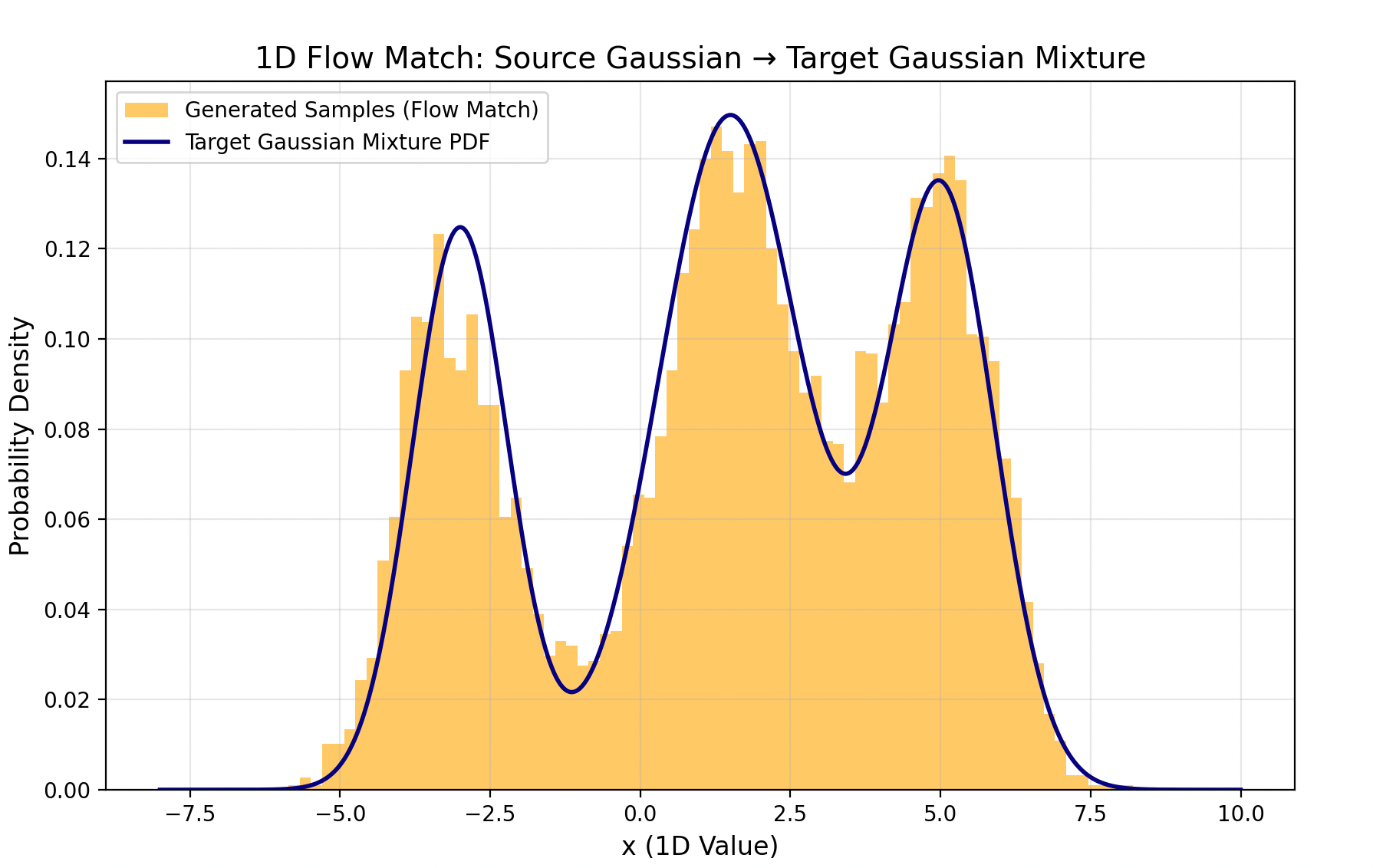
-
-
其他结果图(从高斯建立多个高斯):
-