车辆横向控制的目标是使车辆能够稳定、精准地跟踪预设的参考轨迹。纯追踪(Pure Pursuit)算法 是一种基于几何追踪的经典控制算法,其核心思想是模仿人类驾驶员的行为:眼睛注视前方道路上的一个点,然后调整方向盘使车辆落在这个点上。
1. 纯追踪算法的几何原理
Pure Pursuit 的核心是将车辆的后轴中心作为当前位置,并在参考路径上选择一个"预瞄点"(Look-ahead point)。算法的任务是计算一个圆弧半径,使得车辆从当前位置出发,通过该圆弧刚好经过预瞄点。
数学推导过程
我们假设车辆采用经典的单轨模型(Bicycle Model):

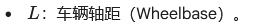



根据三角形的正弦定理或几何比例,我们可以得出以下关系:
-
在车辆坐标系中,预瞄点的纵向距离 x 为
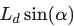 。
。 -
根据几何圆弧特性,半径 R 与这些参数的关系为:
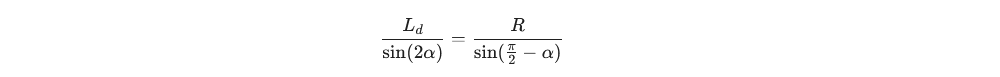
依据的几何公式如下(大角对大边):
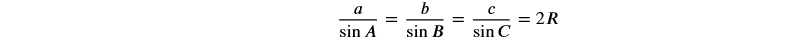
简化后得到:
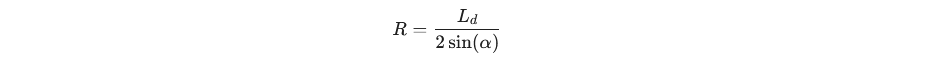
计算转向角 δ
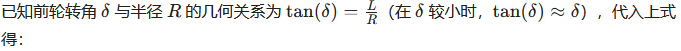
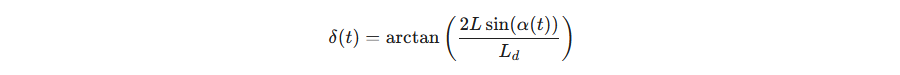
这是 Pure Pursuit 的核心控制律。
2. 工程实际控制方法
在实际的自动驾驶工程开发中,仅仅有数学公式是不够的,还需要处理参数自适应、路径搜索和稳定性问题。
A. 预瞄距离 Ld 的动态调整
预瞄距离是算法中最关键的超参数:
- 短预瞄距离: 跟踪精度高,曲线切合度好,但容易导致车辆转向过度,产生震荡。
- 长预瞄距离: 驾驶平滑度高,但切弯严重,在大弯道处会有较大的横向偏差。
工程常用方案: 将 L d 与车速 v 关联:
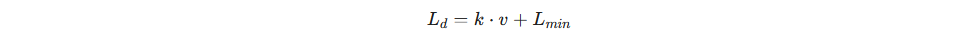
其中 k 是前视增益,Lmin 是低速时的最小预瞄距离。
B. 预瞄点的寻找算法
-
最近点搜索: 首先找到路径上离车辆当前位置最近的点。
-
正向搜索: 从最近点开始,沿着路径方向累加线段长度,直到距离等于 Ld。
-
插值: 如果路径点较稀疏,需要通过线性插值精确锁定 Ld 所在的坐标。
C. 控制流程
-
获取当前车辆位姿(GPS/IMU)和当前速度。
-
在全局路径中搜索符合当前 Ld 的预瞄点 (gx,gy)。
-
将预瞄点转换到车辆坐标系,计算夹角 α。
-
根据公式计算目标前轮转角 δ。
-
将 δ 转化为底盘的转向执行命令(如 CAN 总线报文)。
3. Pure Pursuit 的优缺点总结
| 特性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 优点 | 计算量极小,鲁棒性强(对路径的局部噪声不敏感),易于实现。 |
| 缺点 | "切弯"现象: 在急转弯处会向内侧偏移;延迟感: 缺乏前瞻性的反馈,对大曲率路径跟踪效果不如 MPC 或 LQR。 |
| 适用场景 | 低速园区自动驾驶(扫地机、物流车)、简单的路径跟随任务。 |
4. 进阶改进方向
如果你在实践中发现 Pure Pursuit 抖动或偏差过大,可以考虑:
-
增加前馈控制: 根据路径曲率直接计算一个基础转角。
-
引入 PID 补偿: 对横向误差进行额外的增益补偿。
-
切换至 Stanley 算法: Stanley 算法不仅考虑预瞄点,还考虑当前轴心的横向误差,在高速场景下表现更好。
5.代码示例
matlab
bash
% plot_ppControl.m
% clear all; close all; clc;
%
% line=load('path.txt');
% pointout=load('point_out.txt')
% pointin=load('pointIn.txt')
figure(1)
plot(path(:,1),path(:,2),'k-o');
hold on
% plot(pointout(1:14000,1),pointout(1:14000,2),'r-o');
plot(pointin(:,1),pointin(:,2),'b-o');
plot(0.2,3.6,'r-o');
plot(0.8,3.8,'g-*');
bash
% plotVehicle.m
function [plotPoint,showPoint] = plotVehicle(basePosex,basePosey,baseYawVehicle)
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%% vehicle and haircut %%
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
vehicleShow(1,1) = 0.0;
vehicleShow(1,2) = 0.0;
vehicleShow(2,1) = 0.0;
vehicleShow(2,2) = 3.0;
vehicleShow(3,1) = 0.9;
vehicleShow(3,2) = 0.0;
vehicleShow(4,1) = -0.9;
vehicleShow(4,2) = 0.0;
vehicleShow(5,1) = 0.9;
vehicleShow(5,2) = 3.0;
vehicleShow(6,1) = -0.9;
vehicleShow(6,2) = 3.0;
vehicleShow(7,1) = -0.9;
vehicleShow(7,2) = 3.4;
vehicleShow(8,1) = -0.9;
vehicleShow(8,2) = 2.6;
vehicleShow(9,1) = 0.9;
vehicleShow(9,2) = 3.4;
vehicleShow(10,1) = 0.9;
vehicleShow(10,2) = 2.6;
vehicleShow(11,1) = -0.9;
vehicleShow(11,2) = 0.4;
vehicleShow(12,1) = -0.9;
vehicleShow(12,2) = -0.4;
vehicleShow(13,1) = 0.9;
vehicleShow(13,2) = 0.4;
vehicleShow(14,1) = 0.9;
vehicleShow(14,2) = -0.4;
vehicleShow(15,1) = 0.0;
vehicleShow(15,2) = 3.6;
vehicleShow(16,1) = -0.1;
vehicleShow(16,2) = 3.5;
vehicleShow(17,1) = 0.1;
vehicleShow(17,2) = 3.5;
for ii_temp =1:17
xDelta = vehicleShow(ii_temp,1)*cos(baseYawVehicle-3.1415926/2) + vehicleShow(ii_temp,2)*cos(baseYawVehicle);
yDelta = vehicleShow(ii_temp,1)*sin(baseYawVehicle-3.1415926/2) + vehicleShow(ii_temp,2)*sin(baseYawVehicle);
vehicleShow(ii_temp,1) = xDelta + basePosex;
vehicleShow(ii_temp,2) = yDelta + basePosey;
end
%%
plotPoint(1,:) = vehicleShow(1,:);
plotPoint(2,:) = vehicleShow(2,:);
plotPoint(3,:) = vehicleShow(5,:);
plotPoint(4,:) = vehicleShow(10,:);
plotPoint(5,:) = vehicleShow(9,:);
plotPoint(6,:) = vehicleShow(5,:);
plotPoint(7,:) = vehicleShow(6,:);
plotPoint(8,:) = vehicleShow(7,:);
plotPoint(9,:) = vehicleShow(8,:);
plotPoint(10,:) = vehicleShow(6,:);
plotPoint(11,:) = vehicleShow(2,:);
plotPoint(12,:) = vehicleShow(1,:);
plotPoint(13,:) = vehicleShow(4,:);
plotPoint(14,:) = vehicleShow(11,:);
plotPoint(15,:) = vehicleShow(12,:);
plotPoint(16,:) = vehicleShow(4,:);
plotPoint(17,:) = vehicleShow(3,:);
plotPoint(18,:) = vehicleShow(14,:);
plotPoint(19,:) = vehicleShow(13,:);
% ͷ
showPoint(1,:) = vehicleShow(2,:);
showPoint(2,:) = vehicleShow(15,:);
showPoint(3,:) = vehicleShow(16,:);
showPoint(4,:) = vehicleShow(15,:);
showPoint(5,:) = vehicleShow(17,:);
showPoint(6,:) = vehicleShow(15,:);
showPoint(7,:) = vehicleShow(2,:);
end
bash
% PP_controler.m
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%%%% PP controller %%
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
clear all;close all;clc;
% init simuling value
v = 1; % speed of vehicle
dt = 0.1; % cyc time 0.1s
L=2.5; % the wheelbase of vehicle
curp=[0 0 0]; % reset origin pose of vehicle
% plot component
showVehicle = repmat(19,2);
showHaircut = repmat(7,2);
% simulink trajectory path
x = 0:0.1:50;
y = sin(x/5);
path = [x' y'];
for i=2:length(path)
dx = path(i,1)-path(i-1,1);
dy = path(i,2)-path(i-1,2);
path(i-1,3) = atan2(dy,dx);
end
path(length(path),3) = path(length(path)-1,3);
figure(2)
plot(path(:,1),path(:,2),'r.');
title('轨迹和定位');
axis equal;
xlabel('m');
ylabel('m');
% legend({'目标轨迹'},'location','southeast');
ax = gca;
ax.FontSize = 16;
hold on;
% main function
k=1; % aimming delta time 1.0s
ld = k*v; % aimming front distance
for i=1:length(path)
% 找路径最近点索引
d = path(:,1:2) - curp(1:2);
dis = d(:,1).^2 + d(:,2).^2;
[~,ind] = min(dis);
% 预瞄点索引
ind = ind+3;
if ind >length(path)
ind = length(path);
end
dx = curp(1) - path(ind,1);
dy = curp(2) - path(ind,2);
u = atan2(2*L*sin(curp(3) - atan2(dy, dx)),ld);
if u>0.524
u = 0.524;
elseif u<-0.524
u = -0.524;
end
curp(1) = curp(1) + dt*v*cos(curp(3));
curp(2) = curp(2) + dt*v*sin(curp(3));
curp(3) = curp(3) + dt*v*tan(u)/L;
[showVehicle,showHaircut] = plotVehicle(curp(1),curp(2),curp(3));
plot(curp(1),curp(2),'g.');
% plot(showVehicle(:,1),showVehicle(:,2),"g-*");
% plot(showHaircut(:,1),showHaircut(:,2),"r-*");
pause(dt)
end
% plot path
figure(1)
plot(path(:,3),'b.');
hold on;
title('航向角计算数值');
xlabel('times(0.1s)');
ylabel('randa');
legend({'航向计算'},'location','southeast');
ax = gca;
ax.FontSize = 16;
hold off
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%%%% NO MORE %%%%
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%python
bash
from celluloid import Camera # 保存动图时用,pip install celluloid
import numpy as np
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import math
L=2 # 车辆轴距,单位:m
v = 2 # 初始速度
x_0=0 # 初始x
y_0=-3 #初始y
psi_0=0 # 初始航向角
dt=0.1 # 时间间隔,单位:s
lam = 0.1 # 前视距离系数
c=2 # 前视距离
class KinematicModel_3:
"""假设控制量为转向角delta_f和加速度a
"""
def __init__(self, x, y, psi, v, L, dt):
self.x = x
self.y = y
self.psi = psi
self.v = v
self.L = L
# 实现是离散的模型
self.dt = dt
def update_state(self, a, delta_f):
self.x = self.x+self.v*math.cos(self.psi)*self.dt
self.y = self.y+self.v*math.sin(self.psi)*self.dt
self.psi = self.psi+self.v/self.L*math.tan(delta_f)*self.dt
self.v = self.v+a*self.dt
def get_state(self):
return self.x, self.y, self.psi, self.v
def cal_target_index(robot_state, refer_path, l_d):
"""得到前视目标点
Args:
robot_state (_type_): 当前车辆位置
refer_path (_type_): 参考轨迹(数组)
l_d:前视距离
Returns:
_type_: 前视目标点的索引
"""
dists = []
for xy in refer_path:
dis = np.linalg.norm(robot_state-xy)
dists.append(dis)
min_index = np.argmin(dists)
delta_l = np.linalg.norm(refer_path[min_index]-robot_state)
# 搜索前视目标点
while l_d > delta_l and (min_index+1) < len(refer_path):
delta_l = np.linalg.norm(refer_path[min_index+1]-robot_state)
min_index += 1
return min_index
def pure_pursuit_control(robot_state,current_ref_point,l_d,psi):
"""pure pursuit
Args:
robot_state (_type_): 车辆位置
current_ref_point (_type_): 当前参考路点
l_d:前视距离
return:返回前轮转向角delta
"""
alpha = math.atan2(current_ref_point[1]-robot_state[1], current_ref_point[0]-robot_state[0])-psi
delta = math.atan2(2*L*np.sin(alpha),l_d)
return delta
def main():
# set reference trajectory
refer_path = np.zeros((1000, 2))
refer_path[:, 0] = np.linspace(0, 100, 1000) # 直线
refer_path[:, 1] = 2*np.sin(refer_path[:, 0]/3.0) + \
2.5*np.cos(refer_path[:, 0]/2.0) # 生成正弦轨迹
ugv = KinematicModel_3(x_0, y_0, psi_0, v, L, dt)
x_ = []
y_ = []
fig = plt.figure(1)
# 保存动图用
camera = Camera(fig)
for i in range(600):
robot_state = np.zeros(2)
robot_state[0] = ugv.x
robot_state[1] = ugv.y
l_d = lam*ugv.v+c # 注意,这里的运动学模型使用的速度v就是车身纵向速度vx
ind = cal_target_index(robot_state, refer_path, l_d) # 搜索前视路点
delta = pure_pursuit_control(robot_state, refer_path[ind], l_d,ugv.psi)
ugv.update_state(0, delta) # 加速度设为0,恒速
x_.append(ugv.x)
y_.append(ugv.y)
# 显示动图
plt.cla()
plt.plot(refer_path[:, 0], refer_path[:, 1], '-.b', linewidth=1.0)
plt.plot(x_, y_, "-r", label="trajectory")
plt.plot(refer_path[ind, 0], refer_path[ind, 1], "go", label="target")
# plt.axis("equal")
plt.grid(True)
plt.pause(0.001)
# camera.snap()
# animation = camera.animate()
# animation.save('trajectory.gif')
plt.figure(2)
plt.plot(refer_path[:, 0], refer_path[:, 1], '-.b', linewidth=1.0)
plt.plot(x_, y_, 'r')
plt.show()
if __name__=='__main__':
main()cmake
bash
#include "stdio.h"
//=============================================================================
namespace algorithm
{
typedef struct CPosition
{
float m_p_x{0.0};
float m_p_y{0.0};
float m_p_yaw{0.0};
} CPosition;
typedef struct CPPCtrlParams
{
float m_curCmode{0.0}; //>! 1.0 aimDistance no cor; 2.0 aimDistance dynamtic cor
float m_wheelBase{2.87};
float m_maxSaCtrl{0.72};
float m_aimDistance{3.0};
} CPPCtrlParams;
typedef struct CPPaimDisDev
{
float m_aimDis{1.0};
float m_yawDev{0.2};
} CPPaimDisDev;
typedef struct CDeviation
{
float m_longiDevN{0.0};
float m_lateralDevN{0.0};
float m_oriDevN{0.0};
float m_longiDevB{0.0};
float m_lateralDevB{0.0};
float m_oriDevB{0.0};
} CDeviation;
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
class CCTRLpp
{
public:
CCTRLpp();
bool loadKeyPoints(const CPosition &f_curPosi, const CPosition &f_targetPosi);
float getSaCtrlValue() { return m_saCtrlValue; }
algorithm::CPosition getPurePurCurPosi() { return m_ppPosi; }
algorithm::CPosition getPurePurTargePosi() { return m_targetPosi; }
//>!
void initCtrUnit(CPPCtrlParams &f_ppCtrParams);
void setPurePurCurPosi(algorithm::CPosition &f_ppPosi) { m_ppPosi = f_ppPosi; }
void setPurePurTargePosi(algorithm::CPosition &f_ppPosi) { m_targetPosi = f_ppPosi; }
private:
void runCtrlpp();
void runPurePursuitCtrller();
private:
// See in the above remark how this value is calculated
// some init value in the magnitude of the real value
CPosition m_ppPosi;
CPosition m_targetPosi;
CDeviation m_posiDeviation;
CPPaimDisDev m_aimDisAndDev;
CPPCtrlParams m_ppCtrParams;
float m_perGoal;
float m_vehVelocity;
float m_pVehicle;
float m_wheelBase;
float m_timeDev;
float m_saCtrlValue;
float m_maxSaValue;
};
} // namespace algorithm
bash
#include "math.h"
#include "../inc/algorithm_eridev_pp.hpp"
//=============================================================================
namespace algorithm
{
CCTRLpp::CCTRLpp()
: m_perGoal(10.0),
m_vehVelocity(1.0),
m_pVehicle(1.0),
m_wheelBase(3.0),
m_timeDev(0.02),
m_saCtrlValue(0.0)
{
}
void CCTRLpp::runPurePursuitCtrller()
{
//>! u = atan2(2*l*sin(dev_yaw),aimDis)
float l_targetDis = m_aimDisAndDev.m_aimDis;
float l_sinB = (l_targetDis < 0.0) ? sin(m_aimDisAndDev.m_yawDev + M_PI_2) : sin(m_aimDisAndDev.m_yawDev);
float l_saCtrlValue = atan2((2 * m_wheelBase * l_sinB), l_targetDis);
m_saCtrlValue = (fabs(l_saCtrlValue) > m_maxSaValue) ? ((l_saCtrlValue < 0.0) ? -m_maxSaValue : m_maxSaValue) : l_saCtrlValue;
printf("the setting max sa value %f \n", m_maxSaValue);
return;
}
void CCTRLpp::runCtrlpp()
{
//>! ppCtrl params calculate
m_posiDeviation.m_longiDevN = m_targetPosi.m_p_x - m_ppPosi.m_p_x;
m_posiDeviation.m_lateralDevN = m_targetPosi.m_p_y - m_ppPosi.m_p_y;
m_posiDeviation.m_oriDevN = atan2(m_posiDeviation.m_lateralDevN, m_posiDeviation.m_longiDevN) - m_ppPosi.m_p_yaw;
m_aimDisAndDev.m_yawDev = m_posiDeviation.m_oriDevN;
runPurePursuitCtrller();
return;
}
bool CCTRLpp::loadKeyPoints(const CPosition &f_curPosi, const CPosition &f_targetPosi)
{
m_ppPosi = f_curPosi;
m_targetPosi = f_targetPosi;
runCtrlpp();
return true;
}
void CCTRLpp::initCtrUnit(CPPCtrlParams &f_ppCtrParams)
{
m_wheelBase = f_ppCtrParams.m_wheelBase;
m_aimDisAndDev.m_aimDis = f_ppCtrParams.m_aimDistance;
m_maxSaValue = f_ppCtrParams.m_maxSaCtrl;
return;
}
} // namespace algorithm
bash
#include "iostream"
#include "cmath"
#include "fstream"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "signal.h"
#include "unistd.h"
#include "vector"
#include "./inc/algorithm_eridev_pp.hpp"
algorithm::CCTRLpp m_ctrlppAlgo;
algorithm::CPosition getAimPosi();
algorithm::CPosition getCurPosi();
int main()
{
//>! filter deviations and init ctrl
algorithm::CPPCtrlParams l_ctrlParamSet = algorithm::CPPCtrlParams{1.0, 3.0, 0.84, 3.0};
m_ctrlppAlgo.initCtrUnit(l_ctrlParamSet);
//>! ppControl main function
if(m_ctrlppAlgo.loadKeyPoints(getCurPosi(), getAimPosi()))
{
float l_saCtrl = m_ctrlppAlgo.getSaCtrlValue();
printf("Pure pursuit ouput ctrl value: %f\n", l_saCtrl*57.3);
}
return 0;
}
algorithm::CPosition getAimPosi()
{
algorithm::CPosition l_tempPosition;
l_tempPosition.m_p_x = 2.0;
l_tempPosition.m_p_y = 3.0;
l_tempPosition.m_p_yaw = 0.8;
return l_tempPosition;
}
algorithm::CPosition getCurPosi()
{
algorithm::CPosition l_tempPosition;
l_tempPosition.m_p_x = 0.0;
l_tempPosition.m_p_y = 0.0;
l_tempPosition.m_p_yaw = 0.0;
return l_tempPosition;
}
//=========================================================================================================================//