创建基本几何对象------点、线、面
点
Point(x,y,[z])
查看点的属性和常用方法
point.coords 返回坐标(返回坐标迭代器)
tuple(point.coords) 转换为元组格式
point.bounds 返回点的边界(minx, miny, maxx, maxy)
point.has_z 判断是否有z值
线
LineString(coordinates)
查看线的属性和常用方法
line.coords
tuple(line.coords)
line.length 计算线的长度,单位与坐标单位一致
tuple(line.coords[0]) 线的起点
tuple(line.coords[-1] 线的终点
line.bounds
面
Polygon(shell,[holes]) holes可选
查看面的属性和常用方法
tuple(polygon.exterior.coords) 多边形的外部边界坐标
tuple(polygon.interiors.coords) 多边形的内部孔洞坐标
polygon.area
polygon.length
polygon.bounds
len(polygon.interiors)>0 判断是否包含孔洞
代码示例
python
from shapely.geometry import Point,LineString,Polygon
import geopandas as gpd
#点
point=Point(116.33,25.55)
print(f'坐标:{point.coords}')
print(f'坐标:{tuple(point.coords)}')
print(f'边界:{point.bounds}')
print(f'是否含z值:{point.has_z}')
#线
coords=[
(116.40,39.91),
(116.41,39.92),
(116.42,39.93),
]
line=LineString(coords)
print(f'坐标:{tuple(line.coords)}')
print(f'线的起点:{tuple(line.coords)[0]}')
print(f'线的终点:{tuple(line.coords)[-1]}')
print(f'边界:{line.bounds}')
print(f'长度:{line.length:.4f}')
#多边形
shell=[
(116.39, 39.90),
(116.41, 39.90),
(116.41, 39.92),
(116.39, 39.92),
(116.39, 39.90) #与点1一致,保证封闭
]
hole=[
(116.395, 39.905),
(116.405, 39.905),
(116.405, 39.915),
(116.395, 39.915),
(116.395, 39.905)
]
polygon=Polygon(shell,[hole])
print(f'外边界坐标:{tuple(polygon.exterior.coords)}')
print(f'面积:{polygon.area:.4f}')
print(f'周长:{polygon.length:.4f}')
print(f'是否包含孔洞:{len(polygon.interiors)>0}')
print(f'边界:{polygon.bounds}')
print(f'孔洞坐标:{tuple(polygon.interiors[0].coords)}')#返回第一个孔洞的坐标简单操作代码示例
python
from shapely.geometry import Point,LineString,Polygon
import geopandas as gpd
try:
shp=r'E:\tempFile\postgis-workshop-2018\data\nyc_census_blocks.shp'
nyc_census=gpd.read_file(shp)
except FileNotFoundError:
print('未找到文件')
except UnicodeDecodeError:
print('中文乱码')
except Exception as e:
print(f'具体错误:{e}')
else:
#获取空间参考信息
print(f'空间参考:{nyc_census.crs}')
#查看所有字段名称
fields_name=nyc_census.columns.tolist()
#提取第一个要素的所有数据,包括字段和值
feature1=nyc_census.iloc[0]
for field in fields_name:
print(f'{field}:{feature1[field]}')
#提取第一个几何要素
geom1=nyc_census.geometry.iloc[0]
print('几何要素类型',type(geom1))
print('几何要素面积',round(geom1.area,3))
#提取第一个面要素的中心点
centroid=geom1.centroid
print(f'中心点坐标:{centroid.coords[:]}')
#提取行政区的边界线
boundary1=geom1.boundary
print(f'边界线长度:{boundary1.length:.4f}')判别几何对象的空间关系
相交
a.intersects(b)
包含与被包含
a.contains(b) 判断a是否包含b
b.within(a) 判断b是否完全落在a内,即b是否被a包含
完整代码
在本代码示例中,合并queens的多边形时出现了报错,这是因为参与运算的几何对象存在拓扑无效问题(比如自相交、边界重叠、几何碎片等),导致 GEOS 库(Shapely/GeoPandas 底层的几何运算库)无法正常执行 unary_union 合并。因此需要进行拓扑修复。
python
from shapely.geometry import Point,LineString,Polygon
import geopandas as gpd
from shapely.validation import make_valid # 导入几何修复函数
try:
nei=r'E:\tempFile\postgis-workshop-2018\data\nyc_neighborhoods.shp'
cen=r'E:\tempFile\postgis-workshop-2018\data\nyc_census_blocks.shp'
sta=r'E:\tempFile\postgis-workshop-2018\data\nyc_subway_stations.shp'
neigh=gpd.read_file(nei)
census=gpd.read_file(cen)
stats=gpd.read_file(sta)
except FileNotFoundError:
print('未找到文件')
except UnicodeDecodeError:
print('中文乱码')
except Exception as e:
print(f'具体错误:{e}')
else:
#判断两个多边形是否相交
feature1=neigh[neigh['NAME']=='Flatbush']
poly1=feature1.geometry.iloc[0]
poly2=census.geometry.iloc[33485]
print(f'是否相交:{poly1.intersects(poly2)}')
#判断两个多边形是否包含
poly3=census.geometry.iloc[32974]
print(f'是否包含:{poly1.contains(poly3)}')
#判断地铁站点是否落在多多边形内
feature2=neigh[neigh['BORONAME']=='Queens']
#先标记无效几何
feature2['valid']=feature2.geometry.is_valid
invalid_count=len(feature2[~feature2['valid']])
print(f'发现无效几何数量:{invalid_count}')
#修复无效几何
feature2['fixed']=feature2.geometry.apply(lambda geom:make_valid(geom) if not geom.is_valid else geom)
#替换原geometry列,方便后续操作
feature2_fixed=feature2.set_geometry('fixed')
queens_union=feature2_fixed.geometry.unary_union
stations=(stats.geometry.iloc[:])
point_in_poly=[]
for p in stations:
if p.within(queens_union):
point_in_poly.append(p)
print(f'落在queens区域内的地铁站点数量:{len(point_in_poly)}')扩展生成几何对象------缓冲区、泰森多边形
缓冲区和泰森多边形分别在个人专栏矢量数据的空间分析(二)-CSDN博客和矢量数据的空间分析(四)-CSDN博客已详细记录过。
几何对象的旋转、平移、缩放
旋转
rotate(geom,angle,origin='center',use_radians=False)
平移
translate(geom,xoff=0.0,yoff=0.0)
缩放
scale(geom,xfact=1.0,yfact=1.0)
完整代码
python
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import geopandas as gpd
from shapely.affinity import *
import math
try:
cen=r'E:\tempFile\postgis-workshop-2018\data\nyc_census_blocks.shp'
census=gpd.read_file(cen)
except FileNotFoundError:
print('未找到文件')
except UnicodeDecodeError:
print('中文乱码')
except Exception as e:
print(f'具体错误:{e}')
else:
parcel=census.geometry.iloc[2351]
#计算地块最小外接矩形的角度
min_rect=parcel.minimum_rotated_rectangle
rect_coords=min_rect.exterior.coords
rotate_rad=-math.atan2((rect_coords[1][1]-rect_coords[0][1]),(rect_coords[1][0]-rect_coords[0][0]))
#旋转使其最小外接矩形水平
parcel1=rotate(parcel,rotate_rad,origin=parcel.centroid,use_radians=True)
#缩放
parcel2=scale(parcel1,xfact=0.85,yfact=0.85,origin=parcel.centroid)
#平移
parcel3=translate(parcel2,xoff=6.0,yoff=-50.5)
#可视化
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False
#plt无法直接绘制shapely几何对象,而GeoSeries/GeoDataFrame 支持直接 plot()
parcel_geo=gpd.GeoSeries([parcel])
parcel1_geo=gpd.GeoSeries([parcel1])
parcel2_geo=gpd.GeoSeries([parcel2])
parcel3_geo=gpd.GeoSeries([parcel3])
fig,ax=plt.subplots(2,2,figsize=(14,12))
## 计算所有几何对象的总边界,统一所有子图的坐标范围
all_geoms = gpd.GeoSeries([parcel, parcel1, parcel2, parcel3])
x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max = all_geoms.total_bounds
#设置缓冲边界
x_min-=100
x_max+=100
y_min-=100
y_max+=100
parcel_geo.plot(ax=ax[0,0],color='green',edgecolor='black',linewidth=2.0)
ax[0,0].set_title('origin',fontsize=14)
ax[0,0].set_xlim(x_min, x_max)
ax[0,0].set_ylim(y_min, y_max)
ax[0,0].set_aspect('equal') # 保持坐标比例一致,避免图形变形
parcel1_geo.plot(ax=ax[0,1],color='green',edgecolor='black',linewidth=2.0)
ax[0,1].set_title('rotate',fontsize=14)
ax[0,1].set_xlim(x_min, x_max)
ax[0,1].set_ylim(y_min, y_max)
ax[0,1].set_aspect('equal')
parcel2_geo.plot(ax=ax[1,0],color='green',edgecolor='black',linewidth=2.0)
ax[1,0].set_title('scale',fontsize=14)
ax[1,0].set_xlim(x_min, x_max)
ax[1,0].set_ylim(y_min, y_max)
ax[1,0].set_aspect('equal')
parcel3_geo.plot(ax=ax[1,1],color='green',edgecolor='black',linewidth=2.0)
ax[1,1].set_title('translate',fontsize=14)
ax[1,1].set_xlim(x_min, x_max)
ax[1,1].set_ylim(y_min, y_max)
ax[1,1].set_aspect('equal')
fig.suptitle('变换对比',fontsize=16,y=0.98)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show() 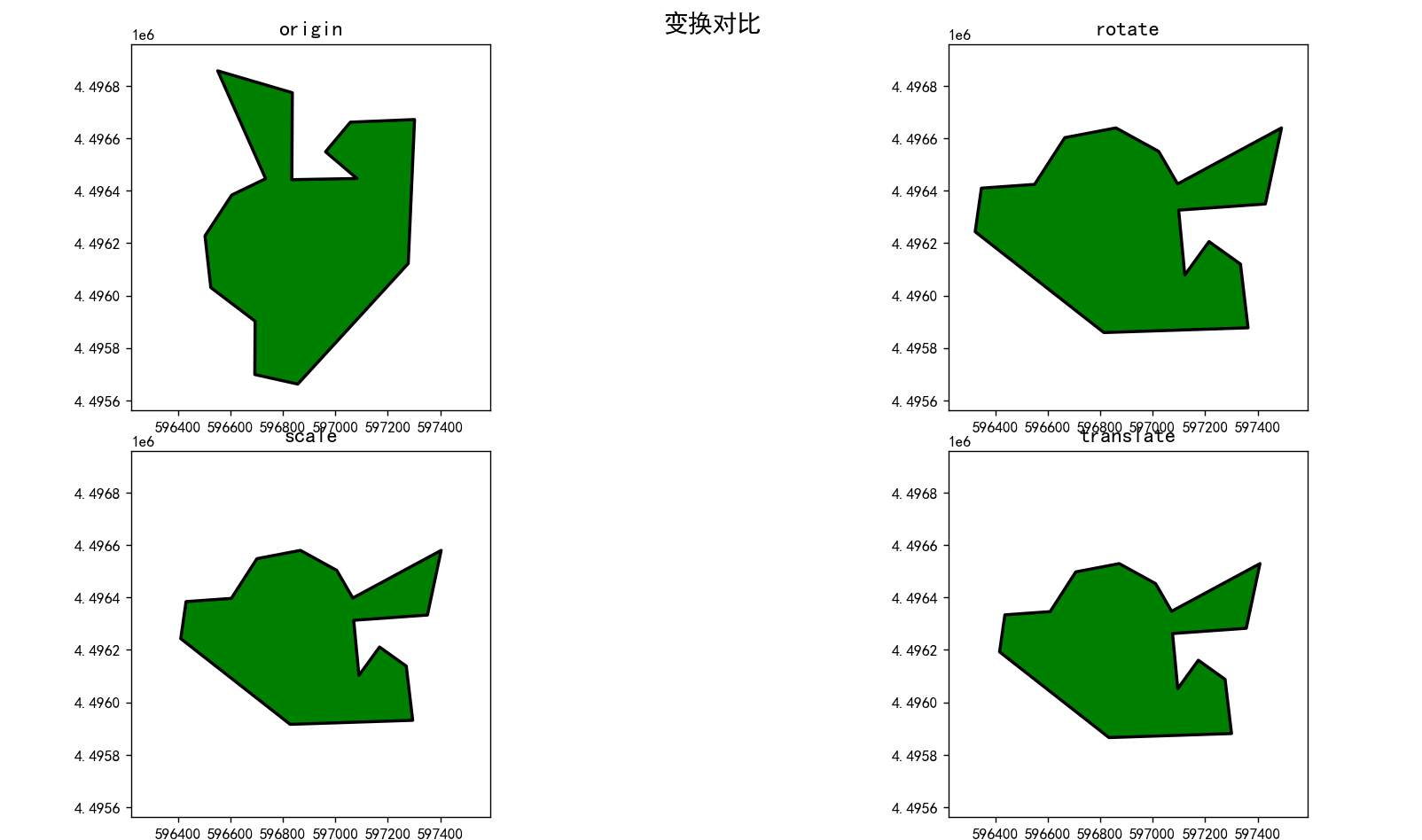
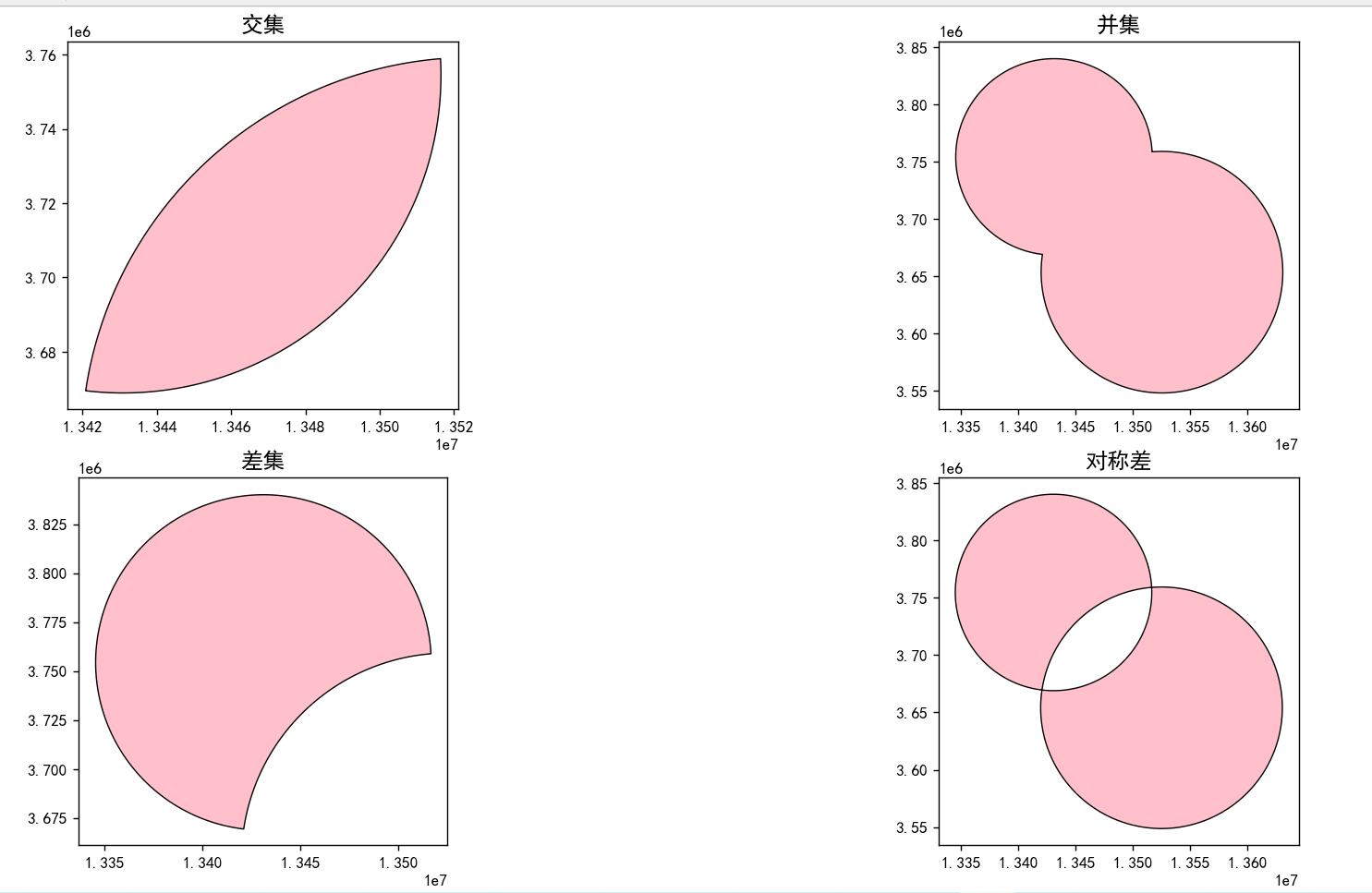
几何对象的运算
并集
a.union(b)
交集
a.intersection(b)
差集
a.difference(b)获取a中不属于b的部分
对称差
a.symmetric_difference(b)
完整代码
python
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import geopandas as gpd
from shapely.affinity import *
try:
circle1=r'C:\Users\Lenovo\Desktop\Python\data\vector\circle\circle1.shp'
circle2=r'C:\Users\Lenovo\Desktop\Python\data\vector\circle\circle2.shp'
c1=gpd.read_file(circle1)
c2=gpd.read_file(circle2)
except FileNotFoundError:
print('未找到文件')
except UnicodeDecodeError:
print('中文乱码')
except Exception as e:
print(f'具体错误:{e}')
else:
geom1=c1.geometry.iloc[0]
geom2=c2.geometry.iloc[0]
#交集
intersect=geom1.intersection(geom2)
#并集
union=geom1.union(geom2)
#差集
diff=geom1.difference(geom2)
#对称差
sym_diff=geom1.symmetric_difference(geom2)
#可视化
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False
fig,ax=plt.subplots(2,2,figsize=(12,10))
#转换为plt支持绘制的类型GeoSeries GeoDataFrame
intersect_geom=gpd.GeoSeries([intersect])
union_geom=gpd.GeoSeries([union])
diff_geom=gpd.GeoSeries([diff])
sym_diff_geom=gpd.GeoSeries([sym_diff])
intersect_geom.plot(ax=ax[0,0],color='pink',edgecolor='black',linewidth=0.8)
ax[0,0].set_title('交集',fontsize=14)
union_geom.plot(ax=ax[0,1],color='pink',edgecolor='black',linewidth=0.8)
ax[0,1].set_title('并集',fontsize=14)
diff_geom.plot(ax=ax[1,0],color='pink',edgecolor='black',linewidth=0.8)
ax[1,0].set_title('差集',fontsize=14)
sym_diff_geom.plot(ax=ax[1,1],color='pink',edgecolor='black',linewidth=0.8)
ax[1,1].set_title('对称差',fontsize=14)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()