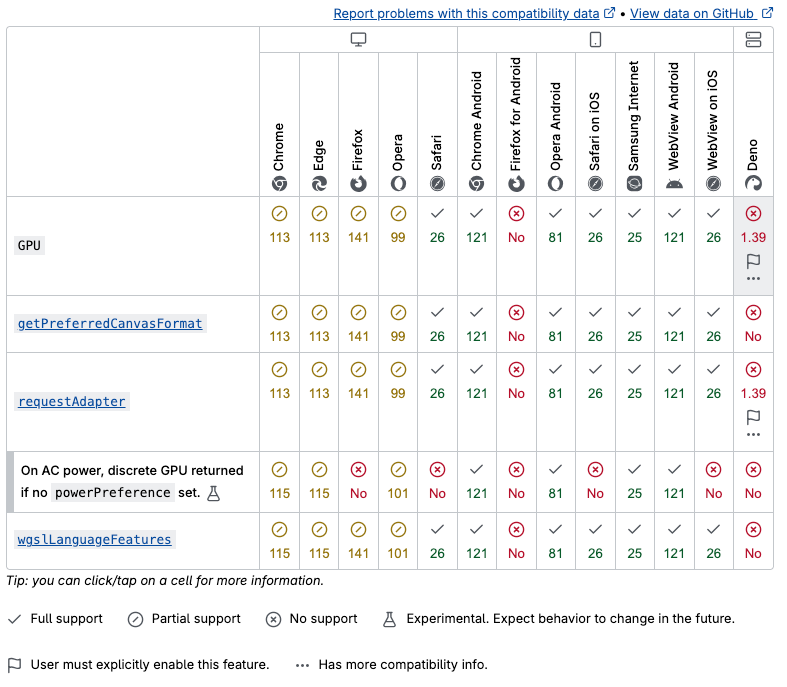
大家好,我是CC,在这里欢迎大家的到来~
背景
最近业务上需要个滤镜功能,高级点的且可以直接应用的那种,但是 Fabric.js 上只提供了基础滤镜(像黑白、复古等等)和自定义滤镜(调节单个参数,像亮度、对比度、饱和度等等)。原本设想通过组合各个参数设定好来滤镜使用,但是很快就被现实打败------找不到合适的参数数据,自己也不动设计。后经人指导可以基于 LUT 进行实现。
LUT(Lookup Table,查找表)是一种颜色映射技术,通过预定义的颜色转换规则,将输入颜色映射到输出颜色。
这是一张 LUT 图:
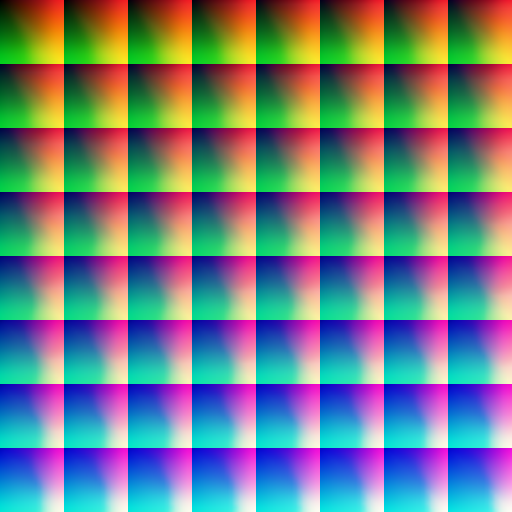
基于这张图实现的滤镜的逻辑大概是:
- 颜色映射:通过查找表将输入颜色映射到输出颜色
- 3D到2D转换:将3D颜色空间展开为2D纹理存储
- 三线性插值:在3D颜色空间中进行插值计算
- GPU加速:利用WebGPU的并行计算能力高效处理每个像素
快速入门WebGPU
先看图理解
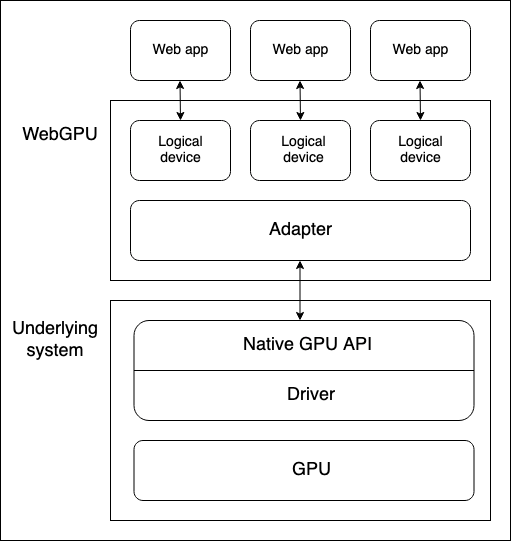
上边是浏览器的 WebGPU 对象,通过 Adapter(适配器)来匹配底层系统(电脑真实存在的物理设备)的 GPU,后续调用的也是 GPU 的原生 API。
下面介绍 WebGPU 常用 API 和原理。
调用
WebGPU 对象支持在 window 中调用,也可以在 worker 中调用。
TypeScript
Navigator.gpu
WorkerNavigator.gpu获取适配器
TypeScript
const adapter = await Navigator.gpu.requestAdapter()
const adapter = await Navigator.gpu.requestAdapter({
powerPreference: 'low-power' // 默认值,也可选 high-performance(非必要使用)
})获取 GPU Device
TypeScript
const adapter = await Navigator.gpu.requestAdapter()
const device = await adapter.requestDevice({
defaultQueue: '',
label: '',
requiredFeatures: [],
requiredLimits:
})管线和着色器
管线(pipeline)是一个逻辑结构,可通过编程完成程序工作。
目前管线包括渲染管线和计算管线,渲染管线用于图形渲染,计算管线用于通用计算。
渲染管线包括两个阶段:顶点着色阶段和片元着色阶段。
使用生产机器人的流水线来比喻 WebGPU、pipeline 和 shader 之间的关系。
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ WebGPU 工厂 │
│ ┌──────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Pipeline 生产线 │ │
│ │ ┌──────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐ │ │
│ │ │ 顶点着色器 │ │片段着色器 │ │ │
│ │ │(车体成型机器人) │ │(喷漆机器人) │ │ │
│ │ └──────────────┘ └──────────────┘ │ │
│ │ ↓ ↓ │ │
│ │ 车架成型 上色完成 │ │
│ └──────────────────────────────────────┘ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────┘
关键关系:
1. 工厂(WebGPU)提供生产环境
2. 生产线(Pipeline)定义生产流程
3. 机器人(Shader)执行具体任务
4. 三者缺一不可,协同工作着色器使用
WebGPU 着色器语言是用称为 WebGPU 着色器语言(WGSL)的低级的类 Rust 语言编写的。
建立渲染管线
顶点着色阶段(@vertex 代码块)接受包含位置和颜色的数据分块,根据给定的位置定位顶点,插入颜色,然后将数据传入到片元着色器阶段。
片元着色阶段(@fragment 代码块)接受来自顶点着色器阶段的数据,并根据给定的颜色为顶点着色。
TypeScript
const shaders = `
struct VertexOut {
@builtin(position) position : vec4f,
@location(0) color : vec4f
}
@vertex
fn vertex_main(@location(0) position: vec4f,
@location(1) color: vec4f) -> VertexOut
{
var output : VertexOut;
output.position = position;
output.color = color;
return output;
}
@fragment
fn fragment_main(fragData: VertexOut) -> @location(0) vec4f
{
return fragData.color;
}
`;
const shaderModule = device.createShaderModule({
code: shaders,
});
const pipelineDescriptor = {
vertex: {
module: shaderModule,
entryPoint: "vertex_main",
buffers: vertexBuffers,
},
fragment: {
module: shaderModule,
entryPoint: "fragment_main",
targets: [
{
format: navigator.gpu.getPreferredCanvasFormat(),
},
],
},
primitive: {
topology: "triangle-list",
},
layout: "auto",
};
const renderPipeline = device.createRenderPipeline(pipelineDescriptor);创建缓冲区
TypeScript
const vertices = new Float32Array([
0.0, 0.6, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, -0.5, -0.6, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0.5, -0.6, 0, 1, 0,
0, 1, 1,
]);
const vertexBuffer = device.createBuffer({
size: vertices.byteLength, // make it big enough to store vertices in
usage: GPUBufferUsage.VERTEX | GPUBufferUsage.COPY_DST,
});
device.queue.writeBuffer(vertexBuffer, 0, vertices, 0, vertices.length);配置 canvas 上下文
TypeScript
const canvas = document.querySelector("#gpuCanvas");
const context = canvas.getContext("webgpu");
context.configure({
device: device,
format: navigator.gpu.getPreferredCanvasFormat(), // 纹理texture格式
alphaMode: "premultiplied", // 半透明纹理时使用的 alpha 模式
});运行渲染管线
TypeScript
const commandEncoder = device.createCommandEncoder();
const textureView = context.getCurrentTexture().createView();
const renderPassDescriptor = {
colorAttachments: [
{
clearValue: { r: 0.0, g: 0.5, b: 1.0, a: 1.0 },
loadOp: "clear",
storeOp: "store",
view: textureView,
},
],
};
const passEncoder = commandEncoder.beginRenderPass(renderPassDescriptor);
const passEncoder = commandEncoder.beginRenderPass(renderPassDescriptor);
passEncoder.setPipeline(pipeline);
passEncoder.setBindGroup(0, bindGroup);
passEncoder.draw(6);
passEncoder.end();
device.queue.submit([commandEncoder.finish()]);滤镜实现
基础类
TypeScript
export class WebGPUFilter {
private canvas: HTMLCanvasElement;
private device: GPUDevice | null = null;
private context: GPUCanvasContext | null = null;
private pipeline: GPURenderPipeline | null = null;
private sampler: GPUSampler | null = null;
constructor() {
this.canvas = document.createElement('canvas');
}
public async init() {
if (!navigator.gpu) {
console.error('WebGPU not supported');
throw new Error('WebGPU not supported');
}
const adapter = await navigator.gpu.requestAdapter();
if (!adapter) {
console.error('No WebGPU adapter found');
throw new Error('No WebGPU adapter found');
}
this.device = await adapter.requestDevice();
this.context = this.canvas.getContext('webgpu');
if (!this.context) {
throw new Error('WebGPU context not found');
}
const presentationFormat = navigator.gpu.getPreferredCanvasFormat();
this.context.configure({
device: this.device,
format: presentationFormat,
alphaMode: 'premultiplied',
});
// Create shader module
const shaderModule = this.device.createShaderModule({
label: 'Filter Shader',
code: `
struct VertexOutput {
@builtin(position) Position : vec4f,
@location(0) v_texCoord : vec2f,
}
@vertex
fn vs_main(@builtin(vertex_index) vertexIndex : u32) -> VertexOutput {
var pos = array<vec2f, 6>(
vec2f(-1.0, -1.0), vec2f(1.0, -1.0), vec2f(-1.0, 1.0),
vec2f(-1.0, 1.0), vec2f(1.0, -1.0), vec2f(1.0, 1.0)
);
// UVs: Top-Left origin for WebGPU textures usually
// But we need to match how the image is drawn.
// Standard quad:
// (-1,-1) -> (0, 1) in GL if 0,0 is bottom left.
// In WebGPU, texture coords 0,0 is top-left.
// If we map (-1,-1) [bottom-left on screen] to (0, 1) [bottom-left in texture uv], it matches.
var tex = array<vec2f, 6>(
vec2f(0.0, 1.0), vec2f(1.0, 1.0), vec2f(0.0, 0.0),
vec2f(0.0, 0.0), vec2f(1.0, 1.0), vec2f(1.0, 0.0)
);
var output : VertexOutput;
output.Position = vec4f(pos[vertexIndex], 0.0, 1.0);
output.v_texCoord = tex[vertexIndex];
return output;
}
struct Uniforms {
intensity : f32,
grid_size : f32,
}
@group(0) @binding(0) var u_image : texture_2d<f32>;
@group(0) @binding(1) var u_image_sampler : sampler;
@group(0) @binding(2) var u_lut : texture_2d<f32>;
@group(0) @binding(3) var u_lut_sampler : sampler;
@group(0) @binding(4) var<uniform> uniforms : Uniforms;
@fragment
fn fs_main(@location(0) v_texCoord : vec2f) -> @location(0) vec4f {
let color = textureSample(u_image, u_image_sampler, v_texCoord);
let blueColor = color.b * (uniforms.grid_size * uniforms.grid_size - 1.0);
var quad1 : vec2f;
quad1.y = floor(floor(blueColor) / uniforms.grid_size);
quad1.x = floor(blueColor) - (quad1.y * uniforms.grid_size);
var quad2 : vec2f;
quad2.y = floor(ceil(blueColor) / uniforms.grid_size);
quad2.x = ceil(blueColor) - (quad2.y * uniforms.grid_size);
let N = uniforms.grid_size * uniforms.grid_size;
let halfPixel = 0.5 / N;
let scale = (N - 1.0) / N;
let r = color.r * scale + halfPixel;
let g = color.g * scale + halfPixel;
var texPos1 : vec2f;
texPos1.x = (quad1.x + r) / uniforms.grid_size;
texPos1.y = (quad1.y + g) / uniforms.grid_size;
var texPos2 : vec2f;
texPos2.x = (quad2.x + r) / uniforms.grid_size;
texPos2.y = (quad2.y + g) / uniforms.grid_size;
let newColor1 = textureSample(u_lut, u_lut_sampler, texPos1);
let newColor2 = textureSample(u_lut, u_lut_sampler, texPos2);
let newColor = mix(newColor1, newColor2, fract(blueColor));
let finalColor = mix(color.rgb, newColor.rgb, uniforms.intensity);
return vec4f(finalColor, color.a);
}
`,
});
this.pipeline = this.device.createRenderPipeline({
label: 'Filter Pipeline',
layout: 'auto',
vertex: {
module: shaderModule,
entryPoint: 'vs_main',
},
fragment: {
module: shaderModule,
entryPoint: 'fs_main',
targets: [{ format: presentationFormat }],
},
primitive: {
topology: 'triangle-list',
},
});
this.sampler = this.device.createSampler({
magFilter: 'linear',
minFilter: 'linear',
});
}
private async createTextureFromImage(
image: HTMLImageElement | HTMLCanvasElement,
flipY = false
): Promise<GPUTexture> {
if (!this.device) throw new Error('Device not initialized');
const texture = this.device.createTexture({
size: [image.width, image.height],
format: 'rgba8unorm',
usage:
GPUTextureUsage.TEXTURE_BINDING |
GPUTextureUsage.COPY_DST |
GPUTextureUsage.RENDER_ATTACHMENT,
});
const source = await createImageBitmap(image, {
imageOrientation: flipY ? 'flipY' : 'none',
premultiplyAlpha: 'none',
});
this.device.queue.copyExternalImageToTexture({ source: source }, { texture: texture }, [
image.width,
image.height,
]);
return texture;
}
public async apply(
sourceImage: HTMLImageElement,
lutImage: HTMLImageElement,
intensity: number
): Promise<HTMLCanvasElement> {
if (!this.device || !this.context || !this.pipeline || !this.sampler) {
// Attempt to init if not ready? Or just return canvas.
// For simplicity, assume init() called.
// If not, try init
if (!this.device) await this.init();
if (!this.device) return this.canvas;
}
const device = this.device!;
const context = this.context!;
const pipeline = this.pipeline!;
const sampler = this.sampler!;
// Resize canvas
if (this.canvas.width !== sourceImage.width || this.canvas.height !== sourceImage.height) {
this.canvas.width = sourceImage.width;
this.canvas.height = sourceImage.height;
// Re-configure context after resize
context.configure({
device: device,
format: navigator.gpu.getPreferredCanvasFormat(),
alphaMode: 'premultiplied',
});
}
// Determine grid size
let gridSize = 8.0;
if (lutImage.width <= 256) {
gridSize = 4.0;
}
// Create Textures
// WebGL implementation had sourceImage flipped Y (flipY=true)
// and LUT not flipped (flipY=false).
// In WebGPU, texture origin is top-left. Our UVs map bottom-left screen to (0,1) texture (bottom-left).
// So we should NOT flip the source image, otherwise (0,0) becomes bottom-left in memory,
// and UV (0,0) [top-left screen] would sample bottom-left of image.
const imageTexture = await this.createTextureFromImage(sourceImage, false);
const lutTexture = await this.createTextureFromImage(lutImage, false);
// Create Uniform Buffer
const uniformBufferSize = 8; // 2 floats * 4 bytes
const uniformBuffer = device.createBuffer({
size: uniformBufferSize,
usage: GPUBufferUsage.UNIFORM | GPUBufferUsage.COPY_DST,
});
const uniformData = new Float32Array([intensity, gridSize]);
device.queue.writeBuffer(uniformBuffer, 0, uniformData);
// Bind Group
const bindGroup = device.createBindGroup({
layout: pipeline.getBindGroupLayout(0),
entries: [
{ binding: 0, resource: imageTexture.createView() },
{ binding: 1, resource: sampler },
{ binding: 2, resource: lutTexture.createView() },
{ binding: 3, resource: sampler },
{ binding: 4, resource: { buffer: uniformBuffer } },
],
});
const commandEncoder = device.createCommandEncoder();
const textureView = context.getCurrentTexture().createView();
const renderPassDescriptor: GPURenderPassDescriptor = {
colorAttachments: [
{
view: textureView,
clearValue: { r: 0.0, g: 0.0, b: 0.0, a: 0.0 },
loadOp: 'clear',
storeOp: 'store',
},
],
};
const passEncoder = commandEncoder.beginRenderPass(renderPassDescriptor);
passEncoder.setPipeline(pipeline);
passEncoder.setBindGroup(0, bindGroup);
passEncoder.draw(6);
passEncoder.end();
device.queue.submit([commandEncoder.finish()]);
// Cleanup resources to avoid memory leaks?
// In WebGPU, JS GC handles wrappers, but we might want to destroy textures manually if we create them every frame.
// However, `apply` returns a canvas that has the content.
// If we destroy `imageTexture` and `lutTexture` immediately, it might be fine because commands are submitted.
// But let's let GC handle it for now unless performance is an issue.
// Note: The canvas is now drawn.
return this.canvas;
}
}使用
TypeScript
// 初始化类
const filter = new WebGPUFilter();
await filter.init();
webgpuFilterRef.value = filter;
// 应用滤镜
webgpuFilterRef.value
.apply(img, filterImg, opacity)
.then((result) => resolve(result))注意
目前 WebGPU 在浏览器兼容性还存在一些问题,使用时需要特殊考虑场景。