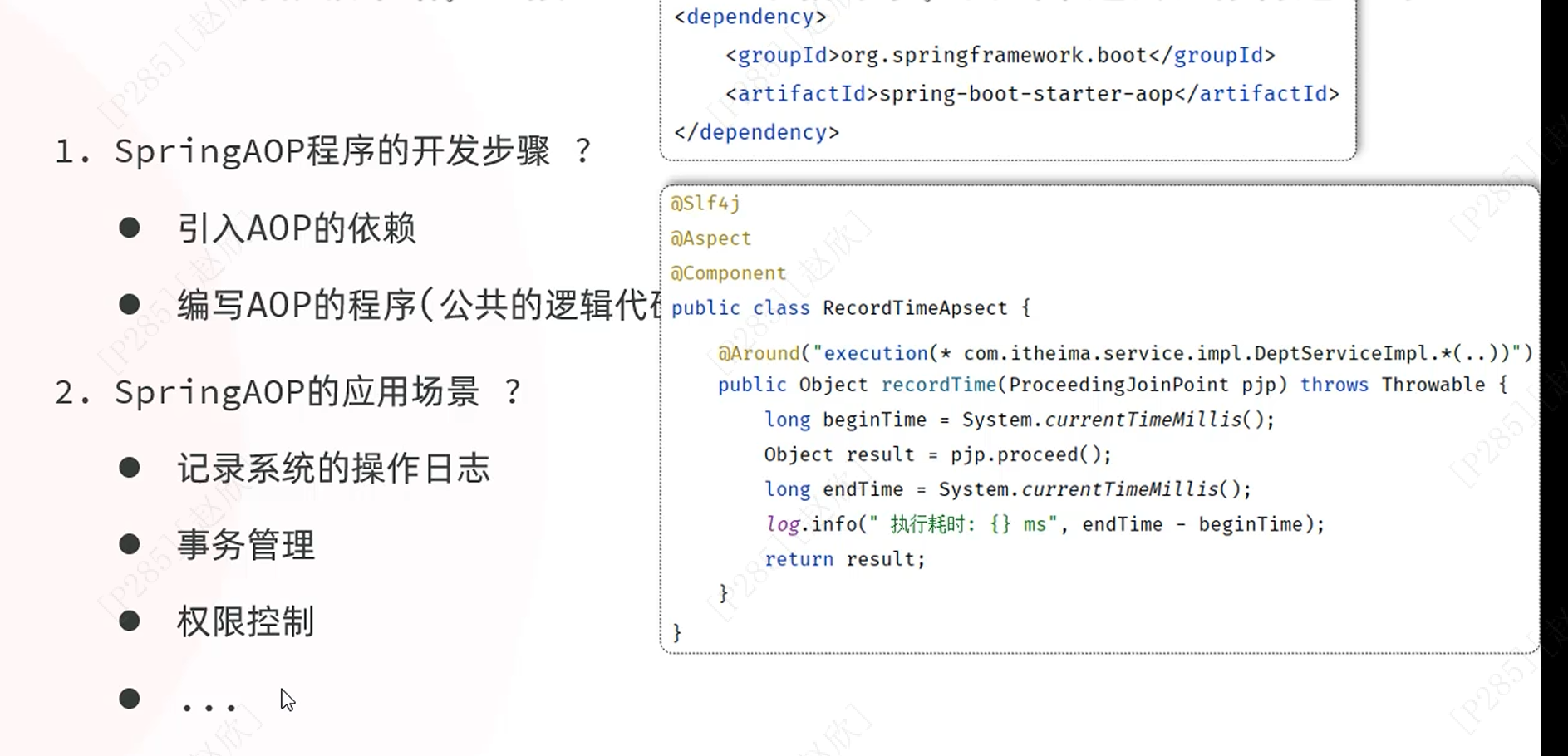
1、概念

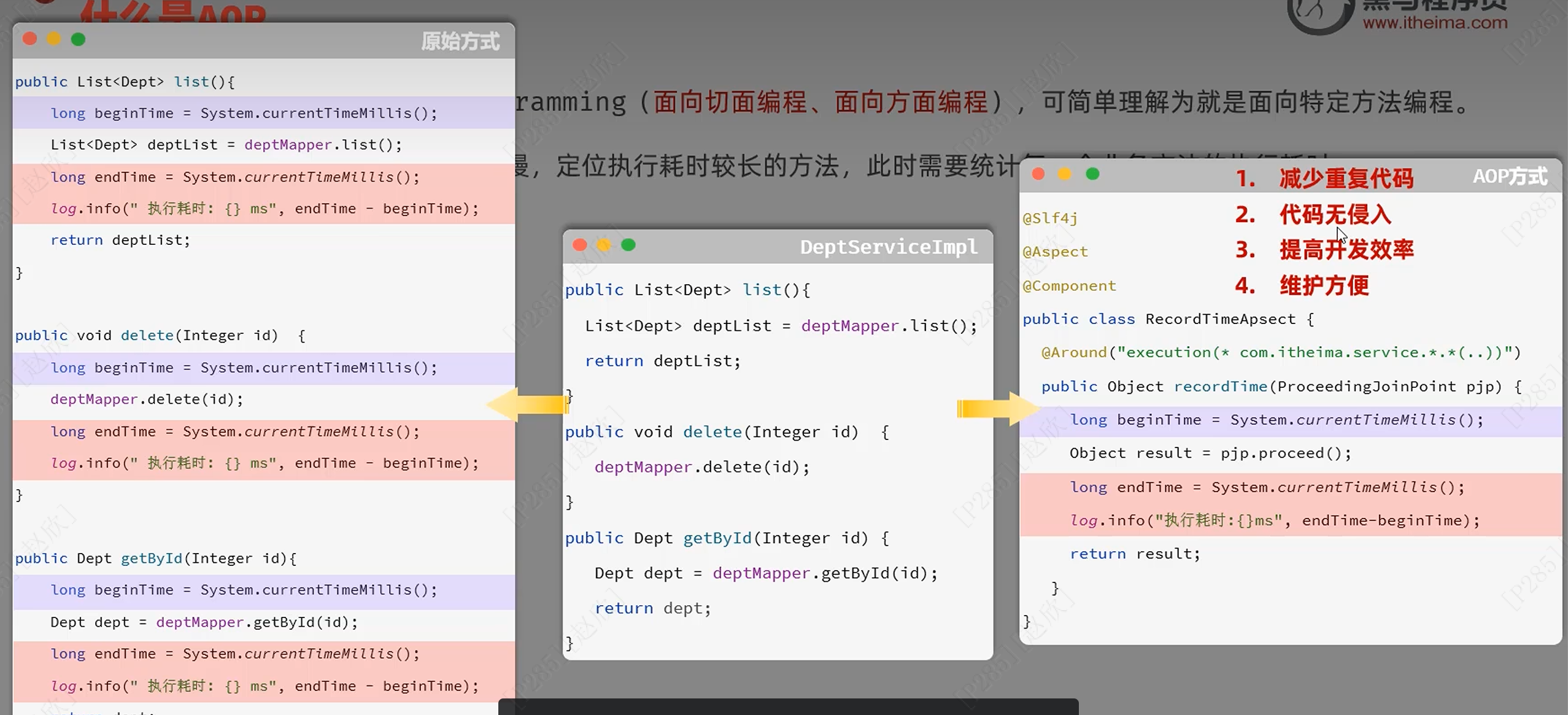

使用AOP:
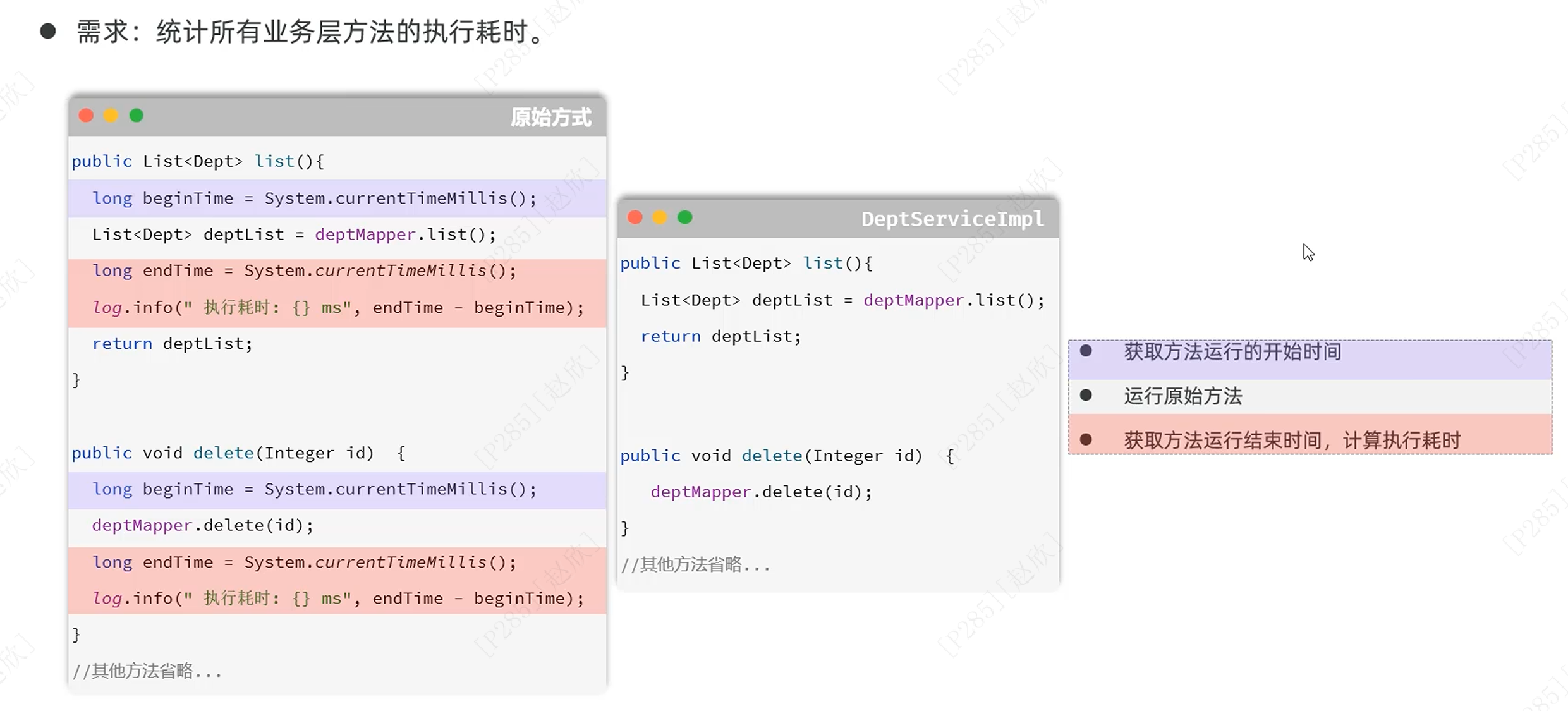
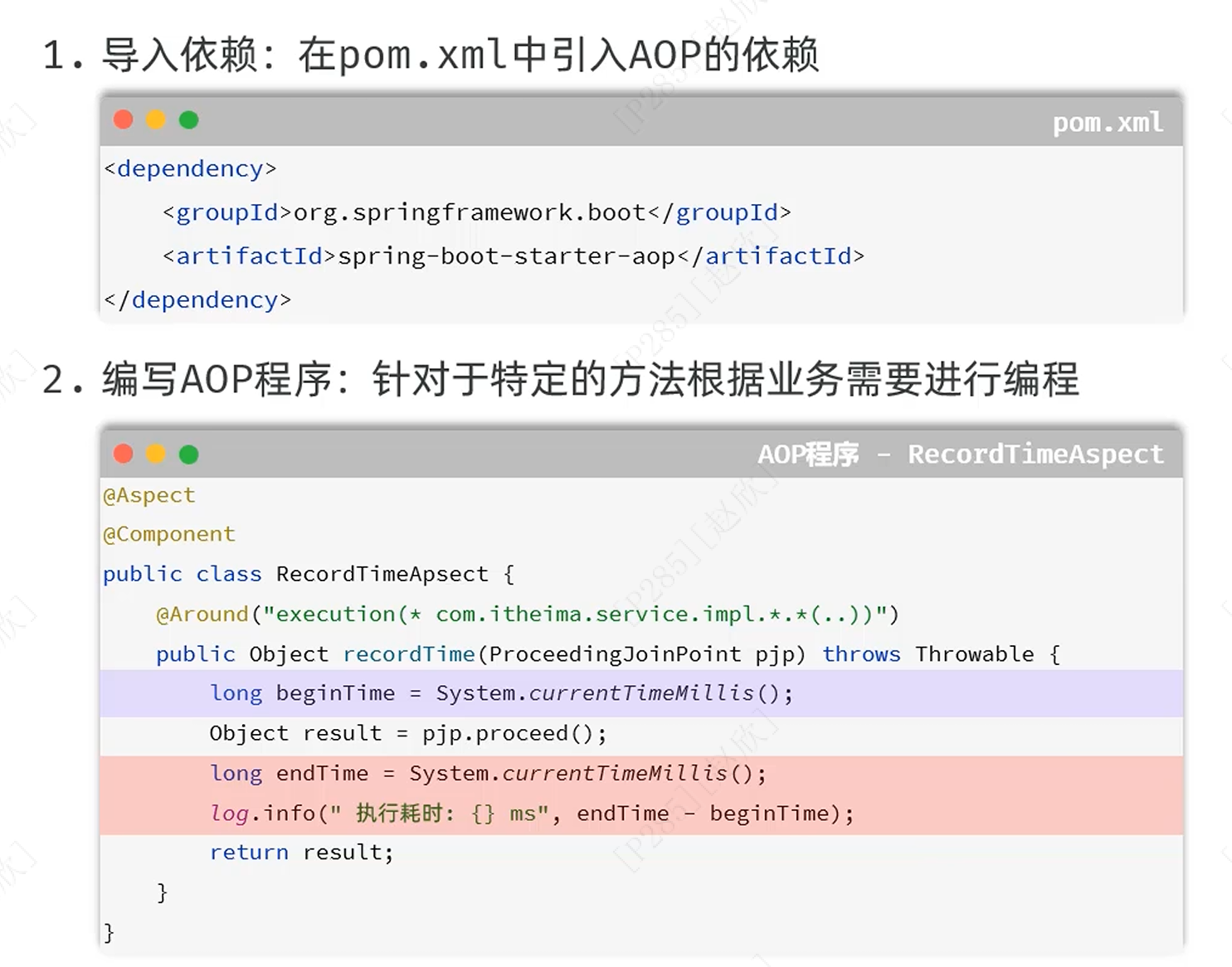
步骤:
之后导入一个文件,只保留了部门的增删查改功能
之后在包下新建一个类:
并输入代码:
package com.itheima.apo;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Slf4j
@Component
@Aspect//标识当前是一个AOP类
public class RecordTimeAspect {
@Around("execution(* com.itheima.service.impl.*.*(..))")//当前AOP对业务层的所有类和所有方法生效
public Object recordTime(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
//记录方法运行时间
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//原始方法执行
Object result=joinPoint.proceed();
//记录方法结束时间并计算执行耗时
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("方法运行时间:{}ms",end-start);
return result;
}
}之后启动项目,并使用增改删的功能,得到如下结果:
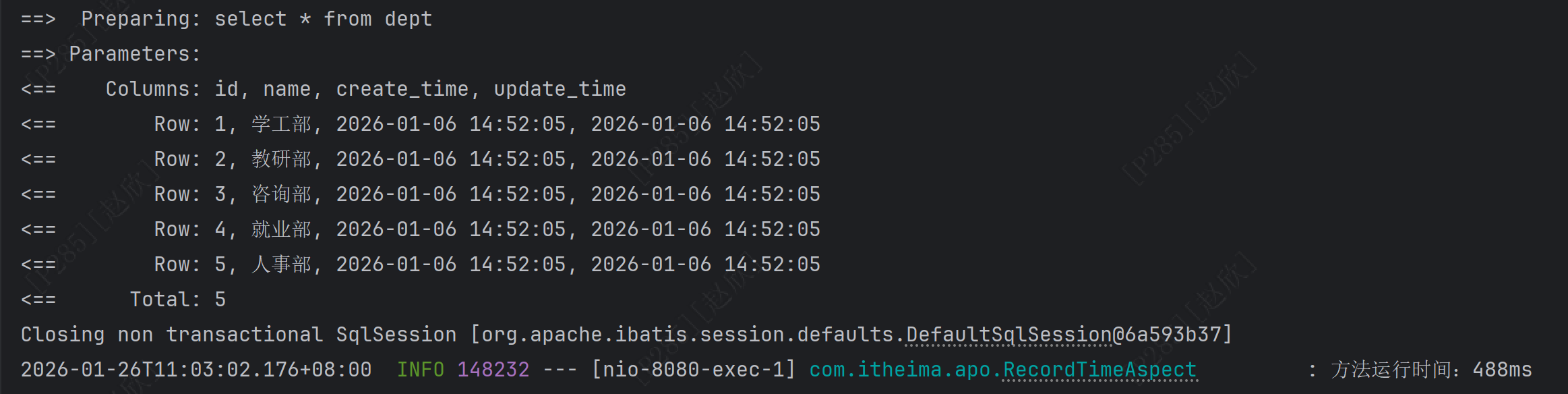



但是当前的结果并不确定哪个方法使用了多少秒,之后在代码中新增一个方法的占位符:
log.info("方法:{} 运行时间:{}ms",joinPoint.getSignature(),end-start);结果如下所示:



可以通过更改注解Around来修改当前AOP代码对那部分生效!
总结:
AOP的核心概念:

AOP通知类型:

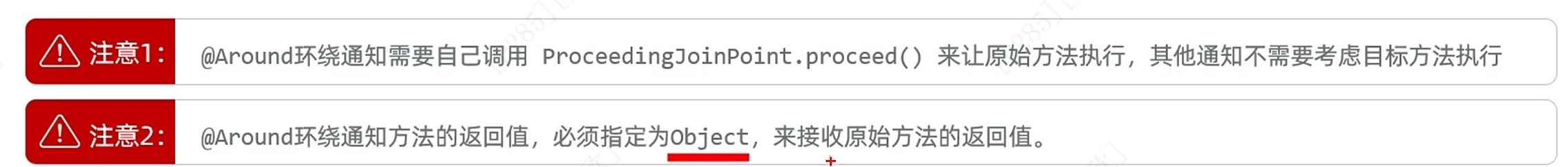
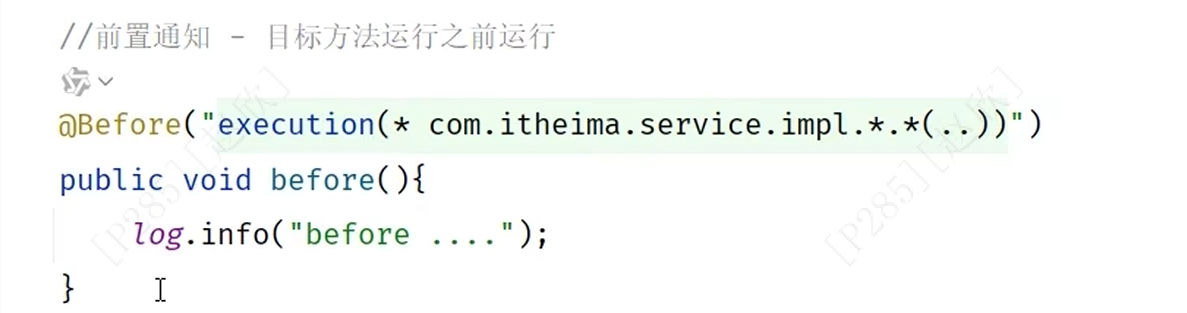
(1)前置通知
(2)环绕通知
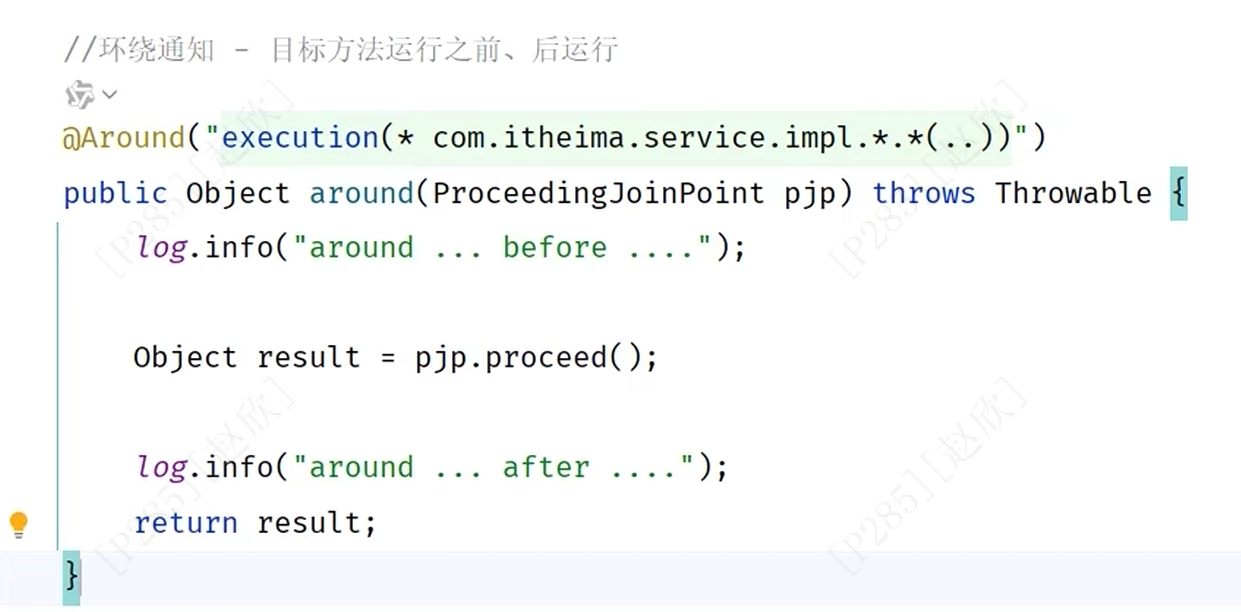
(3)后置通知
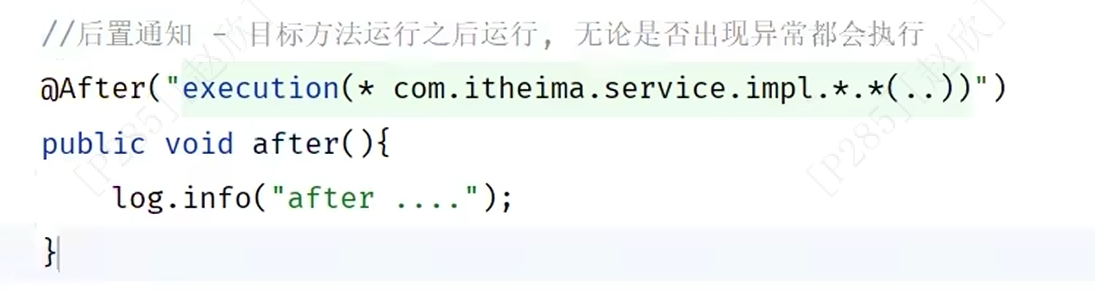
(4)返回后通知
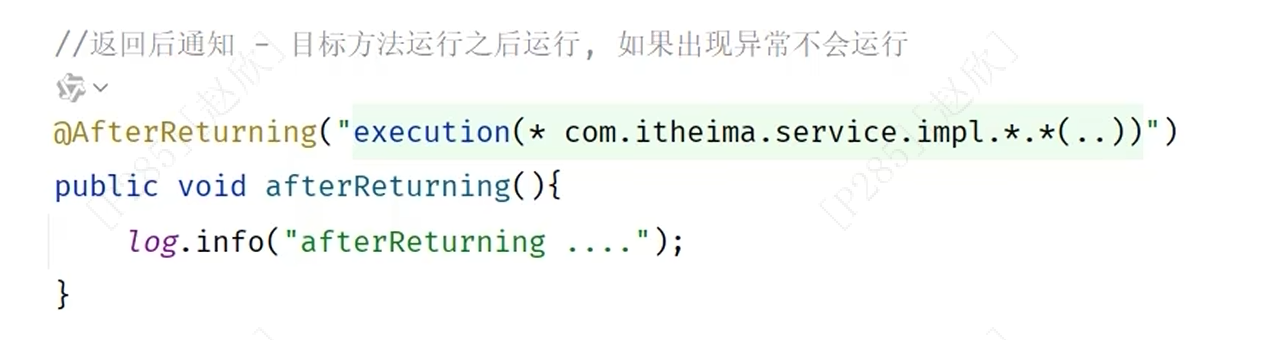
(5)异常后通知

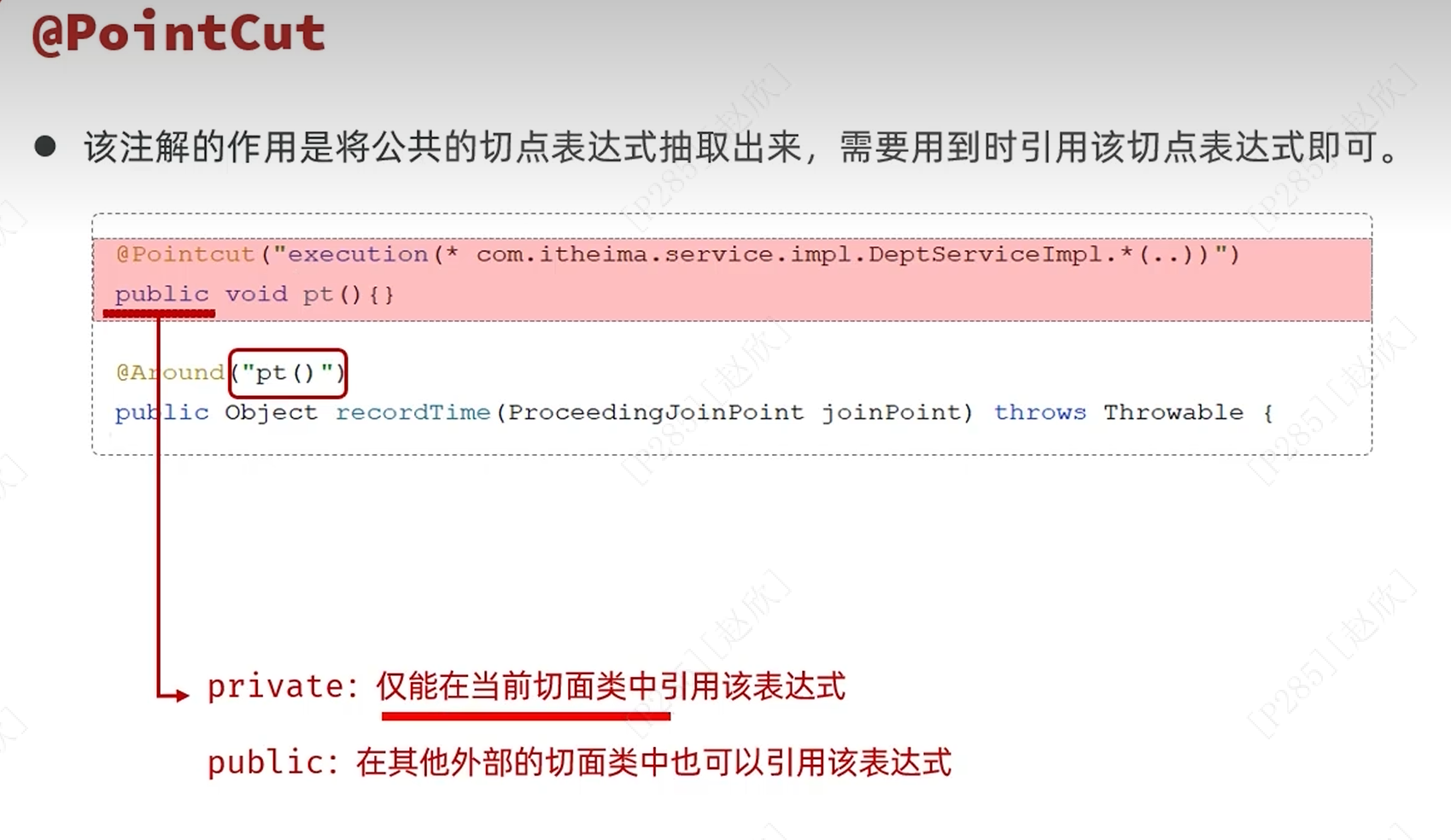
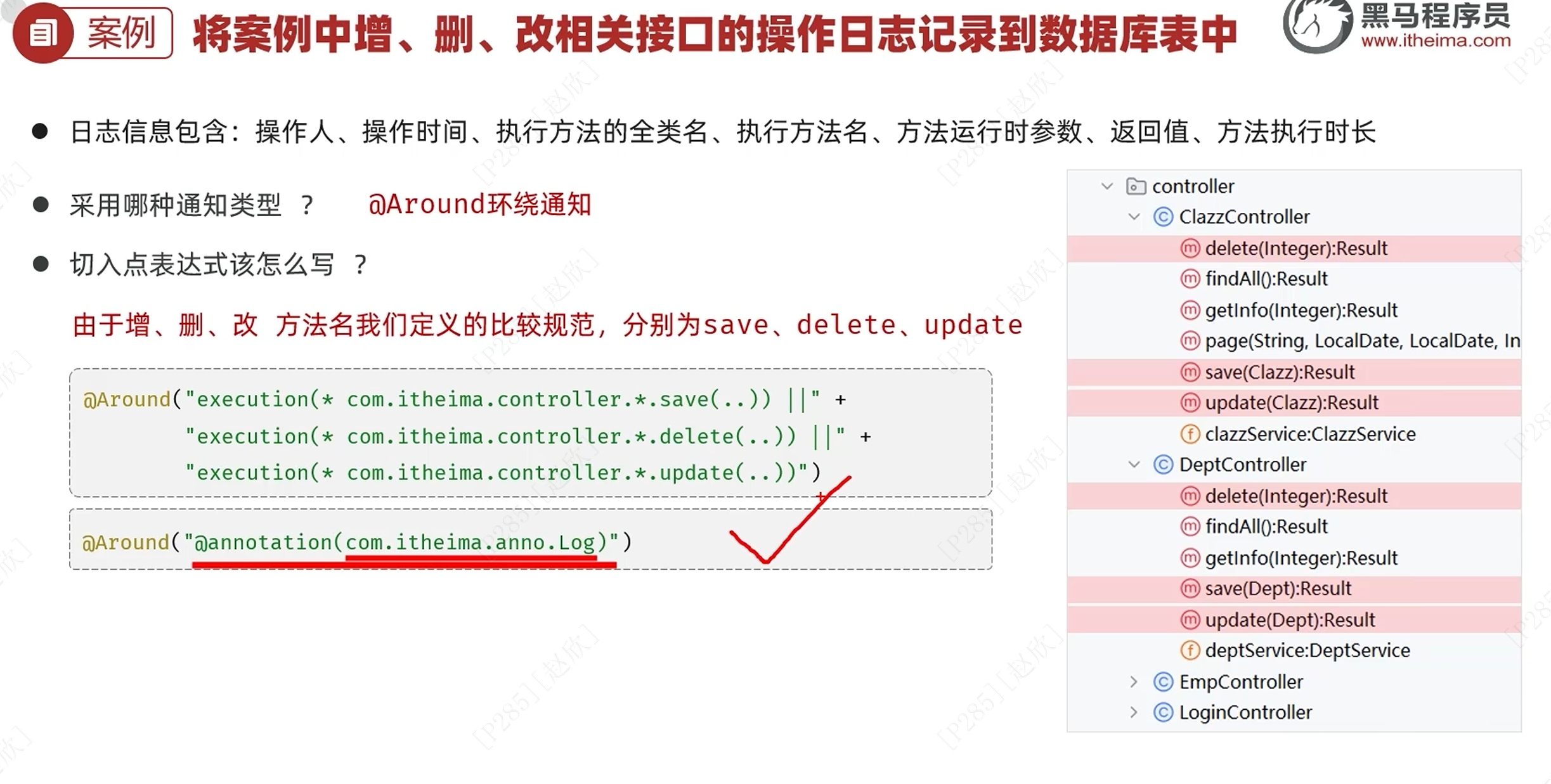
在实际代码中进行更改,将公共的切入点表达式用注解进行提取,之后重命名为pt(),将下面的表达式一一进行更换!
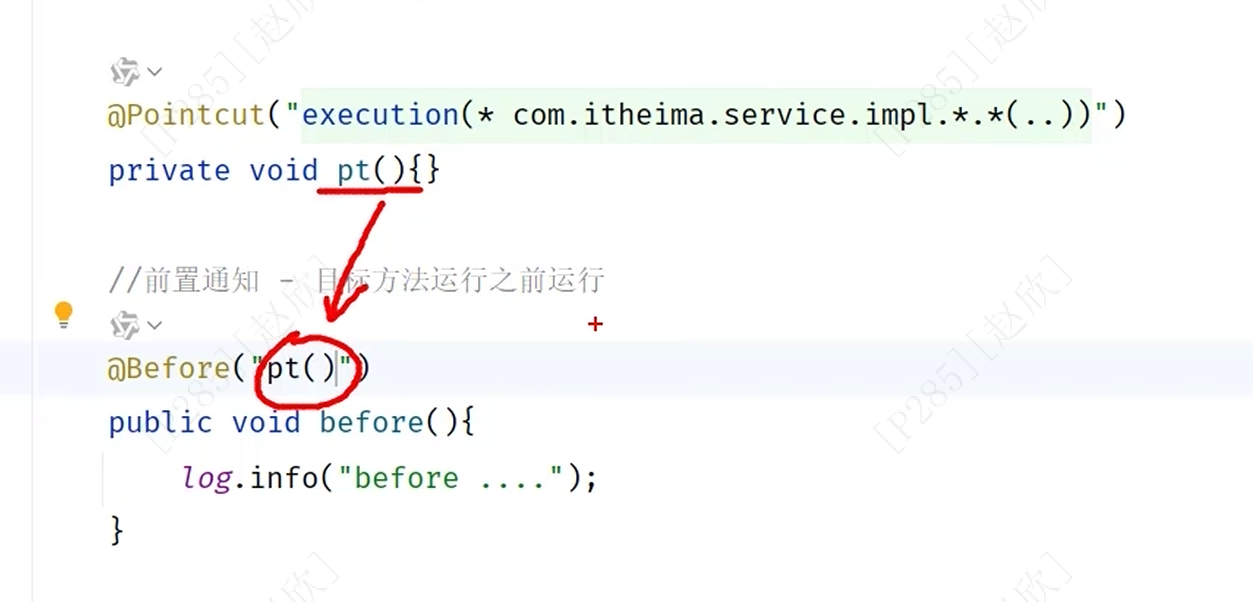
注解的作用域:
总结:
这个顺序就像栈一样,"先进后出",譬如命名分别以a、b、c为首字母
目标方法通知前的执行顺序为:a、b、c
目标方法通知后的执行顺序为:c、b、a

但是在实际中,aspect的命名是和业务有关系的,但此时以默认的字母排序就不是很合适,因此,添加新注解:

譬如:order中的值是相对值,只有和其他的aspect相比数字是最小的,就先执行这个!

切入点表达式:对于访问修饰符(publlic、private等)和异常方法等可以省略

..表示任意个,相当于不论是1个还是2个还是3个都代替了!

del*表示匹配的方法名必须是以del开头的方法,后边任意,表明*还可以表示字母的一部分,相当于模糊匹配!!!

如今要对下面两个进行描述切入点表达式:

"execution(* com.itheima.service.impl.DeptServiceImpl.list(..))||"+"execution(* com.itheima.service.impl.DeptServiceImpl.delete(..))"
可以使用逻辑运算符进行匹配!

总结:

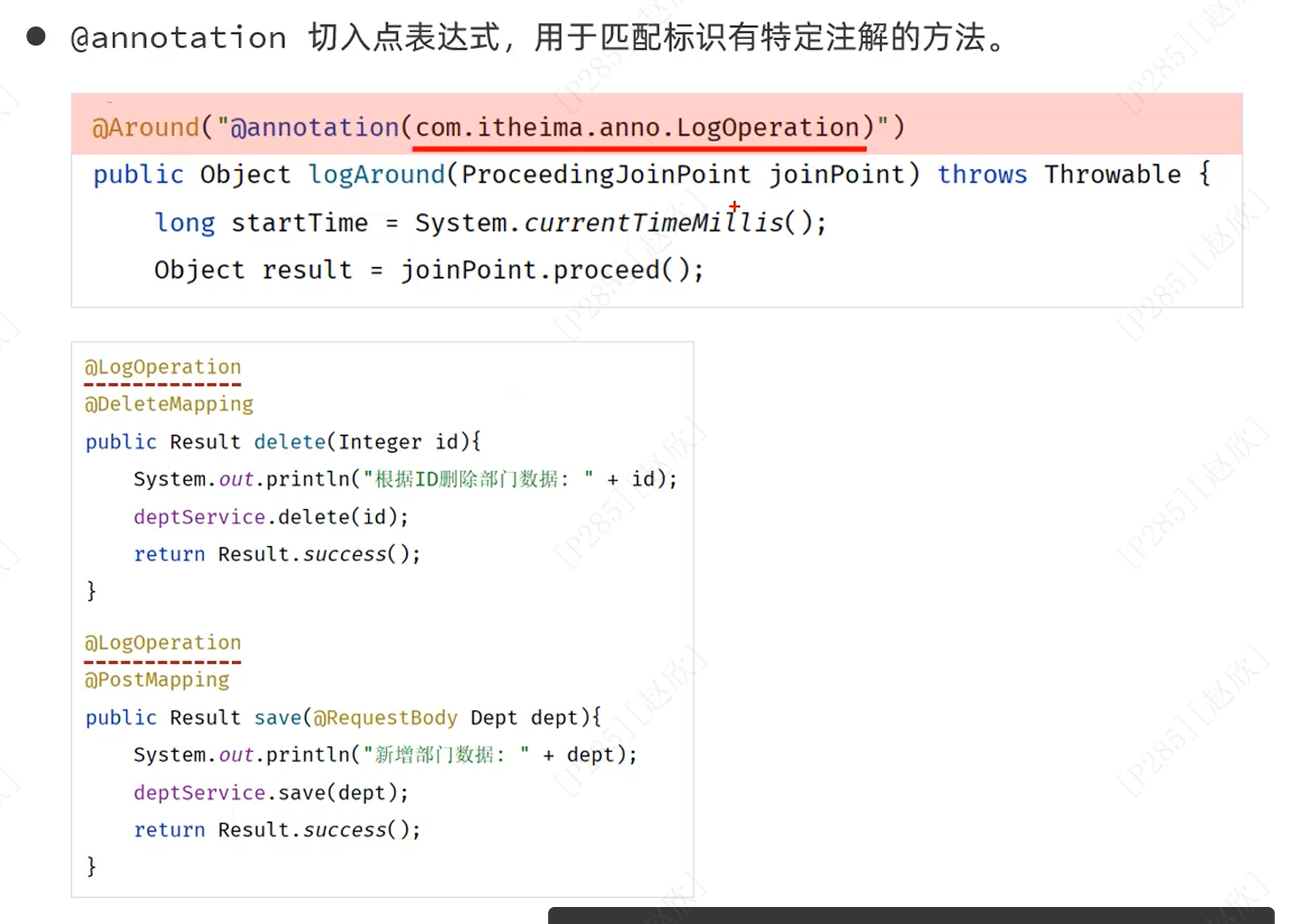
以上切入点表达式一般适用于普通的查询,对于特殊的查询使用逻辑运算符有些繁琐,因此在这里使用第二种写法:
新建一个包并新建一个注解类:
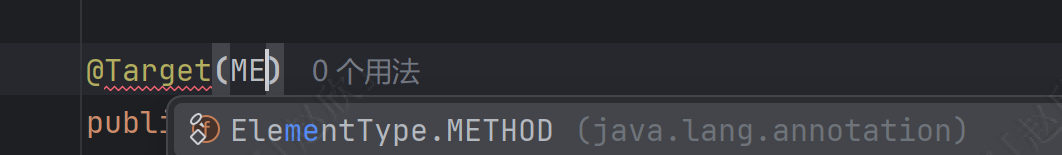
之后在方法上新增一个描述注解的注解:表明以下只能在方法上生效!
之后再加一个注解说明注解什么时候生效:
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)//表明在运行时生效以下是这个类的所有代码:
package com.itheima.anno;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)//表明这个注解只能加在方法上
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)//表明在运行时生效
public @interface LogOperation {
}之后在aspect文件中修改切入点表达式为上述类的位置:
@Before("@annotation(com.itheima.anno.LogOperation)")
public void before(){
log.info("方法开始执行");
}最后在需要调用的方法上添加注解LogOperation即可,如下所示:
@LogOperation
@Override
public List<Dept> list() {
List<Dept> deptList = deptMapper.list();
return deptList;
}
@LogOperation
@Override
public void delete(Integer id) {
deptMapper.delete(id);
}此时在aspect文件中就可以匹配到相关的方法!
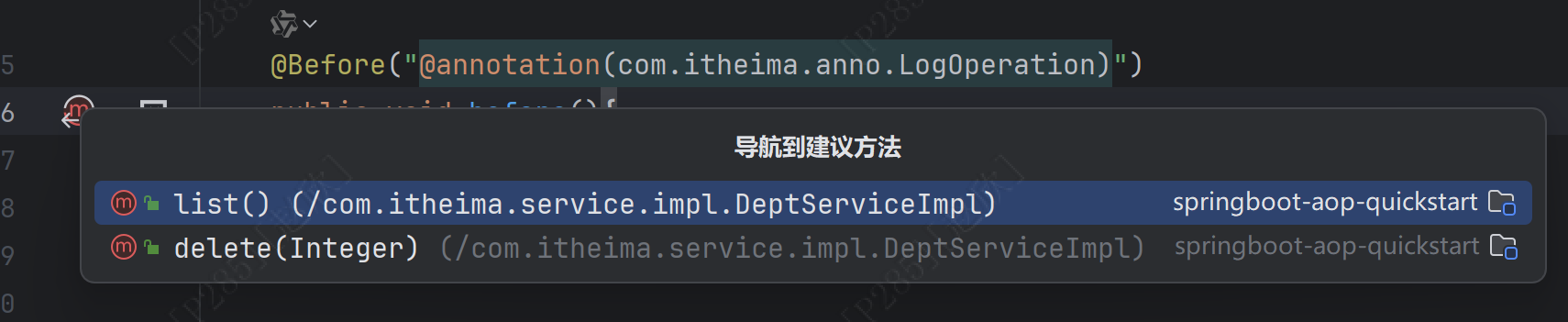
如果是使用环绕通知,需要使用proceedingjoinpoint来调用,如果是其余的使用joinpoint即可!!!
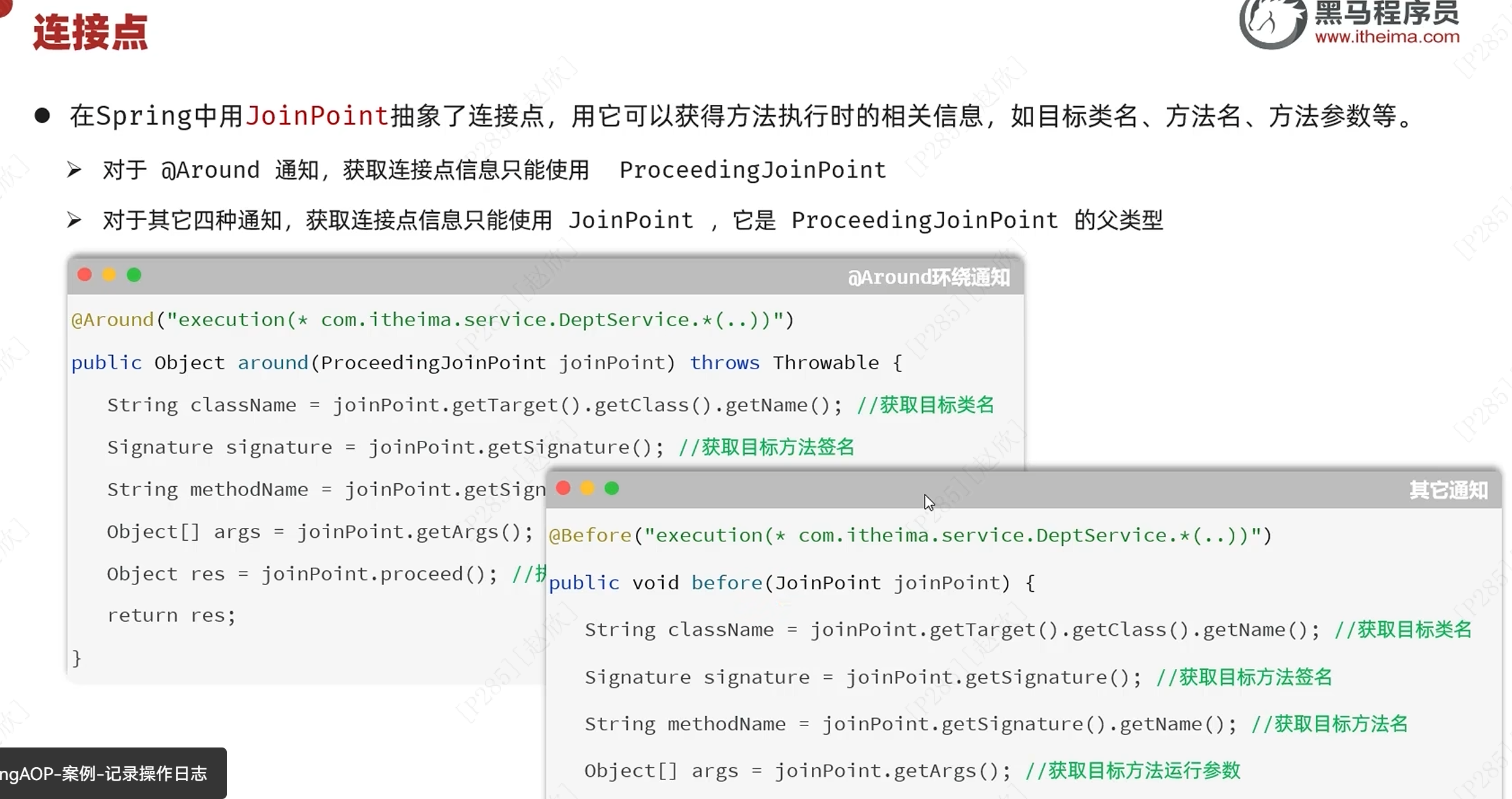
AOP的底层是动态代理技术!
之后在tilas中添加以下功能:
首先在数据库中添加表:
create table operate_log(
id int unsigned primary key auto_increment comment 'ID',
operate_emp_id int unsigned comment '操作人ID',
operate_time datetime comment '操作时间',
class_name varchar(100) comment '操作的类名',
method_name varchar(100) comment '操作的方法名',
method_params varchar(2000) comment '方法参数',
return_value varchar(2000) comment '返回值',
cost_time bigint unsigned comment '方法执行耗时,单位:ms'
) comment '操作日志表';之后在tilas案例的代码中创建相应的实体类,放在pojo软件包中:
package com.itheima.pojo;
import lombok.Data;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
@Data
public class OperateLog {
private Integer id; //ID
private Integer operateEmpId; //操作人ID
private LocalDateTime operateTime; //操作时间
private String className; //操作类名
private String methodName; //操作方法名
private String methodParams; //操作方法参数
private String returnValue; //操作方法返回值
private Long costTime; //操作耗时
}之后在mapper中添加以下代码去实现:
package com.itheima.mapper;
import com.itheima.pojo.OperateLog;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
@Mapper
public interface OperateLogMapper {
//插入日志数据
@Insert("insert into operate_log (operate_emp_id, operate_time, class_name, method_name, method_params, return_value, cost_time) " +
"values (#{operateEmpId}, #{operateTime}, #{className}, #{methodName}, #{methodParams}, #{returnValue}, #{costTime});")
public void insert(OperateLog log);
}之后在相应的pom文件中添加AOP依赖:
<!-- AOP起步依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>之后新建一个anno包,并存放一个注解:
代码如下:
package com.itheima.anno;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)//表明这个注解只能加在方法上
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)//表明在运行时生效
public @interface Log {
}alt+鼠标左键可以同时更改同一列,如下所示!
之后新建包和类:
代码如下:
package com.itheima.aop;
import com.itheima.mapper.OperateLogMapper;
import com.itheima.pojo.OperateLog;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.Arrays;
@Slf4j
@Aspect
@Component
public class OperationLogAspect {
@Autowired
private OperateLogMapper operateLogMapper;
@Around("@annotation(com.itheima.anno.Log)")
public Object logOperation(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//执行目标方法
Object result = joinPoint.proceed();
//计算耗时
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
long costTime = end - start;
//构建日志实体
OperateLog Log = new OperateLog();
Log.setOperateEmpId(getCurrentUserId()); // 这里需要你根据实际情况获取当前用户ID
Log.setOperateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
Log.setClassName(joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName());
Log.setMethodName(joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
Log.setMethodParams(Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()));
Log.setReturnValue(result != null ? result.toString() : "void");
Log.setCostTime(costTime);
// 保存日志
log.info("操作日志:{}",Log);
operateLogMapper.insert(Log);
return result;
}
private Integer getCurrentUserId() {
return 1;
}
}先将getCurrentUserId的返回值暂定为1,之后再更改!
之后在controller中的部门管理中进行修改,以部门的增删改为例,在方法前添加@Log注解:

之后回到aspect文件中,点击图标可得以下三个方法已经绑定AOP方法
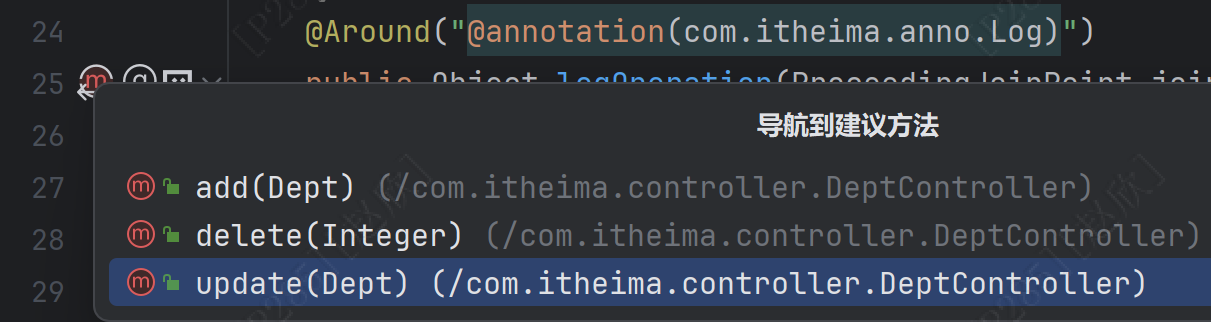
之后启动项目在前端的页面中打开: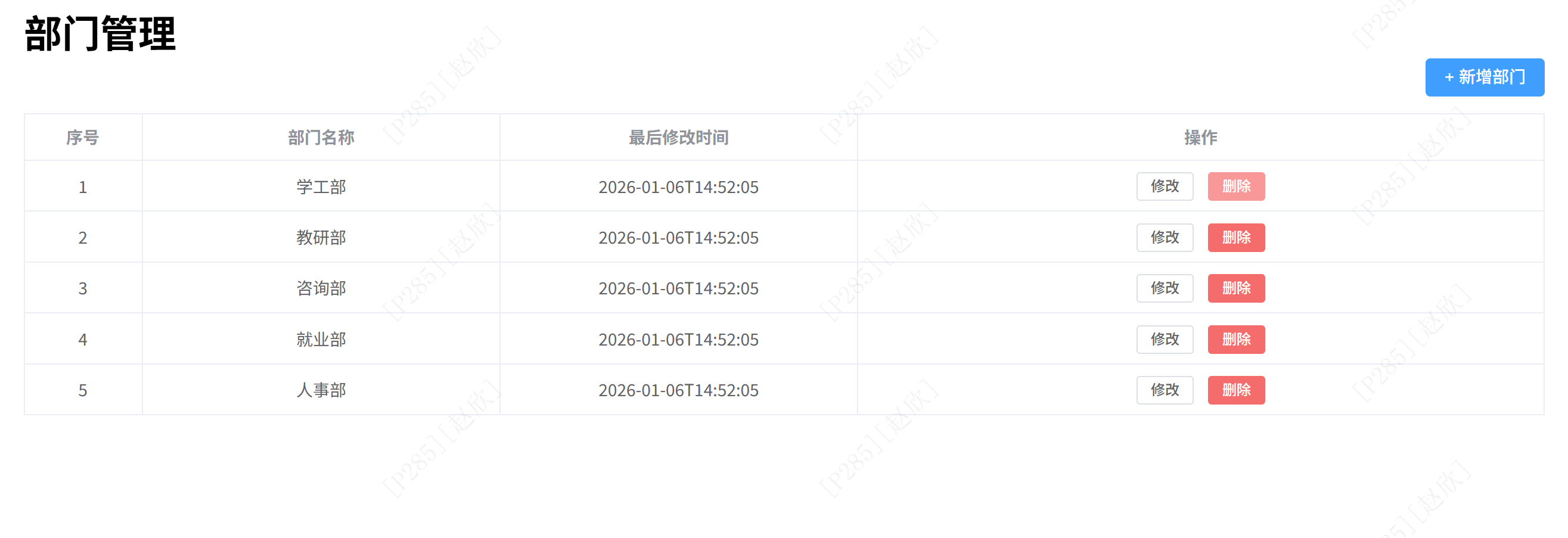
对部门进行增改删的操作,之后查看数据库是否存入数据:
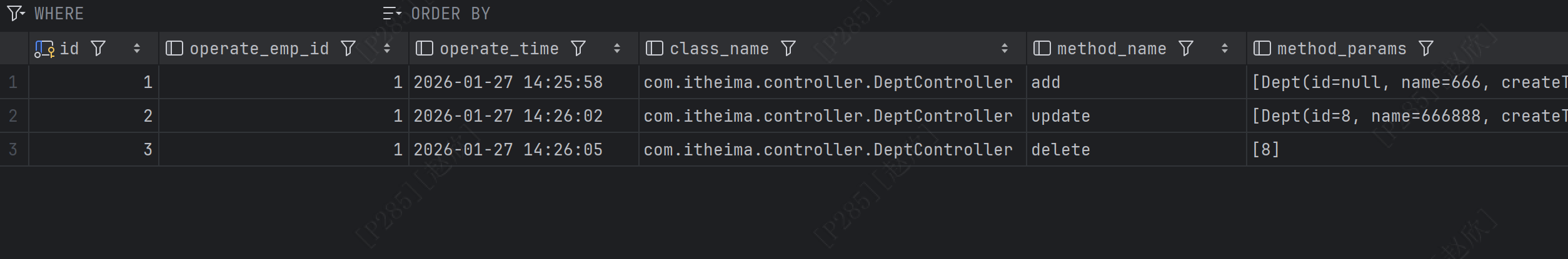
以上数据表明成功实现日志记录!
接下来要对userid进行优化,上面我们返回的是1这并不符合实际!

threadLocal:特点是在哪个线程存的只能在那个线程取!
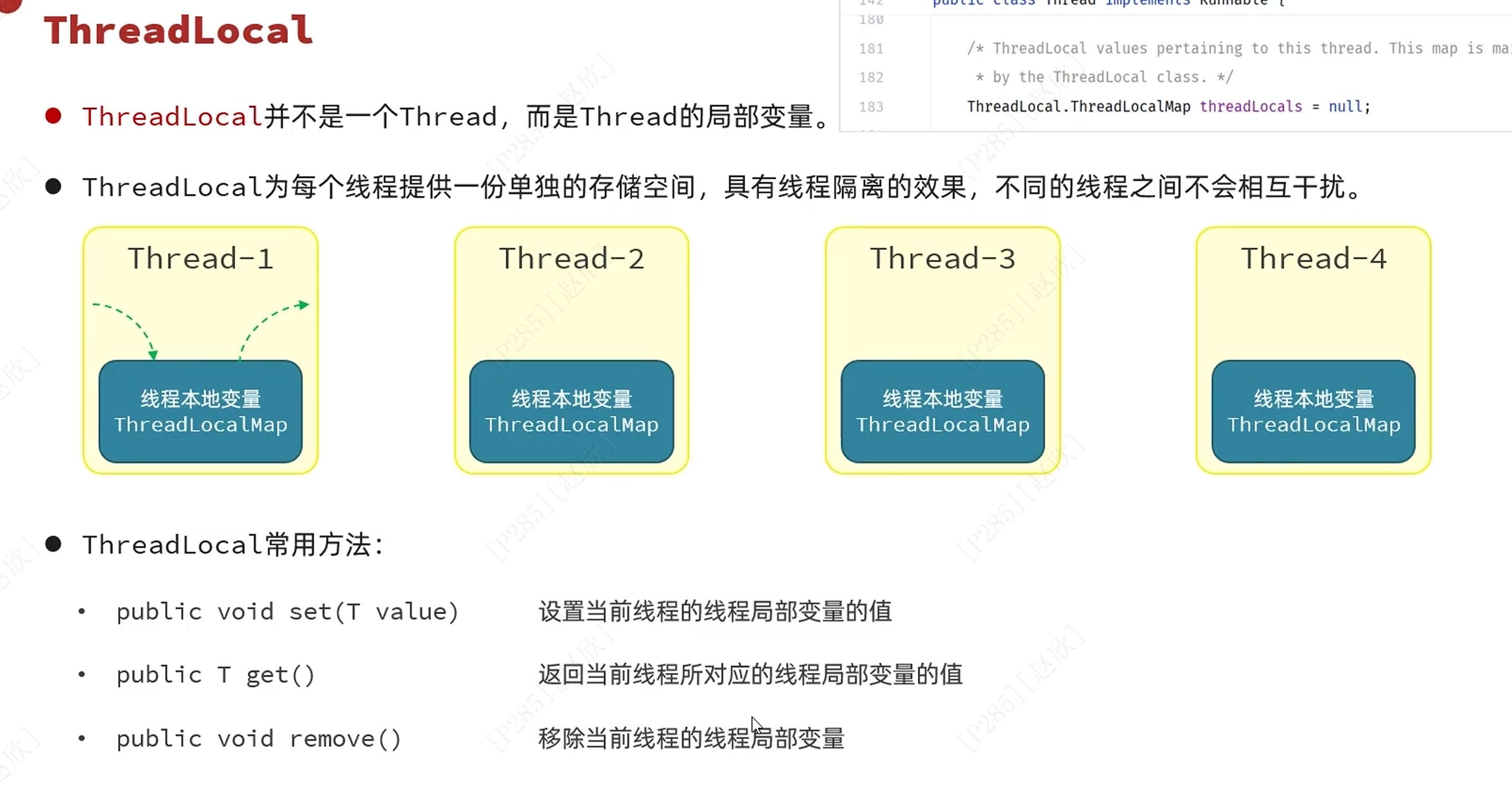
获取用户id步骤:
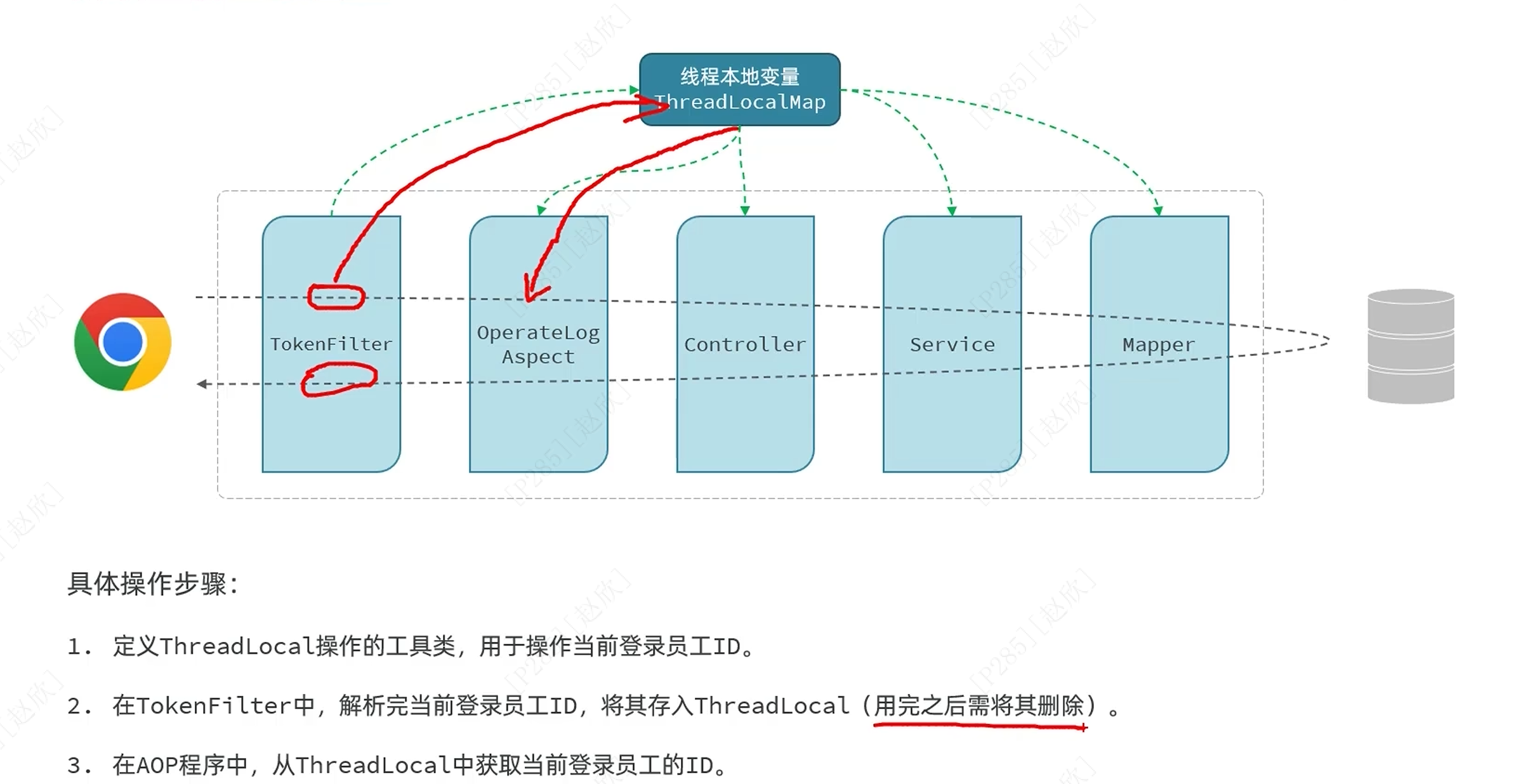
首先在utils包中新增一个类:
代码如下:
package com.itheima.utils;
public class CurrentHolder {
private static final ThreadLocal<Integer> CURRENT_LOCAL = new ThreadLocal<>();
public static void setCurrentId(Integer employeeId) {
CURRENT_LOCAL.set(employeeId);
}
public static Integer getCurrentId() {
return CURRENT_LOCAL.get();
}
public static void remove() {
CURRENT_LOCAL.remove();
}
}之后在解析令牌的代码中更改解析后令牌,还需要通过threadlocal存值并最后放行之后删除存入的值:
//检验令牌,如果不通过响应401
try{
Claims claims=JwtUtils.parseJWT(token);
Integer empId=Integer.valueOf(claims.get("id").toString());
CurrentHolder.setCurrentId(empId);
log.info("当前用户id为:{},将其存入threadlocal",empId);
}catch(Exception e){
response.setStatus(401);
return ;
}
//校验通过则放行
log.info("令牌校验通过");
filterChain.doFilter(request,response);
CurrentHolder.remove();//删除threadlocal中的数据
}最后在AOP类中更改返回的userid:
private Integer getCurrentUserId() {
return CurrentHolder.getCurrentId();
}演示效果:首先使用songjiang,123456进行登录

之后进行增改删的操作,在数据库中进行更改:

查阅数据库之后证明代码更改无误:

总结:
