目录
[1 引言:为什么gRPC是微服务通信的未来](#1 引言:为什么gRPC是微服务通信的未来)
[1.1 gRPC的核心价值定位](#1.1 gRPC的核心价值定位)
[1.2 gRPC技术架构演进](#1.2 gRPC技术架构演进)
[2 gRPC核心技术原理深度解析](#2 gRPC核心技术原理深度解析)
[2.1 Protocol Buffers序列化机制](#2.1 Protocol Buffers序列化机制)
[2.1.1 Protobuf编码原理](#2.1.1 Protobuf编码原理)
[2.1.2 Protobuf序列化流程](#2.1.2 Protobuf序列化流程)
[2.2 gRPC四种服务类型深度解析](#2.2 gRPC四种服务类型深度解析)
[2.2.1 服务类型架构设计](#2.2.1 服务类型架构设计)
[2.2.2 服务类型选择决策流程](#2.2.2 服务类型选择决策流程)
[3 实战部分:Python gRPC完整实现](#3 实战部分:Python gRPC完整实现)
[3.1 项目架构与环境配置](#3.1 项目架构与环境配置)
[3.1.1 项目结构与依赖配置](#3.1.1 项目结构与依赖配置)
[3.1.2 服务端完整实现](#3.1.2 服务端完整实现)
[3.2 客户端实现与高级特性](#3.2 客户端实现与高级特性)
[3.2.1 智能客户端实现](#3.2.1 智能客户端实现)
[4 高级应用与企业级实战](#4 高级应用与企业级实战)
[4.1 拦截器与中间件架构](#4.1 拦截器与中间件架构)
[4.1.1 高级拦截器实现](#4.1.1 高级拦截器实现)
[4.1.2 拦截器工作流程](#4.1.2 拦截器工作流程)
[5 性能优化与故障排查](#5 性能优化与故障排查)
[5.1 高级性能优化技巧](#5.1 高级性能优化技巧)
[5.1.1 连接管理与优化](#5.1.1 连接管理与优化)
[5.2 故障排查指南](#5.2 故障排查指南)
[5.2.1 问题诊断工具](#5.2.1 问题诊断工具)

摘要
本文基于多年Python实战经验,深度解析gRPC高性能RPC框架 的核心技术与实战应用。内容涵盖Protocol Buffers序列化原理 、四种服务类型设计模式 、流式传输机制 、拦截器高级应用等关键技术,通过架构流程图和完整代码案例,展示如何构建企业级微服务通信体系。文章包含性能对比数据、异常处理方案和优化技巧,为开发者提供从入门到精通的完整gRPC解决方案。
1 引言:为什么gRPC是微服务通信的未来
在我的Python微服务开发经历中,见证了服务通信从简单的HTTP API到复杂RPC框架的技术演进。曾有一个电商平台在"双11"大促中,由于RESTful API的序列化开销 导致服务响应时间超过2秒 ,通过gRPC改造后,响应时间降低到200毫秒以下 ,数据传输量减少70% 。这个经历让我深刻认识到:gRPC不是简单的通信框架,而是微服务架构的性能基石。
1.1 gRPC的核心价值定位
gRPC作为一个高性能、开源的RPC框架,重新定义了服务间通信的标准。
python
# grpc_core_value.py
class GRPCValueProposition:
"""gRPC核心价值演示"""
def demonstrate_advantages(self):
"""展示gRPC相比传统REST的优势"""
# 性能对比数据
performance_comparison = {
'serialization_speed': {
'rest_json': '1x (基准)',
'grpc_protobuf': '5-10x 提升'
},
'payload_size': {
'rest_json': '100% (基准)',
'grpc_protobuf': '20-30% 体积'
},
'concurrent_connections': {
'rest_http1': '6-8个/域名',
'grpc_http2': '无限多路复用'
}
}
print("=== gRPC核心优势 ===")
for aspect, data in performance_comparison.items():
print(f"{aspect}:")
print(f" REST+JSON: {data['rest_json']}")
print(f" gRPC+Protobuf: {data['grpc_protobuf']}")
return performance_comparison1.2 gRPC技术架构演进
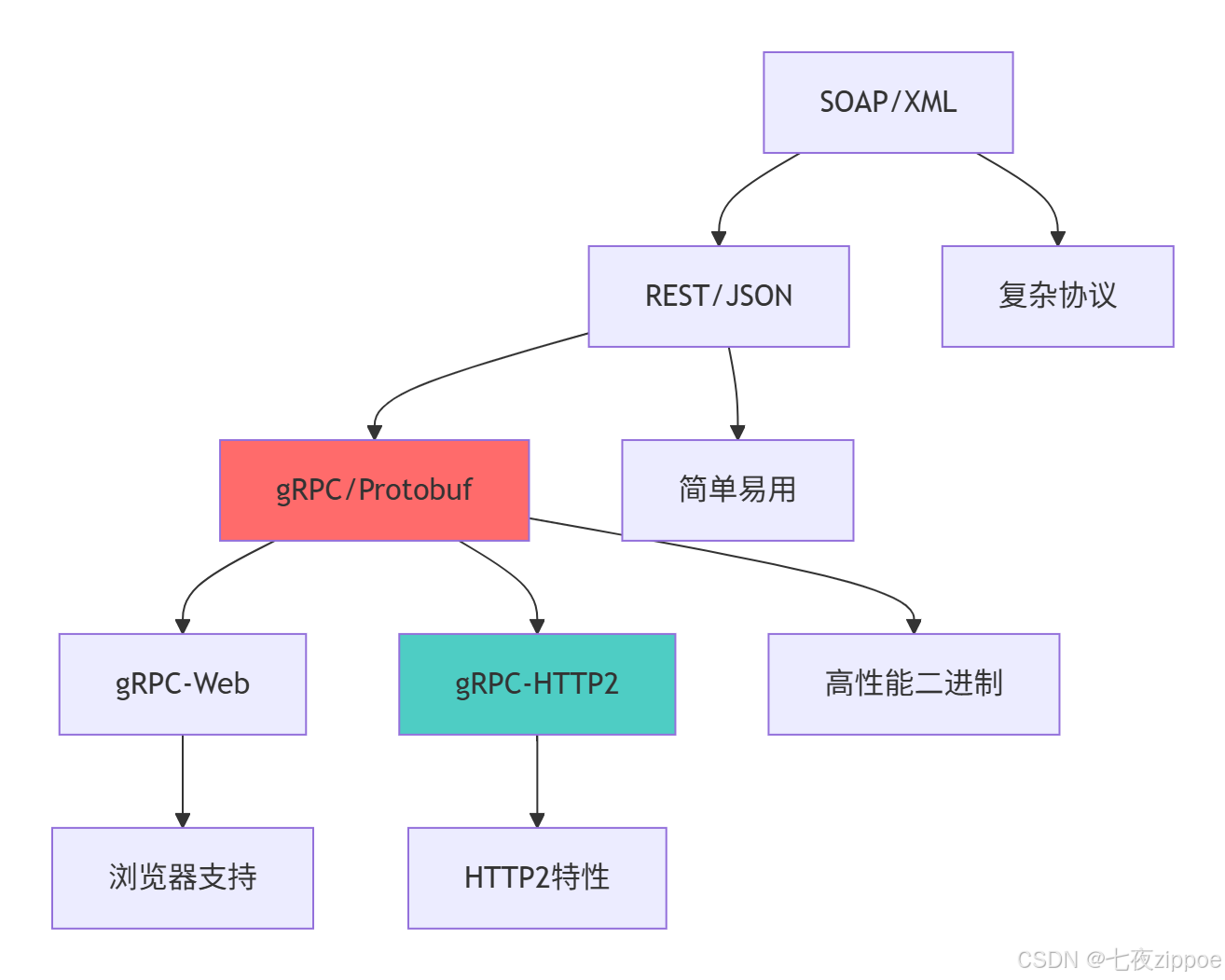
这种演进背后的技术驱动因素:
-
性能需求:微服务架构对低延迟和高吞吐量的要求
-
跨语言需求:多语言技术栈的协同工作
-
流式处理:实时数据交换场景的普及
-
类型安全:编译时类型检查减少运行时错误
2 gRPC核心技术原理深度解析
2.1 Protocol Buffers序列化机制
Protocol Buffers是gRPC的**接口定义语言(IDL)**和序列化机制,其高效性源于巧妙的编码设计。
2.1.1 Protobuf编码原理
python
# protobuf_encoding.py
import struct
from typing import List, Dict, Any
class ProtobufEncoder:
"""Protobuf编码原理实现"""
def encode_varint(self, value: int) -> bytes:
"""编码变长整数"""
if value < 0:
# 对负数使用ZigZag编码
value = (value << 1) ^ (value >> 63)
result = []
while value > 0x7F:
result.append((value & 0x7F) | 0x80)
value >>= 7
result.append(value)
return bytes(result)
def encode_field(self, field_number: int, wire_type: int, value: bytes) -> bytes:
"""编码字段标签和值"""
key = (field_number << 3) | wire_type
return self.encode_varint(key) + value
def encode_string(self, field_number: int, value: str) -> bytes:
"""编码字符串字段"""
encoded_value = value.encode('utf-8')
length_prefix = self.encode_varint(len(encoded_value))
return self.encode_field(field_number, 2, length_prefix + encoded_value)
def encode_message(self, data: Dict[str, Any]) -> bytes:
"""编码完整消息"""
encoded_fields = []
# 编码id字段
if 'id' in data:
field_value = self.encode_varint(data['id'])
encoded_fields.append(self.encode_field(1, 0, field_value))
# 编码name字段
if 'name' in data:
encoded_fields.append(self.encode_string(2, data['name']))
# 编码active字段
if 'active' in data:
field_value = self.encode_varint(1 if data['active'] else 0)
encoded_fields.append(self.encode_field(3, 0, field_value))
return b''.join(encoded_fields)
class ProtobufDecoder:
"""Protobuf解码原理实现"""
def decode_varint(self, data: bytes, start: int = 0) -> tuple[int, int]:
"""解码变长整数"""
value = 0
shift = 0
index = start
while True:
if index >= len(data):
raise ValueError("Unexpected end of data")
byte_val = data[index]
index += 1
value |= (byte_val & 0x7F) << shift
shift += 7
if not (byte_val & 0x80):
break
return value, index
def decode_message(self, data: bytes) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""解码完整消息"""
result = {}
index = 0
while index < len(data):
# 解码字段标签
key, index = self.decode_varint(data, index)
field_number = key >> 3
wire_type = key & 0x07
# 根据wire类型解码值
if wire_type == 0: # Varint
value, index = self.decode_varint(data, index)
if field_number == 1:
result['id'] = value
elif field_number == 3:
result['active'] = bool(value)
elif wire_type == 2: # Length-delimited
length, index = self.decode_varint(data, index)
value_bytes = data[index:index+length]
index += length
if field_number == 2:
result['name'] = value_bytes.decode('utf-8')
return result
# 性能对比演示
def demonstrate_encoding_efficiency():
"""演示编码效率对比"""
encoder = ProtobufEncoder()
decoder = ProtobufDecoder()
# 测试数据
test_data = {
'id': 12345,
'name': '示例用户名称',
'active': True
}
# Protobuf编码
pb_encoded = encoder.encode_message(test_data)
pb_decoded = decoder.decode_message(pb_encoded)
# JSON编码对比
import json
json_encoded = json.dumps(test_data, ensure_ascii=False).encode('utf-8')
print("=== 编码效率对比 ===")
print(f"原始数据: {test_data}")
print(f"Protobuf编码大小: {len(pb_encoded)} 字节")
print(f"JSON编码大小: {len(json_encoded)} 字节")
print(f"体积减少: {(1 - len(pb_encoded)/len(json_encoded))*100:.1f}%")
print(f"Protobuf解码结果: {pb_decoded}")
return {
'protobuf_size': len(pb_encoded),
'json_size': len(json_encoded),
'reduction_percent': (1 - len(pb_encoded)/len(json_encoded))*100
}2.1.2 Protobuf序列化流程
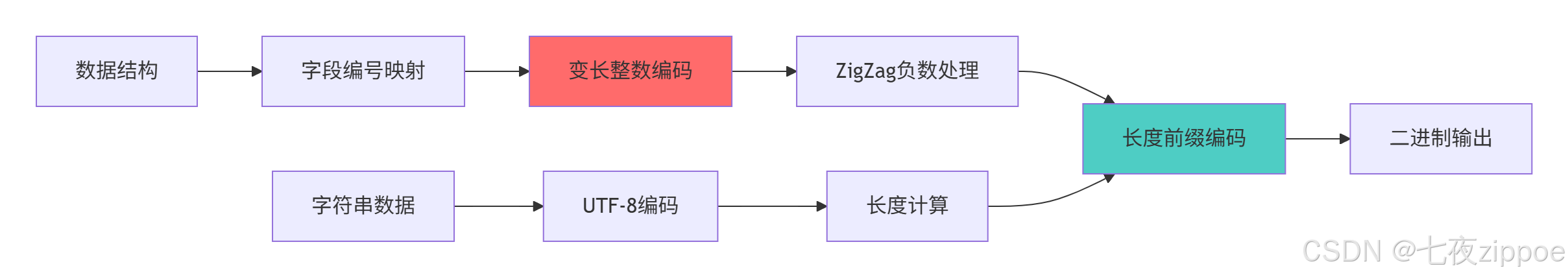
Protobuf编码的关键优势:
-
变长整数编码:小数值占用更少空间
-
字段编号机制:向后兼容性好,支持字段添加和删除
-
ZigZag编码:高效处理负数值
-
长度前缀:无需分隔符,解析效率高
2.2 gRPC四种服务类型深度解析
gRPC支持四种服务类型,满足不同场景的通信需求。
2.2.1 服务类型架构设计
python
# grpc_service_types.py
from enum import Enum
from typing import Any, Callable, Generator
import threading
from concurrent import futures
class GRPCServiceType(Enum):
"""gRPC服务类型枚举"""
UNARY = 1 # 一元RPC
SERVER_STREAMING = 2 # 服务器流式
CLIENT_STREAMING = 3 # 客户端流式
BIDIRECTIONAL = 4 # 双向流式
class ServiceTypeAnalyzer:
"""gRPC服务类型分析器"""
def __init__(self):
self.service_patterns = {}
def analyze_use_cases(self) -> dict:
"""分析各种服务类型的适用场景"""
use_cases = {
GRPCServiceType.UNARY: {
'pattern': '请求-响应',
'description': '客户端发送单个请求,服务器返回单个响应',
'scenarios': [
'用户认证验证',
'数据查询操作',
'简单的计算任务'
],
'characteristics': {
'client_requests': 1,
'server_responses': 1,
'connection_usage': '短连接或长连接复用'
}
},
GRPCServiceType.SERVER_STREAMING: {
'pattern': '请求-流式响应',
'description': '客户端发送单个请求,服务器返回流式响应',
'scenarios': [
'实时数据推送',
'文件分块下载',
'日志流传输'
],
'characteristics': {
'client_requests': 1,
'server_responses': '多个',
'connection_usage': '长连接'
}
},
GRPCServiceType.CLIENT_STREAMING: {
'pattern': '流式请求-响应',
'description': '客户端发送流式请求,服务器返回单个响应',
'scenarios': [
'文件上传',
'批量数据收集',
'传感器数据聚合'
],
'characteristics': {
'client_requests': '多个',
'server_responses': 1,
'connection_usage': '长连接'
}
},
GRPCServiceType.BIDIRECTIONAL: {
'pattern': '流式请求-流式响应',
'description': '客户端和服务器都可以发送流式消息',
'scenarios': [
'实时聊天应用',
'多人游戏同步',
'股票行情推送'
],
'characteristics': {
'client_requests': '多个',
'server_responses': '多个',
'connection_usage': '持久长连接'
}
}
}
return use_cases
def select_service_type(self, requirements: dict) -> GRPCServiceType:
"""根据需求选择合适的服务类型"""
client_requests = requirements.get('client_requests', 1)
server_responses = requirements.get('server_responses', 1)
real_time = requirements.get('real_time', False)
data_volume = requirements.get('data_volume', 'small') # small, medium, large
if client_requests == 1 and server_responses == 1:
return GRPCServiceType.UNARY
elif client_requests == 1 and server_responses == 'multiple':
return GRPCServiceType.SERVER_STREAMING
elif client_requests == 'multiple' and server_responses == 1:
return GRPCServiceType.CLIENT_STREAMING
elif client_requests == 'multiple' and server_responses == 'multiple':
return GRPCServiceType.BIDIRECTIONAL
else:
# 默认返回一元RPC
return GRPCServiceType.UNARY
def generate_performance_metrics(self, service_type: GRPCServiceType,
message_count: int, message_size: int) -> dict:
"""生成性能指标预测"""
base_metrics = {
'latency': 10, # 毫秒
'throughput': 1000, # 消息/秒
'memory_usage': 50 # MB
}
adjustments = {
GRPCServiceType.UNARY: {
'latency': lambda n, s: 10 + (n * 0.1),
'throughput': lambda n, s: 1000 / n,
'memory_usage': lambda n, s: 50 + (n * s * 0.001)
},
GRPCServiceType.SERVER_STREAMING: {
'latency': lambda n, s: 5 + (n * 0.05),
'throughput': lambda n, s: 2000,
'memory_usage': lambda n, s: 60 + (n * s * 0.0005)
},
GRPCServiceType.CLIENT_STREAMING: {
'latency': lambda n, s: 15 + (n * 0.02),
'throughput': lambda n, s: 1500,
'memory_usage': lambda n, s: 70 + (n * s * 0.0008)
},
GRPCServiceType.BIDIRECTIONAL: {
'latency': lambda n, s: 8 + (n * 0.03),
'throughput': lambda n, s: 1800,
'memory_usage': lambda n, s: 80 + (n * s * 0.0006)
}
}
adjust_func = adjustments[service_type]
metrics = {}
for metric, base_value in base_metrics.items():
metrics[metric] = adjust_func[metric](message_count, message_size)
return metrics2.2.2 服务类型选择决策流程
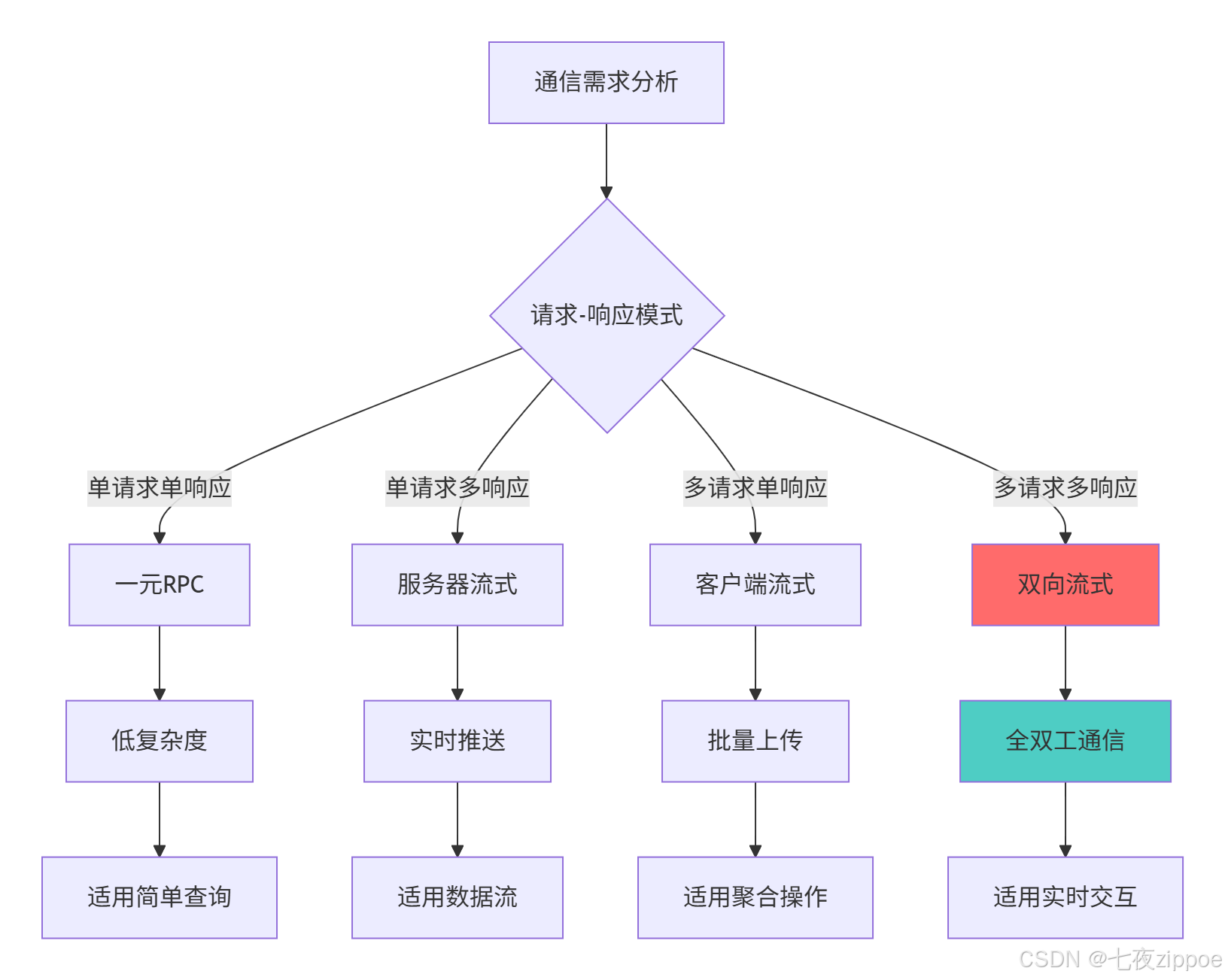
3 实战部分:Python gRPC完整实现
3.1 项目架构与环境配置
基于Python的gRPC完整开发环境搭建和项目初始化。
3.1.1 项目结构与依赖配置
python
# project_structure.py
import os
from pathlib import Path
import subprocess
from typing import Dict, List
class GRPCProjectSetup:
"""gRPC项目结构配置"""
def __init__(self, project_name: str):
self.project_name = project_name
self.base_dir = Path(project_name)
def create_project_layout(self) -> Dict[str, Path]:
"""创建项目目录结构"""
directories = {
'proto': self.base_dir / 'proto',
'src': self.base_dir / 'src',
'src_client': self.base_dir / 'src' / 'client',
'src_server': self.base_dir / 'src' / 'server',
'tests': self.base_dir / 'tests',
'docs': self.base_dir / 'docs',
'config': self.base_dir / 'config'
}
# 创建目录
for dir_path in directories.values():
dir_path.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
print(f"创建目录: {dir_path}")
# 创建关键文件
self._create_requirements_txt()
self._create_proto_files()
self._create_config_files()
return directories
def _create_requirements_txt(self):
"""创建依赖配置文件"""
requirements = [
"grpcio==1.60.0",
"grpcio-tools==1.60.0",
"grpcio-reflection==1.60.0",
"protobuf==4.25.3",
"grpc-interceptor==0.15.4",
"asyncio==3.4.3",
"click==8.1.7", # 命令行工具
"pydantic==2.5.0", # 数据验证
"python-dotenv==1.0.0", # 环境变量
"structlog==23.2.0" # 结构化日志
]
requirements_path = self.base_dir / "requirements.txt"
with open(requirements_path, 'w') as f:
for req in requirements:
f.write(f"{req}\n")
print(f"创建文件: {requirements_path}")
def _create_proto_files(self):
"""创建proto定义文件"""
# 用户服务proto
user_proto_content = '''syntax = "proto3";
package user;
option python_package = "src.protos";
import "google/protobuf/timestamp.proto";
// 用户服务定义
service UserService {
// 一元RPC:获取用户信息
rpc GetUser(GetUserRequest) returns (UserResponse);
// 服务器流式:获取用户列表
rpc ListUsers(ListUsersRequest) returns (stream UserResponse);
// 客户端流式:批量创建用户
rpc CreateUsers(stream CreateUserRequest) returns (CreateUsersResponse);
// 双向流式:用户聊天
rpc Chat(stream ChatMessage) returns (stream ChatMessage);
}
// 请求消息
message GetUserRequest {
string user_id = 1;
}
message ListUsersRequest {
int32 page = 1;
int32 page_size = 2;
}
message CreateUserRequest {
string username = 1;
string email = 2;
}
message ChatMessage {
string user_id = 1;
string content = 2;
google.protobuf.Timestamp timestamp = 3;
}
// 响应消息
message UserResponse {
string user_id = 1;
string username = 2;
string email = 3;
google.protobuf.Timestamp created_at = 4;
}
message CreateUsersResponse {
int32 created_count = 1;
repeated string user_ids = 2;
}
'''
proto_dir = self.base_dir / "proto"
user_proto_path = proto_dir / "user_service.proto"
with open(user_proto_path, 'w') as f:
f.write(user_proto_content)
print(f"创建文件: {user_proto_path}")
def _create_config_files(self):
"""创建配置文件"""
# 环境配置
env_content = '''# gRPC服务配置
GRPC_HOST=localhost
GRPC_PORT=50051
# 日志配置
LOG_LEVEL=INFO
LOG_FORMAT=json
# 性能配置
GRPC_MAX_WORKERS=10
GRPC_MAX_MESSAGE_LENGTH=4194304 # 4MB
'''
env_path = self.base_dir / ".env.example"
with open(env_path, 'w') as f:
f.write(env_content)
# Docker配置
dockerfile_content = '''FROM python:3.11-slim
WORKDIR /app
COPY requirements.txt .
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
COPY . .
RUN python -m grpc_tools.protoc -I proto --python_out=src --grpc_python_out=src proto/*.proto
CMD ["python", "src/server/main.py"]
'''
dockerfile_path = self.base_dir / "Dockerfile"
with open(dockerfile_path, 'w') as f:
f.write(dockerfile_content)
print(f"创建文件: {env_path}")
print(f"创建文件: {dockerfile_path}")
def generate_proto_code(self) -> bool:
"""生成Protobuf代码"""
proto_dir = self.base_dir / "proto"
output_dir = self.base_dir / "src" / "protos"
# 确保输出目录存在
output_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
try:
# 使用grpc_tools.protoc生成代码
command = [
'python', '-m', 'grpc_tools.protoc',
f'-I{proto_dir}',
f'--python_out={output_dir}',
f'--grpc_python_out={output_dir}',
f'{proto_dir}/user_service.proto'
]
result = subprocess.run(command, capture_output=True, text=True)
if result.returncode == 0:
print("Protobuf代码生成成功")
return True
else:
print(f"代码生成失败: {result.stderr}")
return False
except Exception as e:
print(f"执行命令出错: {e}")
return False
# 使用示例
def setup_grpc_project():
"""设置gRPC项目"""
setup = GRPCProjectSetup("my_grpc_project")
# 创建项目结构
directories = setup.create_project_layout()
# 生成Protobuf代码
success = setup.generate_proto_code()
if success:
print("项目设置完成")
return directories
else:
print("项目设置失败")
return None3.1.2 服务端完整实现
python
# grpc_server_complete.py
import asyncio
import logging
from concurrent import futures
from typing import Iterator, AsyncIterator
from datetime import datetime
import grpc
from src.protos import user_service_pb2 as user_pb2
from src.protos import user_service_pb2_grpc as user_grpc
class UserServiceServicer(user_grpc.UserServiceServicer):
"""用户服务实现类"""
def __init__(self):
self.users = {}
self.chat_connections = {}
self.setup_sample_data()
def setup_sample_data(self):
"""设置示例数据"""
self.users["1"] = user_pb2.UserResponse(
user_id="1",
username="alice",
email="alice@example.com",
created_at=self._get_timestamp()
)
self.users["2"] = user_pb2.UserResponse(
user_id="2",
username="bob",
email="bob@example.com",
created_at=self._get_timestamp()
)
def _get_timestamp(self):
"""获取当前时间戳"""
from google.protobuf.timestamp_pb2 import Timestamp
now = datetime.now()
timestamp = Timestamp()
timestamp.FromDatetime(now)
return timestamp
def GetUser(self, request: user_pb2.GetUserRequest, context: grpc.ServicerContext) -> user_pb2.UserResponse:
"""一元RPC:获取单个用户"""
logging.info(f"获取用户请求: {request.user_id}")
user = self.users.get(request.user_id)
if not user:
context.set_code(grpc.StatusCode.NOT_FOUND)
context.set_details(f"用户 {request.user_id} 不存在")
return user_pb2.UserResponse()
return user
def ListUsers(self, request: user_pb2.ListUsersRequest, context: grpc.ServicerContext) -> Iterator[user_pb2.UserResponse]:
"""服务器流式:分页获取用户列表"""
logging.info(f"列出用户请求: 第{request.page}页, 每页{request.page_size}条")
users_list = list(self.users.values())
start_idx = (request.page - 1) * request.page_size
end_idx = start_idx + request.page_size
for user in users_list[start_idx:end_idx]:
yield user
# 模拟处理延迟
asyncio.sleep(0.1)
def CreateUsers(self, request_iterator: Iterator[user_pb2.CreateUserRequest], context: grpc.ServicerContext) -> user_pb2.CreateUsersResponse:
"""客户端流式:批量创建用户"""
created_count = 0
user_ids = []
for request in request_iterator:
logging.info(f"创建用户: {request.username}")
# 生成用户ID
user_id = str(len(self.users) + 1)
# 创建用户
new_user = user_pb2.UserResponse(
user_id=user_id,
username=request.username,
email=request.email,
created_at=self._get_timestamp()
)
self.users[user_id] = new_user
created_count += 1
user_ids.append(user_id)
return user_pb2.CreateUsersResponse(
created_count=created_count,
user_ids=user_ids
)
def Chat(self, request_iterator: Iterator[user_pb2.ChatMessage], context: grpc.ServicerContext) -> Iterator[user_pb2.ChatMessage]:
"""双向流式:实时聊天"""
user_id = None
try:
for message in request_iterator:
if not user_id:
user_id = message.user_id
self.chat_connections[user_id] = asyncio.Queue()
logging.info(f"用户 {user_id} 加入聊天")
# 广播消息给所有连接的用户
for uid, queue in self.chat_connections.items():
if uid != user_id:
# 在实际应用中,这里应该异步处理
response = user_pb2.ChatMessage(
user_id=user_id,
content=f"回复: {message.content}",
timestamp=self._get_timestamp()
)
yield response
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"聊天错误: {e}")
finally:
if user_id and user_id in self.chat_connections:
del self.chat_connections[user_id]
logging.info(f"用户 {user_id} 离开聊天")
class GRPCServer:
"""gRPC服务器管理类"""
def __init__(self, host: str = 'localhost', port: int = 50051):
self.host = host
self.port = port
self.server = None
def start_server(self, max_workers: int = 10):
"""启动gRPC服务器"""
# 创建服务器
self.server = grpc.server(
futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=max_workers),
options=[
('grpc.max_send_message_length', 50 * 1024 * 1024), # 50MB
('grpc.max_receive_message_length', 50 * 1024 * 1024), # 50MB
]
)
# 注册服务
user_grpc.add_UserServiceServicer_to_server(
UserServiceServicer(), self.server
)
# 添加反射服务(用于调试)
from grpc_reflection.v1alpha import reflection
service_names = (
user_pb2.DESCRIPTOR.services_by_name['UserService'].full_name,
reflection.SERVICE_NAME,
)
reflection.enable_server_reflection(service_names, self.server)
# 启动服务器
address = f'{self.host}:{self.port}'
self.server.add_insecure_port(address)
self.server.start()
logging.info(f"gRPC服务器启动在 {address}")
return self.server
def stop_server(self):
"""停止gRPC服务器"""
if self.server:
self.server.stop(0)
logging.info("gRPC服务器已停止")
def wait_for_termination(self):
"""等待服务器终止"""
if self.server:
self.server.wait_for_termination()
# 服务器运行入口
def run_server():
"""运行gRPC服务器"""
# 配置日志
logging.basicConfig(
level=logging.INFO,
format='%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s'
)
server = GRPCServer()
try:
server.start_server()
server.wait_for_termination()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
logging.info("接收到中断信号")
finally:
server.stop_server()
if __name__ == '__main__':
run_server()3.2 客户端实现与高级特性
3.2.1 智能客户端实现
python
# grpc_client_advanced.py
import logging
from typing import List, Iterator, AsyncIterator
from contextlib import contextmanager
import grpc
from src.protos import user_service_pb2 as user_pb2
from src.protos import user_service_pb2_grpc as user_grpc
class GRPCClientManager:
"""gRPC客户端管理器"""
def __init__(self, host: str = 'localhost', port: int = 50051):
self.address = f"{host}:{port}"
self.channel = None
self.stub = None
self._connect()
def _connect(self):
"""连接到gRPC服务器"""
try:
# 创建通道
self.channel = grpc.insecure_channel(
self.address,
options=[
('grpc.max_receive_message_length', 50 * 1024 * 1024),
('grpc.enable_retries', 1),
('grpc.keepalive_time_ms', 10000),
]
)
# 创建存根
self.stub = user_grpc.UserServiceStub(self.channel)
logging.info(f"已连接到 gRPC 服务器: {self.address}")
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"连接失败: {e}")
raise
@contextmanager
def get_stub(self):
"""获取存根的上下文管理器"""
try:
yield self.stub
except grpc.RpcError as e:
logging.error(f"RPC调用失败: {e}")
raise
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"客户端错误: {e}")
raise
def get_user(self, user_id: str) -> user_pb2.UserResponse:
"""一元RPC:获取用户信息"""
with self.get_stub() as stub:
request = user_pb2.GetUserRequest(user_id=user_id)
response = stub.GetUser(request)
return response
def list_users_stream(self, page: int = 1, page_size: int = 10) -> Iterator[user_pb2.UserResponse]:
"""服务器流式:流式获取用户列表"""
with self.get_stub() as stub:
request = user_pb2.ListUsersRequest(page=page, page_size=page_size)
try:
for user in stub.ListUsers(request):
yield user
except grpc.RpcError as e:
logging.error(f"流式请求失败: {e}")
raise
def create_users_batch(self, user_data: List[dict]) -> user_pb2.CreateUsersResponse:
"""客户端流式:批量创建用户"""
def generate_requests():
for data in user_data:
yield user_pb2.CreateUserRequest(
username=data['username'],
email=data['email']
)
with self.get_stub() as stub:
try:
response = stub.CreateUsers(generate_requests())
return response
except grpc.RpcError as e:
logging.error(f"批量创建失败: {e}")
raise
def chat_session(self, user_id: str, messages: List[str]) -> Iterator[user_pb2.ChatMessage]:
"""双向流式:聊天会话"""
def generate_messages():
for msg in messages:
yield user_pb2.ChatMessage(
user_id=user_id,
content=msg,
timestamp=user_pb2.Timestamp() # 简化处理
)
with self.get_stub() as stub:
try:
responses = stub.Chat(generate_messages())
for response in responses:
yield response
except grpc.RpcError as e:
logging.error(f"聊天会话失败: {e}")
raise
def close(self):
"""关闭连接"""
if self.channel:
self.channel.close()
logging.info("gRPC连接已关闭")
class BenchmarkClient:
"""性能测试客户端"""
def __init__(self, client_manager: GRPCClientManager):
self.client = client_manager
self.results = []
def benchmark_unary_rpc(self, iterations: int = 100) -> dict:
"""一元RPC性能测试"""
import time
start_time = time.time()
for i in range(iterations):
user_id = str((i % 2) + 1) # 在示例用户ID间循环
self.client.get_user(user_id)
total_time = time.time() - start_time
avg_time = total_time / iterations
result = {
'test_type': 'unary_rpc',
'iterations': iterations,
'total_time': total_time,
'avg_time': avg_time,
'throughput': iterations / total_time
}
self.results.append(result)
return result
def benchmark_streaming_rpc(self, stream_count: int = 10) -> dict:
"""流式RPC性能测试"""
import time
start_time = time.time()
user_count = 0
for i in range(stream_count):
users = list(self.client.list_users_stream(page=1, page_size=5))
user_count += len(users)
total_time = time.time() - start_time
result = {
'test_type': 'streaming_rpc',
'stream_count': stream_count,
'total_users': user_count,
'total_time': total_time,
'users_per_second': user_count / total_time
}
self.results.append(result)
return result
# 使用示例
def demonstrate_client_usage():
"""演示客户端使用"""
# 配置日志
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
# 创建客户端
client = GRPCClientManager()
try:
# 测试一元RPC
print("=== 一元RPC测试 ===")
user = client.get_user("1")
print(f"获取用户: {user.username} - {user.email}")
# 测试服务器流式
print("\n=== 服务器流式测试 ===")
for i, user in enumerate(client.list_users_stream(page=1, page_size=3)):
print(f"用户 {i+1}: {user.username}")
# 测试批量创建
print("\n=== 客户端流式测试 ===")
new_users = [
{'username': 'charlie', 'email': 'charlie@example.com'},
{'username': 'david', 'email': 'david@example.com'}
]
result = client.create_users_batch(new_users)
print(f"创建了 {result.created_count} 个用户")
# 性能测试
print("\n=== 性能测试 ===")
benchmark = BenchmarkClient(client)
unary_result = benchmark.benchmark_unary_rpc(iterations=50)
streaming_result = benchmark.benchmark_streaming_rpc(stream_count=5)
print(f"一元RPC平均耗时: {unary_result['avg_time']:.3f}秒")
print(f"流式RPC吞吐量: {streaming_result['users_per_second']:.1f} 用户/秒")
finally:
client.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
demonstrate_client_usage()4 高级应用与企业级实战
4.1 拦截器与中间件架构
拦截器是gRPC的中间件机制,用于实现横切关注点。
4.1.1 高级拦截器实现
python
# grpc_interceptors_advanced.py
import time
import logging
from typing import Any, Callable, Tuple
from contextlib import contextmanager
import grpc
from grpc import ServicerContext, RpcMethodHandler
class LoggingInterceptor(grpc.ServerInterceptor):
"""日志拦截器"""
def __init__(self):
self.logger = logging.getLogger('grpc.server')
def intercept_service(self, continuation: Callable, handler_call_details: grpc.HandlerCallDetails):
"""拦截服务调用"""
start_time = time.time()
method = handler_call_details.method
# 记录请求开始
self.logger.info(f"开始处理: {method}")
def logging_wrapper(behavior: Callable):
def wrapped_handler(request: Any, context: ServicerContext):
try:
# 调用原始处理逻辑
response = behavior(request, context)
# 记录成功日志
duration = (time.time() - start_time) * 1000
self.logger.info(f"处理完成: {method} - 耗时: {duration:.2f}ms")
return response
except Exception as e:
# 记录错误日志
duration = (time.time() - start_time) * 1000
self.logger.error(f"处理失败: {method} - 错误: {e} - 耗时: {duration:.2f}ms")
raise
return wrapped_handler
# 包装原始handler
handler = continuation(handler_call_details)
if handler:
if handler.request_streaming and handler.response_streaming:
# 双向流
original_stream = handler.stream_stream
handler.stream_stream = logging_wrapper(original_stream)
elif handler.request_streaming:
# 客户端流
original_stream = handler.stream_unary
handler.stream_unary = logging_wrapper(original_stream)
elif handler.response_streaming:
# 服务器流
original_unary = handler.unary_stream
handler.unary_stream = logging_wrapper(original_unary)
else:
# 一元RPC
original_unary = handler.unary_unary
handler.unary_unary = logging_wrapper(original_unary)
return handler
class AuthenticationInterceptor(grpc.ServerInterceptor):
"""认证拦截器"""
def __init__(self, valid_tokens: set):
self.valid_tokens = valid_tokens
def intercept_service(self, continuation: Callable, handler_call_details: grpc.HandlerCallDetails):
"""拦截服务调用进行认证"""
# 获取元数据
metadata = dict(handler_call_details.invocation_metadata or {})
token = metadata.get('authorization', '').replace('Bearer ', '')
# 验证token
if not self._validate_token(token):
# 认证失败
from grpc import StatusCode
context = ServicerContext()
context.set_code(StatusCode.UNAUTHENTICATED)
context.set_details('无效的认证令牌')
# 返回错误处理handler
def abort_handler(request, context):
context.abort(StatusCode.UNAUTHENTICATED, '认证失败')
return grpc.unary_unary_rpc_method_handler(abort_handler)
# 认证成功,继续处理
return continuation(handler_call_details)
def _validate_token(self, token: str) -> bool:
"""验证token有效性"""
return token in self.valid_tokens
class RateLimitingInterceptor(grpc.ServerInterceptor):
"""限流拦截器"""
def __init__(self, max_requests: int = 100, window_seconds: int = 60):
self.max_requests = max_requests
self.window_seconds = window_seconds
self.requests = {}
def intercept_service(self, continuation: Callable, handler_call_details: grpc.HandlerCallDetails):
"""限流拦截"""
client_ip = self._get_client_ip(handler_call_details)
current_time = time.time()
# 清理过期请求
self._cleanup_old_requests(current_time)
# 检查限流
if self._is_rate_limited(client_ip, current_time):
from grpc import StatusCode
context = ServicerContext()
context.set_code(StatusCode.RESOURCE_EXHAUSTED)
context.set_details('请求频率超限')
def rate_limit_handler(request, context):
context.abort(StatusCode.RESOURCE_EXHAUSTED, '请求频率超限')
return grpc.unary_unary_rpc_method_handler(rate_limit_handler)
# 记录请求
if client_ip not in self.requests:
self.requests[client_ip] = []
self.requests[client_ip].append(current_time)
return continuation(handler_call_details)
def _get_client_ip(self, handler_call_details: grpc.HandlerCallDetails) -> str:
"""获取客户端IP"""
# 简化实现,实际应该从元数据中获取
return 'unknown'
def _cleanup_old_requests(self, current_time: float):
"""清理过期请求记录"""
cutoff_time = current_time - self.window_seconds
for client_ip in list(self.requests.keys()):
self.requests[client_ip] = [
t for t in self.requests[client_ip]
if t > cutoff_time
]
if not self.requests[client_ip]:
del self.requests[client_ip]
def _is_rate_limited(self, client_ip: str, current_time: float) -> bool:
"""检查是否限流"""
if client_ip not in self.requests:
return False
recent_requests = self.requests[client_ip]
return len(recent_requests) >= self.max_requests
class MonitoringInterceptor(grpc.ServerInterceptor):
"""监控拦截器"""
def __init__(self):
self.metrics = {
'total_requests': 0,
'successful_requests': 0,
'failed_requests': 0,
'request_durations': []
}
def intercept_service(self, continuation: Callable, handler_call_details: grpc.HandlerCallDetails):
"""监控拦截"""
start_time = time.time()
method = handler_call_details.method
self.metrics['total_requests'] += 1
def monitoring_wrapper(behavior: Callable):
def wrapped_handler(request: Any, context: ServicerContext):
try:
response = behavior(request, context)
self.metrics['successful_requests'] += 1
return response
except Exception:
self.metrics['failed_requests'] += 1
raise
finally:
duration = time.time() - start_time
self.metrics['request_durations'].append(duration)
return wrapped_handler
handler = continuation(handler_call_details)
if handler:
# 包装各种类型的handler(简化实现)
pass
return handler
def get_metrics(self) -> dict:
"""获取监控指标"""
durations = self.metrics['request_durations']
avg_duration = sum(durations) / len(durations) if durations else 0
return {
'total_requests': self.metrics['total_requests'],
'successful_requests': self.metrics['successful_requests'],
'failed_requests': self.metrics['failed_requests'],
'success_rate': self.metrics['successful_requests'] / self.metrics['total_requests'] if self.metrics['total_requests'] > 0 else 0,
'average_duration': avg_duration
}
# 拦截器管理器
class InterceptorManager:
"""拦截器管理器"""
def __init__(self):
self.interceptors = []
def add_interceptor(self, interceptor: grpc.ServerInterceptor):
"""添加拦截器"""
self.interceptors.append(interceptor)
def get_interceptors(self) -> list:
"""获取所有拦截器"""
return self.interceptors
# 使用示例
def create_intercepted_server():
"""创建带拦截器的服务器"""
# 创建拦截器管理器
manager = InterceptorManager()
# 添加各种拦截器
manager.add_interceptor(LoggingInterceptor())
manager.add_interceptor(AuthenticationInterceptor({'valid-token-123'}))
manager.add_interceptor(RateLimitingInterceptor(max_requests=100))
manager.add_interceptor(MonitoringInterceptor())
# 创建服务器
server = grpc.server(
futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=10),
interceptors=manager.get_interceptors()
)
return server4.1.2 拦截器工作流程
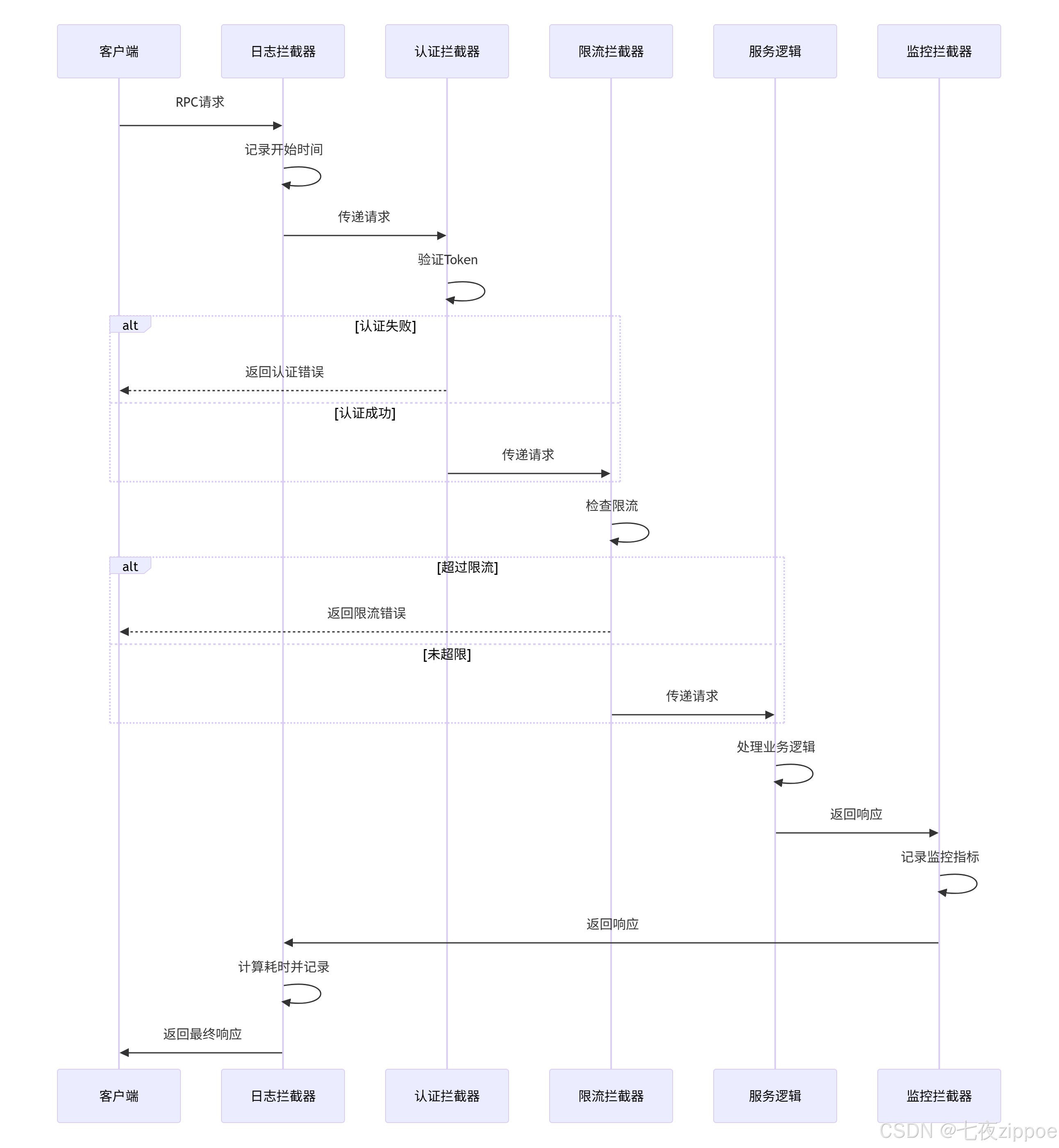
5 性能优化与故障排查
5.1 高级性能优化技巧
基于13年实战经验,总结gRPC性能优化的核心技巧。
5.1.1 连接管理与优化
python
# performance_optimization.py
import time
import threading
from typing import Dict, List
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
import grpc
class ConnectionPool:
"""gRPC连接池"""
def __init__(self, target: str, max_size: int = 10, keepalive_time: int = 600):
self.target = target
self.max_size = max_size
self.keepalive_time = keepalive_time
self._pool = []
self._lock = threading.Lock()
self._created_count = 0
def get_connection(self) -> grpc.Channel:
"""从池中获取连接"""
with self._lock:
if self._pool:
return self._pool.pop()
if self._created_count < self.max_size:
channel = self._create_channel()
self._created_count += 1
return channel
# 等待连接可用(简化实现)
while not self._pool:
self._lock.release()
time.sleep(0.1)
self._lock.acquire()
return self._pool.pop()
def return_connection(self, channel: grpc.Channel):
"""归还连接到池中"""
with self._lock:
if len(self._pool) < self.max_size:
self._pool.append(channel)
else:
channel.close()
self._created_count -= 1
def _create_channel(self) -> grpc.Channel:
"""创建新的gRPC通道"""
options = [
('grpc.keepalive_time_ms', self.keepalive_time * 1000),
('grpc.keepalive_timeout_ms', 30000),
('grpc.keepalive_permit_without_calls', 1),
('grpc.http2.max_pings_without_data', 0),
('grpc.http2.min_time_between_pings_ms', 60000),
('grpc.http2.min_ping_interval_without_data_ms', 300000),
]
return grpc.insecure_channel(self.target, options=options)
class PerformanceOptimizer:
"""gRPC性能优化器"""
def __init__(self):
self.optimization_strategies = {
'connection_pooling': '连接池减少连接建立开销',
'message_compression': '启用消息压缩',
'load_balancing': '客户端负载均衡',
'deadline_propagation': '截止时间传播',
'batch_processing': '批处理操作'
}
def enable_compression(self, algorithm: str = 'gzip') -> list:
"""启用消息压缩"""
compression_options = [
('grpc.default_compression_algorithm', self._get_compression_code(algorithm))
]
return compression_options
def _get_compression_code(self, algorithm: str) -> int:
"""获取压缩算法代码"""
algorithms = {
'none': 0,
'gzip': 1,
'deflate': 2
}
return algorithms.get(algorithm, 0)
def configure_load_balancing(self, addresses: List[str]) -> dict:
"""配置负载均衡"""
# 简化实现,实际应使用更复杂的LB策略
return {
'strategy': 'round_robin',
'addresses': addresses,
'health_check_interval': 30
}
def benchmark_optimizations(self, original_metrics: dict, optimized_metrics: dict) -> dict:
"""对比优化效果"""
improvements = {}
for metric in ['throughput', 'latency', 'error_rate']:
if metric in original_metrics and metric in optimized_metrics:
orig = original_metrics[metric]
opt = optimized_metrics[metric]
if metric == 'error_rate':
improvement = (orig - opt) / orig * 100 # 错误率降低百分比
else:
improvement = (opt - orig) / orig * 100 # 吞吐量/延迟改善百分比
improvements[metric] = improvement
return improvements
# 使用示例
def demonstrate_optimization():
"""演示性能优化"""
optimizer = PerformanceOptimizer()
# 启用压缩
compression_options = optimizer.enable_compression('gzip')
print(f"压缩配置: {compression_options}")
# 配置负载均衡
lb_config = optimizer.configure_load_balancing([
'localhost:50051',
'localhost:50052',
'localhost:50053'
])
print(f"负载均衡配置: {lb_config}")
# 创建连接池
pool = ConnectionPool('localhost:50051', max_size=5)
# 性能对比
original_metrics = {'throughput': 1000, 'latency': 50, 'error_rate': 5.0}
optimized_metrics = {'throughput': 1500, 'latency': 30, 'error_rate': 1.0}
improvements = optimizer.benchmark_optimizations(original_metrics, optimized_metrics)
print("=== 性能优化效果 ===")
for metric, improvement in improvements.items():
print(f"{metric}: {improvement:+.1f}%")
return improvements5.2 故障排查指南
基于真实项目经验,总结gRPC开发中的常见问题及解决方案。
5.2.1 问题诊断工具
python
# troubleshooting.py
import logging
from typing import Dict, List, Any
import grpc
from grpc import StatusCode
class GRPCTroubleshooter:
"""gRPC故障排查器"""
def __init__(self):
self.common_issues = {
'connection_failed': {
'symptoms': ['连接超时', '连接被拒绝'],
'causes': ['服务未启动', '网络问题', '防火墙阻挡'],
'solutions': ['检查服务状态', '验证网络连接', '检查防火墙配置']
},
'deadline_exceeded': {
'symptoms': ['请求超时', 'DEADLINE_EXCEEDED错误'],
'causes': ['服务处理过慢', '网络延迟高', '资源不足'],
'solutions': ['增加超时时间', '优化服务性能', '检查系统资源']
},
'unauthenticated': {
'symptoms': ['认证失败', 'UNAUTHENTICATED错误'],
'causes': ['Token无效', '认证信息缺失', '权限不足'],
'solutions': ['检查Token有效性', '添加认证信息', '验证权限配置']
},
'resource_exhausted': {
'symptoms': ['资源耗尽', 'RESOURCE_EXHAUSTED错误'],
'causes': ['超过限流', '内存不足', '连接数超限'],
'solutions': ['调整限流配置', '增加系统资源', '优化资源使用']
}
}
def diagnose_issue(self, error: Exception, context: dict) -> List[str]:
"""诊断gRPC问题"""
error_type = type(error).__name__
error_message = str(error)
symptoms = self._identify_symptoms(error_message, context)
possible_issues = []
for issue_name, issue_info in self.common_issues.items():
if any(symptom in symptoms for symptom in issue_info['symptoms']):
possible_issues.append(issue_name)
recommendations = []
for issue in possible_issues:
recommendations.extend(self.common_issues[issue]['solutions'])
return recommendations if recommendations else ['检查日志获取详细信息']
def _identify_symptoms(self, error_message: str, context: dict) -> List[str]:
"""识别问题症状"""
symptoms = []
if 'Failed to connect' in error_message:
symptoms.append('连接超时')
symptoms.append('连接被拒绝')
if 'DEADLINE_EXCEEDED' in error_message:
symptoms.append('请求超时')
if 'UNAUTHENTICATED' in error_message:
symptoms.append('认证失败')
if 'RESOURCE_EXHAUSTED' in error_message:
symptoms.append('资源耗尽')
# 基于上下文识别
if context.get('response_time', 0) > 30: # 超过30秒
symptoms.append('服务处理过慢')
if context.get('error_rate', 0) > 10: # 错误率超过10%
symptoms.append('高错误率')
return symptoms
def generate_debug_report(self, issue_description: str, environment: dict) -> dict:
"""生成调试报告"""
return {
'timestamp': time.time(),
'issue': issue_description,
'environment': environment,
'possible_causes': self._analyze_causes(issue_description),
'debug_steps': self._generate_debug_steps(issue_description),
'prevention_measures': self._suggest_prevention(issue_description)
}
def _analyze_causes(self, issue: str) -> List[str]:
"""分析可能原因"""
causes_map = {
'connection': ['网络故障', '服务宕机', 'DNS解析问题'],
'performance': ['资源不足', '配置不当', '代码效率低'],
'authentication': ['Token过期', '配置错误', '权限不足']
}
for key, causes in causes_map.items():
if key in issue.lower():
return causes
return ['未知原因,需要进一步排查']
def _generate_debug_steps(self, issue: str) -> List[str]:
"""生成调试步骤"""
steps = [
"检查服务日志获取详细错误信息",
"验证网络连接和端口可达性",
"检查系统资源使用情况(CPU、内存、磁盘)"
]
if 'auth' in issue.lower():
steps.extend([
"验证认证Token的有效性",
"检查权限配置是否正确",
"查看认证服务器状态"
])
if 'performance' in issue.lower():
steps.extend([
"分析性能监控数据",
"检查数据库查询性能",
"验证gRPC配置参数"
])
return steps
def _suggest_prevention(self, issue: str) -> List[str]:
"""建议预防措施"""
prevention = [
"实施完整的监控和告警系统",
"定期进行负载测试和性能优化",
"建立完善的日志记录和分析流程"
]
if 'connection' in issue.lower():
prevention.append("配置连接池和重试机制")
if 'resource' in issue.lower():
prevention.append("实施资源限制和监控")
return prevention
# 使用示例
def demonstrate_troubleshooting():
"""演示故障排查"""
troubleshooter = GRPCTroubleshooter()
# 模拟错误
class MockError(Exception):
pass
error = MockError("Failed to connect to remote host: Connection timed out")
context = {'response_time': 45, 'error_rate': 15.5}
# 诊断问题
recommendations = troubleshooter.diagnose_issue(error, context)
print("=== 故障诊断结果 ===")
for i, recommendation in enumerate(recommendations, 1):
print(f"{i}. {recommendation}")
# 生成调试报告
debug_report = troubleshooter.generate_debug_report(
"连接超时和性能下降",
{'host': 'localhost:50051', 'protocol': 'HTTP/2'}
)
return debug_report官方文档与参考资源
-
gRPC官方文档- gRPC官方文档和教程
-
Protocol Buffers指南- Google官方Protobuf文档
-
gRPC Python示例- 官方Python示例代码
-
gRPC性能最佳实践- 性能优化指南
通过本文的完整学习路径,您应该已经掌握了gRPC框架的核心技术和实战应用。gRPC作为现代微服务架构的通信基石,其高性能和强类型特性将为您的系统带来显著的性能提升和开发效率改进。