一、
压测目的
相信很多同学对于连接池技术还是比较感兴趣的,但对于pgbouncer是否能够承担起连接池的重任,可能很多同学都有点持怀疑的态度。
那么,本文以centos7,采用pgbench内置压测工具,通过两种连接方式来进行数据库压测,以得出pgbouncer哪些参数会影响连接池的性能;连接池和直连数据库到底哪个孰优孰劣,每一种连接压测后的tps详解。
二、
实验环境介绍
本次压测实验采用VMware虚拟机,虚拟机安装的操作系统是centos7,postgresql数据库的版本是12.4,两种压测都是远程连接,也就是说一种压测是通过数据库原生端口开始,一种压测是通过pgbouncer的端口开始。pgbouncer的版本是最新版本的1.5.1
bash
[root@centos1 ~]# su - postgres
Last login: Thu Jan 29 20:22:42 CST 2026 on pts/4
-bash-4.2$ psql -p 6432 -d pgbouncer -U postgres
Password for user postgres:
psql (12.4, server 1.25.1/bouncer)
Type "help" for help.硬件方面,cpu是16核心,内存是8G,pgbouncer开放的端口是6432,数据库开放的端口是15433
bash
[root@centos1 ~]# netstat -antup |grep 15433
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:15433 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1334/postmaster
tcp6 0 0 :::15433 :::* LISTEN 1334/postmaster
[root@centos1 ~]# netstat -antup |grep 6432
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:6432 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1300/pgbouncer
tcp6 0 0 :::6432 :::* LISTEN 1300/pgbouncer
[root@centos1 ~]# free -mh
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 7.6G 217M 6.6G 309M 798M 6.9G
Swap: 0B 0B 0B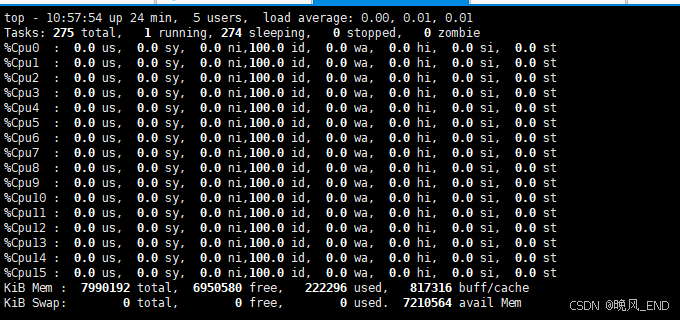
软件方面,pgbouncer配置的主要参数如下:
bash
client_idle_timeout = 600
idle_transaction_timeout = 300
server_lifetime = 600
server_idle_timeout = 399
max_db_connections = 800
reserve_pool_timeout = 1
reserve_pool_size = 200
default_pool_size = 400
max_client_conn = 2000
server_check_delay = 10
server_check_query = select 1
max_prepared_statements = 599
pool_mode = transaction数据库方面所有参数都是原始默认参数,除了端口修改为了15433,连接数修改为了5000
三、
pgbench的安装部署
生成一个2000W条的大表,然后对该表做查询,写入的测试,从而得出数据库的性能和并发指标,下面是大表的创建代码:
随机数函数:
bash
create or replace function gen_id(
a date,
b date
)
returns text as $$
select lpad((random()*99)::int::text, 3, '0') ||
lpad((random()*99)::int::text, 3, '0') ||
lpad((random()*99)::int::text, 3, '0') ||
to_char(a + (random()*(b-a))::int, 'yyyymmdd') ||
lpad((random()*99)::int::text, 3, '0') ||
random()::int ||
(case when random()*10 >9 then 'xy' else (random()*9)::int::text end ) ;
$$ language sql strict;创建测试表结构:
bash
CREATE SEQUENCE test START 1;
create table if not exists testpg (
"id" int8 not null DEFAULT nextval('test'::regclass),
CONSTRAINT "user_vendorcode_pkey" PRIMARY KEY ("id"),
"suijishuzi" VARCHAR ( 255 ) COLLATE "pg_catalog"."default"
);插入2000W条数据,根据机器性能,大概5到10分钟左右:
bash
insert into testpg SELECT generate_series(1,20000000) as xm, gen_id('1949-01-01', '2023-10-16') as num;随机更新字段suijishuzi:
bash
-- 文件名:update_test.sql
BEGIN;
-- 生成随机数(1~100)决定更新范围
\set update_range random(1, 100)
-- 随机选择要更新的 ID(确保 ID 存在)
\set target_id random(1, :scale)
-- 执行更新操作
UPDATE testpg
SET suijishuzi = md5(random()::text) -- 生成随机字符串作为新值
WHERE id = :target_id;
COMMIT;创建数据库pgbench,并生成pgbench的内置表:
bash
create database pgbench;
pgbench -U postgres -i pgbench以上表准备完毕后,就可以开始正式压测了,压测主要是使用 update_test.sql这个SQL脚本,模拟高并发下的更新性能,每次压测完毕后,等待五分钟以让top命令恢复正常状态,并尽量去掉缓存的影响
四、
正式压测记录
第一组,pgbouncer连接池
预编译模式,400个数据库连接数,15个进程,压测时间30秒
bash
pgbench -M prepared -v -r -P 1 -f ./update_test.sql -c 400 -j 15 -T 30 -D scale=20000000 -Upostgres -d postgres1 -P 5 -h 192.168.123.100 -p6432cpu使用率在百分之十左右,内存使用1G左右,压测报告如下:
bash
transaction type: ./update_test.sql
scaling factor: 1
query mode: prepared
number of clients: 400
number of threads: 15
duration: 30 s
number of transactions actually processed: 112967
latency average = 103.640 ms
latency stddev = 67.994 ms
tps = 3751.554637 (including connections establishing)
tps = 3751.934390 (excluding connections establishing)
statement latencies in milliseconds:
27.082 BEGIN;
0.168 \set update_range random(1, 100)
0.122 \set target_id random(1, :scale)
34.674 UPDATE testpg
41.599 COMMIT;第二组,pgbouncer连接池
预编译模式,400个数据库连接数,15个进程,压测时间300秒,和第一组间隔3分钟
bash
pgbench -M prepared -v -r -P 1 -f ./update_test.sql -c 400 -j 15 -T 300 -D scale=20000000 -Upostgres -d postgres1 -P 5 -h 192.168.123.100 -p6432cpu使用率为百分之十三,截图截稍晚了
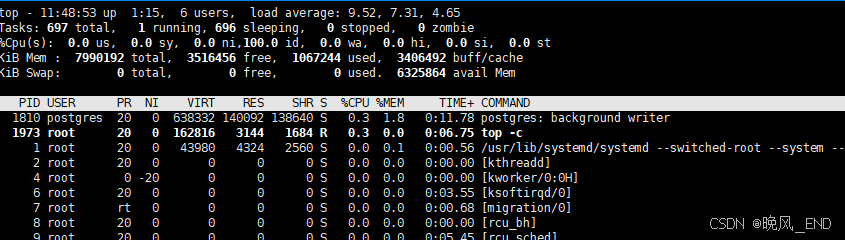
压测报告如下:
bash
transaction type: ./update_test.sql
scaling factor: 1
query mode: prepared
number of clients: 400
number of threads: 15
duration: 300 s
number of transactions actually processed: 1606670
latency average = 73.662 ms
latency stddev = 44.483 ms
tps = 5355.159074 (including connections establishing)
tps = 5355.321370 (excluding connections establishing)
statement latencies in milliseconds:
19.377 BEGIN;
0.141 \set update_range random(1, 100)
0.115 \set target_id random(1, :scale)
26.258 UPDATE testpg
27.769 COMMIT;以这两组压测对比,可以看到第二次压测明显tps升高了,那么,原因是什么呢?
推测是pgbouncer连接池发挥作用了,在第一次压测时,创建了大量的连接,导致tps下降,第二次压测直接拿第一次创建的连接复用,因此,tps大幅度提升;其次是update阶段和commit阶段,也有百分之三十左右的提升。
第三组。数据库直连
和第二组间隔三分钟,预编译模式,400个数据库连接数,15个进程,压测时间30秒,压测报告如下:
bash
transaction type: ./update_test.sql
scaling factor: 1
query mode: prepared
number of clients: 400
number of threads: 15
duration: 30 s
number of transactions actually processed: 127742
latency average = 78.970 ms
latency stddev = 75.434 ms
tps = 4227.694815 (including connections establishing)
tps = 4233.449310 (excluding connections establishing)
statement latencies in milliseconds:
15.675 BEGIN;
0.756 \set update_range random(1, 100)
0.236 \set target_id random(1, :scale)
23.724 UPDATE testpg
38.572 COMMIT;cpu使用率最高到百分之二十多一点,内存使用1G左右
第四组,数据库直连
和第三组间隔三分钟,预编译模式,400个数据库连接数,15个进程,压测时间300秒,压测报告如下:
bash
transaction type: ./update_test.sql
scaling factor: 1
query mode: prepared
number of clients: 400
number of threads: 15
duration: 300 s
number of transactions actually processed: 1536284
latency average = 67.016 ms
latency stddev = 73.166 ms
tps = 5108.252035 (including connections establishing)
tps = 5108.422198 (excluding connections establishing)
statement latencies in milliseconds:
13.348 BEGIN;
0.652 \set update_range random(1, 100)
0.202 \set target_id random(1, :scale)
18.535 UPDATE testpg
34.278 COMMIT;可以看到,直连数据库的性能和pgbouncer连接池的性能接近,但资源消耗完全和连接池无法相比,最高cpu使用达到了百分之三十五,并且idle进程大起大落的很厉害,内存使用方面两者基本一致,都是1G左右
第五组,数据库直连
和第四组间隔10来分钟,直接运行模式,400个数据库连接数,15个进程,压测时间300秒,压测报告如下:
bash
transaction type: ./update_test.sql
scaling factor: 1
query mode: simple
number of clients: 400
number of threads: 15
duration: 300 s
number of transactions actually processed: 1440749
latency average = 71.457 ms
latency stddev = 69.900 ms
tps = 4796.305166 (including connections establishing)
tps = 4796.657038 (excluding connections establishing)
statement latencies in milliseconds:
14.275 BEGIN;
0.695 \set update_range random(1, 100)
0.209 \set target_id random(1, :scale)
19.858 UPDATE testpg
36.417 COMMIT;最高cpu使用率百分之三十五左右,内存仍然是使用1G左右,没有太大变化
第六组,pgbouncer连接池
和第五组间隔10来分钟,直接运行模式,400个数据库连接数,15个进程,压测时间300秒,压测报告如下:
bash
transaction type: ./update_test.sql
scaling factor: 1
query mode: simple
number of clients: 400
number of threads: 15
duration: 300 s
number of transactions actually processed: 1335101
latency average = 88.733 ms
latency stddev = 55.627 ms
tps = 4448.145554 (including connections establishing)
tps = 4448.234075 (excluding connections establishing)
statement latencies in milliseconds:
23.778 BEGIN;
0.200 \set update_range random(1, 100)
0.152 \set target_id random(1, :scale)
30.420 UPDATE testpg
34.184 COMMIT;最高cpu使用率百分之三十左右,内存仍然是使用1G左右,没有太大变化,第五组和第六组相比,tps性能基本一样,资源使用率cpu方面连接池稍显优势,内存方面两者基本相同。
压测总结:
从这几次压测来看,可以得出一个比较准确的高并发下的postgresql数据库性能,即pgbouncer连接池基本等于数据库直连,但,数据库服务器资源使用明显pgbouncer连接池更低,有数据库连接池的情况要比直连数据库低一半左右的资源使用。 server_check_delay = 10是一个比较安全可靠的连接检测参数,如果设置为默认30,连接池的性能会下降比较多,稍微有点明显,在本次压测中并没有展示此参数,以后补充。
未完待续!!!!!