Flutter for OpenHarmony 实战:打造天气预报应用
文章目录
- [Flutter for OpenHarmony 实战:打造天气预报应用](#Flutter for OpenHarmony 实战:打造天气预报应用)
-
- 一、项目背景与功能概述
-
- [1.1 天气预报应用的需求分析](#1.1 天气预报应用的需求分析)
- [1.2 为什么选择Flutter for OpenHarmony](#1.2 为什么选择Flutter for OpenHarmony)
- 二、技术选型与架构设计
-
- [2.1 技术栈选择](#2.1 技术栈选择)
- [2.2 应用架构设计](#2.2 应用架构设计)
- [2.3 数据流设计](#2.3 数据流设计)
- 三、数据模型设计与API集成
-
- [3.1 高德天气API接口分析](#3.1 高德天气API接口分析)
- [3.2 数据模型类设计](#3.2 数据模型类设计)
- [3.3 城市配置与编码映射](#3.3 城市配置与编码映射)
- 四、UI界面设计与实现
-
- [4.1 整体布局结构](#4.1 整体布局结构)
- [4.2 当前天气卡片设计](#4.2 当前天气卡片设计)
- [4.3 天气详情网格](#4.3 天气详情网格)
- [4.4 预报列表设计](#4.4 预报列表设计)
- 五、主题切换功能实现
-
- [5.1 主题状态管理](#5.1 主题状态管理)
- [5.2 主题应用方案](#5.2 主题应用方案)
- [5.3 主题适配组件](#5.3 主题适配组件)
- [5.4 天气图标映射](#5.4 天气图标映射)
- 六、完整代码实现
-
- [6.1 网络请求核心逻辑](#6.1 网络请求核心逻辑)
- [6.2 错误处理与加载状态](#6.2 错误处理与加载状态)
- [6.3 城市选择器实现](#6.3 城市选择器实现)
- 八、总结
本文将详细介绍如何使用Flutter for OpenHarmony框架开发一款功能完整的天气预报应用。文章涵盖了高德地图天气API的集成、数据模型设计、网络请求处理、UI界面设计、主题切换等核心技术点。通过本文学习,读者将掌握Flutter在鸿蒙平台上进行网络请求和数据处理的方法,了解移动应用开发的完整流程。
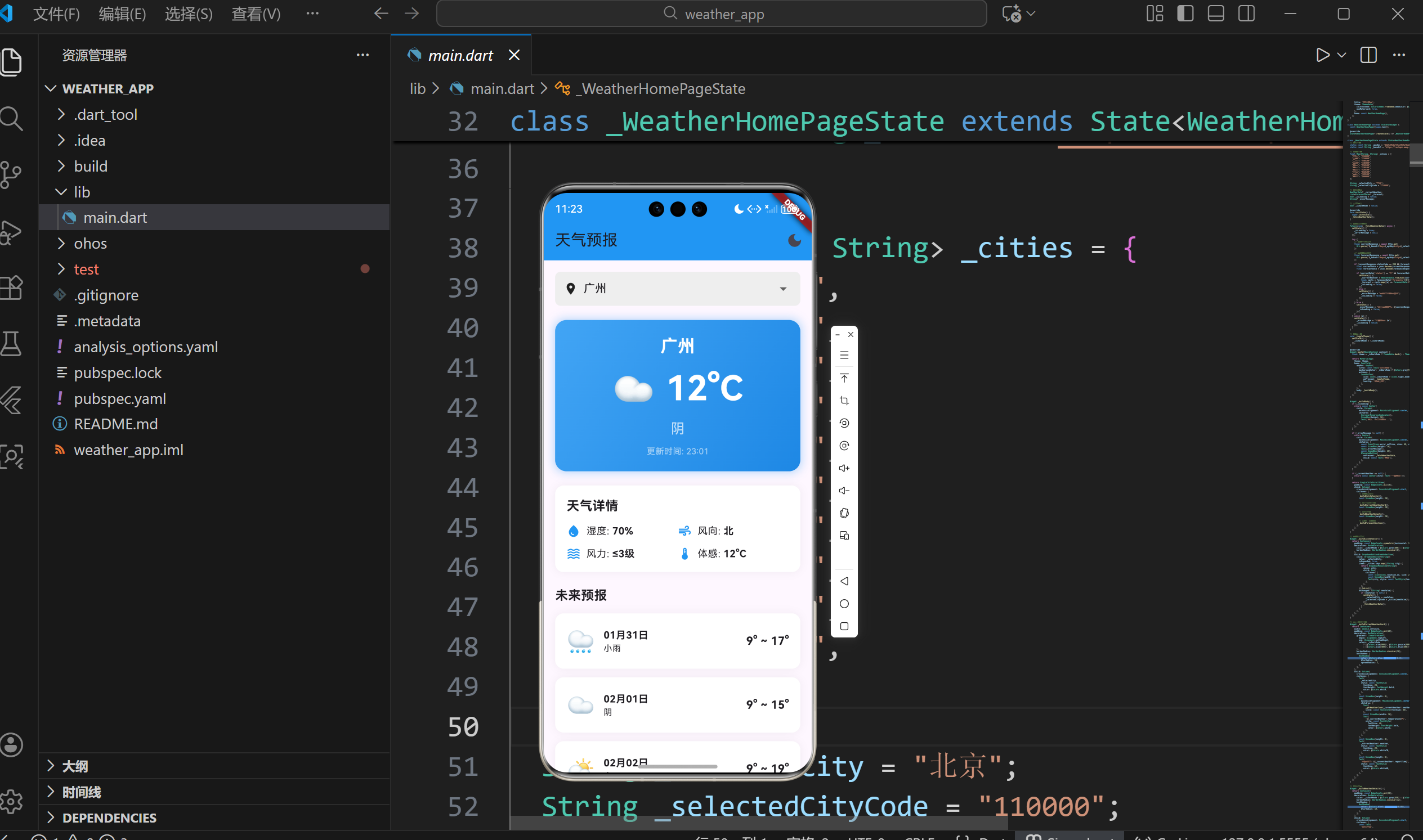
一、项目背景与功能概述
1.1 天气预报应用的需求分析
天气预报是移动应用中最常见的功能之一,它涉及网络请求、数据解析、UI展示等多个技术环节。开发一个高质量的天气预报应用需要考虑以下核心需求:
基础功能模块
- 实时天气数据显示(温度、天气状况、湿度、风力等)
- 未来几天天气预报展示
- 多城市切换支持
- 主题切换(日间/夜间模式)
用户体验优化
- 流畅的加载动画
- 优雅的错误提示
- 直观的天气图标展示
- 响应式布局适配
1.2 为什么选择Flutter for OpenHarmony
Flutter在开发天气预报类应用时具有明显优势:
网络请求能力
- 提供强大的http包支持RESTful API调用
- 异步编程模型确保UI不阻塞
- 完善的错误处理机制
UI渲染性能
- 60fps流畅动画体验
- 丰富的Widget组件库
- Material Design设计语言支持
跨平台一致性
- 一套代码在鸿蒙、iOS、Android上表现一致
- 响应式布局自动适配不同屏幕
二、技术选型与架构设计
2.1 技术栈选择
数据源选择
- 高德地图天气API:提供稳定可靠的天气数据服务
- 免费额度充足,适合开发和学习使用
- 数据格式标准,易于解析
网络请求库
- http包:Flutter官方推荐的轻量级HTTP客户端
- 支持异步请求、超时控制、错误处理
- 与Dart的async/await语法完美配合
状态管理
- StatefulWidget:基础的状态管理方案
- setState:简单直观的状态更新机制
- 适合中小型应用的状态管理需求
2.2 应用架构设计
采用分层架构设计,保证代码的可维护性和可扩展性:
表现层 (Presentation Layer)
├── WeatherHomePage (主页面)
├── WeatherCard (天气卡片)
├── ForecastCard (预报卡片)
└── CitySelector (城市选择器)
业务逻辑层 (Business Logic Layer)
├── _fetchWeatherData (数据获取)
├── _toggleTheme (主题切换)
└── _getWeatherIcon (图标映射)
数据层 (Data Layer)
├── WeatherData (实时天气模型)
├── ForecastData (预报数据模型)
└── API配置与城市映射2.3 数据流设计
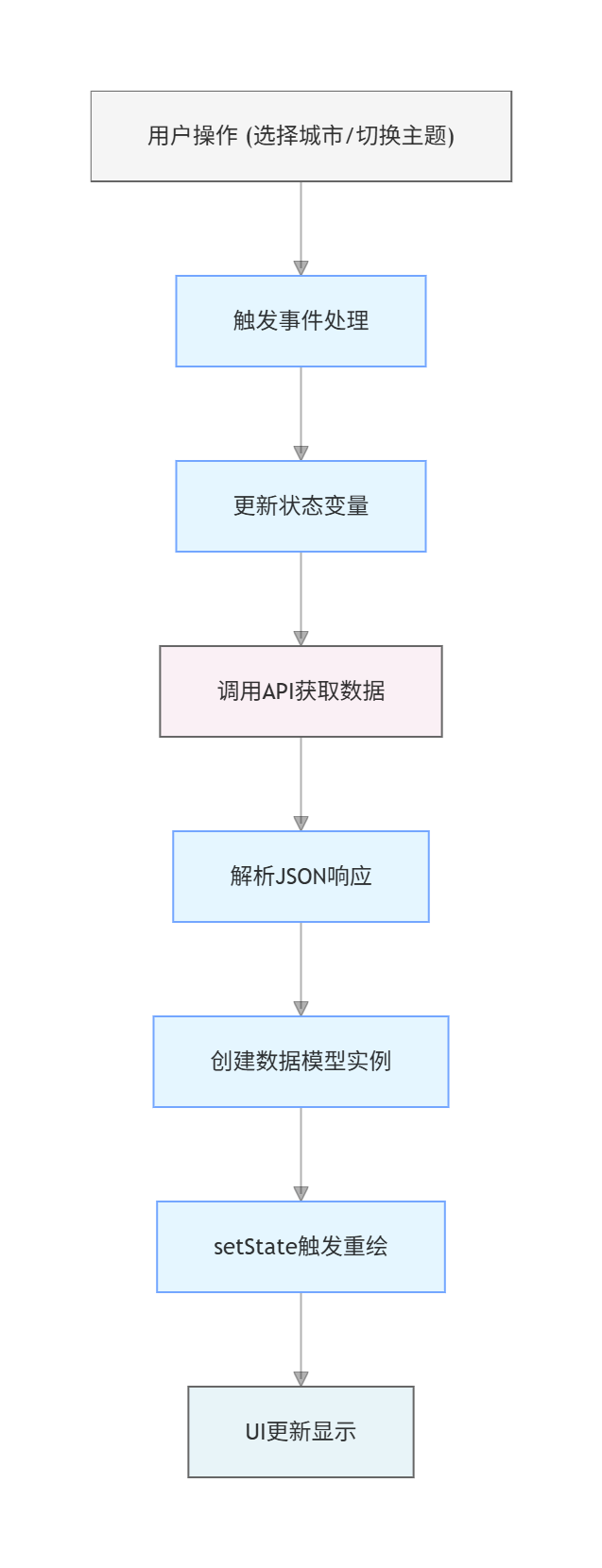
三、数据模型设计与API集成
3.1 高德天气API接口分析
高德地图天气API提供两种查询模式:
实时天气查询
html
URL: https://restapi.amap.com/v3/weather/weatherInfo
参数:
- key: API密钥
- city: 城市编码(adcode)
- extensions: base(基础实况天气)
返回数据结构:
{
"status": "1",
"lives": [{
"province": "北京",
"city": "北京市",
"weather": "晴",
"temperature": "15",
"winddirection": "西",
"windpower": "3级",
"humidity": "25",
"reporttime": "2024-01-15 14:00:00"
}]
}天气预报查询
html
参数: extensions: all(预报天气)
返回数据结构:
{
"status": "1",
"forecasts": [{
"city": "北京市",
"casts": [
{
"date": "2024-01-15",
"dayweather": "晴",
"nightweather": "晴",
"daytemp": "18",
"nighttemp": "5"
}
]
}]
}3.2 数据模型类设计
WeatherData实时天气模型
dart
class WeatherData {
final String province; // 省份
final String city; // 城市
final String weather; // 天气状况
final String temperature; // 温度
final String windDirection; // 风向
final String windPower; // 风力
final String humidity; // 湿度
final String reportTime; // 更新时间
WeatherData({
required this.province,
required this.city,
required this.weather,
required this.temperature,
required this.windDirection,
required this.windPower,
required this.humidity,
required this.reportTime,
});
factory WeatherData.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) {
// 格式化时间显示
String formatTime(String reportTime) {
try {
final dateTime = DateTime.parse(reportTime);
return '${dateTime.hour.toString().padLeft(2, '0')}:${dateTime.minute.toString().padLeft(2, '0')}';
} catch (e) {
return reportTime;
}
}
return WeatherData(
province: json['province'] ?? '',
city: json['city'] ?? '',
weather: json['weather'] ?? '',
temperature: json['temperature'] ?? '',
windDirection: json['winddirection'] ?? '',
windPower: json['windpower'] ?? '',
humidity: json['humidity'] ?? '',
reportTime: formatTime(json['reporttime'] ?? ''),
);
}
}ForecastData预报数据模型
dart
class ForecastData {
final String date; // 日期
final String dayWeather; // 白天天气
final String nightTemp; // 夜间温度
final String dayTemp; // 白天温度
ForecastData({
required this.date,
required this.dayWeather,
required this.nightTemp,
required this.dayTemp,
});
factory ForecastData.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) {
// 格式化日期显示
String formatDate(String dateStr) {
try {
final parts = dateStr.split('-');
if (parts.length == 3) {
return '${parts[1]}月${parts[2]}日';
}
return dateStr;
} catch (e) {
return dateStr;
}
}
return ForecastData(
date: formatDate(json['date'] ?? ''),
dayWeather: json['dayweather'] ?? '',
nightTemp: json['nighttemp'] ?? '',
dayTemp: json['daytemp'] ?? '',
);
}
}3.3 城市配置与编码映射
dart
final Map<String, String> _cities = {
"北京": "110000",
"上海": "310000",
"广州": "440100",
"深圳": "440300",
"成都": "510100",
"杭州": "330100",
"武汉": "420100",
"西安": "610100",
"南京": "320100",
"重庆": "500000",
};使用Map结构将城市名称映射到高德API所需的adcode,便于用户选择时快速查找对应编码。
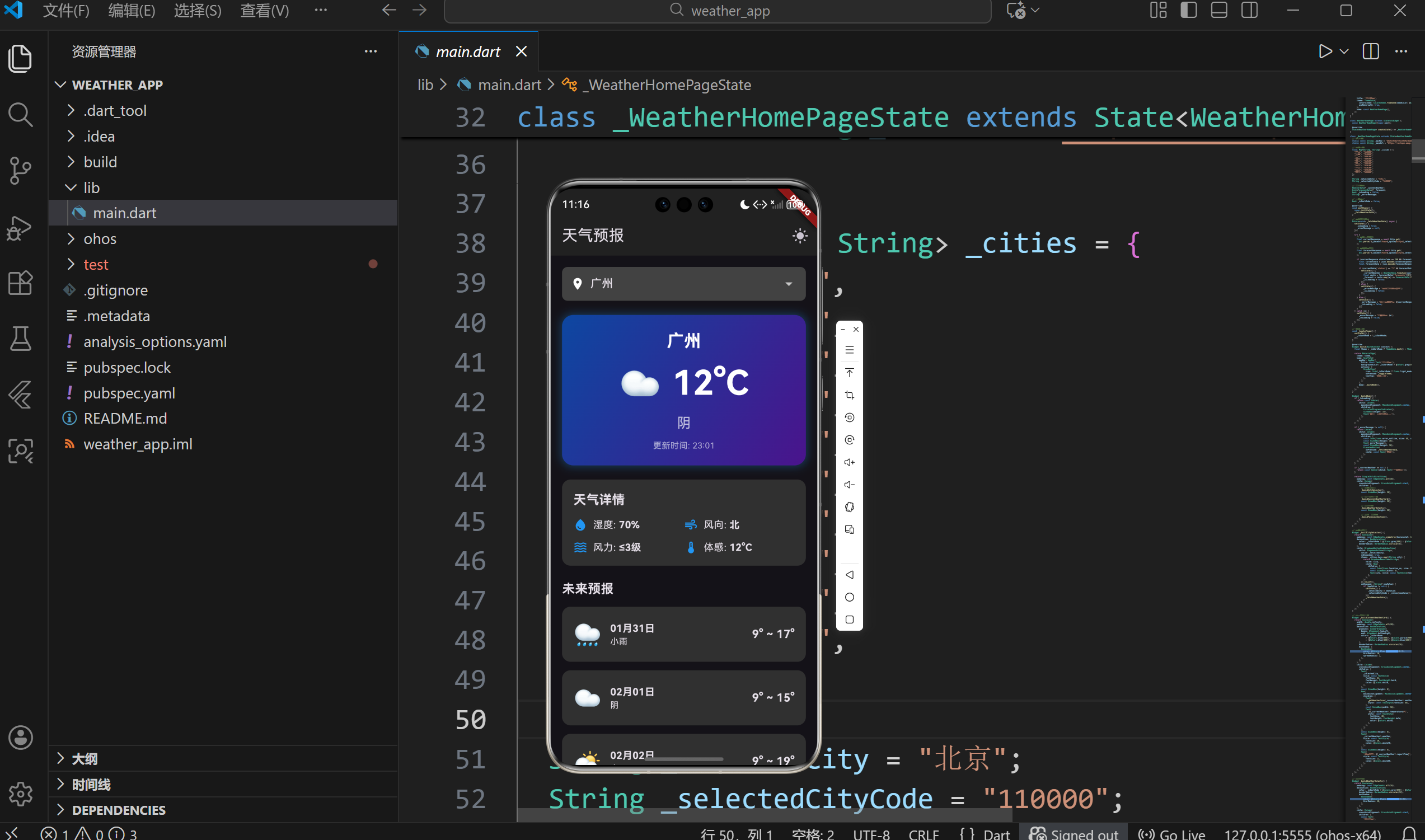
四、UI界面设计与实现
4.1 整体布局结构
应用采用垂直滚动的单页面布局:
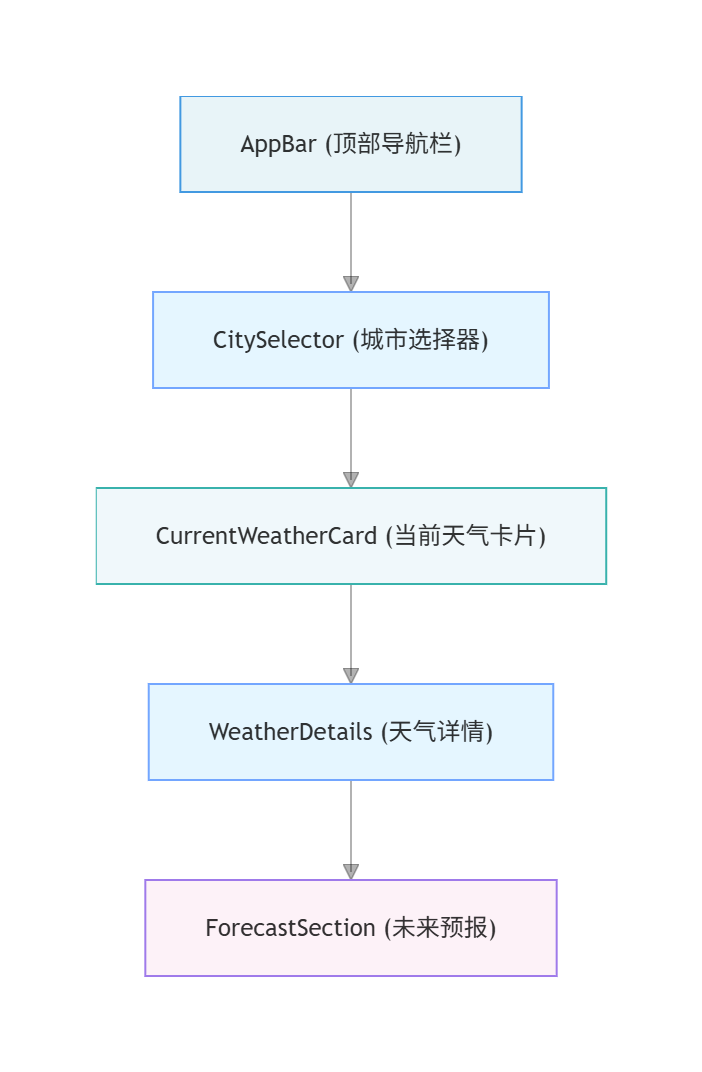
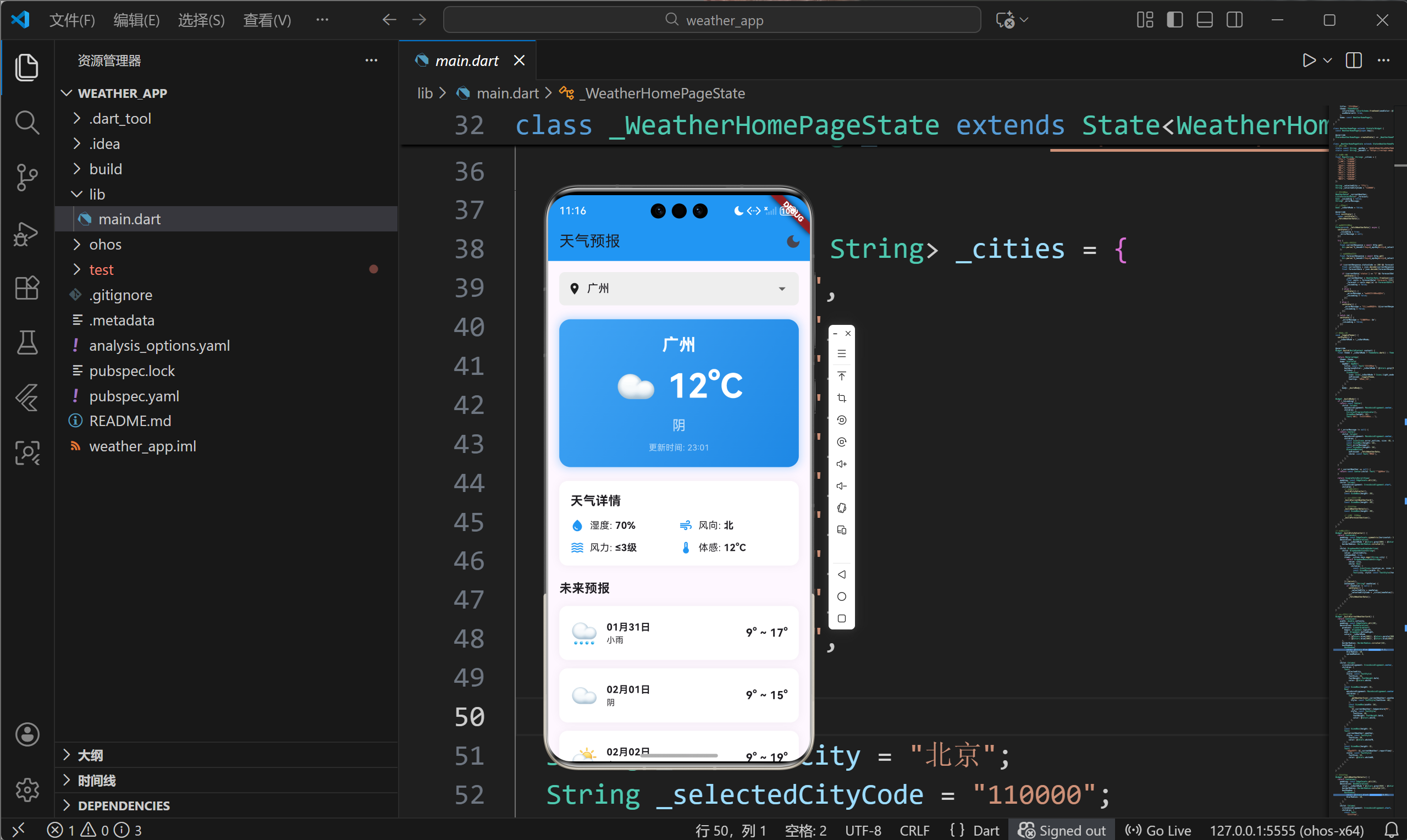
4.2 当前天气卡片设计
当前天气卡片是应用的视觉焦点,采用渐变背景和大字号温度显示:
dart
Widget _buildCurrentWeatherCard() {
return Container(
width: double.infinity,
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(20),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
gradient: LinearGradient(
begin: Alignment.topLeft,
end: Alignment.bottomRight,
colors: _isDarkMode
? [Colors.blue[900]!, Colors.purple[900]!]
: [Colors.blue[400]!, Colors.blue[600]!],
),
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(16),
boxShadow: [
BoxShadow(
color: Colors.blue.withOpacity(0.3),
blurRadius: 10,
spreadRadius: 2,
),
],
),
child: Column(
children: [
Text(_selectedCity, style: titleStyle),
Row(
children: [
Text(_getWeatherIcon(_currentWeather!.weather)),
Text('${_currentWeather!.temperature}°C'),
],
),
Text(_currentWeather!.weather),
],
),
);
}设计要点
- 渐变背景增强视觉层次
- 圆角和阴影营造卡片悬浮效果
- 天气图标和温度并排显示
- 主题切换时背景色自动调整
4.3 天气详情网格
天气详情采用2x2网格布局,展示湿度、风向、风力等信息:
dart
Widget _buildWeatherDetails() {
return Container(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(16),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: _isDarkMode ? Colors.grey[850] : Colors.white,
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(12),
boxShadow: [
BoxShadow(
color: Colors.black.withOpacity(0.05),
blurRadius: 10,
),
],
),
child: Column(
children: [
Row(
children: [
Expanded(child: _buildDetailItem(Icons.water_drop, '湿度', '${_currentWeather!.humidity}%')),
Expanded(child: _buildDetailItem(Icons.air, '风向', _currentWeather!.windDirection)),
],
),
Row(
children: [
Expanded(child: _buildDetailItem(Icons.waves, '风力', '${_currentWeather!.windPower}级')),
Expanded(child: _buildDetailItem(Icons.thermostat, '体感', '${_currentWeather!.temperature}°C')),
],
),
],
),
);
}4.4 预报列表设计
未来预报使用垂直卡片列表展示:
dart
Widget _buildForecastCard(ForecastData data) {
return Container(
margin: const EdgeInsets.only(bottom: 12),
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(16),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: _isDarkMode ? Colors.grey[850] : Colors.white,
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(12),
boxShadow: [
BoxShadow(
color: Colors.black.withOpacity(0.05),
blurRadius: 10,
),
],
),
child: Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceBetween,
children: [
Row(
children: [
Text(_getWeatherIcon(data.dayWeather)),
Column(
children: [
Text(data.date),
Text(data.dayWeather),
],
),
],
),
Text('${data.nightTemp}° ~ ${data.dayTemp}°'),
],
),
);
}
五、主题切换功能实现
5.1 主题状态管理
使用布尔值记录当前主题模式:
dart
bool _isDarkMode = false;
void _toggleTheme() {
setState(() {
_isDarkMode = !_isDarkMode;
});
}5.2 主题应用方案
在build方法中动态创建ThemeData:
dart
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
final theme = _isDarkMode ? ThemeData.dark() : ThemeData.light();
return MaterialApp(
theme: theme,
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
backgroundColor: _isDarkMode ? Colors.grey[900] : Colors.blue,
actions: [
IconButton(
icon: Icon(_isDarkMode ? Icons.light_mode : Icons.dark_mode),
onPressed: _toggleTheme,
),
],
),
body: _buildBody(),
),
);
}5.3 主题适配组件
所有UI组件都需要根据主题模式调整颜色:
dart
// 背景色适配
color: _isDarkMode ? Colors.grey[850] : Colors.white,
// 文字颜色适配
color: _isDarkMode ? Colors.white70 : Colors.black87,5.4 天气图标映射
根据天气描述返回对应的Emoji图标:
dart
String _getWeatherIcon(String weather) {
if (weather.contains('晴')) return '☀️';
if (weather.contains('多云')) return '⛅';
if (weather.contains('阴')) return '☁️';
if (weather.contains('雨')) return '🌧️';
if (weather.contains('雪')) return '❄️';
if (weather.contains('雾') || weather.contains('霾')) return '🌫️';
return '🌤️';
}
六、完整代码实现
6.1 网络请求核心逻辑
dart
Future<void> _fetchWeatherData() async {
setState(() {
_isLoading = true;
_errorMessage = null;
});
try {
// 获取实时天气
final currentResponse = await http.get(
Uri.parse("$_baseUrl?key=$_apiKey&city=$_selectedCityCode&extensions=base"),
);
// 获取预报天气
final forecastResponse = await http.get(
Uri.parse("$_baseUrl?key=$_apiKey&city=$_selectedCityCode&extensions=all"),
);
if (currentResponse.statusCode == 200 && forecastResponse.statusCode == 200) {
final currentData = json.decode(currentResponse.body);
final forecastData = json.decode(forecastResponse.body);
if (currentData['status'] == "1" && forecastData['status'] == "1") {
setState(() {
_currentWeather = WeatherData.fromJson(currentData['lives'][0]);
final casts = forecastData['forecasts'][0]['casts'] as List;
_forecast = casts.map((e) => ForecastData.fromJson(e)).toList();
_isLoading = false;
});
} else {
setState(() {
_errorMessage = "获取天气数据失败";
_isLoading = false;
});
}
} else {
setState(() {
_errorMessage = "网络请求失败: ${currentResponse.statusCode}";
_isLoading = false;
});
}
} catch (e) {
setState(() {
_errorMessage = "发生错误: $e";
_isLoading = false;
});
}
}6.2 错误处理与加载状态
dart
Widget _buildBody() {
if (_isLoading) {
return const Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
CircularProgressIndicator(),
SizedBox(height: 16),
Text('正在加载天气数据...'),
],
),
);
}
if (_errorMessage != null) {
return Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
const Icon(Icons.error_outline, size: 48, color: Colors.red),
const SizedBox(height: 16),
Text(_errorMessage!),
const SizedBox(height: 16),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: _fetchWeatherData,
child: const Text('重试'),
),
],
),
);
}
if (_currentWeather == null) {
return const Center(child: Text('暂无数据'));
}
return SingleChildScrollView(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(16),
child: Column(
children: [
_buildCitySelector(),
_buildCurrentWeatherCard(),
_buildWeatherDetails(),
_buildForecastSection(),
],
),
);
}6.3 城市选择器实现
dart
Widget _buildCitySelector() {
return Container(
padding: const EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 12),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: _isDarkMode ? Colors.grey[800] : Colors.grey[200],
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(8),
),
child: DropdownButtonHideUnderline(
child: DropdownButton<String>(
value: _selectedCity,
isExpanded: true,
items: _cities.keys.map((String city) {
return DropdownMenuItem<String>(
value: city,
child: Row(
children: [
const Icon(Icons.location_on, size: 20),
const SizedBox(width: 8),
Text(city, style: const TextStyle(fontSize: 16)),
],
),
);
}).toList(),
onChanged: (String? newValue) {
if (newValue != null) {
setState(() {
_selectedCity = newValue;
_selectedCityCode = _cities[newValue]!;
});
_fetchWeatherData();
}
},
),
),
);
}八、总结
本文详细介绍了使用Flutter for OpenHarmony开发天气预报应用的完整过程,涵盖了以下核心技术点:
- 网络请求:使用http包调用高德天气API,处理异步请求和错误
- 数据模型:设计WeatherData和ForecastData模型,实现JSON数据解析
- UI设计:构建卡片式布局,实现主题切换功能
- 状态管理:使用setState管理加载状态、错误状态和数据状态
这个项目展示了Flutter在数据驱动型应用开发中的优势,代码结构清晰,易于扩展。读者可以基于此项目添加更多功能,如定位服务、天气预警、数据缓存等。
通过本文的学习,读者应该能够独立开发类似的网络应用,掌握Flutter在鸿蒙平台上的跨平台开发技巧。
欢迎加入开源鸿蒙跨平台社区 : 开源鸿蒙跨平台开发者社区