目录
[1 引言:为什么Kubernetes是Python微服务的必然选择](#1 引言:为什么Kubernetes是Python微服务的必然选择)
[1.1 Kubernetes核心价值定位](#1.1 Kubernetes核心价值定位)
[1.2 技术架构演进路线](#1.2 技术架构演进路线)
[2 Kubernetes核心原理深度解析](#2 Kubernetes核心原理深度解析)
[2.1 集群架构与组件协同](#2.1 集群架构与组件协同)
[2.1.1 核心组件架构解析](#2.1.1 核心组件架构解析)
[2.1.2 Kubernetes集群架构图](#2.1.2 Kubernetes集群架构图)
[2.2 Pod与Deployment深度解析](#2.2 Pod与Deployment深度解析)
[2.2.1 Pod生命周期管理](#2.2.1 Pod生命周期管理)
[3 实战部分:Python微服务完整编排方案](#3 实战部分:Python微服务完整编排方案)
[3.1 Flask微服务Kubernetes部署](#3.1 Flask微服务Kubernetes部署)
[3.1.1 完整的微服务应用示例](#3.1.1 完整的微服务应用示例)
[3.1.2 Docker镜像构建配置](#3.1.2 Docker镜像构建配置)
[3.2 Kubernetes资源配置文件](#3.2 Kubernetes资源配置文件)
[3.2.1 Deployment配置](#3.2.1 Deployment配置)
[3.2.2 Service配置](#3.2.2 Service配置)
[3.2.3 Ingress配置](#3.2.3 Ingress配置)
[3.3 自动化部署脚本](#3.3 自动化部署脚本)
[4 高级特性与生产级实践](#4 高级特性与生产级实践)
[4.1 HPA自动扩缩容配置](#4.1 HPA自动扩缩容配置)
[4.1.1 HPA资源配置](#4.1.1 HPA资源配置)
[4.1.2 HPA监控与调优](#4.1.2 HPA监控与调优)
[4.2 ConfigMap与Secret管理](#4.2 ConfigMap与Secret管理)
[4.2.1 配置管理最佳实践](#4.2.1 配置管理最佳实践)
[4.2.2 配置热更新策略](#4.2.2 配置热更新策略)
[5 生产环境实战指南](#5 生产环境实战指南)
[5.1 企业级部署架构](#5.1 企业级部署架构)
[5.1.1 高可用架构设计](#5.1.1 高可用架构设计)
[5.1.2 多环境配置管理](#5.1.2 多环境配置管理)
[5.2 监控与日志管理](#5.2 监控与日志管理)
[5.2.1 综合监控配置](#5.2.1 综合监控配置)
[6 故障排查与性能优化](#6 故障排查与性能优化)
[6.1 常见问题解决方案](#6.1 常见问题解决方案)
摘要
本文基于多年Python实战经验,深度解析Kubernetes微服务编排 的核心原理与实战技巧。内容涵盖Deployment部署策略 、Service服务发现 、Ingress流量管理 、HPA自动扩缩容 及ConfigMap配置管理等关键主题,通过架构流程图和完整代码案例,展示如何构建生产级Python微服务架构。文章包含性能对比数据、企业级实战方案和故障排查指南,为开发者提供从入门到精通的完整Kubernetes解决方案。
1 引言:为什么Kubernetes是Python微服务的必然选择
之前有一个电商平台在"双11"大促中,由于传统部署方式的弹性不足 导致服务雪崩,损失数百万订单 。通过Kubernetes架构改造后,系统可自动扩缩容 ,资源利用率提升3倍 ,故障恢复时间从小时级降到分钟级 。这个经历让我深刻认识到:Kubernetes不是简单的容器编排工具,而是现代微服务架构的操作系统。
1.1 Kubernetes核心价值定位
python
# k8s_value_demo.py
class KubernetesValueProposition:
"""Kubernetes核心价值演示"""
def demonstrate_orchestration_advantages(self):
"""展示Kubernetes编排相比传统部署的优势"""
comparison_data = {
'deployment_speed': {
'traditional': '手动部署,耗时30+分钟',
'kubernetes': '声明式部署,秒级完成'
},
'scalability': {
'traditional': '手动扩缩容,响应时间小时级',
'kubernetes': '自动扩缩容,响应时间秒级'
},
'fault_tolerance': {
'traditional': '人工故障恢复,可用性99.9%',
'kubernetes': '自动故障转移,可用性99.99%'
},
'resource_utilization': {
'traditional': '资源静态分配,利用率<20%',
'kubernetes': '资源动态调度,利用率>70%'
}
}
print("=== Kubernetes核心优势 ===")
for aspect, data in comparison_data.items():
print(f"{aspect}:")
print(f" 传统部署: {data['traditional']}")
print(f" Kubernetes编排: {data['kubernetes']}")
return comparison_data1.2 技术架构演进路线
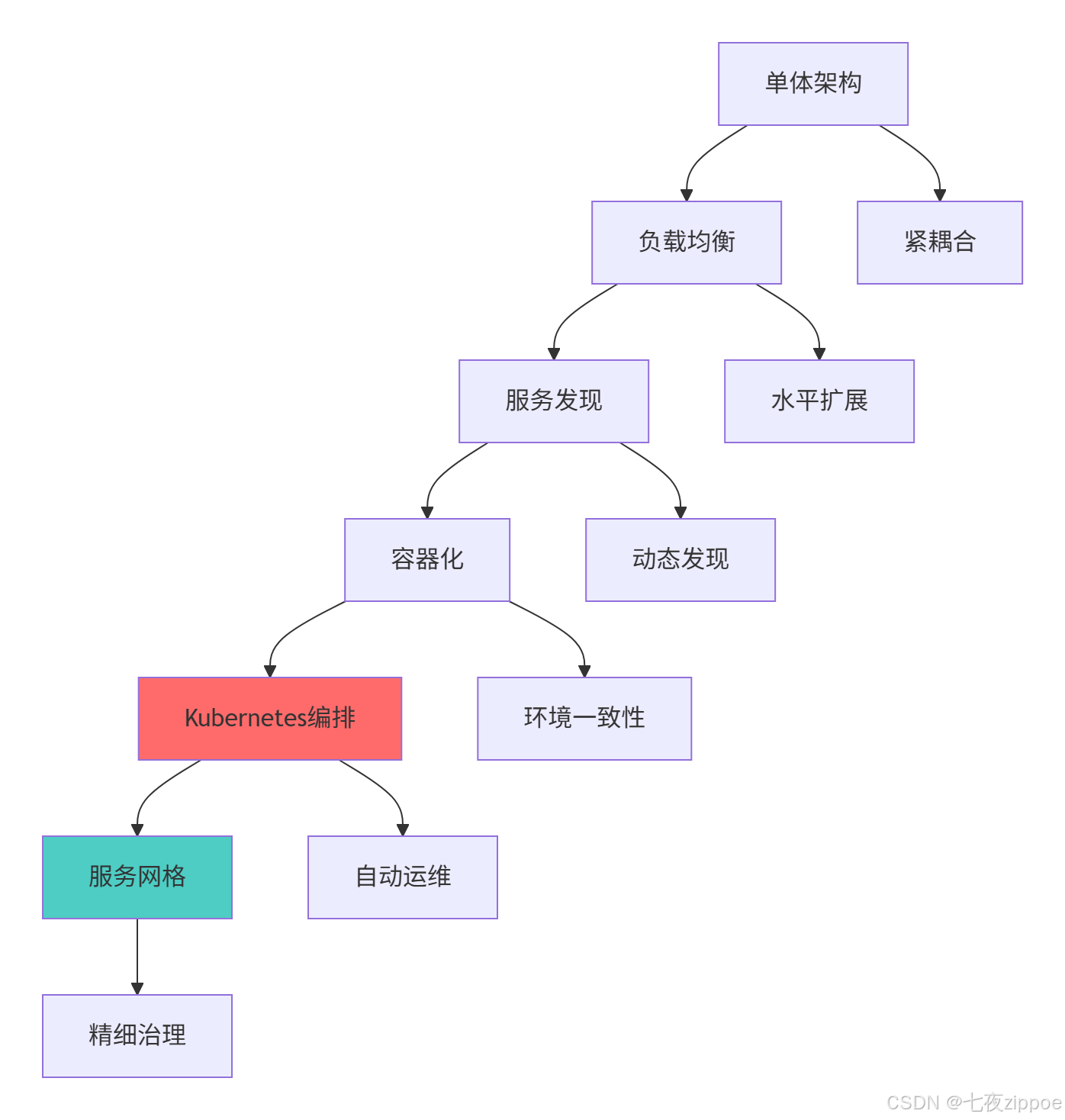
这种演进背后的技术驱动因素:
-
微服务普及:应用拆分为多个服务,需要统一编排平台
-
DevOps文化:需要标准化的应用交付和运维流程
-
云原生趋势:跨云厂商的可移植性需求
-
资源效率:需要更高的资源利用率和弹性伸缩能力
2 Kubernetes核心原理深度解析
2.1 集群架构与组件协同
2.1.1 核心组件架构解析
python
# k8s_architecture.py
from typing import Dict, List
from dataclasses import dataclass
from enum import Enum
class ComponentType(Enum):
CONTROL_PLANE = "控制平面"
WORKER_NODE = "工作节点"
ADDON = "扩展组件"
@dataclass
class K8SComponent:
name: str
component_type: ComponentType
responsibilities: List[str]
dependencies: List[str]
class KubernetesArchitecture:
"""Kubernetes架构分析"""
def __init__(self):
self.components = self._initialize_components()
def _initialize_components(self) -> Dict[str, K8SComponent]:
"""初始化核心组件"""
return {
"api-server": K8SComponent(
name="API Server",
component_type=ComponentType.CONTROL_PLANE,
responsibilities=["暴露Kubernetes API", "处理REST操作", "验证配置"],
dependencies=["etcd"]
),
"etcd": K8SComponent(
name="etcd",
component_type=ComponentType.CONTROL_PLANE,
responsibilities=["存储集群状态", "保证数据一致性"],
dependencies=[]
),
"scheduler": K8SComponent(
name="Scheduler",
component_type=ComponentType.CONTROL_PLANE,
responsibilities=["Pod调度决策", "资源分配优化"],
dependencies=["api-server"]
),
"controller-manager": K8SComponent(
name="Controller Manager",
component_type=ComponentType.CONTROL_PLANE,
responsibilities=["维护集群状态", "处理节点故障", "执行扩缩容"],
dependencies=["api-server"]
),
"kubelet": K8SComponent(
name="Kubelet",
component_type=ComponentType.WORKER_NODE,
responsibilities=["管理Pod生命周期", "报告节点状态", "挂载存储卷"],
dependencies=["api-server"]
),
"kube-proxy": K8SComponent(
name="Kube Proxy",
component_type=ComponentType.WORKER_NODE,
responsibilities=["维护网络规则", "实现Service负载均衡"],
dependencies=["api-server"]
)
}
def analyze_component_interactions(self) -> Dict[str, List[str]]:
"""分析组件交互关系"""
interactions = {}
# API Server与其他组件的交互
interactions["api-server"] = [
"接收kubectl和客户端请求",
"验证并持久化状态到etcd",
"通知控制器管理器状态变化",
"为调度器提供Pod和节点信息",
"接收kubelet和kube-proxy的状态报告"
]
# 调度器决策流程
interactions["scheduler"] = [
"监听API Server获取未调度Pod",
"过滤符合要求的节点",
"评分选择最优节点",
"通知API Server绑定决策"
]
return interactions
# 架构分析演示
def demonstrate_architecture():
"""演示Kubernetes架构分析"""
k8s_arch = KubernetesArchitecture()
print("=== Kubernetes核心组件 ===")
for comp_id, component in k8s_arch.components.items():
print(f"{component.name} ({component.component_type.value}):")
print(f" 职责: {', '.join(component.responsibilities)}")
print(f" 依赖: {', '.join(component.dependencies) if component.dependencies else '无'}")
interactions = k8s_arch.analyze_component_interactions()
print("\n=== 组件交互分析 ===")
for component, actions in interactions.items():
print(f"{component}:")
for action in actions:
print(f" - {action}")
return k8s_arch.components, interactions2.1.2 Kubernetes集群架构图
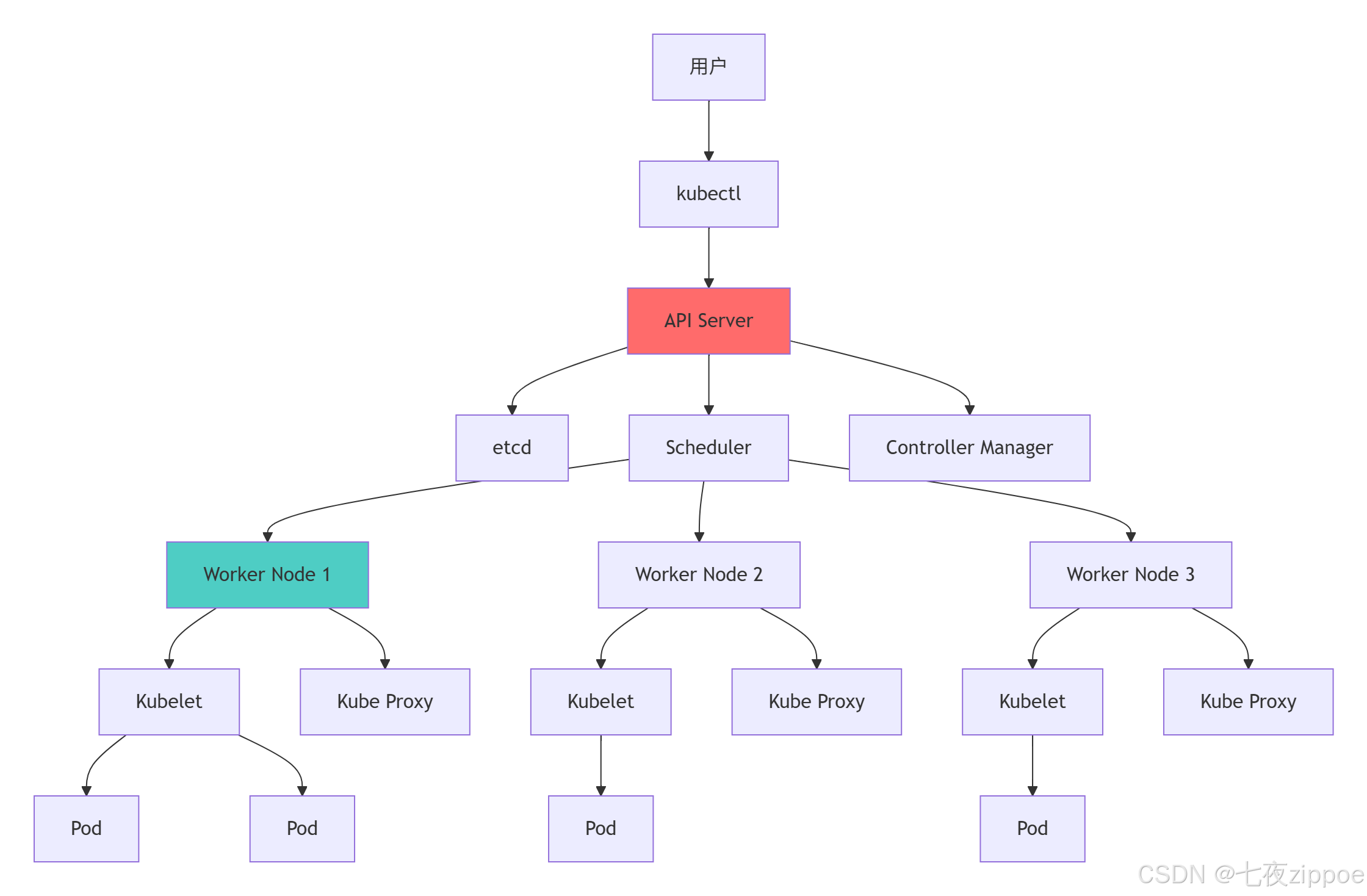
架构设计的关键优势:
-
声明式API:描述期望状态,系统自动维护实际状态
-
控制回路:持续监控和修复偏差,保证系统稳定性
-
松散耦合:组件通过API交互,可独立升级和扩展
-
水平扩展:无状态设计支持集群规模线性扩展
2.2 Pod与Deployment深度解析
2.2.1 Pod生命周期管理
python
# pod_management.py
from datetime import datetime
from typing import Dict, List, Optional
from enum import Enum
class PodPhase(Enum):
PENDING = "Pending"
RUNNING = "Running"
SUCCEEDED = "Succeeded"
FAILED = "Failed"
UNKNOWN = "Unknown"
class PodCondition(Enum):
POD_SCHEDULED = "PodScheduled"
READY = "Ready"
INITIALIZED = "Initialized"
CONTAINERS_READY = "ContainersReady"
class PodManager:
"""Pod生命周期管理器"""
def __init__(self):
self.pods = {}
self.deployments = {}
def create_pod_template(self, name: str, image: str, ports: List[int],
resources: Dict, env_vars: Dict) -> Dict:
"""创建Pod模板"""
return {
"metadata": {
"name": name,
"labels": {"app": name}
},
"spec": {
"containers": [{
"name": f"{name}-container",
"image": image,
"ports": [{"containerPort": port} for port in ports],
"resources": resources,
"env": [{"name": k, "value": v} for k, v in env_vars.items()],
"livenessProbe": {
"httpGet": {"path": "/health", "port": ports[0]},
"initialDelaySeconds": 30,
"periodSeconds": 10
},
"readinessProbe": {
"httpGet": {"path": "/ready", "port": ports[0]},
"initialDelaySeconds": 5,
"periodSeconds": 5
}
}],
"restartPolicy": "Always"
}
}
def simulate_pod_lifecycle(self, pod_template: Dict) -> Dict[str, List[str]]:
"""模拟Pod生命周期"""
events = []
current_phase = PodPhase.PENDING
# 调度阶段
events.append(f"{datetime.now()}: Pod创建请求已接收")
events.append(f"{datetime.now()}: 调度器寻找合适节点")
# 拉取镜像
events.append(f"{datetime.now()}: 开始拉取镜像 {pod_template['spec']['containers'][0]['image']}")
events.append(f"{datetime.now()}: 镜像拉取完成")
# 启动容器
events.append(f"{datetime.now()}: 启动容器")
current_phase = PodPhase.RUNNING
events.append(f"{datetime.now()}: Pod进入Running状态")
# 健康检查
events.append(f"{datetime.now()}: 开始健康检查")
events.append(f"{datetime.now()}: 就绪检查通过")
# 模拟运行
events.append(f"{datetime.now()}: Pod正常运行中")
return {
"phase": current_phase,
"events": events
}
class DeploymentController:
"""Deployment控制器模拟"""
def __init__(self):
self.replica_sets = {}
self.scaling_history = []
def create_deployment(self, name: str, replicas: int, pod_template: Dict) -> Dict:
"""创建Deployment"""
deployment = {
"metadata": {"name": name},
"spec": {
"replicas": replicas,
"selector": {"matchLabels": pod_template["metadata"]["labels"]},
"template": pod_template,
"strategy": {
"type": "RollingUpdate",
"rollingUpdate": {
"maxSurge": 1,
"maxUnavailable": 0
}
}
},
"status": {
"availableReplicas": 0,
"readyReplicas": 0,
"updatedReplicas": 0
}
}
# 模拟创建ReplicaSet
rs_name = f"{name}-rs-{int(datetime.now().timestamp())}"
self.replica_sets[rs_name] = {
"deployment": name,
"replicas": replicas,
"podTemplate": pod_template
}
self.scaling_history.append({
"timestamp": datetime.now(),
"deployment": name,
"action": "create",
"replicas": replicas
})
return deployment
def scale_deployment(self, deployment_name: str, new_replicas: int):
"""扩缩容Deployment"""
# 查找对应的ReplicaSet
rs_to_update = None
for rs_name, rs_data in self.replica_sets.items():
if rs_data["deployment"] == deployment_name:
rs_to_update = rs_name
break
if rs_to_update:
old_replicas = self.replica_sets[rs_to_update]["replicas"]
self.replica_sets[rs_to_update]["replicas"] = new_replicas
self.scaling_history.append({
"timestamp": datetime.now(),
"deployment": deployment_name,
"action": "scale",
"from": old_replicas,
"to": new_replicas
})
print(f"Deployment {deployment_name} 从 {old_replicas} 副本扩展到 {new_replicas} 副本")
def rolling_update(self, deployment_name: str, new_image: str):
"""滚动更新Deployment"""
# 创建新的ReplicaSet
new_rs_name = f"{deployment_name}-rs-{int(datetime.now().timestamp())}"
# 查找当前ReplicaSet
current_rs = None
for rs_name, rs_data in self.replica_sets.items():
if rs_data["deployment"] == deployment_name:
current_rs = rs_data
break
if current_rs:
# 更新Pod模板中的镜像
new_pod_template = current_rs["podTemplate"].copy()
new_pod_template["spec"]["containers"][0]["image"] = new_image
# 创建新的ReplicaSet
self.replica_sets[new_rs_name] = {
"deployment": deployment_name,
"replicas": 0, # 初始为0,逐步增加
"podTemplate": new_pod_template
}
# 模拟滚动更新过程
print(f"开始滚动更新 {deployment_name} 到镜像 {new_image}")
self.scaling_history.append({
"timestamp": datetime.now(),
"deployment": deployment_name,
"action": "update",
"image": new_image
})
# 生命周期管理演示
def demonstrate_pod_management():
"""演示Pod和Deployment管理"""
pod_manager = PodManager()
deployment_controller = DeploymentController()
# 创建Pod模板
pod_template = pod_manager.create_pod_template(
name="webapp",
image="python:3.9-slim",
ports=[5000],
resources={
"requests": {"cpu": "100m", "memory": "128Mi"},
"limits": {"cpu": "500m", "memory": "512Mi"}
},
env_vars={"ENVIRONMENT": "production", "LOG_LEVEL": "info"}
)
# 模拟Pod生命周期
lifecycle = pod_manager.simulate_pod_lifecycle(pod_template)
print("=== Pod生命周期模拟 ===")
for event in lifecycle["events"]:
print(f" {event}")
# 创建Deployment
deployment = deployment_controller.create_deployment(
name="webapp-deployment",
replicas=3,
pod_template=pod_template
)
# 模拟扩缩容
deployment_controller.scale_deployment("webapp-deployment", 5)
deployment_controller.scale_deployment("webapp-deployment", 2)
# 模拟滚动更新
deployment_controller.rolling_update("webapp-deployment", "python:3.9-slim-updated")
return lifecycle, deployment_controller.scaling_history3 实战部分:Python微服务完整编排方案
3.1 Flask微服务Kubernetes部署
3.1.1 完整的微服务应用示例
python
# flask_microservice.py
from flask import Flask, jsonify
import os
import socket
import logging
from datetime import datetime
app = Flask(__name__)
# 配置日志
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def hello():
"""基础健康检查端点"""
return jsonify({
"message": "Hello from Flask Microservice",
"hostname": socket.gethostname(),
"timestamp": datetime.now().isoformat(),
"version": "1.0.0"
})
@app.route('/health')
def health_check():
"""健康检查端点"""
try:
# 检查关键依赖(如数据库连接等)
# 这里简化处理,实际应该检查真实依赖
status = "healthy"
dependencies = {
"database": "connected",
"cache": "connected",
"storage": "available"
}
except Exception as e:
status = "unhealthy"
dependencies = {"error": str(e)}
return jsonify({
"status": status,
"timestamp": datetime.now().isoformat(),
"dependencies": dependencies
})
@app.route('/api/users')
def get_users():
"""示例API端点"""
# 模拟数据获取
users = [
{"id": 1, "name": "Alice", "email": "alice@example.com"},
{"id": 2, "name": "Bob", "email": "bob@example.com"},
{"id": 3, "name": "Charlie", "email": "charlie@example.com"}
]
logger.info(f"返回 {len(users)} 个用户数据")
return jsonify({
"users": users,
"count": len(users),
"host": socket.gethostname()
})
@app.route('/api/users/<int:user_id>')
def get_user(user_id):
"""获取特定用户信息"""
# 模拟数据库查询
user = {"id": user_id, "name": f"User{user_id}", "email": f"user{user_id}@example.com"}
return jsonify({
"user": user,
"host": socket.gethostname()
})
if __name__ == '__main__':
port = int(os.environ.get('PORT', 5000))
debug = os.environ.get('DEBUG', 'False').lower() == 'true'
logger.info(f"启动Flask微服务,端口: {port}, 调试模式: {debug}")
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=port, debug=debug)3.1.2 Docker镜像构建配置
# Dockerfile
# 多阶段构建:构建阶段
FROM python:3.9-slim as builder
# 安装构建依赖
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y \
build-essential \
curl \
&& rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
# 创建虚拟环境
RUN python -m venv /opt/venv
ENV PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
# 安装Python依赖
COPY requirements.txt .
RUN pip install --upgrade pip && \
pip install -r requirements.txt
# 生产阶段
FROM python:3.9-slim as production
# 安装运行时依赖
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y \
curl \
&& rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
# 复制虚拟环境
COPY --from=builder /opt/venv /opt/venv
ENV PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
# 创建非root用户
RUN groupadd -r appuser && useradd -r -g appuser appuser
# 创建应用目录
WORKDIR /app
# 复制应用代码
COPY --chown=appuser:appuser . .
# 切换用户
USER appuser
# 暴露端口
EXPOSE 5000
# 健康检查
HEALTHCHECK --interval=30s --timeout=10s --start-period=5s --retries=3 \
CMD curl -f http://localhost:5000/health || exit 1
# 启动命令
CMD ["python", "flask_microservice.py"]
# requirements.txt
flask==2.3.3
gunicorn==21.2.03.2 Kubernetes资源配置文件
3.2.1 Deployment配置
# deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: flask-microservice
namespace: default
labels:
app: flask-microservice
version: v1
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: flask-microservice
strategy:
type: RollingUpdate
rollingUpdate:
maxSurge: 1
maxUnavailable: 25%
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: flask-microservice
version: v1
spec:
containers:
- name: flask-app
image: your-registry/flask-microservice:latest
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- containerPort: 5000
protocol: TCP
env:
- name: PORT
value: "5000"
- name: DEBUG
value: "false"
- name: LOG_LEVEL
value: "INFO"
resources:
requests:
cpu: "100m"
memory: "128Mi"
limits:
cpu: "500m"
memory: "512Mi"
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /health
port: 5000
initialDelaySeconds: 30
periodSeconds: 10
timeoutSeconds: 5
failureThreshold: 3
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /health
port: 5000
initialDelaySeconds: 5
periodSeconds: 5
timeoutSeconds: 3
failureThreshold: 3
securityContext:
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 1000
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
restartPolicy: Always3.2.2 Service配置
# service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: flask-service
namespace: default
labels:
app: flask-microservice
spec:
selector:
app: flask-microservice
ports:
- name: http
protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 5000
type: ClusterIP
sessionAffinity: None3.2.3 Ingress配置
# ingress.yaml
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: flask-ingress
namespace: default
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "true"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-body-size: "10m"
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx
tls:
- hosts:
- flask-app.example.com
secretName: flask-tls-secret
rules:
- host: flask-app.example.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: flask-service
port:
number: 80
- path: /api
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: flask-service
port:
number: 803.3 自动化部署脚本
python
# deploy_scripts.py
import subprocess
import yaml
import time
from typing import Dict, List
class KubernetesDeployer:
"""Kubernetes部署管理器"""
def __init__(self, kubeconfig: str = None):
self.kubeconfig = kubeconfig
self.namespace = "default"
def apply_config(self, yaml_file: str) -> bool:
"""应用Kubernetes配置"""
try:
cmd = ["kubectl", "apply", "-f", yaml_file]
if self.kubeconfig:
cmd.extend(["--kubeconfig", self.kubeconfig])
result = subprocess.run(cmd, capture_output=True, text=True, check=True)
print(f"✅ 成功应用配置: {yaml_file}")
return True
except subprocess.CalledProcessError as e:
print(f"❌ 应用配置失败: {yaml_file}")
print(f"错误: {e.stderr}")
return False
def wait_for_deployment_ready(self, deployment_name: str, timeout: int = 300) -> bool:
"""等待Deployment就绪"""
print(f"⏳ 等待Deployment {deployment_name} 就绪...")
start_time = time.time()
while time.time() - start_time < timeout:
try:
cmd = [
"kubectl", "rollout", "status",
f"deployment/{deployment_name}",
"--timeout=30s"
]
if self.kubeconfig:
cmd.extend(["--kubeconfig", self.kubeconfig])
result = subprocess.run(cmd, capture_output=True, text=True, check=True)
print(f"✅ Deployment {deployment_name} 已就绪")
return True
except subprocess.CalledProcessError:
# 检查Pod状态
cmd = ["kubectl", "get", "pods", "-l", f"app={deployment_name}"]
if self.kubeconfig:
cmd.extend(["--kubeconfig", self.kubeconfig])
result = subprocess.run(cmd, capture_output=True, text=True)
print("当前Pod状态:")
print(result.stdout)
time.sleep(10)
print(f"❌ Deployment {deployment_name} 就绪超时")
return False
def get_service_url(self, service_name: str) -> str:
"""获取服务访问URL"""
try:
# 检查Ingress
cmd = ["kubectl", "get", "ingress", service_name]
if self.kubeconfig:
cmd.extend(["--kubeconfig", self.kubeconfig])
result = subprocess.run(cmd, capture_output=True, text=True)
if result.returncode == 0:
return f"通过Ingress访问: https://flask-app.example.com"
# 检查LoadBalancer
cmd = ["kubectl", "get", "svc", service_name]
result = subprocess.run(cmd, capture_output=True, text=True)
if "LoadBalancer" in result.stdout:
return f"通过LoadBalancer访问"
return f"集群内访问: http://{service_name}"
except Exception as e:
return f"无法确定访问URL: {str(e)}"
def deploy_full_stack(self) -> bool:
"""部署完整应用栈"""
deployment_files = [
"deployment.yaml",
"service.yaml",
"ingress.yaml"
]
print("🚀 开始部署Flask微服务到Kubernetes...")
# 按顺序应用配置
for file in deployment_files:
if not self.apply_config(file):
return False
# 等待部署完成
if not self.wait_for_deployment_ready("flask-microservice"):
return False
# 显示访问信息
url = self.get_service_url("flask-service")
print(f"🌐 应用部署完成!")
print(f" 访问地址: {url}")
print(f" 健康检查: {url}/health")
print(f" API端点: {url}/api/users")
return True
# 部署演示
def demonstrate_deployment():
"""演示完整部署流程"""
deployer = KubernetesDeployer()
# 模拟部署过程
success = deployer.deploy_full_stack()
if success:
print("🎉 部署成功!")
# 显示部署状态
commands = [
"kubectl get pods -l app=flask-microservice",
"kubectl get svc flask-service",
"kubectl get ingress flask-ingress"
]
for cmd in commands:
try:
result = subprocess.run(cmd.split(), capture_output=True, text=True)
print(f"\n{cmd}:")
print(result.stdout)
except Exception as e:
print(f"执行命令失败: {cmd} - {e}")
return success4 高级特性与生产级实践
4.1 HPA自动扩缩容配置
4.1.1 HPA资源配置
# hpa.yaml
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: flask-hpa
namespace: default
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: flask-microservice
minReplicas: 2
maxReplicas: 10
metrics:
- type: Resource
resource:
name: cpu
target:
type: Utilization
averageUtilization: 70
- type: Resource
resource:
name: memory
target:
type: Utilization
averageUtilization: 80
behavior:
scaleUp:
policies:
- type: Pods
value: 2
periodSeconds: 60
stabilizationWindowSeconds: 0
selectPolicy: Max
scaleDown:
policies:
- type: Pods
value: 1
periodSeconds: 60
stabilizationWindowSeconds: 300
selectPolicy: Min4.1.2 HPA监控与调优
python
# hpa_monitor.py
import time
import json
from datetime import datetime
from typing import Dict, List
class HPAMonitor:
"""HPA监控器"""
def __init__(self, deployment_name: str, namespace: str = "default"):
self.deployment_name = deployment_name
self.namespace = namespace
self.metrics_history = []
def get_hpa_status(self) -> Dict:
"""获取HPA状态"""
try:
cmd = [
"kubectl", "get", "hpa", self.deployment_name,
"-n", self.namespace,
"-o", "json"
]
result = subprocess.run(cmd, capture_output=True, text=True, check=True)
hpa_data = json.loads(result.stdout)
status = {
"timestamp": datetime.now().isoformat(),
"current_replicas": hpa_data["status"]["currentReplicas"],
"desired_replicas": hpa_data["status"]["desiredReplicas"],
"current_cpu_util": hpa_data["status"].get("currentCPUUtilizationPercentage", 0),
"target_cpu_util": hpa_data["spec"]["metrics"][0]["resource"]["target"]["averageUtilization"]
}
self.metrics_history.append(status)
return status
except Exception as e:
print(f"获取HPA状态失败: {e}")
return {}
def analyze_scaling_patterns(self) -> Dict:
"""分析扩缩容模式"""
if len(self.metrics_history) < 2:
return {}
# 计算平均指标
avg_cpu = sum(m["current_cpu_util"] for m in self.metrics_history) / len(self.metrics_history)
avg_replicas = sum(m["current_replicas"] for m in self.metrics_history) / len(self.metrics_history)
# 检测频繁扩缩容
scaling_events = 0
for i in range(1, len(self.metrics_history)):
if self.metrics_history[i]["current_replicas"] != self.metrics_history[i-1]["current_replicas"]:
scaling_events += 1
scaling_frequency = scaling_events / len(self.metrics_history)
return {
"average_cpu_utilization": avg_cpu,
"average_replicas": avg_replicas,
"scaling_frequency": scaling_frequency,
"total_scaling_events": scaling_events,
"optimization_suggestions": self._generate_suggestions(avg_cpu, scaling_frequency)
}
def _generate_suggestions(self, avg_cpu: float, scaling_frequency: float) -> List[str]:
"""生成优化建议"""
suggestions = []
if avg_cpu < 30:
suggestions.append("当前CPU利用率较低,可以考虑降低HPA目标阈值以节省资源")
elif avg_cpu > 80:
suggestions.append("CPU利用率持续较高,建议增加maxReplicas或优化应用性能")
if scaling_frequency > 0.3: # 30%的时间在扩缩容
suggestions.append("检测到频繁扩缩容,建议调整stabilizationWindowSeconds减少抖动")
if not suggestions:
suggestions.append("当前HPA配置运行良好,建议持续监控")
return suggestions
def monitor_continuous(self, duration_minutes: int = 10):
"""持续监控HPA状态"""
print(f"开始监控HPA,持续时间: {duration_minutes} 分钟")
end_time = time.time() + duration_minutes * 60
while time.time() < end_time:
status = self.get_hpa_status()
if status:
print(f"[{status['timestamp']}] 副本数: {status['current_replicas']}, "
f"CPU使用率: {status['current_cpu_util']}%")
time.sleep(30) # 每30秒检查一次
# 分析结果
analysis = self.analyze_scaling_patterns()
print("\n=== HPA监控分析报告 ===")
for key, value in analysis.items():
print(f"{key}: {value}")
# HPA监控演示
def demonstrate_hpa_monitoring():
"""演示HPA监控"""
monitor = HPAMonitor("flask-microservice")
# 模拟短期监控
print("开始HPA监控演示...")
# 在实际环境中,这里会真实监控HPA状态
# 为演示目的,我们模拟一些数据
simulated_data = [
{"current_replicas": 3, "current_cpu_util": 65},
{"current_replicas": 4, "current_cpu_util": 72},
{"current_replicas": 4, "current_cpu_util": 68},
{"current_replicas": 3, "current_cpu_util": 62},
{"current_replicas": 3, "current_cpu_util": 58}
]
for data in simulated_data:
data["timestamp"] = datetime.now().isoformat()
monitor.metrics_history.append(data)
time.sleep(1)
analysis = monitor.analyze_scaling_patterns()
return analysis4.2 ConfigMap与Secret管理
4.2.1 配置管理最佳实践
# configmap.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: flask-config
namespace: default
data:
application.yml: |
server:
port: 5000
logging:
level:
root: INFO
com.example: DEBUG
database:
host: postgresql.default.svc.cluster.local
port: 5432
name: myapp
cache:
enabled: true
ttl: 3600
logback.xml: |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration>
<appender name="CONSOLE" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<encoder>
<pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} - %msg%n</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<root level="INFO">
<appender-ref ref="CONSOLE" />
</root>
</configuration>
# secret.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: flask-secrets
namespace: default
type: Opaque
data:
database-password: cGFzc3dvcmQxMjM= # base64编码的密码
api-key: YXBpLWtleS1zZWNyZXQ= # base64编码的API密钥
jwt-secret: anN0LXNlY3JldC1rZXk= # base64编码的JWT密钥
stringData:
# 这些数据会自动base64编码
database-url: postgresql://username:password@host:5432/dbname4.2.2 配置热更新策略
python
# config_manager.py
import os
import yaml
import time
from typing import Dict, Any
class ConfigManager:
"""配置管理器"""
def __init__(self, config_map_path: str = "/etc/config/application.yml"):
self.config_map_path = config_map_path
self.last_modified = 0
self.current_config = {}
self.load_config()
def load_config(self):
"""加载配置"""
if os.path.exists(self.config_map_path):
with open(self.config_map_path, 'r') as f:
self.current_config = yaml.safe_load(f)
self.last_modified = os.path.getmtime(self.config_map_path)
def check_for_updates(self) -> bool:
"""检查配置更新"""
if not os.path.exists(self.config_map_path):
return False
current_modified = os.path.getmtime(self.config_map_path)
if current_modified > self.last_modified:
print("检测到配置更新,重新加载配置...")
self.load_config()
return True
return False
def get_config_value(self, key: str, default: Any = None) -> Any:
"""获取配置值"""
keys = key.split('.')
value = self.current_config
try:
for k in keys:
value = value[k]
return value
except (KeyError, TypeError):
return default
def watch_config_changes(self):
"""监听配置变化"""
print("开始监听配置变化...")
while True:
if self.check_for_updates():
# 配置已更新,执行相应操作
self.on_config_updated()
time.sleep(30) # 每30秒检查一次
def on_config_updated(self):
"""配置更新回调"""
# 重新初始化相关组件
log_level = self.get_config_value('logging.level.root', 'INFO')
print(f"配置已更新,新日志级别: {log_level}")
# 这里可以添加更多配置更新后的处理逻辑
# 比如重新连接数据库、刷新缓存等
# 配置使用示例
def demonstrate_config_usage():
"""演示配置使用"""
config = ConfigManager()
# 获取配置值
db_host = config.get_config_value('database.host', 'localhost')
log_level = config.get_config_value('logging.level.root', 'INFO')
print(f"数据库主机: {db_host}")
print(f"日志级别: {log_level}")
# 模拟配置更新监听
print("启动配置监听器...")
return config5 生产环境实战指南
5.1 企业级部署架构
5.1.1 高可用架构设计
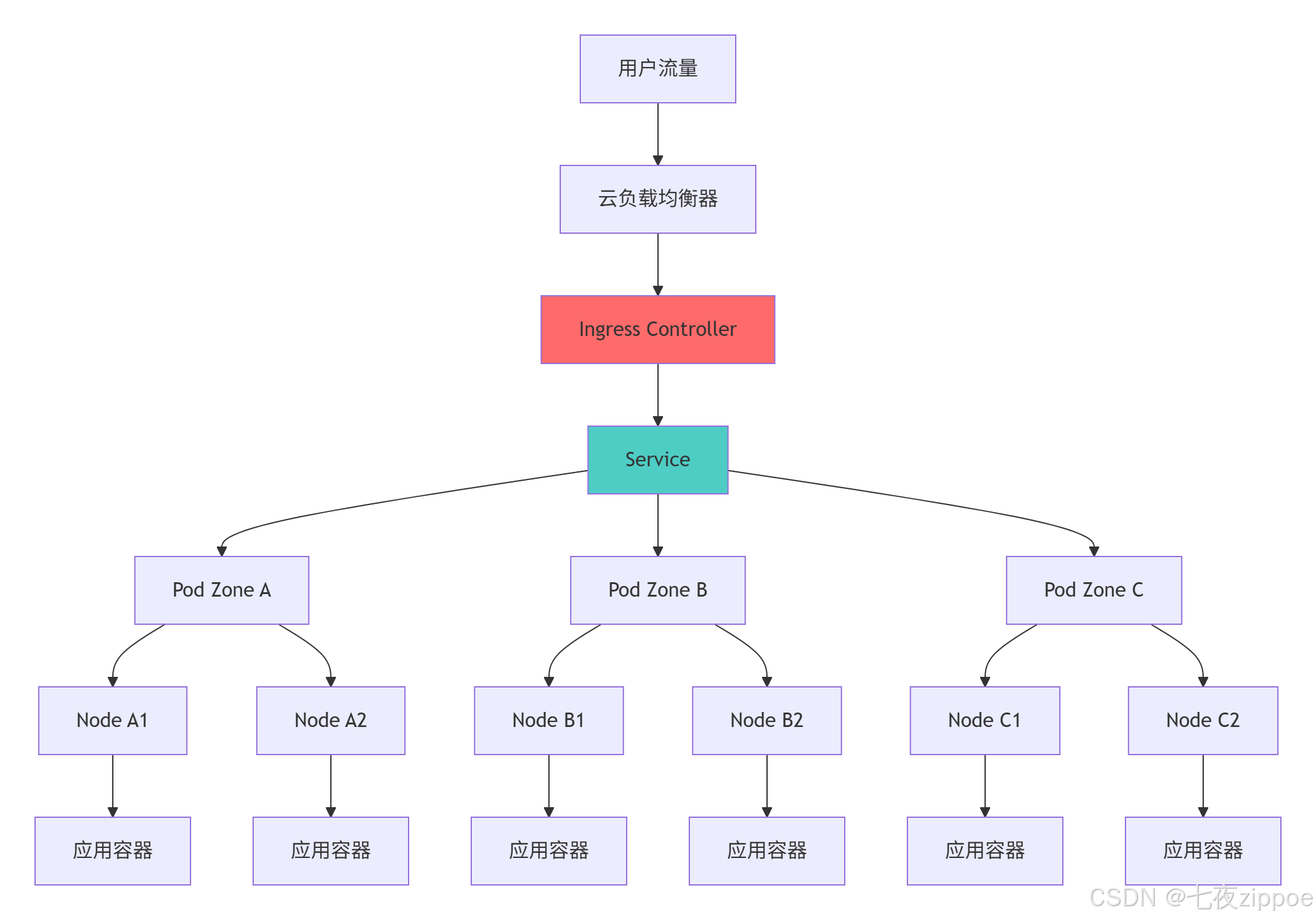
5.1.2 多环境配置管理
# kustomization.yaml
apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Kustomization
namespace: my-app
resources:
- deployment.yaml
- service.yaml
- ingress.yaml
- hpa.yaml
configMapGenerator:
- name: app-config
files:
- config/application.yml
secretGenerator:
- name: app-secrets
commands:
database-password: "echo -n $DB_PASSWORD | base64"
images:
- name: flask-microservice
newTag: latest
commonLabels:
app: flask-microservice
environment: production5.2 监控与日志管理
5.2.1 综合监控配置
# monitoring.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: flask-monitoring
labels:
app: flask-microservice
monitor: "true"
spec:
selector:
app: flask-microservice
ports:
- name: metrics
port: 5000
targetPort: 5000
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: prometheus-config
data:
prometheus.yml: |
global:
scrape_interval: 15s
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'flask-app'
static_configs:
- targets: ['flask-monitoring:5000']
metrics_path: /metrics6 故障排查与性能优化
6.1 常见问题解决方案
python
# troubleshooting.py
import subprocess
import json
from typing import Dict, List
class KubernetesTroubleshooter:
"""Kubernetes故障排查器"""
def diagnose_deployment_issues(self, deployment_name: str) -> Dict:
"""诊断部署问题"""
issues = []
# 检查Deployment状态
deployment_status = self._get_deployment_status(deployment_name)
if not deployment_status.get("available"):
issues.append("Deployment副本不可用")
# 检查Pod状态
pod_issues = self._check_pods(deployment_name)
issues.extend(pod_issues)
# 检查服务发现
service_issues = self._check_service(deployment_name)
issues.extend(service_issues)
return {
"deployment": deployment_name,
"issues_found": len(issues),
"issues": issues,
"suggestions": self._generate_troubleshooting_suggestions(issues)
}
def _get_deployment_status(self, deployment_name: str) -> Dict:
"""获取Deployment状态"""
try:
cmd = [
"kubectl", "get", "deployment", deployment_name,
"-o", "json"
]
result = subprocess.run(cmd, capture_output=True, text=True, check=True)
deployment = json.loads(result.stdout)
return {
"available": deployment["status"].get("availableReplicas", 0) > 0,
"ready": deployment["status"].get("readyReplicas", 0),
"desired": deployment["status"].get("replicas", 0)
}
except Exception as e:
return {"error": str(e)}
def _check_pods(self, deployment_name: str) -> List[str]:
"""检查Pod状态"""
issues = []
try:
cmd = [
"kubectl", "get", "pods",
"-l", f"app={deployment_name}",
"-o", "wide"
]
result = subprocess.run(cmd, capture_output=True, text=True, check=True)
# 分析Pod状态
lines = result.stdout.strip().split('\n')[1:] # 跳过标题行
for line in lines:
if "Error" in line or "CrashLoopBackOff" in line:
issues.append(f"Pod异常: {line.split()[0]}")
except Exception as e:
issues.append(f"检查Pod状态失败: {e}")
return issues
# 故障排查演示
def demonstrate_troubleshooting():
"""演示故障排查流程"""
troubleshooter = KubernetesTroubleshooter()
diagnosis = troubleshooter.diagnose_deployment_issues("flask-microservice")
print("=== Kubernetes故障诊断报告 ===")
print(f"部署名称: {diagnosis['deployment']}")
print(f"发现问题: {diagnosis['issues_found']}个")
for issue in diagnosis['issues']:
print(f"⚠️ {issue}")
for suggestion in diagnosis['suggestions']:
print(f"💡 {suggestion}")
return diagnosis官方文档与参考资源
-
Kubernetes官方文档- Kubernetes官方完整文档
-
Kubernetes API参考- 官方API文档
-
Kubernetes最佳实践- 生产环境最佳实践
-
Prometheus监控指南- 监控解决方案文档
通过本文的完整学习路径,您应该已经掌握了Kubernetes编排Python微服务的核心技术和实战技巧。Kubernetes作为云原生时代的操作系统,其正确实施将直接决定微服务架构的可靠性、可扩展性和可维护性。