Flutter for OpenHarmony 实战:网络请求与JSON解析完全指南
文章目录
- [Flutter for OpenHarmony 实战:网络请求与JSON解析完全指南](#Flutter for OpenHarmony 实战:网络请求与JSON解析完全指南)
-
- 摘要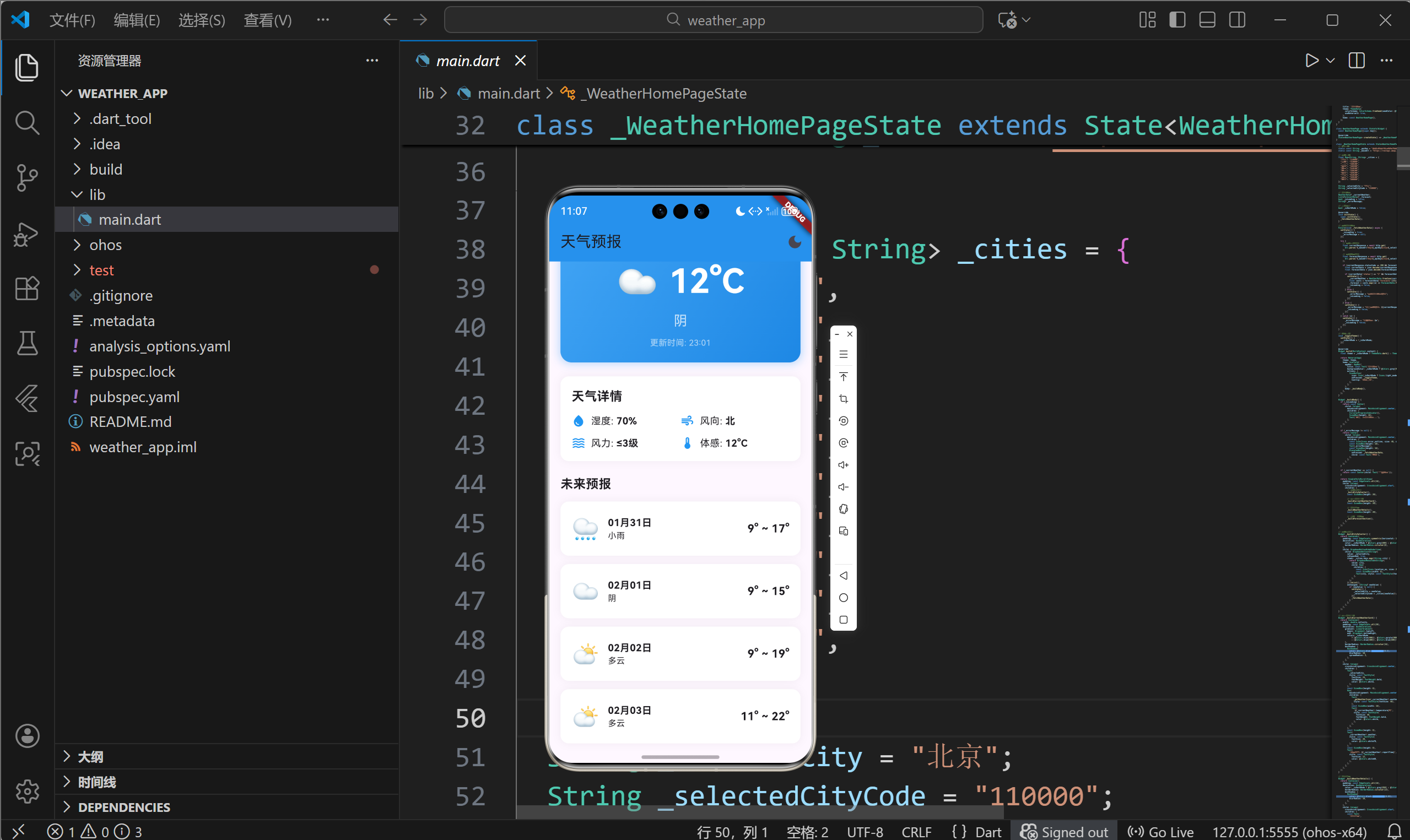
- 一、HTTP网络请求基础
-
- [1.1 HTTP协议概述](#1.1 HTTP协议概述)
- [1.2 RESTful API设计规范](#1.2 RESTful API设计规范)
- [1.3 异步网络请求的必要性](#1.3 异步网络请求的必要性)
- 二、http包使用详解
-
- [2.1 http包简介](#2.1 http包简介)
- [2.2 GET请求基础用法](#2.2 GET请求基础用法)
- [2.3 带参数的GET请求](#2.3 带参数的GET请求)
- [2.4 响应对象解析](#2.4 响应对象解析)
- 三、异步编程与错误处理
-
- [3.1 Dart异步编程模型](#3.1 Dart异步编程模型)
- [3.2 并发请求处理](#3.2 并发请求处理)
- [3.3 错误处理策略](#3.3 错误处理策略)
- [3.4 超时处理](#3.4 超时处理)
- 四、JSON数据解析技术
-
- [4.1 JSON数据结构分析](#4.1 JSON数据结构分析)
- [4.2 dart:convert基础使用](#4.2 dart:convert基础使用)
- [4.3 解析嵌套JSON](#4.3 解析嵌套JSON)
- [4.4 类型安全访问](#4.4 类型安全访问)
- 五、数据模型类设计最佳实践
-
- [5.1 为什么需要数据模型类](#5.1 为什么需要数据模型类)
- [5.2 数据模型类设计](#5.2 数据模型类设计)
- [5.3 使用模型类解析数据](#5.3 使用模型类解析数据)
- [5.4 列表数据解析](#5.4 列表数据解析)
- 六、API集成实战案例
-
- [6.1 完整的请求封装](#6.1 完整的请求封装)
- [6.2 在State中使用API](#6.2 在State中使用API)
- [6.3 加载状态管理](#6.3 加载状态管理)
- 七、性能优化与缓存策略
-
- [7.1 减少不必要的请求](#7.1 减少不必要的请求)
- [7.2 使用缓存](#7.2 使用缓存)
- [7.3 请求去重](#7.3 请求去重)
- 八、总结
摘要
网络请求和数据处理是移动应用开发的核心技能。本文以天气预报应用为例,深入讲解Flutter for OpenHarmony平台上的HTTP网络请求技术、JSON数据解析方法、异步编程模型以及错误处理策略。通过本文学习,读者将掌握Flutter中http包的使用技巧,了解数据模型设计的最佳实践,为开发复杂的网络应用打下坚实基础。
一、HTTP网络请求基础
1.1 HTTP协议概述
HTTP(HyperText Transfer Protocol)是应用层协议,定义了客户端与服务器之间数据传输的规范。
常见HTTP方法
- GET:获取资源
- POST:创建资源
- PUT:更新资源
- DELETE:删除资源
状态码含义
- 200:请求成功
- 400:客户端错误
- 401:未授权
- 404:资源未找到
- 500:服务器错误
1.2 RESTful API设计规范
天气预报应用使用的是RESTful风格的API:
基础URL: https://restapi.amap.com/v3/weather/weatherInfo
实时天气请求:
GET /v3/weather/weatherInfo?key=YOUR_KEY&city=110000&extensions=base
预报天气请求:
GET /v3/weather/weatherInfo?key=YOUR_KEY&city=110000&extensions=allAPI参数说明
- key:开发者密钥,用于身份验证
- city:城市编码(adcode)
- extensions:数据类型(base=实况,all=预报)
1.3 异步网络请求的必要性
移动应用中的网络请求必须异步执行,原因如下:
UI响应性
- 网络请求耗时较长(几百毫秒到几秒)
- 同步请求会阻塞UI线程,导致界面卡顿
- 用户体验要求操作即时响应
系统稳定性
- 主线程阻塞可能导致应用无响应(ANR)
- 现代操作系统禁止在主线程执行网络操作
二、http包使用详解
2.1 http包简介
http是Dart官方推荐的轻量级HTTP客户端库:
主要特性
- 简洁易用的API设计
- 支持所有HTTP方法
- 完善的异步支持
- 自动处理编码和压缩
添加依赖
yaml
dependencies:
http: ^1.2.0安装命令:
bash
flutter pub get2.2 GET请求基础用法
dart
import 'package:http/http.dart' as http;
// 简单GET请求
Future<void> fetchData() async {
final url = Uri.parse('https://api.example.com/data');
final response = await http.get(url);
if (response.statusCode == 200) {
print(response.body);
}
}2.3 带参数的GET请求
dart
// 方式一:URL拼接
final url = Uri.parse(
'https://restapi.amap.com/v3/weather/weatherInfo?key=$_apiKey&city=$_cityCode&extensions=base'
);
// 方式二:使用queryParameters(推荐)
final url = Uri.https('restapi.amap.com', '/v3/weather/weatherInfo', {
'key': _apiKey,
'city': _cityCode,
'extensions': 'base',
});使用queryParameters的优势
- 自动处理特殊字符转义
- 代码可读性更好
- 便于动态添加参数
2.4 响应对象解析
http.Response对象包含以下主要属性:
dart
class Response {
// 状态码
int statusCode;
// 响应体(字符串)
String body;
// 响应头
Map<String, String> headers;
// 请求信息
Request request;
}使用示例
dart
final response = await http.get(url);
// 检查状态码
if (response.statusCode == 200) {
// 获取响应体
String data = response.body;
// 获取响应头
String contentType = response.headers['content-type'] ?? '';
}三、异步编程与错误处理
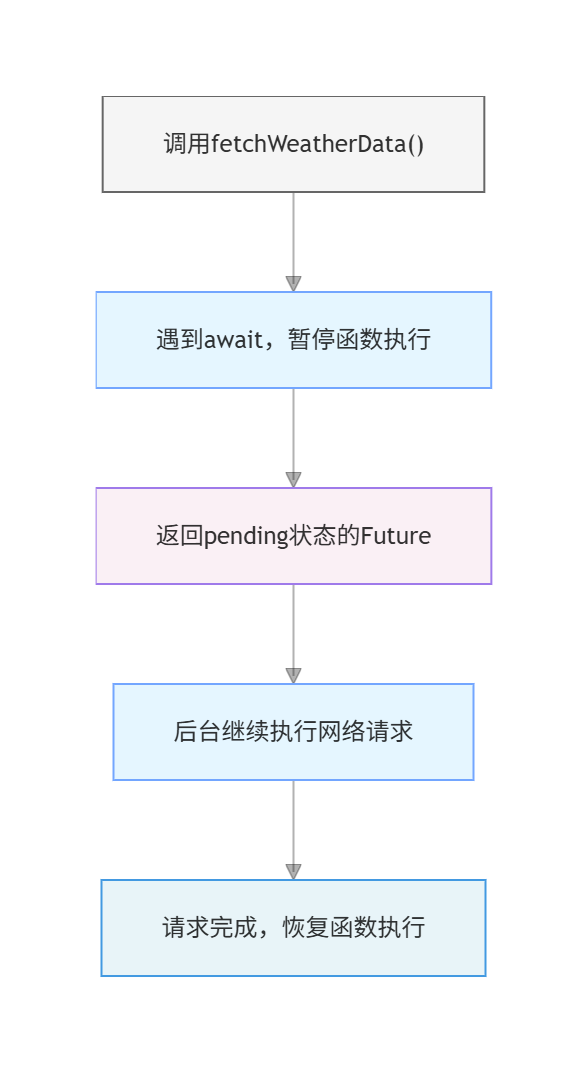
3.1 Dart异步编程模型
Dart使用Future和async/await处理异步操作:
dart
// 异步函数定义
Future<void> fetchWeatherData() async {
// await等待异步操作完成
final response = await http.get(url);
// 继续执行后续代码
}执行流程
3.2 并发请求处理
天气预报需要同时获取实时天气和预报数据:
dart
Future<void> _fetchWeatherData() async {
try {
// 并发发起两个请求
final currentResponse = await http.get(
Uri.parse("$_baseUrl?key=$_apiKey&city=$_selectedCityCode&extensions=base"),
);
final forecastResponse = await http.get(
Uri.parse("$_baseUrl?key=$_apiKey&city=$_selectedCityCode&extensions=all"),
);
// 处理响应...
} catch (e) {
// 错误处理
}
}改进:使用Future.wait并发执行
dart
Future<void> _fetchWeatherData() async {
try {
// 同时发起两个请求
final responses = await Future.wait([
http.get(Uri.parse("$_baseUrl?key=$_apiKey&city=$_selectedCityCode&extensions=base")),
http.get(Uri.parse("$_baseUrl?key=$_apiKey&city=$_selectedCityCode&extensions=all")),
]);
final currentResponse = responses[0];
final forecastResponse = responses[1];
// 处理响应...
} catch (e) {
// 错误处理
}
}3.3 错误处理策略
dart
Future<void> _fetchWeatherData() async {
setState(() {
_isLoading = true;
_errorMessage = null;
});
try {
final response = await http.get(url);
// HTTP状态码检查
if (response.statusCode == 200) {
final data = json.decode(response.body);
// 业务状态码检查
if (data['status'] == "1") {
setState(() {
_weatherData = parseData(data);
_isLoading = false;
});
} else {
setState(() {
_errorMessage = "API返回错误: ${data['info']}";
_isLoading = false;
});
}
} else {
setState(() {
_errorMessage = "HTTP错误: ${response.statusCode}";
_isLoading = false;
});
}
} catch (e) {
// 捕获所有异常
setState(() {
_errorMessage = "网络请求失败: $e";
_isLoading = false;
});
}
}错误类型
- SocketException:网络连接失败
- HttpException:HTTP解析错误
- FormatException:JSON格式错误
- TimeoutException:请求超时
3.4 超时处理
dart
import 'dart:async';
Future<void> fetchWeatherWithTimeout() async {
try {
final response = await http.get(url).timeout(
const Duration(seconds: 10),
onTimeout: () {
// 超时后的处理
throw Exception('请求超时,请检查网络连接');
},
);
} catch (e) {
print('错误: $e');
}
}四、JSON数据解析技术
4.1 JSON数据结构分析
高德天气API返回的JSON结构:
json
{
"status": "1",
"info": "OK",
"infocode": "10000",
"lives": [
{
"province": "北京",
"city": "北京市",
"weather": "晴",
"temperature": "15",
"winddirection": "西",
"windpower": "3级",
"humidity": "25",
"reporttime": "2024-01-15 14:00:00"
}
]
}数据特点
- 最外层是状态信息
- lives是一个数组(虽然通常只有一个元素)
- 实际天气数据在lives[0]中
4.2 dart:convert基础使用
dart
import 'dart:convert';
// JSON字符串解析为Dart对象
Map<String, dynamic> data = json.decode(jsonString);
// Dart对象编码为JSON字符串
String jsonString = json.encode(dartObject);4.3 解析嵌套JSON
dart
// 解析响应
final response = await http.get(url);
final data = json.decode(response.body);
// 检查状态
if (data['status'] == "1" && data['lives'] != null) {
// 获取lives数组
List<dynamic> lives = data['lives'];
// 获取第一个元素
Map<String, dynamic> liveData = lives[0];
// 提取字段
String city = liveData['city'] ?? '';
String weather = liveData['weather'] ?? '';
String temperature = liveData['temperature'] ?? '';
}4.4 类型安全访问
dart
// 使用null安全操作符
String city = liveData['city'] ?? '未知';
int temperature = int.tryParse(liveData['temperature'] ?? '0') ?? 0;
// 使用??提供默认值
List<dynamic> casts = forecastData['forecasts']?[0]['casts'] as List? ?? [];五、数据模型类设计最佳实践
5.1 为什么需要数据模型类
原始解析方式的问题
dart
// 不好的做法
Text(data['lives'][0]['temperature'])问题
- 类型不安全
- 代码重复
- 难以维护
- 没有编译时检查
使用数据模型的优势
dart
// 好的做法
Text(weatherData.temperature)优势
- 类型安全
- 代码清晰
- 便于复用
- 支持IDE自动补全
5.2 数据模型类设计
dart
class WeatherData {
final String province;
final String city;
final String weather;
final String temperature;
final String windDirection;
final String windPower;
final String humidity;
final String reportTime;
WeatherData({
required this.province,
required this.city,
required this.weather,
required this.temperature,
required this.windDirection,
required this.windPower,
required this.humidity,
required this.reportTime,
});
// 工厂构造函数:从JSON创建实例
factory WeatherData.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) {
return WeatherData(
province: json['province'] ?? '',
city: json['city'] ?? '',
weather: json['weather'] ?? '',
temperature: json['temperature'] ?? '',
windDirection: json['winddirection'] ?? '',
windPower: json['windpower'] ?? '',
humidity: json['humidity'] ?? '',
reportTime: _formatTime(json['reporttime'] ?? ''),
);
}
// 私有辅助方法
static String _formatTime(String reportTime) {
try {
final dateTime = DateTime.parse(reportTime);
return '${dateTime.hour.toString().padLeft(2, '0')}:${dateTime.minute.toString().padLeft(2, '0')}';
} catch (e) {
return reportTime;
}
}
}5.3 使用模型类解析数据
dart
// 从API响应创建模型实例
final data = json.decode(response.body);
if (data['status'] == "1") {
setState(() {
_currentWeather = WeatherData.fromJson(data['lives'][0]);
});
}
// 在UI中使用
Text(_currentWeather!.temperature)5.4 列表数据解析
dart
class ForecastData {
final String date;
final String dayWeather;
final String nightTemp;
final String dayTemp;
ForecastData({
required this.date,
required this.dayWeather,
required this.nightTemp,
required this.dayTemp,
});
factory ForecastData.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) {
return ForecastData(
date: _formatDate(json['date'] ?? ''),
dayWeather: json['dayweather'] ?? '',
nightTemp: json['nighttemp'] ?? '',
dayTemp: json['daytemp'] ?? '',
);
}
static String _formatDate(String dateStr) {
try {
final parts = dateStr.split('-');
if (parts.length == 3) {
return '${parts[1]}月${parts[2]}日';
}
return dateStr;
} catch (e) {
return dateStr;
}
}
}
// 解析列表数据
final casts = forecastData['forecasts'][0]['casts'] as List;
_forecast = casts.map((e) => ForecastData.fromJson(e)).toList();六、API集成实战案例
6.1 完整的请求封装
dart
class WeatherApiClient {
static const String _baseUrl = "https://restapi.amap.com/v3/weather/weatherInfo";
static const String _apiKey = "YOUR_API_KEY";
// 获取实时天气
static Future<WeatherData> getCurrentWeather(String cityCode) async {
final url = Uri.parse("$_baseUrl?key=$_apiKey&city=$cityCode&extensions=base");
try {
final response = await http.get(url).timeout(
const Duration(seconds: 10),
);
if (response.statusCode != 200) {
throw Exception('HTTP错误: ${response.statusCode}');
}
final data = json.decode(response.body);
if (data['status'] != "1") {
throw Exception('API错误: ${data['info']}');
}
return WeatherData.fromJson(data['lives'][0]);
} catch (e) {
throw Exception('获取天气失败: $e');
}
}
// 获取天气预报
static Future<List<ForecastData>> getForecast(String cityCode) async {
final url = Uri.parse("$_baseUrl?key=$_apiKey&city=$cityCode&extensions=all");
try {
final response = await http.get(url).timeout(
const Duration(seconds: 10),
);
if (response.statusCode != 200) {
throw Exception('HTTP错误: ${response.statusCode}');
}
final data = json.decode(response.body);
if (data['status'] != "1") {
throw Exception('API错误: ${data['info']}');
}
final casts = data['forecasts'][0]['casts'] as List;
return casts.map((e) => ForecastData.fromJson(e)).toList();
} catch (e) {
throw Exception('获取预报失败: $e');
}
}
}6.2 在State中使用API
dart
class _WeatherHomePageState extends State<WeatherHomePage> {
WeatherData? _currentWeather;
List<ForecastData>? _forecast;
bool _isLoading = false;
String? _errorMessage;
Future<void> _fetchWeatherData() async {
setState(() {
_isLoading = true;
_errorMessage = null;
});
try {
// 并发获取两种数据
final results = await Future.wait([
WeatherApiClient.getCurrentWeather(_selectedCityCode),
WeatherApiClient.getForecast(_selectedCityCode),
]);
setState(() {
_currentWeather = results[0] as WeatherData;
_forecast = results[1] as List<ForecastData>;
_isLoading = false;
});
} catch (e) {
setState(() {
_errorMessage = e.toString();
_isLoading = false;
});
}
}
}6.3 加载状态管理
dart
Widget _buildBody() {
// 加载中
if (_isLoading) {
return const Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
CircularProgressIndicator(),
SizedBox(height: 16),
Text('正在加载天气数据...'),
],
),
);
}
// 错误状态
if (_errorMessage != null) {
return Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
const Icon(Icons.error_outline, size: 48, color: Colors.red),
const SizedBox(height: 16),
Text(_errorMessage!),
const SizedBox(height: 16),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: _fetchWeatherData,
child: const Text('重试'),
),
],
),
);
}
// 数据加载成功
if (_currentWeather == null) {
return const Center(child: Text('暂无数据'));
}
return SingleChildScrollView(
child: Column(
children: [
_buildCurrentWeatherCard(),
_buildForecastSection(),
],
),
);
}此处插入图片:加载中、错误、成功三种状态的截图
七、性能优化与缓存策略
7.1 减少不必要的请求
添加本地缓存
dart
class WeatherCache {
static final Map<String, CachedData> _cache = {};
static bool isValid(String key) {
final cached = _cache[key];
if (cached == null) return false;
// 缓存10分钟有效
final age = DateTime.now().difference(cached.timestamp);
return age.inMinutes < 10;
}
static WeatherData? getWeather(String city) {
if (!isValid(city)) return null;
return _cache[city]?.data;
}
static void setWeather(String city, WeatherData data) {
_cache[city] = CachedData(
data: data,
timestamp: DateTime.now(),
);
}
}
class CachedData {
final WeatherData data;
final DateTime timestamp;
CachedData({required this.data, required this.timestamp});
}7.2 使用缓存
dart
Future<void> _fetchWeatherData() async {
// 检查缓存
final cached = WeatherCache.getWeather(_selectedCityCode);
if (cached != null) {
setState(() {
_currentWeather = cached;
_isLoading = false;
});
return;
}
// 请求新数据
try {
final weather = await WeatherApiClient.getCurrentWeather(_selectedCityCode);
WeatherCache.setWeather(_selectedCityCode, weather);
setState(() {
_currentWeather = weather;
_isLoading = false;
});
} catch (e) {
// 错误处理
}
}7.3 请求去重
防止用户快速切换城市时发起多个请求:
dart
class _WeatherHomePageState extends State<WeatherHomePage> {
String _pendingRequestCity = '';
Future<void> _fetchWeatherData() async {
final city = _selectedCityCode;
// 如果有正在进行的请求,忽略
if (_pendingRequestCity == city) return;
_pendingRequestCity = city;
try {
final weather = await WeatherApiClient.getCurrentWeather(city);
// 只处理最新的请求结果
if (_selectedCityCode == city) {
setState(() {
_currentWeather = weather;
});
}
} finally {
if (_selectedCityCode == city) {
_pendingRequestCity = '';
}
}
}
}八、总结
本文深入讲解了Flutter for OpenHarmony平台上的网络请求和JSON解析技术,主要内容包括:
- http包使用:掌握GET请求、参数传递、响应处理
- 异步编程:理解Future、async/await的工作原理
- 错误处理:学会捕获各种异常,提供友好的错误提示
- JSON解析:使用dart:convert处理API响应数据
- 数据模型:设计类型安全的数据模型类
- 性能优化:实现缓存和请求去重提升用户体验
这些技术是开发网络应用的基础,掌握后可以应对大多数API集成场景。通过不断实践,读者可以开发出更复杂、更稳定的网络应用。
欢迎加入开源鸿蒙跨平台社区 : 开源鸿蒙跨平台开发者社区