二叉树
- 1、二叉树思路总结
-
- [1.1 树的自顶向下和自底向上遍历](#1.1 树的自顶向下和自底向上遍历)
- [1.2 深度和高度](#1.2 深度和高度)
- [1.3 递归函数有无返回值的判断](#1.3 递归函数有无返回值的判断)
- [1.4 前中后序两两组合确定二叉树](#1.4 前中后序两两组合确定二叉树)
- [1.5 递归函数有返回值时,如何区分搜索一条边还是搜索整个树](#1.5 递归函数有返回值时,如何区分搜索一条边还是搜索整个树)
- [1.6 递归函数前加if](#1.6 递归函数前加if)
- 2、二叉树的前序遍历(力扣144)
- 3、二叉树的后序遍历(力扣145)
- 4、二叉树的中序遍历(力扣94)
- [5、 二叉树的层序遍历(力扣102)](#5、 二叉树的层序遍历(力扣102))
- [6、二叉树的层序遍历 II(力扣107)](#6、二叉树的层序遍历 II(力扣107))
- 7、二叉树的右视图(力扣199)
- 8、二叉树的层平均值(力扣637)
- [9、N 叉树的层序遍历(力扣429)](#9、N 叉树的层序遍历(力扣429))
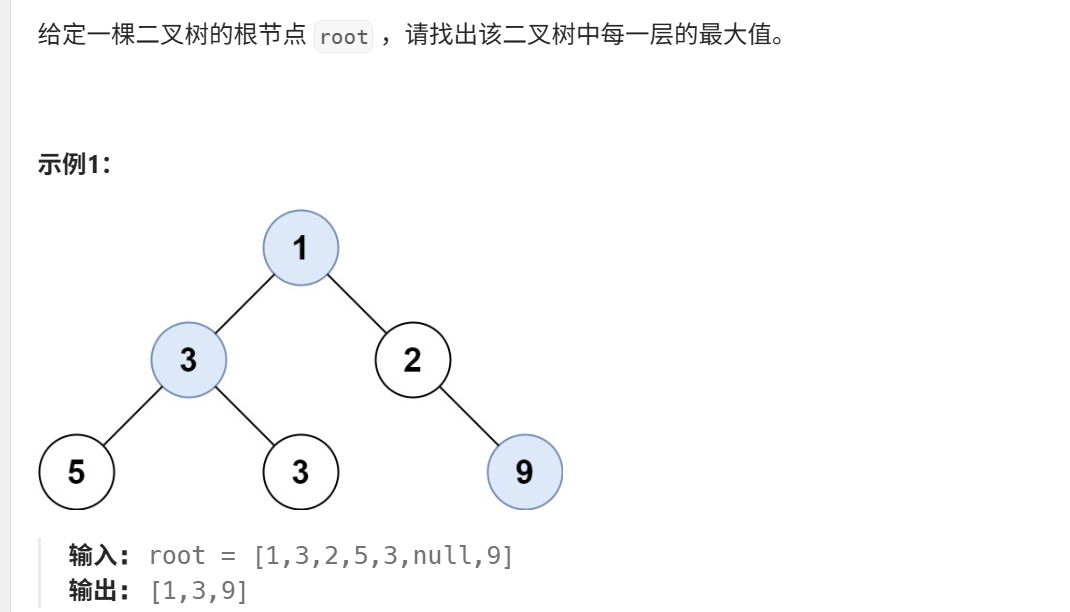
- 10、在每个树行中找最大值(力扣515)
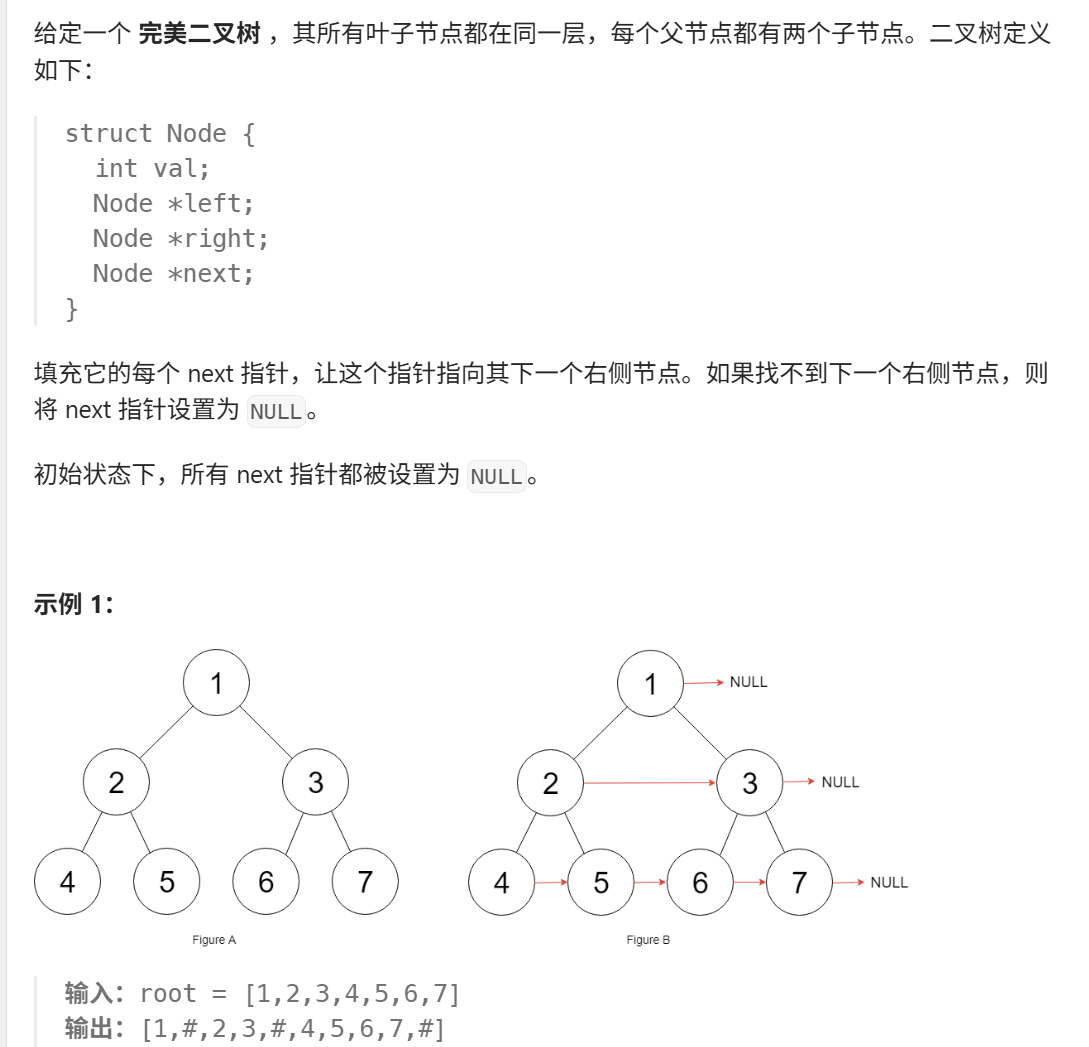
- 11、填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针(力扣116)
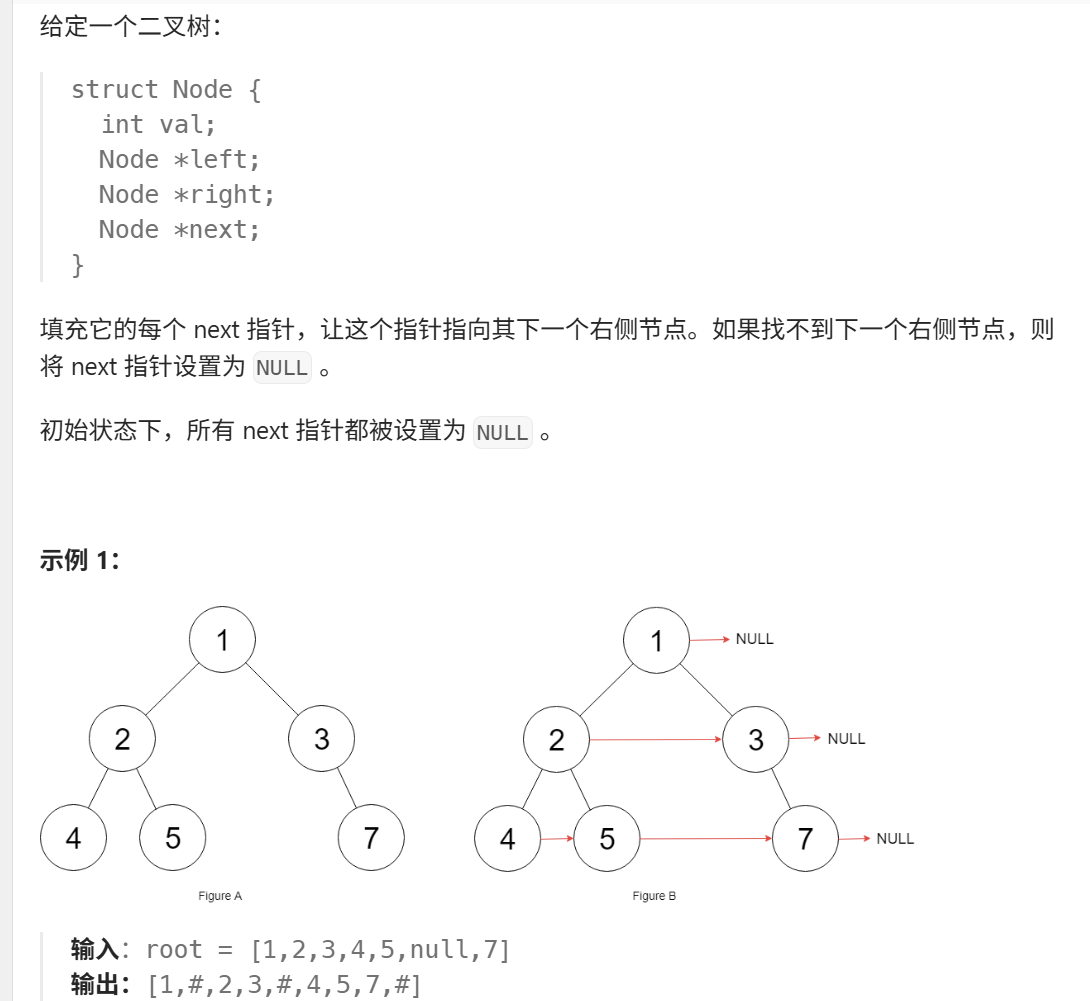
- [12、填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II(力扣117)](#12、填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II(力扣117))
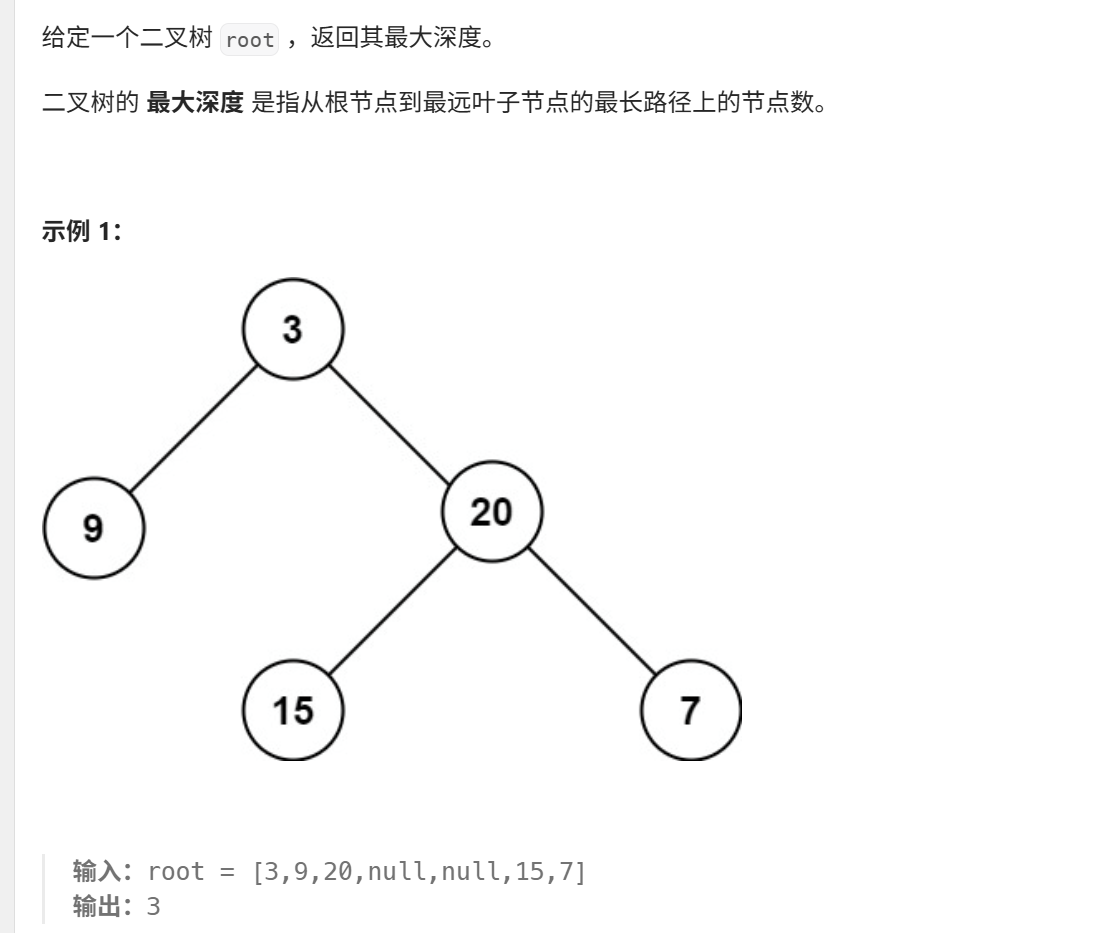
- 13、二叉树的最大深度(力扣104)
- 14、二叉树的最小深度(力扣111)
- 15、完全二叉树的节点个数(力扣222)
- 16、平衡二叉树(力扣110)
- 17、二叉树的所有路径(力扣257)
- 18、左叶子之和(力扣404)
- 19、找树左下角的值(力扣513)
- 20、路径总和(力扣112)
进阶二叉树算法题请点击LeetCode_二叉树2
1、二叉树思路总结
1.1 树的自顶向下和自底向上遍历
- 自顶向下
前序遍历:先看当前节点的情况,再看当前节点的左子节点和右子节点的情况,然后层层向下,但是存在的问题是可能存在重复遍历的情况。 - 自底向上
后序遍历:先看当前节点的左子节点和右子节点的情况,再看当前节点的情况,然后层层向上,不存在重复遍历,节省复杂度。典型题:平衡二叉树(力扣110)
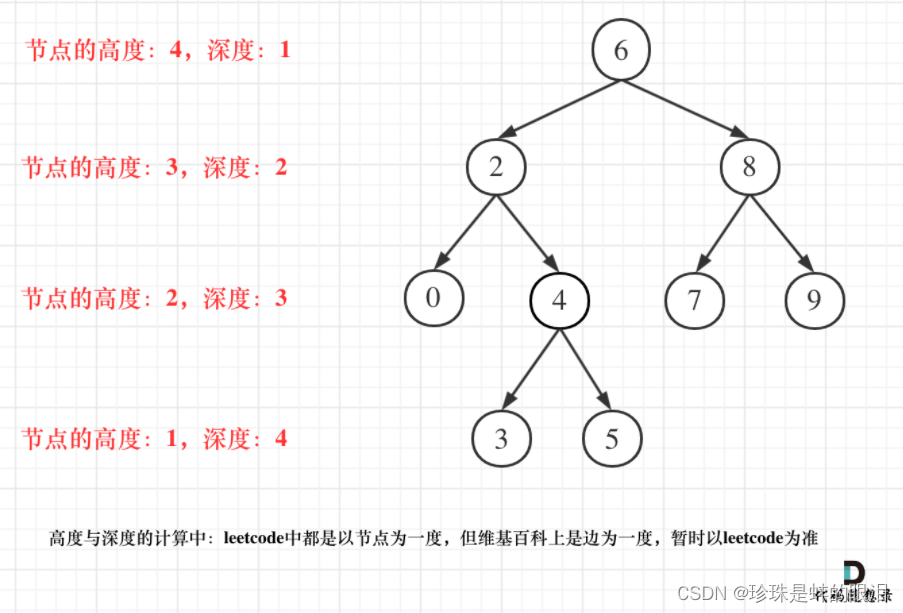
1.2 深度和高度
- 二叉树的高度和深度是等价的。
- 二叉树节点的深度 :指从根节点到该节点的最长路径包含的节点个数。求深度:可以从上到下去查 所以需要前序遍历(中左右)。
二叉树节点的高度:指从该节点到叶子节点的最长路径包含的节点个数。求高度:从下到上去查,所以只能后序遍历(左右中)。
1.3 递归函数有无返回值的判断
- 如果需要搜索整棵二叉树且不用处理递归返回值,递归函数就不要返回值。(113.路径总和ii)
- 如果需要搜索整棵二叉树且需要处理递归返回值,递归函数就需要返回值。 (236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先)
- 如果要搜索其中一条符合条件的路径,那么递归一定需要返回值,因为遇到符合条件的路径了就要及时返回。(路径总和112)
1.4 前中后序两两组合确定二叉树
- 前序和中序可以唯一确定一棵二叉树。
- 后序和中序可以唯一确定一棵二叉树。
- 前序和后序不能唯一确定一棵二叉树
1.5 递归函数有返回值时,如何区分搜索一条边还是搜索整个树
- 搜索一条边的写法(直接返回)
java
if(递归函数(root.left)) return;
if(递归函数(root.right)) return;- 搜索整个树的写法(用left和right变量接住返回值,进行逻辑处理)
java
left = 递归函数(root.left)
right = 递归函数(root.right)
left 和 right 的逻辑处理1.6 递归函数前加if
什么时候递归函数前面加if,什么时候不加if?一般情况来说:如果让空节点(空指针)进入递归,就不加if,如果不让空节点进入递归,就加if限制一下, 终止条件也会相应的调整。
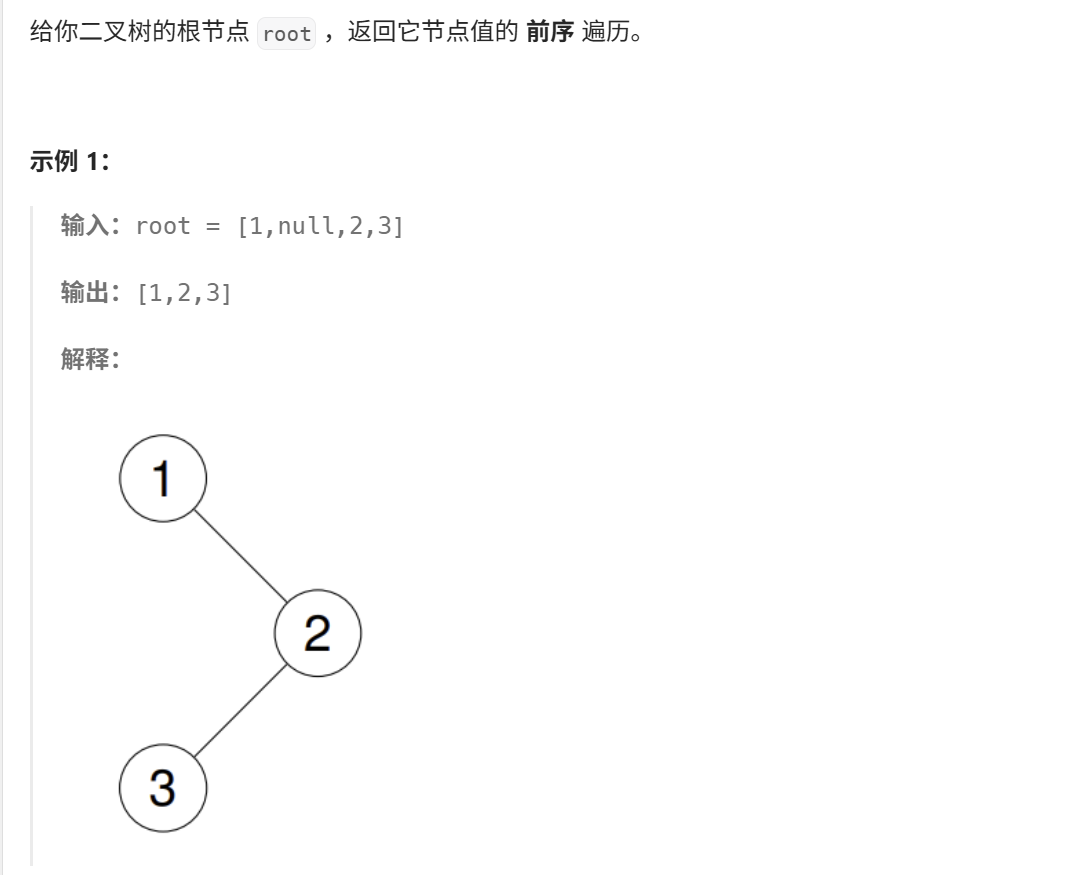
2、二叉树的前序遍历(力扣144)
java
//1.递归
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
preOrder(root,list);
return list;
}
public void preOrder(TreeNode root,List<Integer> list){
if(root == null){
return;
}
list.add(root.val);
preOrder(root.left,list);
preOrder(root.right,list);
}
java
//2.迭代,利用栈
public static List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null){
return list;
}
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();
stack.push(root);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
list.add(node.val);
// 先右子结点入栈
if(node.right != null){
stack.push(node.right);
}
// 再左子结点入栈
if(node.left != null){
stack.push(node.left);
}
}
return list;
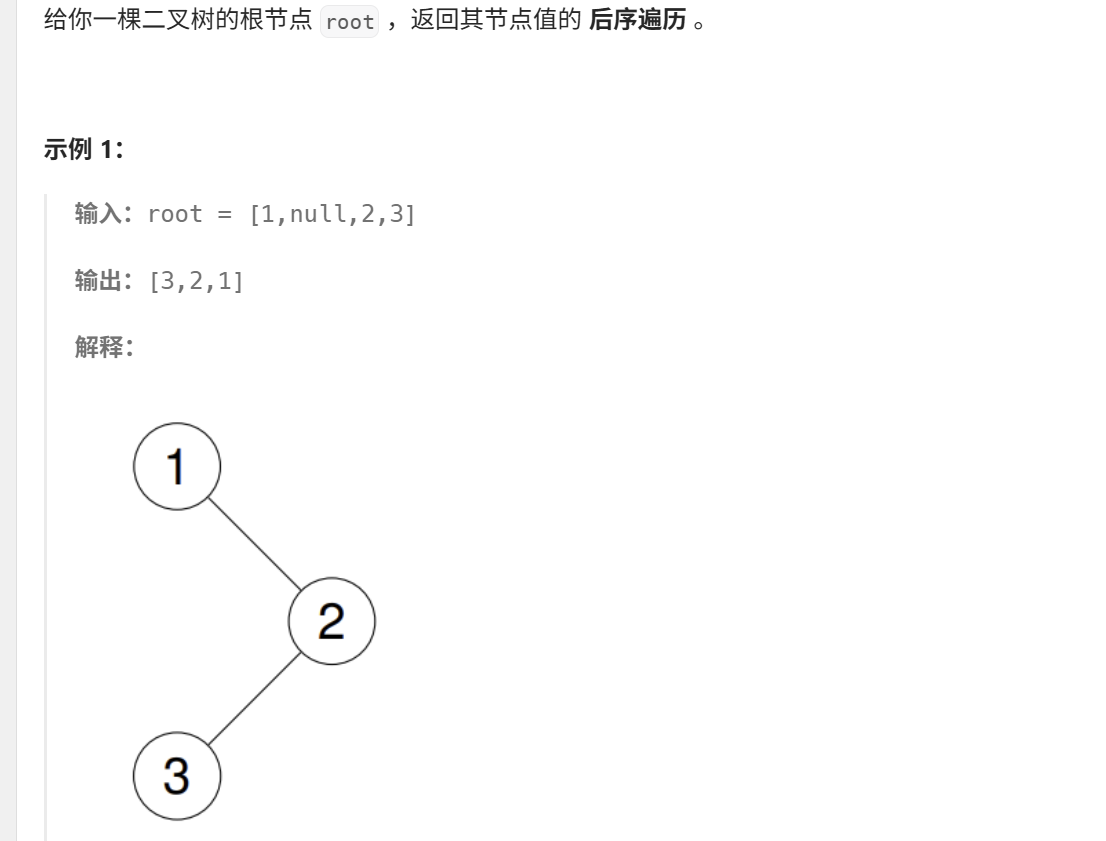
}3、二叉树的后序遍历(力扣145)
java
//1.递归
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
postOrder(root,list);
return list;
}
public void postOrder(TreeNode root,List<Integer> list){
if(root == null){
return;
}
postOrder(root.left,list42
postOrder(root.right,list);
list.add(root.val);
}
java
//2.迭代(利用栈,多了一次反转)
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal2(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null){
return list;
}
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();
stack.push(root);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
list.add(node.val);
if(node.left != null){
stack.push(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null){
stack.push(node.right);
}
}
// 此时顺序为根右左,反转即为:左右根
Collections.reverse(list);
return list;
}
java
//3.迭代(利用栈,推荐使用)
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null) return list;
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();
//由于在某颗子树访问完成以后,接着就要回溯到其父节点去
//因此可以用pre来记录访问历史,在回溯到父节点时,可以由此来判断,上一个访问的节点是否为右子结点
TreeNode cur = root, pre = null;
while(cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()){
// 沿着左子树一直到空为止
while(cur != null){
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}
//从栈中弹出的节点,其左子树一定已经访问了
cur = stack.pop();
//如果没有右子树或者右子树已经访问完了,表示可以访问当前节点了
if(cur.right == null || cur.right == pre){
list.add(cur.val);
//更新pre,记录上一个访问的节点
pre = cur;
//切记将cur置为空
cur = null;
}else{
//如果右子树还没有访问,先访问右子树
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.right;
}
}
return list;
}4、二叉树的中序遍历(力扣94)

java
//1.递归
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
inOrder(root,list);
return list;
}
public void inOrder(TreeNode root,List<Integer> list){
if(root == null){
return;
}
inOrder(root.left,list);
list.add(root.val);
inOrder(root.right,list);
}
java
//2.迭代(利用栈)
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal2(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null){
return list;
}
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
// 两种情况,要么左子树到底,要么弹栈
while(cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()){
//沿着左子树一直为空为止
if(cur != null){
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}else{
//开始往外弹栈
cur = stack.pop();
list.add(cur.val);
//弹栈过程中考虑右子树
cur = cur.right;
}
}
return list;
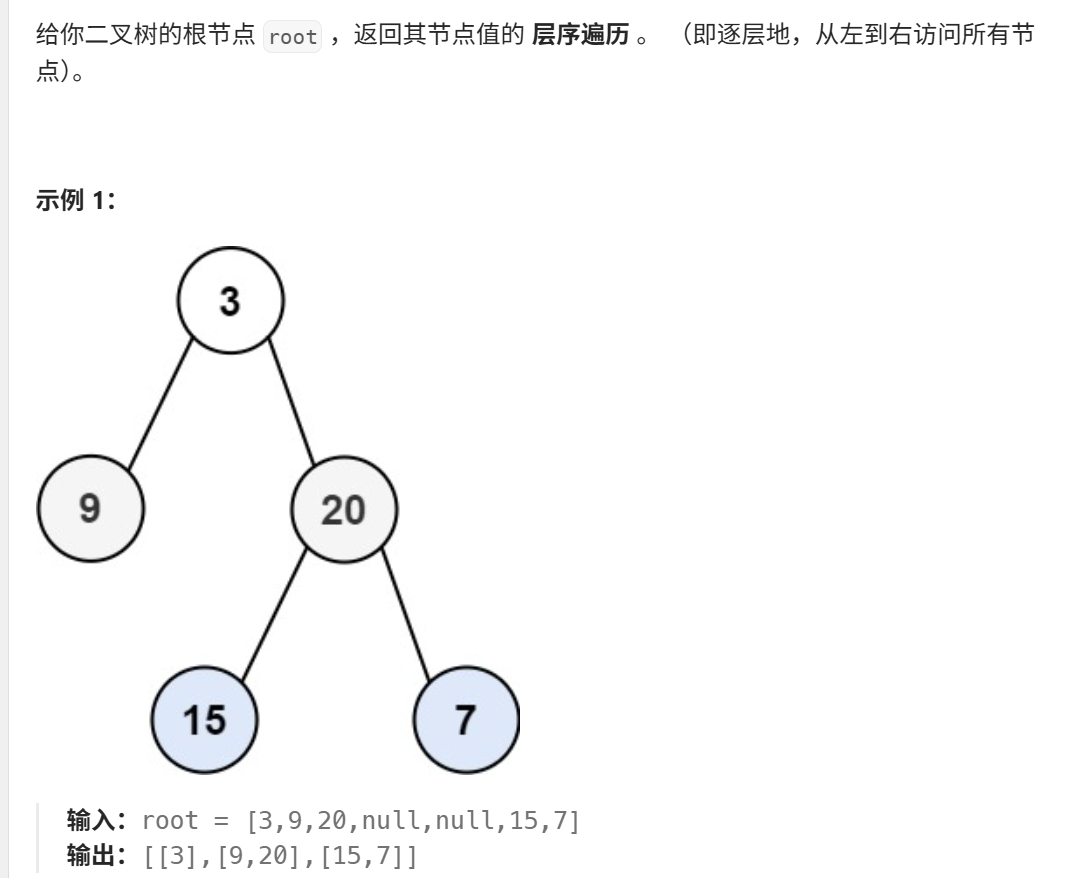
}5、 二叉树的层序遍历(力扣102)
java
// 1.利用队列
class Solution {
public static List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return list;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> level = new ArrayList<>();
// 必须用len暂存长度
int len = queue.size();
/* 遍历当前层,并将当前层所有节点的左右子节点入队列 */
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
level.add(node.val);
if (node.left != null) {
queue.add(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
list.add(level);
}
return list;
}
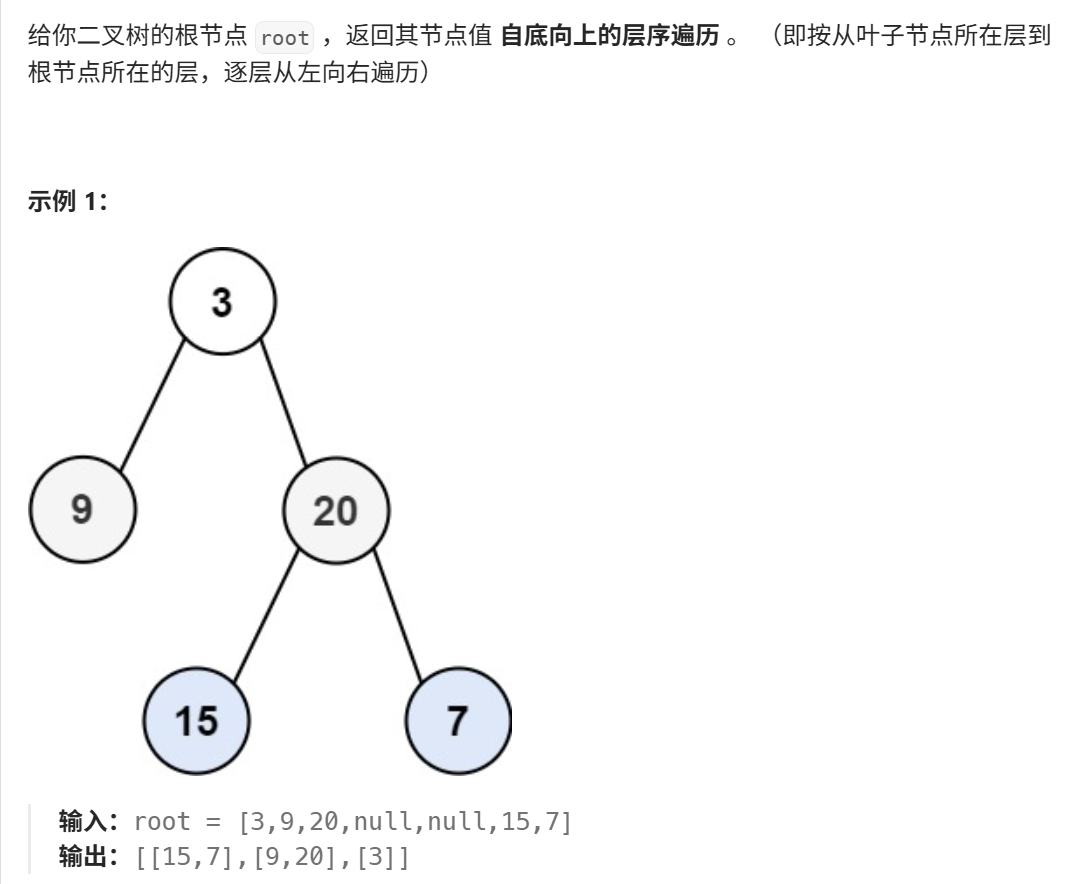
}6、二叉树的层序遍历 II(力扣107)
java
//1.层序遍历+栈
public static List<List<Integer>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null){
return list;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
Deque<List<Integer>> stack = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
List<Integer> level = new ArrayList<>();
int len = queue.size();
for(int i = 0;i < len;i ++){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
level.add(node.val);
if(node.left != null){
queue.add(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null){
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
stack.push(level);
}
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
list.add(stack.pop());
}
return list;
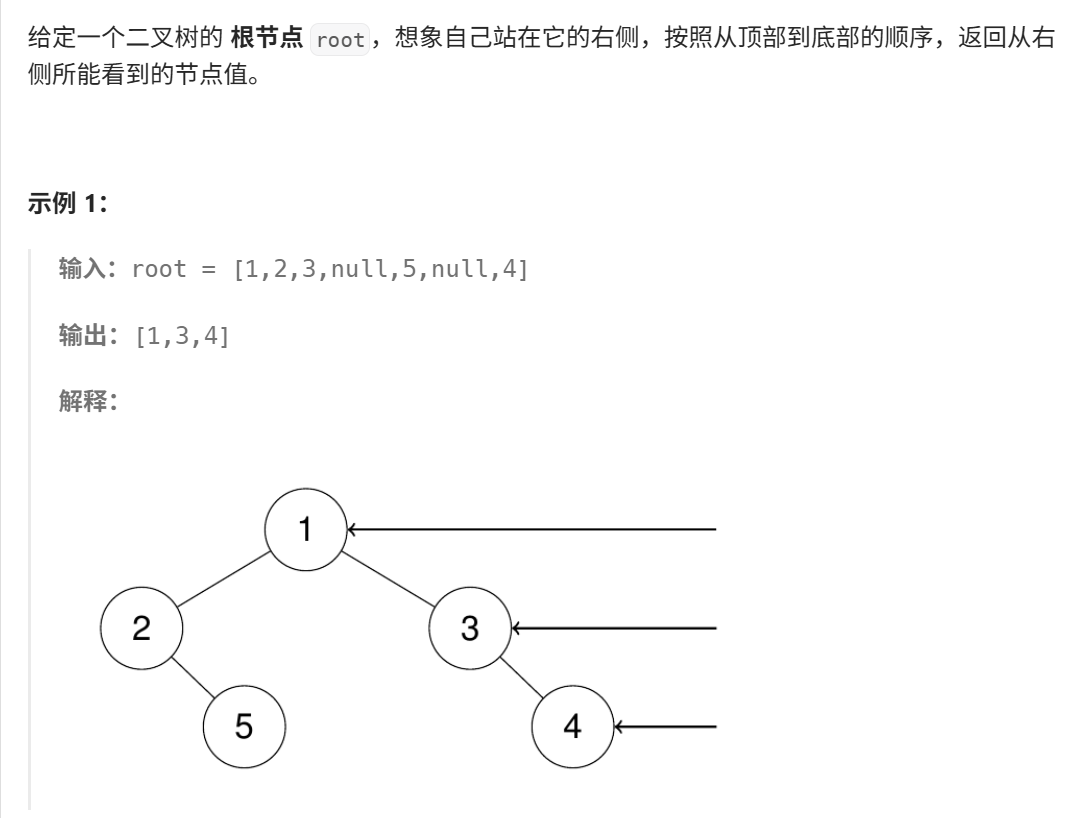
}7、二叉树的右视图(力扣199)
java
//1.利用队列先进先出
public static List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null){
return list;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int len = queue.size();
for(int i = 0;i < len;i ++){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
//只将每一层的最后一个加入到结果集
if(i == len - 1){
list.add(node.val);
}
if(node.left != null){
queue.add(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null){
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
}
return list;
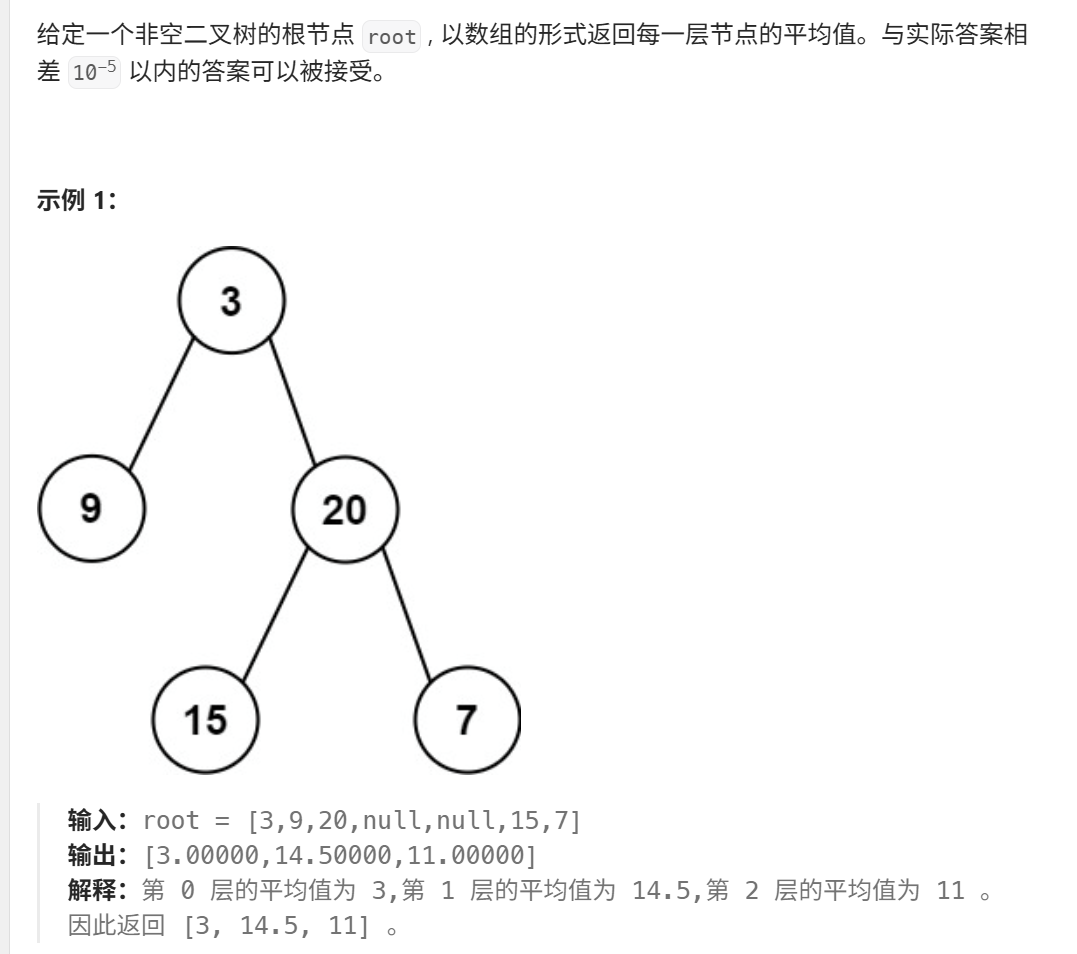
}8、二叉树的层平均值(力扣637)
java
//1.利用队列
public static List<Double> averageOfLevels(TreeNode root) {
List<Double> list = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int len = queue.size();
double sum = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < len;i++){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
sum += node.val;
if(node.left != null){
queue.add(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null){
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
list.add(sum / len);
}
return list;
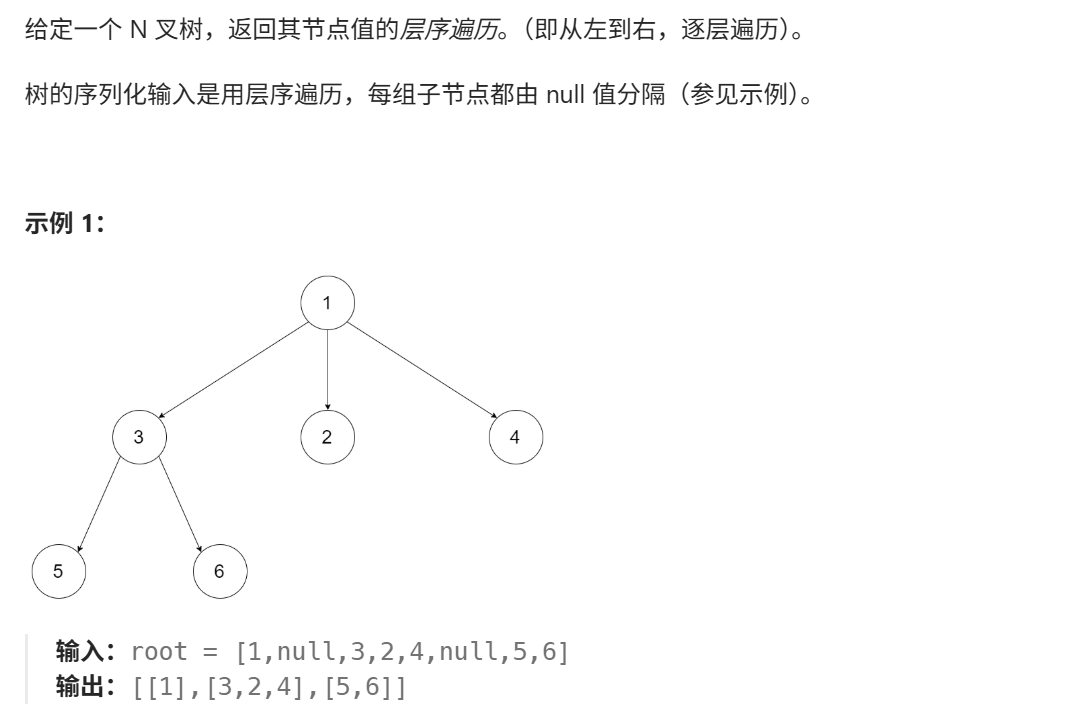
}9、N 叉树的层序遍历(力扣429)
java
//1.利用队列
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(Node root) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null){
return list;
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
List<Integer> level = new ArrayList<>();
int len = queue.size();
for(int i = 0;i < len;i ++){
Node node = queue.poll();
level.add(node.val);
if(node.children != null){
List<Node> cur = node.children;
for(Node n : cur){
queue.add(n);
}
}
}
list.add(level);
}
return list;
}10、在每个树行中找最大值(力扣515)
java
//1.利用队列
public List<Integer> largestValues(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null){
return list;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int len = queue.size();
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for(int i = 0;i < len;i ++){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
max = Math.max(max,node.val);
if(node.left != null){
queue.add(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null){
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
list.add(max);
}
return list;
}11、填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针(力扣116)
java
//1.队列(非常数空间)
class Solution {
public static Node connect(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return root;
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int len = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
Node curNode = queue.poll();
/* 当前层依次串接 */
if (i < len - 1) {
curNode.next = queue.peek();
}
if (curNode.left != null) {
queue.add(node1.left);
}
if (curNode.right != null) {
queue.add(node1.right);
}
}
}
return root;
}
}
java
//2.常数空间
class Solution {
public Node connect(Node root) {
if (null == root){
return root;
}
/* 站在当前树层,将下一层的结点串接起来。此结点用于标识每一层最左边的结点 */
Node mostLeftNode = root;
/* 如果有下一层 */
while (mostLeftNode.left != null){
Node curNode = mostLeftNode;
/* 从左到右移动 */
while (curNode != null){
curNode.left.next = curNode.right;
if (curNode.next != null){
curNode.right.next = curNode.next.left;
}
curNode = curNode.next;
}
/* 一层遍历完,从下一层的最左边再开始 */
mostLeftNode = mostLeftNode.left;
}
return root;
}
}12、填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II(力扣117)
java
//1.队列(非常数空间)
public Node connect1(Node root) {
if(root == null){
return root;
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int len = queue.size();
for(int i = 0;i < len;i ++){
Node node = queue.poll();
if(i < len - 1){
node.next = queue.peek();
}
if(node.left != null){
queue.add(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null){
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
}
return root;
}
java
// 2.常数空间
class Solution {
public Node connect(Node root) {
if (root == null){
return root;
}
Node curNode = root;
/* 遍历本层,连接下层 */
while (curNode != null){
/* 维持每一层最左边的结点,便于切换到下一层 */
Node mostLeftNode = new Node(0);
/* 遍历到的结点的前一个结点 */
Node preNode = mostLeftNode;
while (curNode != null){
if (curNode.left != null){
preNode.next = curNode.left;
preNode = preNode.next;
}
if (curNode.right != null){
preNode.next = curNode.right;
preNode = preNode.next;
}
/* 继续向右遍历 */
curNode = curNode.next;
}
/* 切换到下一层 */
curNode = mostLeftNode.next;
}
return root;
}
}13、二叉树的最大深度(力扣104)
java
//1.递归(传入一个结点,返回以此结点为根结点的最大深度)
public static int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
java
//2.利用队列,遍历完一层深度加1
public int maxDepth2(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
int deepth = 0;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int len = queue.size();
for(int i = 0;i < len;i ++){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if(node.left != null){
queue.add(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null){
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
deepth ++;
}
return deepth;
}14、二叉树的最小深度(力扣111)
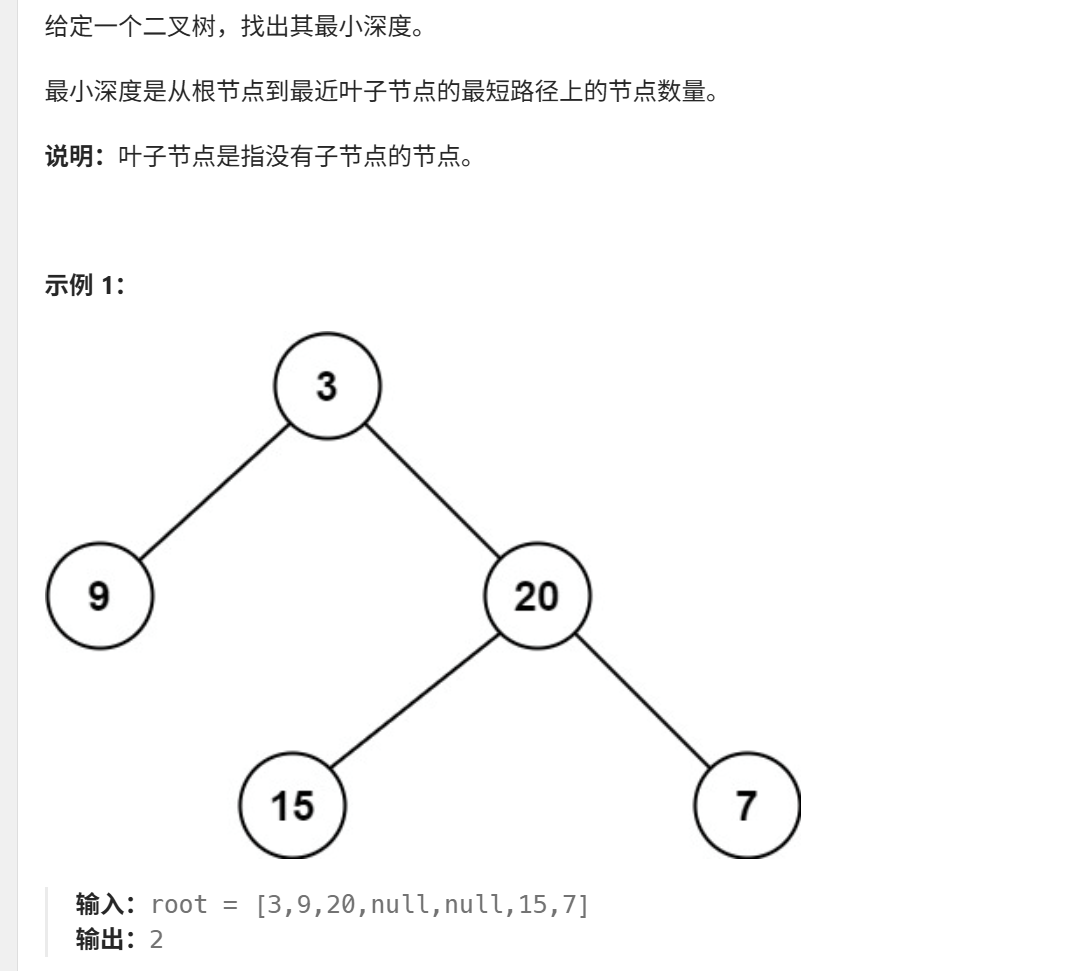
此题注意点:找到离根节点最近的那个"叶子节点"
java
//1.递归
/*
* 1.确定递归函数参数和返回值:传入一个节点,返回以此节点为根节点的树的最小深度
* 2.确定递归的终止条件:当所传入的节点为null,返回为0
* 3.确定每一层的逻辑:
* 1.当前节点为null,返回0;
* 2.当前节点的左子节点和右子节点均为null,返回1;
* 3.当前节点的左节点或右节点为null,返回 len1 + len2 + 1
* 4.当前节点的左子节点和右子节点均不为null,返回以两者为根节点的子树的较小值
* */
public static int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
return 1;
}
int len1 = minDepth(root.left);
int len2 = minDepth(root.right);
if(root.left == null || root.right == null){
return len1 + len2 + 1;
}
return Math.min(len1,len2) + 1;
}
java
//对递归进行简化,情况2和情况4可以合二为一;情况3可以拆分为两个条件
public static int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
if(root.left == null && root.right != null){
return minDepth(root.right) + 1;
}
if(root.right == null && root.left != null){
return minDepth(root.left) + 1;
}
return Math.min(minDepth(root.left), minDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
java
//2.队列(层次遍历,比较简单)
public int minDepth2(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
int depth = 1;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int len = queue.size();
for(int i = 0;i < len;i++){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
//找到了一个叶子节点,直接返回结果
if(node.left == null && node.right == null){
return depth;
}
if(node.left != null){
queue.add(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null){
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
depth ++;
}
return depth;
}15、完全二叉树的节点个数(力扣222)
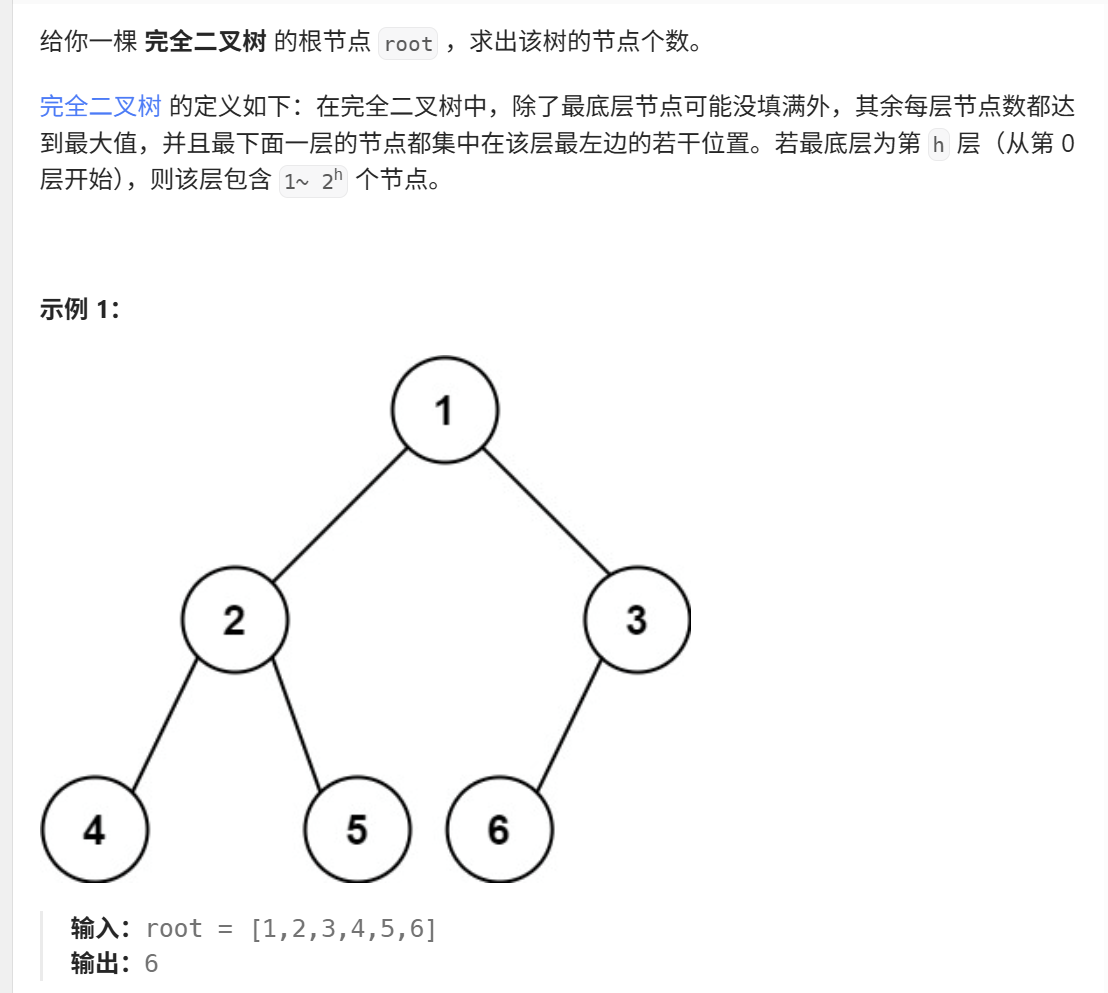
java
//1.递归
//首先确定递归函数的参数和返回值
//参数:传入一个节点;返回值:返回以此节点为根节点的树的节点总数量
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
//如果当前节点为null,直接返回0
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
//以此节点的左子节点为根节点的树的节点数量
int leftCount = countNodes(root.left);
//以此节点的右子节点为根节点的树的节点数量
int rightCount = countNodes(root.right);
//返回以此节点为根节点的树的节点数量为 leftCount + rightCount + 此节点的数量1
return leftCount + rightCount + 1;
}
java
//2.考虑完全二叉树的特点
public int countNodes1(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
//计算以根节点的左子节点为根节点的完全二叉树的高度
int leftDepth = maxDepth(root.left);
//计算以根节点的右子节点为根节点的完全二叉树的高度
int rightDepth = maxDepth(root.right);
//如果相等,说明以根节点的左子节点为根节点的完全二叉树是满二叉树,总的节点数量为
//此满二叉树节点数量+根节点数量1+以根节点的右子节点为根节点的完全二叉树的节点数量
if(leftDepth == rightDepth){
return (int)Math.pow(2,leftDepth) + count(root.right);
//如果不相等,说明以根节点的右子节点为根节点的完全二叉树是满二叉树,总的节点数量为
//此满二叉树节点数量+根节点数量1+以根节点的左子节点为根节点的完全二叉树的节点数量
}else{
return (int)Math.pow(2,rightDepth) + count(root.left);
}
}
//计算以此节点为根节点的完全二叉树的节点个数
public int count(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
return count(root.left) + count(root.right) + 1;
}
//计算以此节点为根节点的完全二叉树的高度
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
return maxDepth(root.left) + 1;
}16、平衡二叉树(力扣110)
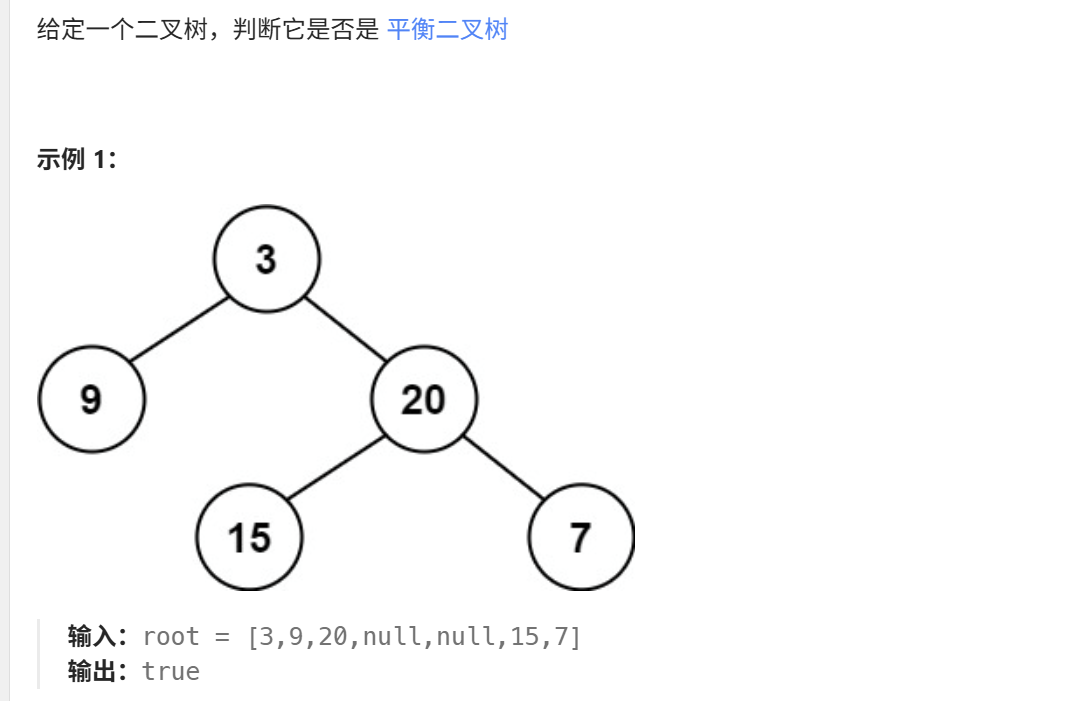
java
//1.二叉树的层次遍历,判断每一个节点的左右子树的高度是否满足要求(自顶向下)
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return true;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int len = queue.size();
for(int i = 0;i < len;i ++){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if(Math.abs(Depth(node.left) - Depth(node.right)) > 1){
return false;
}
if(node.left != null){
queue.add(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null){
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
}
return true;
}
//传入一个节点,返回以此节点为根节点的树高度
public int Depth(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
return Math.max(Depth(root.left), Depth(root.right)) + 1;
}
java
//2.递归(自顶向下)
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return true;
}
if(Math.abs(Depth(root.left) - Depth(root.right)) > 1){
return false;
}
return isBalanced(root.left) && isBalanced(root.right);
}
//输入一个节点,返回以此节点为根节点的树的高度
public int Depth(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
return Math.max(Depth(root.left), Depth(root.right)) + 1;
}
java
//3.递归(自底向上)
//后续遍历,先看最底下的树是否是平衡二叉树,再层层往上递归
//时间和空间复杂度都是o(n)
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
return Depth(root) >= 0;
}
public int Depth(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
int leftDepth = Depth(root.left);
int rightDepth = Depth(root.right);
if((leftDepth == -1) || (rightDepth == -1) || Math.abs(leftDepth - rightDepth) > 1){
return -1;
}else{
return Math.max(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1;
}
}17、二叉树的所有路径(力扣257)
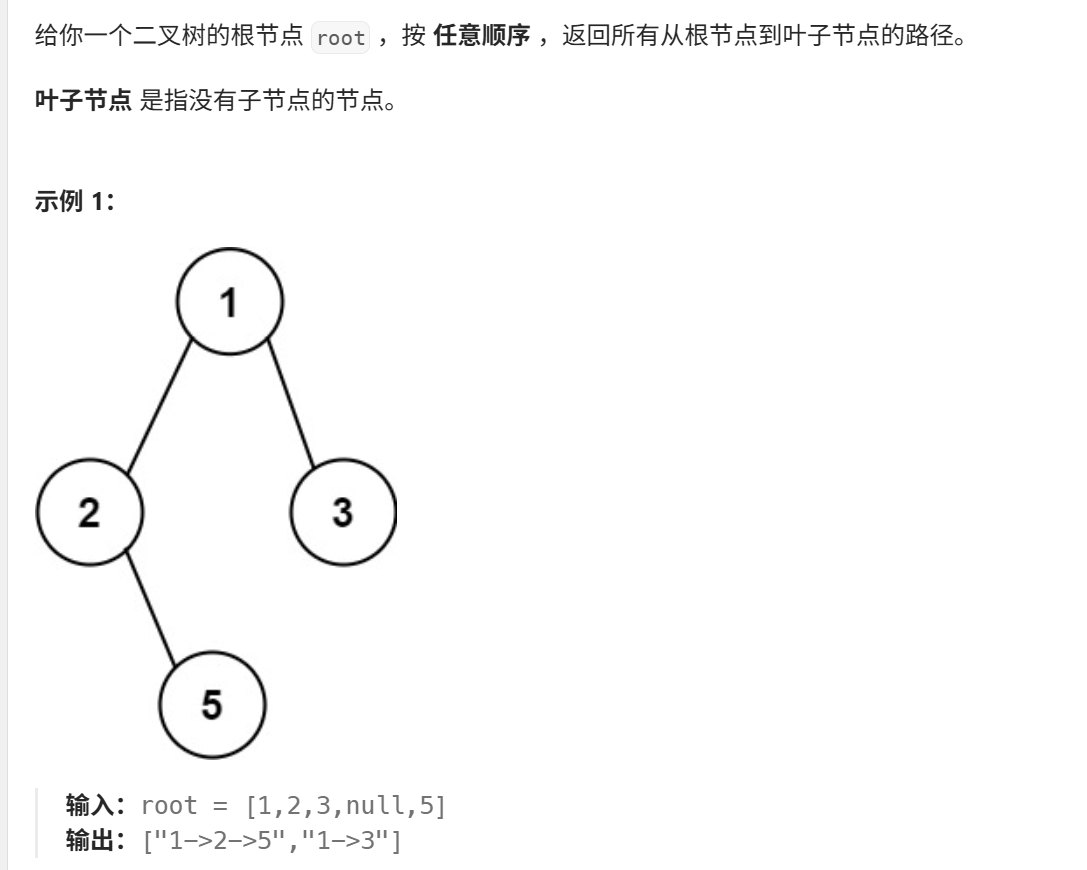
java
//1.回溯(时间和空间复杂度都是O(n2))
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null){
return res;
}
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
travelsal(root, path, res);
return res;
}
//递归+回溯
//递归函数:每次传入当前节点;path记录从根节点到此节点的路径上的所有节点,便于回溯;
//res记录最终的结果,每到达一个左右节点均为null的节点,就回溯从根节点到此节点路径
//上的所有节点,连成一个String,放到res中
public void travelsal(TreeNode root, List<Integer> path, List<String> res){
path.add(root.val);
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
int len = path.size();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for(int i = 0;i < len - 1;i ++){
sb.append(path.get(i));
sb.append("->");
}
sb.append(path.get(len - 1));
res.add(sb.toString());
}
if(root.left != null){
travelsal(root.left, path,res);
//到这一步,说明上面加入的root.left节点已经用过了,需要及时删除
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
if(root.right != null){
travelsal(root.right, path,res);
//到这一步,说明上面加入的root.right节点已经用过了,需要及时删除
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
java
//2.栈(难以想到,不推荐使用)
public List<String> binaryTreePaths2(TreeNode root) {
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null){
return res;
}
Deque<Object> stack = new LinkedList<>();
//装入节点
stack.push(root);
//装入从根节点到此节点的路径
stack.push(root.val + "");
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
//取出到此节点的路径
String path = (String)stack.pop();
//取出此节点
TreeNode node = (TreeNode)stack.pop();
//如果当前节点的左右子节点均为null,说明此节点为叶子结点,将路径放入返回集合
if(node.left == null && node.right == null){
res.add(path);
}
//如果左子节点不为null,将左子节点和到左子节点的路径压栈
if(node.left != null){
stack.push(node.left);
stack.push(path + "->" + node.left.val);
}
//同样处理右子节点
if(node.right != null){
stack.push(node.right);
stack.push(path + "->" + node.right.val);
}
}
return res;
}
java
//3.递归(时空复杂度都是O(n2))
public List<String> binaryTreePaths3(TreeNode root) {
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null) return res;
binary(res, new StringBuilder(), root);
return res;
}
public void binary(List<String> res, StringBuilder sb, TreeNode root){
sb.append(root.val);
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
res.add(sb.toString());
}
if(root.left != null){
//因为每次传进去的都是new的StringBuilder,不用回溯
binary(res, new StringBuilder(sb).append("->"), root.left);
}
if(root.right != null){
binary(res, new StringBuilder(sb).append("->"), root.right);
}
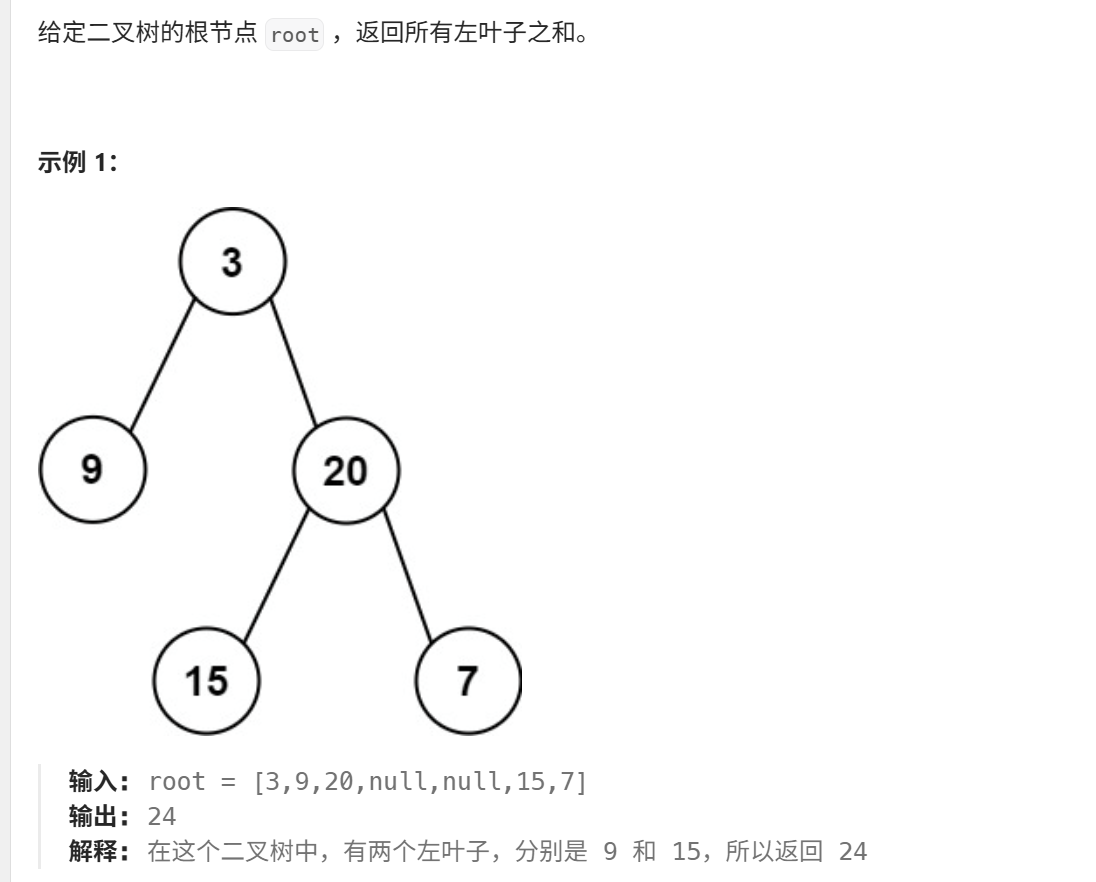
}18、左叶子之和(力扣404)
java
//1.层序遍历(当然也可以使用其他的遍历方式,判断每一个节点的左子节点是不是叶子节点)
public int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode root) {
int sum = 0;
if(root == null){
return sum;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int len = queue.size();
for(int i = 0;i < len;i ++){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
//站在当前层看下一层:
//如果当前节点的左子节点不为空,并且当前节点的左子节点的左子节点和右子节点均为空,则此节点的左子节点为左叶子节点
if(node.left != null && node.left.left == null && node.left.right == null){
sum += node.left.val;
}
if(node.left != null){
queue.add(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null){
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
}
return sum;
}
java
//2.递归
//递归函数:每次传入一个节点,返回以此节点为根节点的树的左叶子节点的和
//自底向上,使用后序遍历
public int sumOfLeftLeaves2(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
// 左
int leftValue = sumOfLeftLeaves(root.left);
// 右
int rightValue = sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right);
// 当前结点
int midValue = 0;
if(root.left != null && root.left.left == null && root.left.right == null){
midValue = root.left.val;
}
return leftValue + rightValue + midValue;
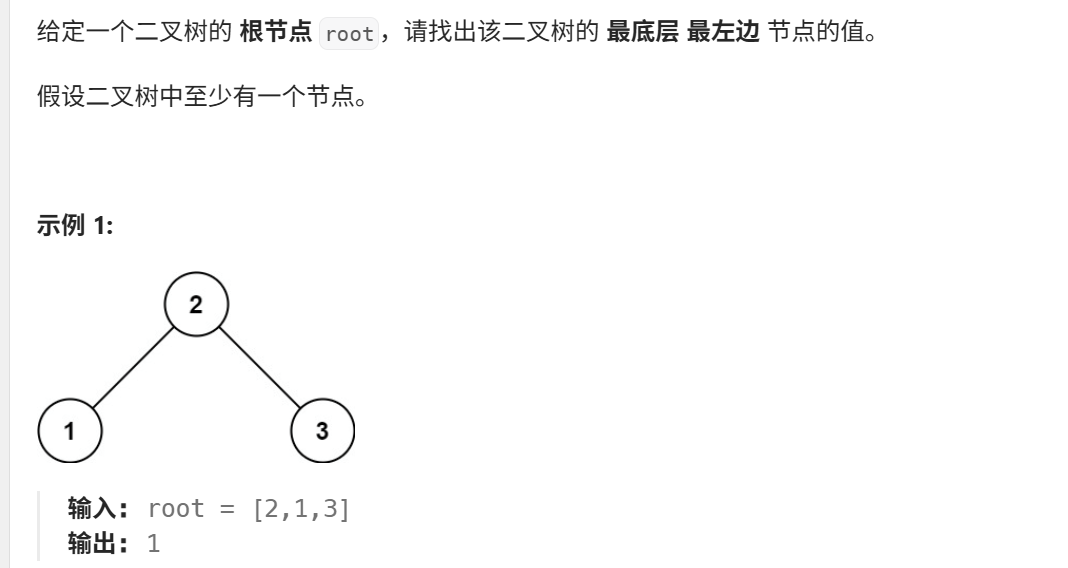
}19、找树左下角的值(力扣513)
java
//1.层序遍历,每遍历到每层的第一个节点时,将返回值替换为此节点值
public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
int res = root.val;
boolean flag = true;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int len = queue.size();
for(int i = 0; i < len; i ++){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
// 遍历到每一层的第一个结点时flag=true
if(flag){
res = node.val;
flag = false;
}
if(node.left != null){
queue.add(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null){
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
flag = true;
}
return res;
}
java
//2.递归,采用前序遍历
//用来记录最大深度
private int Deep = -1;
//返回值
private int value = 0;
public int findBottomLeftValue2(TreeNode root) {
value = root.val;
findLeftValue(root, 0);
return value;
}
//递归函数
//传入节点和当前节点的深度
//采用前序遍历,保证每次到达最大深度所取得值是最左边的
private void findLeftValue(TreeNode root, int deep){
if(root == null){
return;
}
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
//保证每次到达一个更大深度时,所取的值是最左边的
if(deep > Deep){
value = root.val;
// 更新最大深度
Deep = deep;
}
}
findLeftValue(root.left, deep + 1);
findLeftValue(root.right, deep + 1);
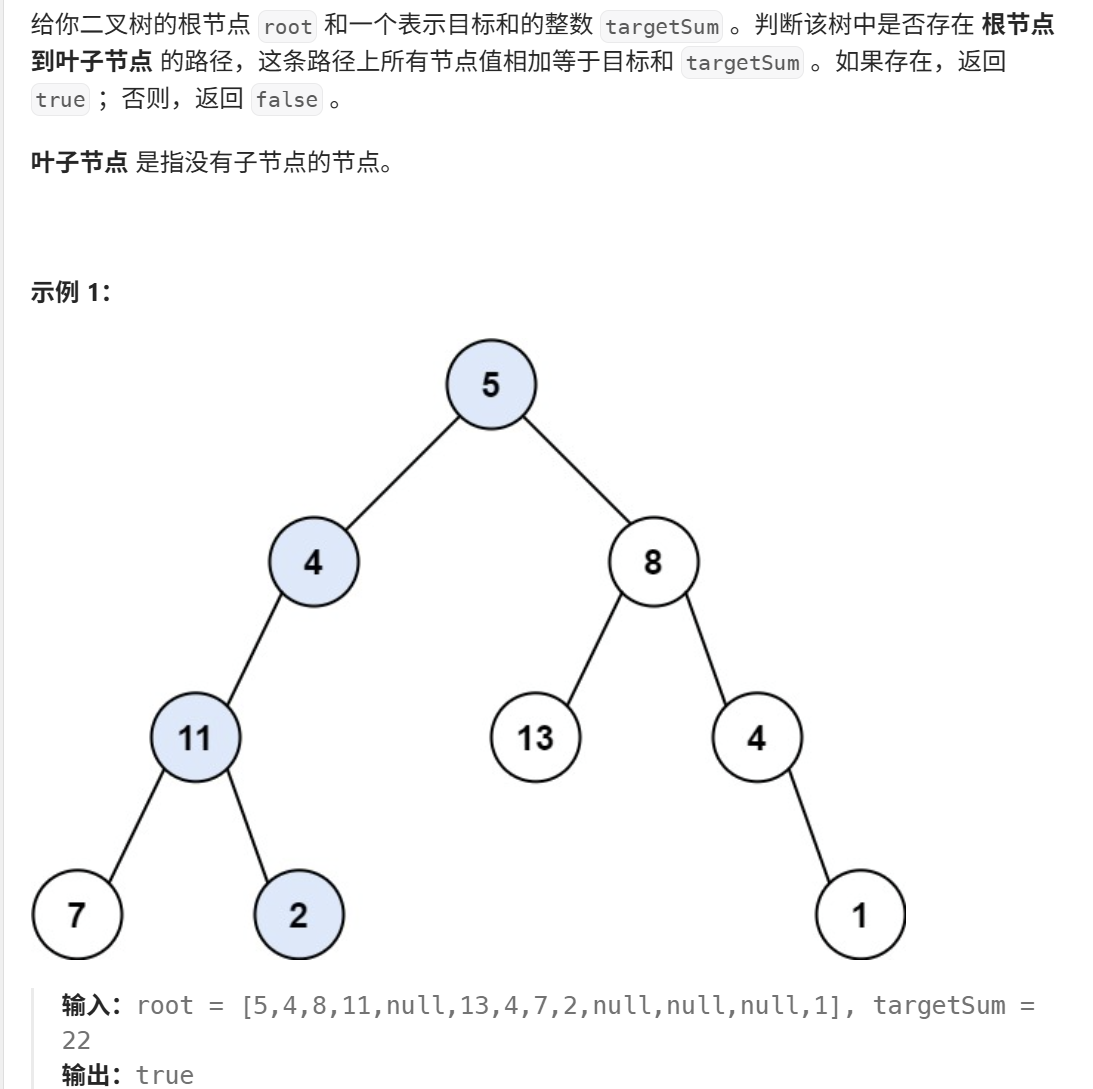
}20、路径总和(力扣112)
java
//1.递归,每次传入递归函数的是相减的值,代码比较简洁
public boolean hasPathSum2(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if(root == null){
return false;
}
// 当前结点为叶子结点且路径和符合要求
if(root.left == null && root.right == null && targetSum - root.val == 0){
return true;
}
return hasPathSum(root.left, targetSum - root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right, targetSum - root.val);
}
java
//2.层序遍历,利用两个队列,分别存放节点和到此节点路径上的节点的和
public boolean hasPathSum3(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if(root == null){
return false;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queueNode = new LinkedList<>();
Queue<Integer> queueInt = new LinkedList<>();
queueNode.add(root);
queueInt.add(root.val);
while(!queueNode.isEmpty()){
int len = queueNode.size();
for(int i = 0; i < len; i ++){
TreeNode node = queueNode.poll();
int value = queueInt.poll();
if(node.left == null && node.right == null && value == targetSum){
return true;
}
if(node.left != null){
queueNode.add(node.left);
queueInt.add(node.left.val + value);
}
if(node.right != null){
queueNode.add(node.right);
queueInt.add(node.right.val + value);
}
}
}
return false;
}