本期内容为自己总结归档,共分十一章,本人遇到过的面试问题会重点标记。
(若有任何疑问,可在评论区告诉我,看到就回复)
一、装饰器模式的核心概念
1.1 装饰器模式的定义
装饰器模式(Decorator Pattern)允许向一个现有的对象添加新的功能,同时又不改变其结构。这种模式创建了一个装饰类,用来包装原有的类,并在保持类方法签名完整性的前提下,提供了额外的功能。
装饰器模式的核心思想:使用组合替代继承,实现功能的动态扩展。
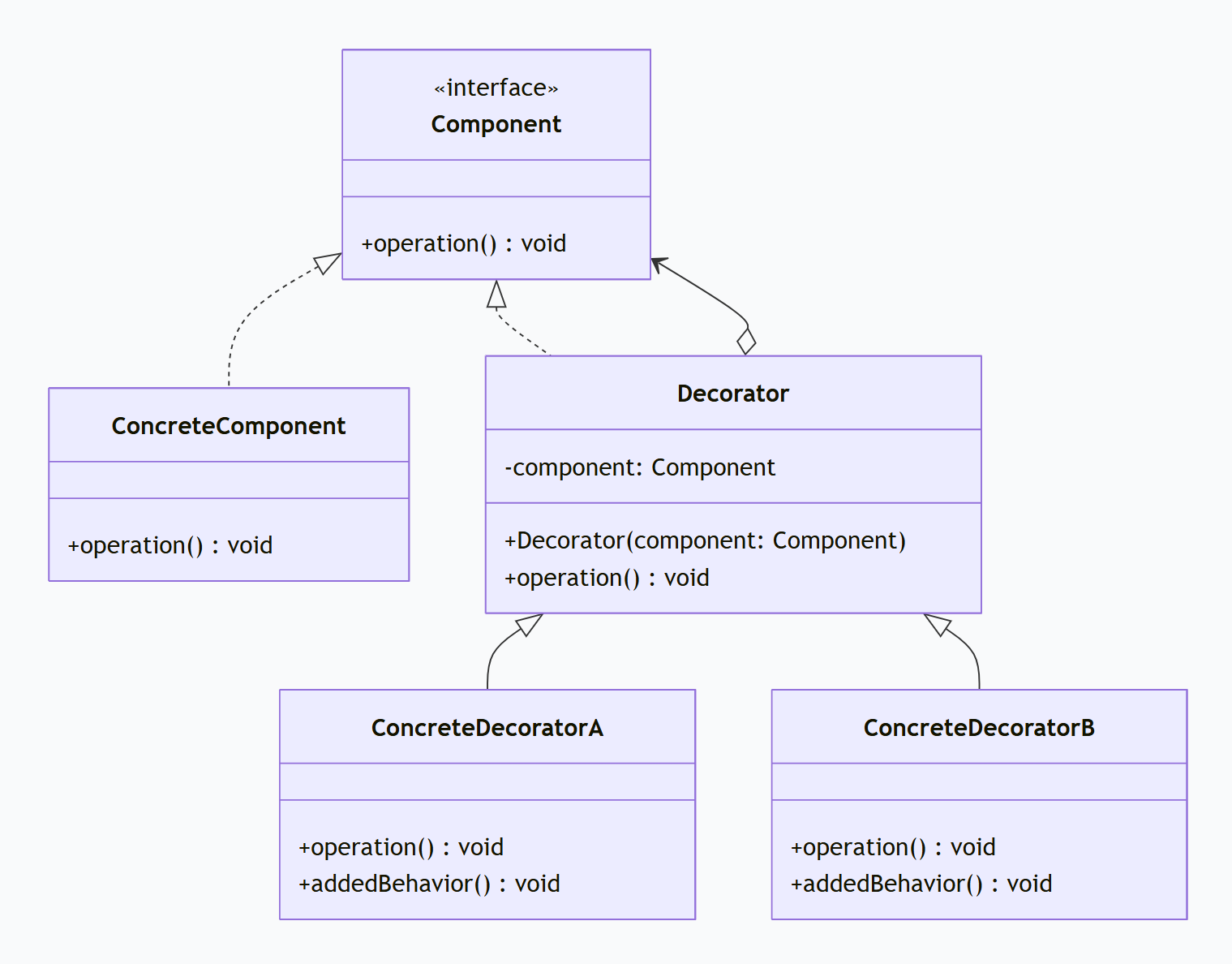
1.2 ⭐装饰器模式的结构
装饰器模式包含四个关键角色:
-
Component(组件接口):定义对象的接口,可以动态地给这些对象添加职责
-
ConcreteComponent(具体组件):实现组件接口,是被装饰的原始对象
-
Decorator(装饰器):实现组件接口,并持有一个组件对象的引用
-
ConcreteDecorator(具体装饰器):向组件添加具体的功能
1.3 装饰器模式 vs 继承
装饰器模式提供了比继承更有弹性的替代方案:
| 对比维度 | 继承 | 装饰器模式 |
|---|---|---|
| 扩展方式 | 静态,编译时确定 | 动态,运行时确定 |
| 组合数量 | 有限(单继承) | 无限(任意组合) |
| 灵活性 | 低,不能动态改变 | 高,可以随时添加或移除 |
| 类数量 | 每个组合都需要新类 | 更少的类,更多的组合 |
| 代码复用 | 通过继承复用 | 通过组合复用 |
二、⭐装饰器模式的基础实现
2.1 装饰器解决方案示例
java
// 1. 组件接口:饮料
public interface Beverage {
String getDescription();
double getCost();
}
// 2. 具体组件:基础咖啡
public class Espresso implements Beverage {
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return "浓缩咖啡";
}
@Override
public double getCost() {
return 15.0;
}
}
public class Americano implements Beverage {
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return "美式咖啡";
}
@Override
public double getCost() {
return 20.0;
}
}
public class Latte implements Beverage {
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return "拿铁咖啡";
}
@Override
public double getCost() {
return 25.0;
}
}
// 3. 装饰器抽象类
public abstract class CondimentDecorator implements Beverage {
protected Beverage beverage;
public CondimentDecorator(Beverage beverage) {
this.beverage = beverage;
}
@Override
public abstract String getDescription();
}
// 4. 具体装饰器:各种配料
public class Milk extends CondimentDecorator {
public Milk(Beverage beverage) {
super(beverage);
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return beverage.getDescription() + " + 牛奶";
}
@Override
public double getCost() {
return beverage.getCost() + 5.0;
}
}
public class Sugar extends CondimentDecorator {
public Sugar(Beverage beverage) {
super(beverage);
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return beverage.getDescription() + " + 糖";
}
@Override
public double getCost() {
return beverage.getCost() + 3.0;
}
}
public class Chocolate extends CondimentDecorator {
public Chocolate(Beverage beverage) {
super(beverage);
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return beverage.getDescription() + " + 巧克力";
}
@Override
public double getCost() {
return beverage.getCost() + 8.0;
}
}
public class Cream extends CondimentDecorator {
public Cream(Beverage beverage) {
super(beverage);
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return beverage.getDescription() + " + 奶油";
}
@Override
public double getCost() {
return beverage.getCost() + 6.0;
}
}
// 5. 客户端使用
public class CoffeeShop {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("=== 装饰器模式咖啡店 ===");
// 1. 纯美式咖啡
Beverage americano = new Americano();
System.out.println(americano.getDescription() + " 价格: ¥" + americano.getCost());
// 2. 拿铁 + 牛奶 + 糖
Beverage latte = new Latte();
latte = new Milk(latte);
latte = new Sugar(latte);
System.out.println(latte.getDescription() + " 价格: ¥" + latte.getCost());
// 3. 浓缩咖啡 + 所有配料
Beverage deluxe = new Espresso();
deluxe = new Milk(deluxe);
deluxe = new Sugar(deluxe);
deluxe = new Chocolate(deluxe);
deluxe = new Cream(deluxe);
System.out.println(deluxe.getDescription() + " 价格: ¥" + deluxe.getCost());
// 4. 动态移除装饰器(通过不添加即可)
Beverage simpleCoffee = new Americano();
simpleCoffee = new Milk(simpleCoffee);
// 想要移除牛奶?只需不使用Milk装饰器即可
System.out.println("\n=== 装饰器链结构 ===");
printDecoratorChain(deluxe);
}
private static void printDecoratorChain(Beverage beverage) {
System.out.println("装饰器链:");
while (beverage instanceof CondimentDecorator) {
System.out.println(" ↳ " + beverage.getClass().getSimpleName());
beverage = ((CondimentDecorator) beverage).beverage;
}
System.out.println(" ↳ " + beverage.getClass().getSimpleName());
}
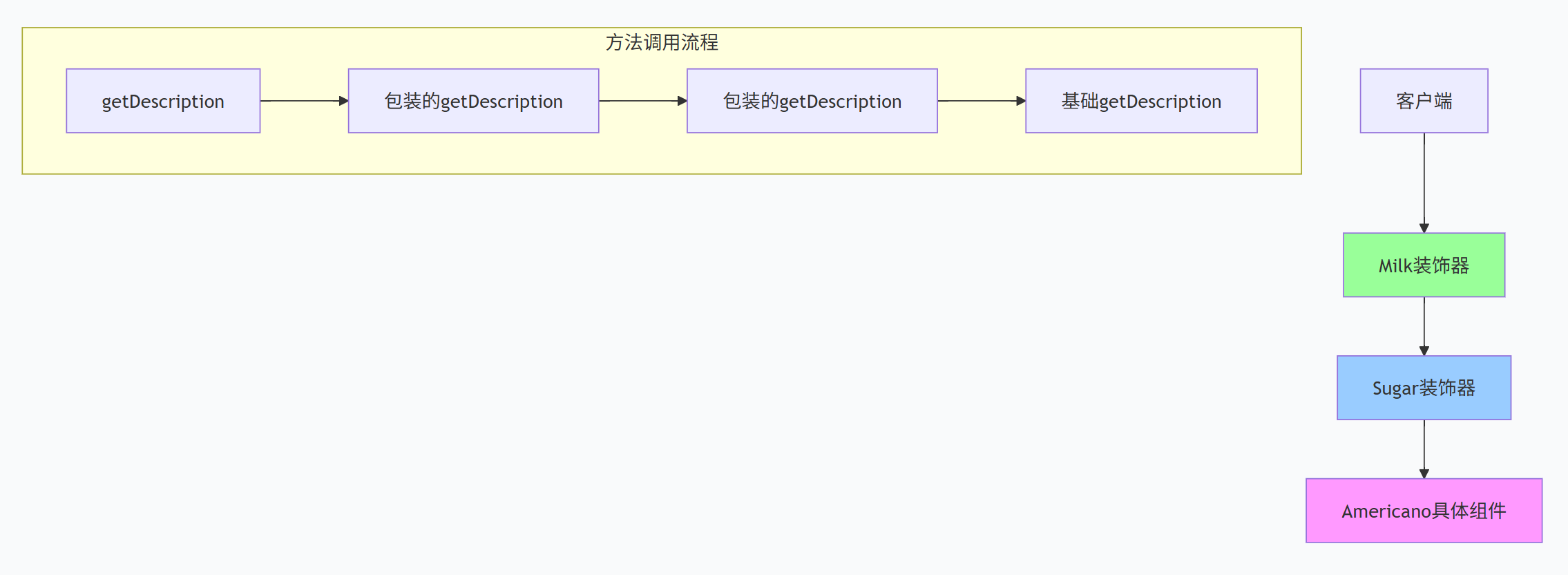
}2.2 装饰器模式的工作原理
装饰器模式通过包装的方式工作:
-
每个装饰器都包装了一个组件
-
调用装饰器的方法时,会先调用被包装组件的方法,然后添加自己的行为
-
可以无限嵌套装饰器,形成装饰器链
三、装饰器模式在Java标准库中的应用
3.1 Java I/O流:装饰器模式的经典应用
java
public class IOStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String data = "Hello, Decorator Pattern!";
// 1. 基本文件输出流
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("test.txt");
fos.write(data.getBytes());
fos.close();
// 2. 添加缓冲功能(装饰器)
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream("test_buffered.txt")
);
bos.write(data.getBytes());
bos.flush();
bos.close();
// 3. 添加数据输出功能
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(
new BufferedOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream("test_data.txt")
)
);
dos.writeUTF(data);
dos.close();
// 4. 读取时也使用装饰器链
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("test.txt");
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(bis);
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int bytesRead = bis.read(buffer);
System.out.println("读取到 " + bytesRead + " 字节");
// 5. 查看装饰器链
System.out.println("\n=== I/O流装饰器链 ===");
InputStream stream = dis;
while (stream != null) {
System.out.println(" ↳ " + stream.getClass().getSimpleName());
// 通过反射获取包装的流
try {
Field inField = FilterInputStream.class.getDeclaredField("in");
inField.setAccessible(true);
stream = (InputStream) inField.get(stream);
} catch (Exception e) {
stream = null;
}
}
}
}3.2 Java I/O流类的设计
Java I/O流类的UML简化结构:
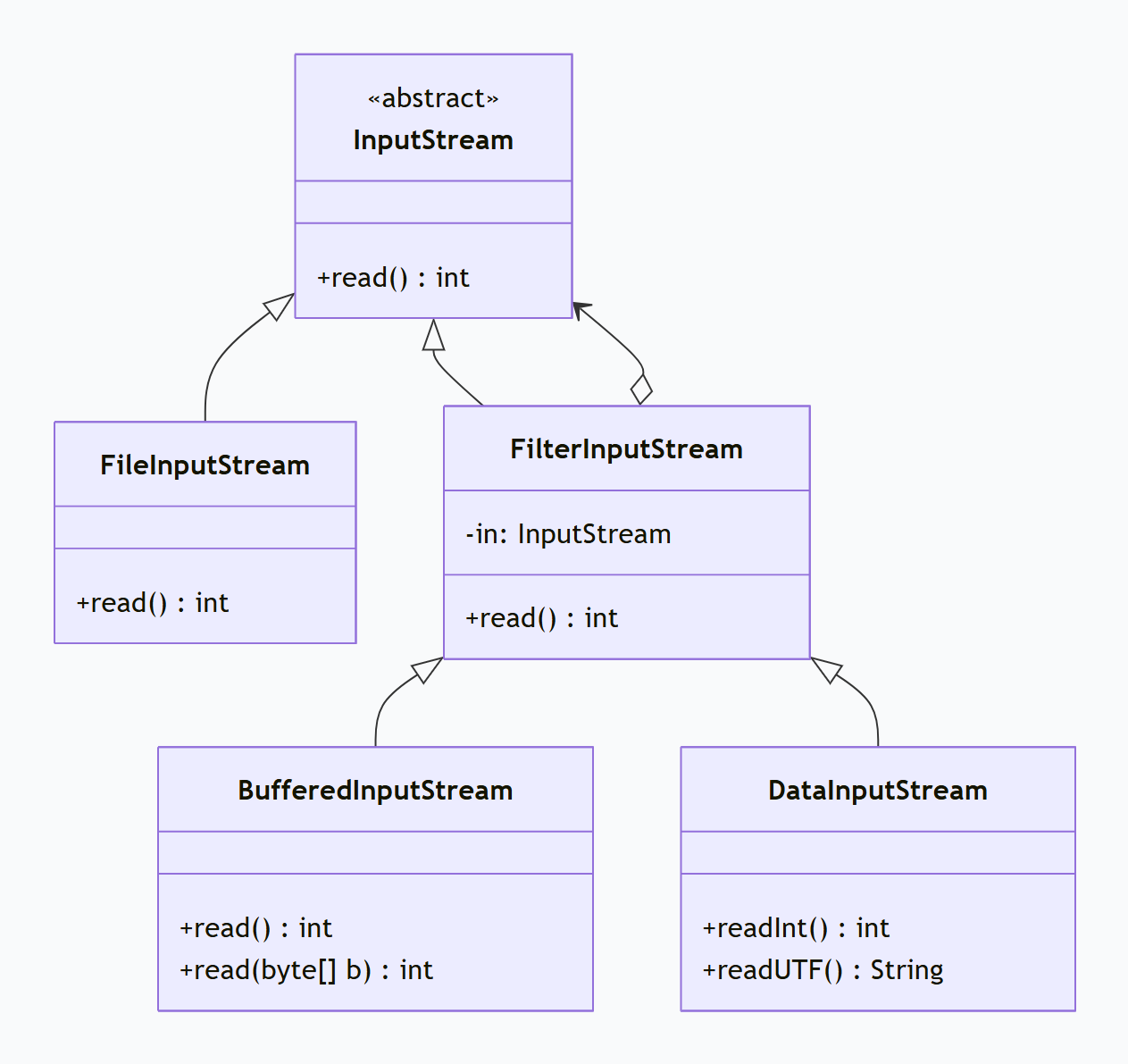
关键点:
-
FilterInputStream是所有装饰器的基类 -
每个装饰器都持有一个
InputStream的引用 -
装饰器可以透明地添加功能(如缓冲、数据类型转换等)
3.3 Java集合框架中的装饰器
java
public class CollectionsDecoratorDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("Apple");
list.add("Banana");
list.add("Cherry");
// 1. 创建不可修改的列表(装饰器)
List<String> unmodifiableList = Collections.unmodifiableList(list);
try {
unmodifiableList.add("Date"); // 抛出异常
} catch (UnsupportedOperationException e) {
System.out.println("不可修改列表不允许添加元素");
}
// 2. 创建同步列表(装饰器)
List<String> synchronizedList = Collections.synchronizedList(list);
// 3. 创建只读视图(装饰器)
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("A", 1);
map.put("B", 2);
Map<String, Integer> readOnlyMap = Collections.unmodifiableMap(map);
// 4. 验证装饰器类型
System.out.println("原始列表类型: " + list.getClass().getSimpleName());
System.out.println("装饰后类型: " + unmodifiableList.getClass().getSimpleName());
}
}四、装饰器模式的高级应用
4.1 带状态的装饰器
装饰器不仅可以添加行为,还可以添加状态:
java
// 带有折扣功能的装饰器
public class DiscountDecorator extends CondimentDecorator {
private double discountRate; // 折扣率,如0.8表示8折
public DiscountDecorator(Beverage beverage, double discountRate) {
super(beverage);
this.discountRate = discountRate;
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return beverage.getDescription() + String.format(" (%.0f折)", discountRate * 10);
}
@Override
public double getCost() {
return beverage.getCost() * discountRate;
}
// 可以动态改变折扣率
public void setDiscountRate(double discountRate) {
this.discountRate = discountRate;
}
}
// 使用示例
public class DiscountDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Beverage coffee = new Americano();
coffee = new Milk(coffee);
coffee = new DiscountDecorator(coffee, 0.8); // 8折
System.out.println("折扣咖啡: " + coffee.getDescription());
System.out.println("原价: ¥" + (new Milk(new Americano()).getCost()));
System.out.println("折扣价: ¥" + coffee.getCost());
}
}4.2 条件装饰器
装饰器可以根据条件决定是否添加功能:
java
public class ConditionalDecorator extends CondimentDecorator {
private boolean condition;
private double extraCost;
private String extraDesc;
public ConditionalDecorator(Beverage beverage, boolean condition,
double extraCost, String extraDesc) {
super(beverage);
this.condition = condition;
this.extraCost = extraCost;
this.extraDesc = extraDesc;
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
if (condition) {
return beverage.getDescription() + " + " + extraDesc;
}
return beverage.getDescription();
}
@Override
public double getCost() {
if (condition) {
return beverage.getCost() + extraCost;
}
return beverage.getCost();
}
public void setCondition(boolean condition) {
this.condition = condition;
}
}4.3 ⭐装饰器工厂
结合工厂模式管理装饰器的创建:
java
public class BeverageFactory {
public static Beverage createBeverage(String base, String... condiments) {
Beverage beverage;
// 创建基础咖啡
switch (base.toLowerCase()) {
case "espresso": beverage = new Espresso(); break;
case "americano": beverage = new Americano(); break;
case "latte": beverage = new Latte(); break;
default: throw new IllegalArgumentException("未知的咖啡类型");
}
// 添加装饰器
for (String condiment : condiments) {
switch (condiment.toLowerCase()) {
case "milk": beverage = new Milk(beverage); break;
case "sugar": beverage = new Sugar(beverage); break;
case "chocolate": beverage = new Chocolate(beverage); break;
case "cream": beverage = new Cream(beverage); break;
default: System.out.println("忽略未知配料: " + condiment);
}
}
return beverage;
}
}
// 使用工厂
Beverage myCoffee = BeverageFactory.createBeverage(
"latte", "milk", "sugar", "chocolate"
);五、装饰器模式在Spring框架中的应用
5.1 Spring AOP中的装饰器模式
Spring AOP(面向切面编程)大量使用了装饰器模式的思想:
java
// 业务接口
public interface UserService {
User getUserById(Long id);
void saveUser(User user);
}
// 业务实现
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Override
public User getUserById(Long id) {
System.out.println("获取用户: " + id);
return new User(id, "张三");
}
@Override
public void saveUser(User user) {
System.out.println("保存用户: " + user.getName());
}
}
// AOP切面(类似装饰器)
@Aspect
@Component
public class LoggingAspect {
@Before("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))")
public void logBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("方法执行前: " + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
}
@AfterReturning(pointcut = "execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))",
returning = "result")
public void logAfterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result) {
System.out.println("方法执行后: " + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
}
@Around("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))")
public Object measurePerformance(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Object result = pjp.proceed();
long elapsed = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
System.out.println("方法执行时间: " + elapsed + "ms");
return result;
}
}5.2 Spring Security中的装饰器
Spring Security使用装饰器模式增强安全功能:
java
// 安全上下文包装器
public class SecurityContextDecorator implements SecurityContext {
private SecurityContext wrappedContext;
public SecurityContextDecorator(SecurityContext wrappedContext) {
this.wrappedContext = wrappedContext;
}
@Override
public Authentication getAuthentication() {
Authentication auth = wrappedContext.getAuthentication();
if (auth != null) {
// 添加额外的安全检查
return new EnhancedAuthentication(auth);
}
return null;
}
@Override
public void setAuthentication(Authentication authentication) {
// 在设置前进行验证
validateAuthentication(authentication);
wrappedContext.setAuthentication(authentication);
}
private void validateAuthentication(Authentication auth) {
// 验证逻辑
}
}
// 增强的认证对象
public class EnhancedAuthentication implements Authentication {
private Authentication original;
public EnhancedAuthentication(Authentication original) {
this.original = original;
}
@Override
public Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities() {
Collection<GrantedAuthority> authorities = new ArrayList<>(
original.getAuthorities()
);
// 添加默认权限
authorities.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_USER"));
return authorities;
}
@Override
public Object getCredentials() {
return original.getCredentials();
}
// 其他方法委托给original...
}六、总结
6.1 何时使用装饰器模式
使用装饰器模式的典型场景:
-
需要动态、透明地添加功能:在不影响其他对象的情况下,动态地给单个对象添加职责
-
需要撤销的功能:装饰器可以轻松地添加或移除
-
通过继承扩展不现实时:子类数量爆炸,或者类定义被隐藏无法用于继承
-
需要大量功能组合:不同功能的排列组合数量庞大
6.2 优缺点
装饰模式的优点:
-
使用装饰模式来实现扩展比继承更加灵活,它可以在不需要创造更多子类的情况下,将对象的功能加以扩展。
-
可以动态地给一个对象附加更多的功能。
-
可以用不同的装饰器 进行多重装饰,装饰的顺序不同,可能产生不同的效果。
-
装饰类和被装饰类可以独立发展,不会相互耦合;装饰模式相当于是继承的一个替代模式。
装饰模式的缺点:
-
与继承相比,用装饰的方式拓展功能更加容易出错,排错也更困难。
-
对于多次装饰的对象,调试时寻找错误可能需要逐级排查,较为烦琐。
6.3 核心要点
设计原则体现:
开闭原则:可以添加新装饰器而不修改现有代码
单一职责:每个装饰器只负责一个特定的功能
组合优于继承:使用组合实现功能的灵活扩展
实现关键:
装饰器和被装饰对象实现相同的接口
装饰器持有被装饰对象的引用
装饰器在被装饰对象行为的前后添加自己的行为
在Java和Spring中的应用:
Java I/O流的经典实现
Java集合框架的视图包装
Spring AOP的切面编程
Spring Web的请求/响应包装
Spring Security的安全增强