文章目录
一、概述
本文档详细介绍了如何使用训练好的MNIST CNN模型进行手写数字预测。我们将从模型加载、数据预处理、预测执行到结果可视化,提供完整的代码示例和详细说明。
二、环境准备
2.1 必需库安装
bash
# 基础依赖
pip install tensorflow numpy matplotlib
# 可选依赖(用于更高级功能)
pip install opencv-python pillow seaborn2.2 文件结构
project/
├── models/
│ ├── mnist_cnn_final.h5 # 训练好的模型
│ └── best_model.h5 # 训练过程中的最佳模型
├── data/
│ ├── t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz # 测试图像
│ └── t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz # 测试标签
├── predict_basic.py # 基础预测脚本
├── predict_interactive.py # 交互式预测脚本
└── requirements.txt # 依赖列表三、基础预测示例
3.1 完整预测脚本
python
"""
基本预测示例:使用训练好的MNIST CNN模型
文件名: predict_basic.py
"""
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from tensorflow import keras
import gzip
class BasicMNISTPredictor:
"""基本MNIST预测器"""
def __init__(self, model_path='models/mnist_cnn_final.h5'):
"""初始化预测器"""
print(f"正在加载模型: {model_path}")
self.model = keras.models.load_model(model_path)
print("✅ 模型加载成功")
print(f"模型输入形状: {self.model.input_shape}")
print(f"模型输出形状: {self.model.output_shape}")
def load_test_data(self):
"""加载测试数据"""
print("\n正在加载测试数据...")
# 加载测试图像
with gzip.open('../data/t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz', 'rb') as f:
test_images = np.frombuffer(f.read(), np.uint8, offset=16)
test_images = test_images.reshape(-1, 28, 28)
# 加载测试标签
with gzip.open('../data/t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz', 'rb') as f:
test_labels = np.frombuffer(f.read(), np.uint8, offset=8)
print(f"测试数据: {test_images.shape}")
return test_images, test_labels
def preprocess_image(self, image):
"""预处理单张图像"""
# 确保图像是28x28
if image.shape != (28, 28):
raise ValueError(f"图像形状应为(28, 28),但得到{image.shape}")
# 添加批处理和通道维度,并归一化
image_processed = image.reshape(1, 28, 28, 1).astype('float32') / 255.0
return image_processed
def predict_single(self, image):
"""预测单张图像"""
# 预处理
image_processed = self.preprocess_image(image)
# 预测
predictions = self.model.predict(image_processed, verbose=0)
# 获取预测结果
predicted_class = np.argmax(predictions[0])
confidence = np.max(predictions[0])
return predicted_class, confidence, predictions[0]
def predict_batch(self, images):
"""批量预测"""
# 预处理
images_processed = images.reshape(-1, 28, 28, 1).astype('float32') / 255.0
# 预测
predictions = self.model.predict(images_processed, verbose=0)
# 获取预测结果
predicted_classes = np.argmax(predictions, axis=1)
confidences = np.max(predictions, axis=1)
return predicted_classes, confidences, predictions
def visualize_single_prediction(self, image, true_label=None):
"""可视化单张图像的预测结果"""
# 预测
predicted_class, confidence, all_probs = self.predict_single(image)
# 创建可视化
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12, 5))
# 左侧:图像
axes[0].imshow(image, cmap='gray')
if true_label is not None:
title = f'预测: {predicted_class} (置信度: {confidence:.2%})'
title += f'\n实际: {true_label}'
color = 'green' if predicted_class == true_label else 'red'
axes[0].set_title(title, color=color, fontsize=14)
else:
axes[0].set_title(f'预测: {predicted_class} (置信度: {confidence:.2%})', fontsize=14)
axes[0].axis('off')
# 右侧:概率分布
bars = axes[1].bar(range(10), all_probs, color='lightblue')
axes[1].set_xlabel('数字', fontsize=12)
axes[1].set_ylabel('概率', fontsize=12)
axes[1].set_title('预测概率分布', fontsize=14)
axes[1].set_xticks(range(10))
axes[1].set_ylim([0, 1])
axes[1].grid(True, alpha=0.3)
# 高亮预测的类别
bars[predicted_class].set_color('red')
# 在每个柱子上添加概率值
for i, (bar, prob) in enumerate(zip(bars, all_probs)):
height = bar.get_height()
axes[1].text(bar.get_x() + bar.get_width() / 2., height,
f'{prob:.3f}',
ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=9)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# 打印详细信息
print(f"\n预测结果: 数字 {predicted_class}")
print(f"置信度: {confidence:.2%}")
print("\n所有类别的概率:")
for i, prob in enumerate(all_probs):
print(f" 数字 {i}: {prob:.4f}")
return predicted_class, confidence
def evaluate_on_test_set(self, num_samples=None):
"""在测试集上评估模型"""
print("\n正在测试集上评估模型...")
# 加载测试数据
test_images, test_labels = self.load_test_data()
# 限制样本数量(如果指定)
if num_samples is not None:
test_images = test_images[:num_samples]
test_labels = test_labels[:num_samples]
# 批量预测
predicted_classes, confidences, _ = self.predict_batch(test_images)
# 计算准确率
accuracy = np.mean(predicted_classes == test_labels)
print(f"\n评估结果:")
print(f"样本数量: {len(test_images)}")
print(f"准确率: {accuracy:.2%}")
print(f"预测错误数: {np.sum(predicted_classes != test_labels)}")
# 显示错误分类的样本
self.show_misclassifications(test_images, test_labels, predicted_classes, max_samples=5)
return accuracy
def show_misclassifications(self, images, true_labels, predicted_labels, max_samples=5):
"""显示错误分类的样本"""
misclassified = np.where(true_labels != predicted_labels)[0]
if len(misclassified) == 0:
print("✅ 所有样本都分类正确!")
return
print(f"\n发现 {len(misclassified)} 个错误分类的样本")
print("前几个错误分类:")
for i, idx in enumerate(misclassified[:max_samples]):
print(f" 样本 {idx}: 预测={predicted_labels[idx]}, 实际={true_labels[idx]}")
# 可视化错误分类
self.visualize_misclassifications(images, true_labels, predicted_labels, misclassified[:max_samples])
def visualize_misclassifications(self, images, true_labels, predicted_labels, misclassified_indices):
"""可视化错误分类的样本"""
num_samples = min(len(misclassified_indices), 10)
if num_samples == 0:
return
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 5, figsize=(15, 6))
axes = axes.ravel()
for i, idx in enumerate(misclassified_indices[:10]):
axes[i].imshow(images[idx], cmap='gray')
axes[i].set_title(f'预测: {predicted_labels[idx]}\n实际: {true_labels[idx]}',
color='red', fontsize=11)
axes[i].axis('off')
# 隐藏多余的子图
for i in range(num_samples, 10):
axes[i].axis('off')
plt.suptitle('错误分类的样本', fontsize=16, color='red')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 1. 初始化预测器
predictor = BasicMNISTPredictor('models/mnist_cnn_final.h5')
# 2. 加载测试数据
test_images, test_labels = predictor.load_test_data()
# 3. 测试单张图像预测
print("\n" + "=" * 50)
print("单张图像预测测试")
print("=" * 50)
for i in range(3): # 测试前3个样本
print(f"\n测试样本 {i}:")
predictor.visualize_single_prediction(test_images[i], test_labels[i])
# 4. 批量预测评估
print("\n" + "=" * 50)
print("批量预测评估")
print("=" * 50)
accuracy = predictor.evaluate_on_test_set(num_samples=100)3.2 运行示例
3.2.1 基本运行
bash
# 确保模型文件存在
python predict_basic.py3.2.2 预期输出
✅ 模型加载成功
模型输入形状: (None, 28, 28, 1)
模型输出形状: (None, 10)
正在加载测试数据...
测试数据: (10000, 28, 28)
==================================================
单张图像预测测试
==================================================
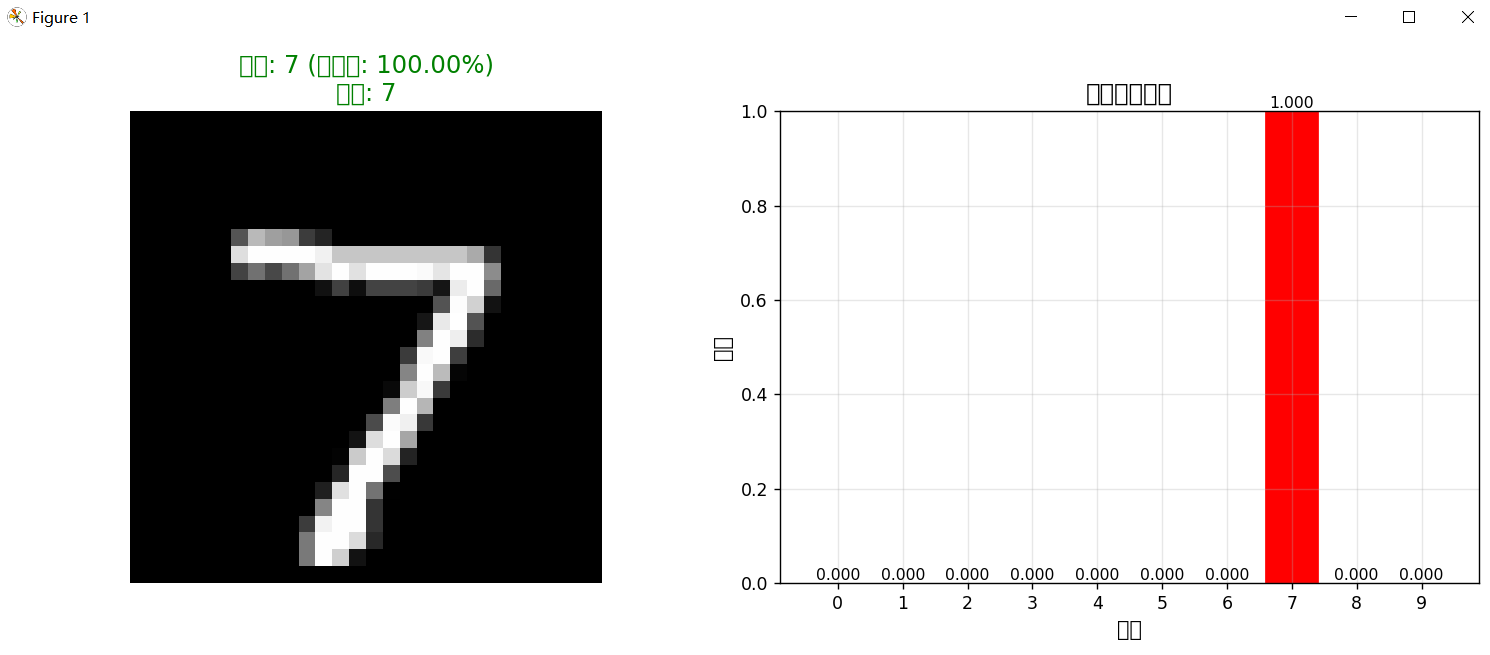
测试样本 0:
预测结果: 数字 7
置信度: 100.00%
所有类别的概率:
数字 0: 0.0000
数字 1: 0.0000
数字 2: 0.0000
数字 3: 0.0000
数字 4: 0.0000
数字 5: 0.0000
数字 6: 0.0000
数字 7: 1.0000
数字 8: 0.0000
数字 9: 0.0000
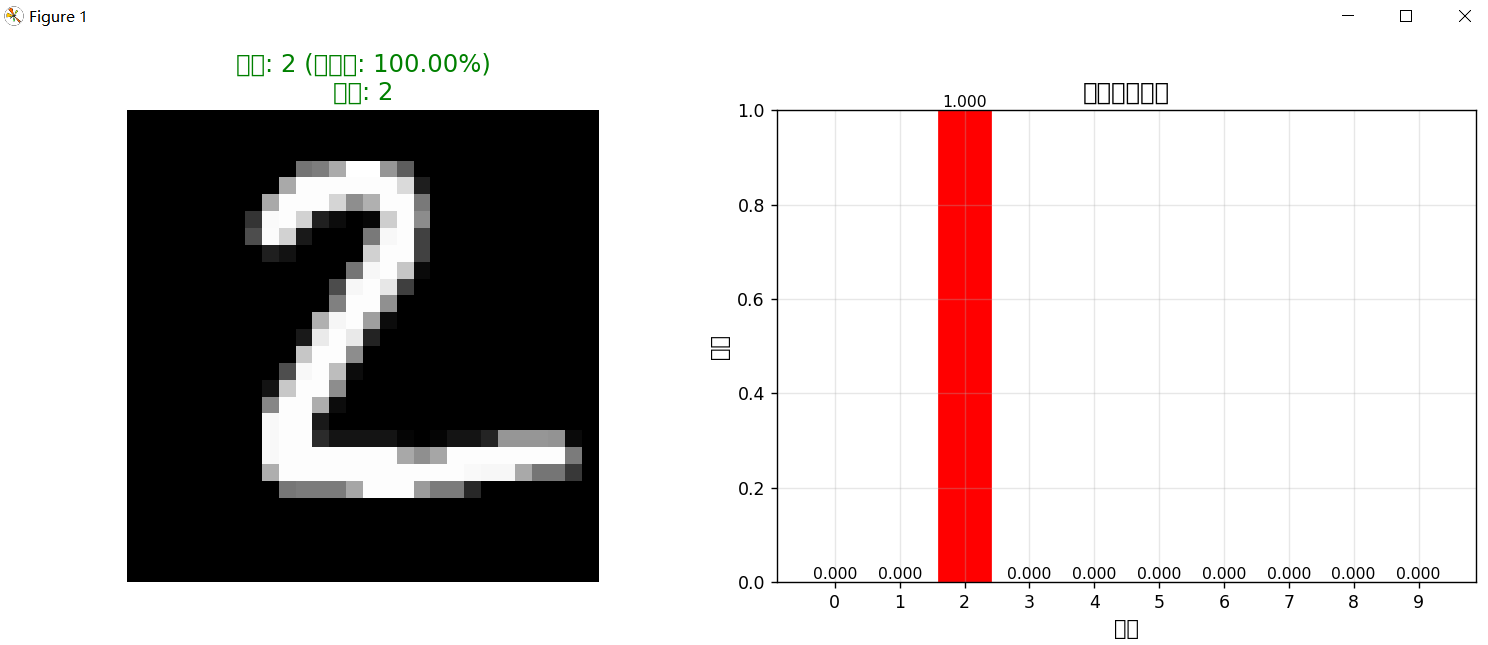
测试样本 1:
预测结果: 数字 2
置信度: 100.00%
所有类别的概率:
数字 0: 0.0000
数字 1: 0.0000
数字 2: 1.0000
数字 3: 0.0000
数字 4: 0.0000
数字 5: 0.0000
数字 6: 0.0000
数字 7: 0.0000
数字 8: 0.0000
数字 9: 0.0000
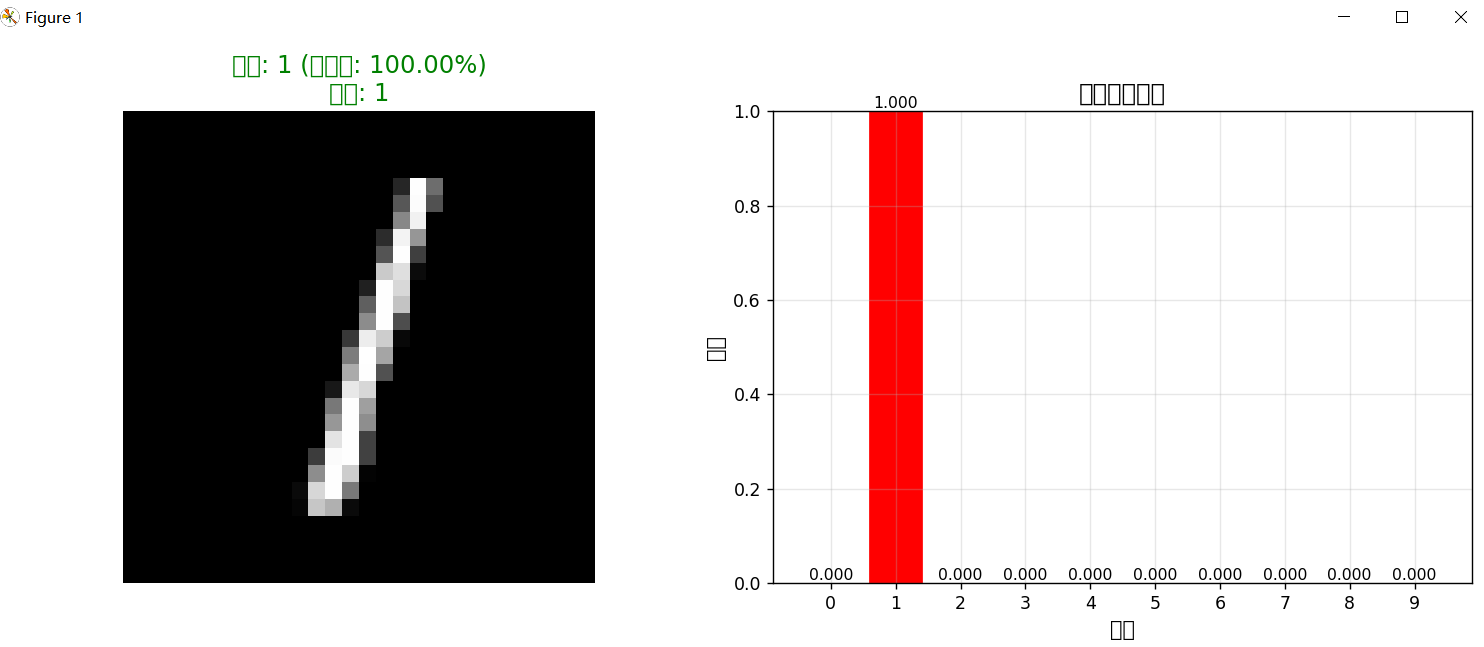
测试样本 2:
预测结果: 数字 1
置信度: 100.00%
所有类别的概率:
数字 0: 0.0000
数字 1: 1.0000
数字 2: 0.0000
数字 3: 0.0000
数字 4: 0.0000
数字 5: 0.0000
数字 6: 0.0000
数字 7: 0.0000
数字 8: 0.0000
数字 9: 0.0000
==================================================
批量预测评估
==================================================
正在测试集上评估模型...
正在加载测试数据...
测试数据: (10000, 28, 28)
评估结果:
样本数量: 100
准确率: 100.00%
预测错误数: 0
✅ 所有样本都分类正确!四、关键技术详解
4.1 模型加载机制
4.1.1 TensorFlow模型格式
python
# HDF5格式模型文件结构
model = keras.models.load_model('mnist_cnn_final.h5')
# 加载的内容包括:
# 1. 模型架构(层结构)
# 2. 权重参数(W和b)
# 3. 优化器状态
# 4. 训练配置
# 5. 损失函数和评估指标4.1.2 模型验证
python
def validate_model(model):
"""验证加载的模型是否有效"""
# 1. 检查输入输出形状
assert model.input_shape == (None, 28, 28, 1), "输入形状不正确"
assert model.output_shape == (None, 10), "输出形状不正确"
# 2. 测试随机输入
test_input = np.random.randn(1, 28, 28, 1).astype('float32')
output = model.predict(test_input)
# 3. 检查输出格式
assert output.shape == (1, 10), "输出格式不正确"
assert np.allclose(np.sum(output), 1.0, atol=1e-5), "输出概率和不为1"
print("✅ 模型验证通过")效果截图