要求:
1.使用os和os.path以及函数的递归完成:
给出一个路径,遍历当前路径所有的文件及文件夹
打印输出所有的文件(遇到文件输出路径,遇到文件夹继续进文件夹)
python
import os #导入os模块
def traverse_files(path): #定义遍历函数
files = os.listdir(path) #以列表形式返回目录下的所有文件及文件夹
for f in files: #路径拼接
real_path = os.path.join(path,f) # 判断路径是文件还是文件夹,是文件时,返回完整路径
if os.path.isfile(real_path):
print(os.path.abspath(real_path))
#是文件夹时,再次调用遍历函数
elif os.path.isdir(real_path):
traverse_files(real_path)
#其他情况
else:
print("其他情况")
pass
#调用函数
traverse_files("D:/python/code") 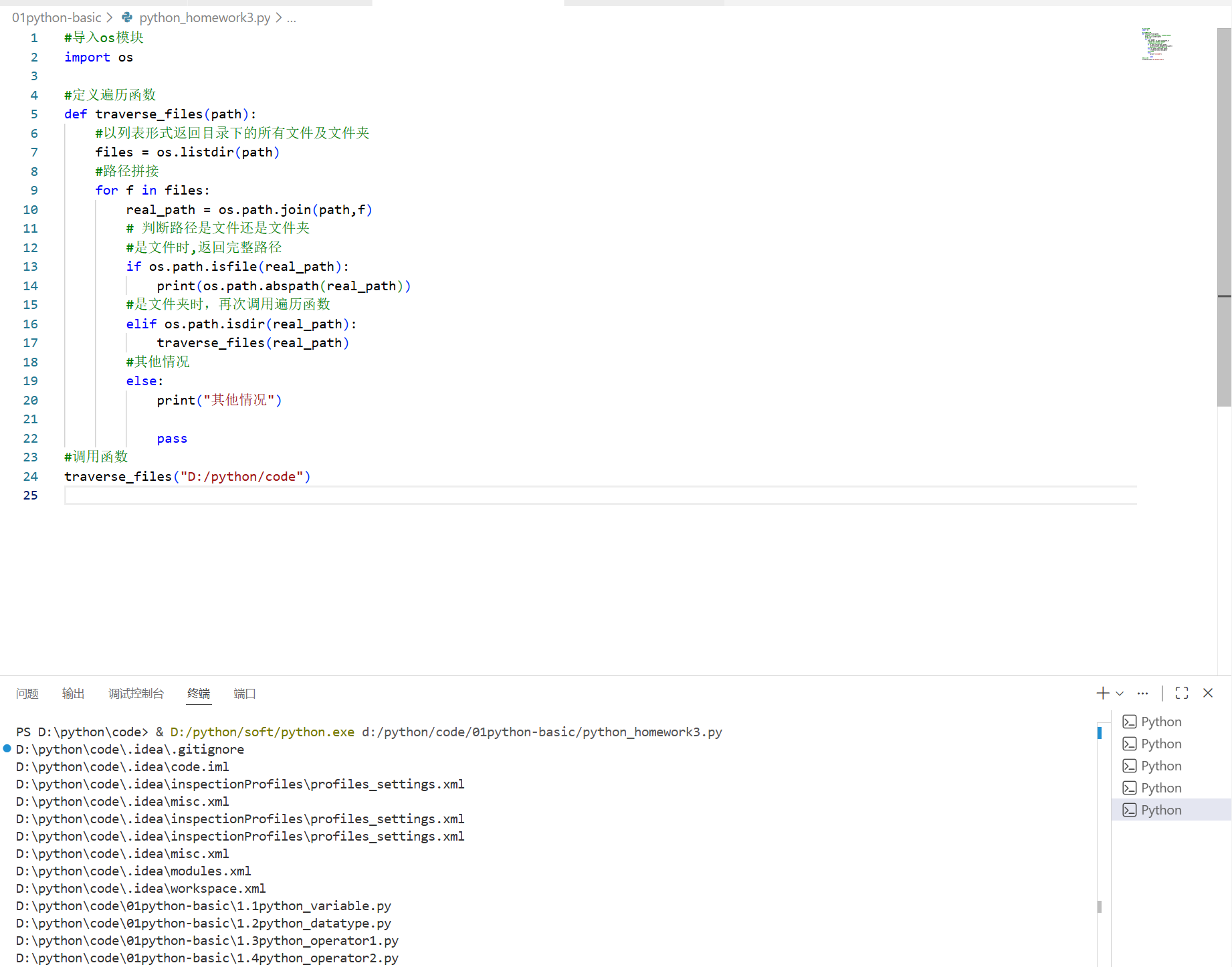
2.使用加密模块及IO模拟登录功能,要求使用文件模拟数据库存储用户名和密码。
python
import hashlib
import os
# 定义模拟数据库的文件路径
DB_FILE = "users.txt"
def hash_password(password):
return hashlib.sha256(password.encode()).hexdigest()
def register_user(username, password):
# 检查用户是否已存在
if os.path.exists(DB_FILE):
with open(DB_FILE, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for line in f:
existing_user, _ = line.strip().split(':')
if existing_user == username:
print("注册失败:用户名已存在。")
return
# 加密密码并写入文件
hashed_pwd = hash_password(password)
with open(DB_FILE, 'a', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(f"{username}:{hashed_pwd}\n")
print("注册成功!")
def login_user(username, password):
if not os.path.exists(DB_FILE):
print("登录失败:用户数据库不存在。")
return False
hashed_pwd = hash_password(password)
with open(DB_FILE, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for line in f:
stored_user, stored_pwd = line.strip().split(':')
if stored_user == username and stored_pwd == hashed_pwd:
print("登录成功!")
return True
print("登录失败:用户名或密码错误。")
return False
# 示例调用
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("=== 用户注册/登录系统 ===")
while True:
choice = input("请选择操作 (1-注册, 2-登录, 3-退出): ")
if choice == '1':
username = input("输入用户名: ")
password = input("输入密码: ")
register_user(username, password)
elif choice == '2':
username = input("输入用户名: ")
password = input("输入密码: ")
login_user(username, password)
elif choice == '3':
break
else:
print("无效选择,请重试。")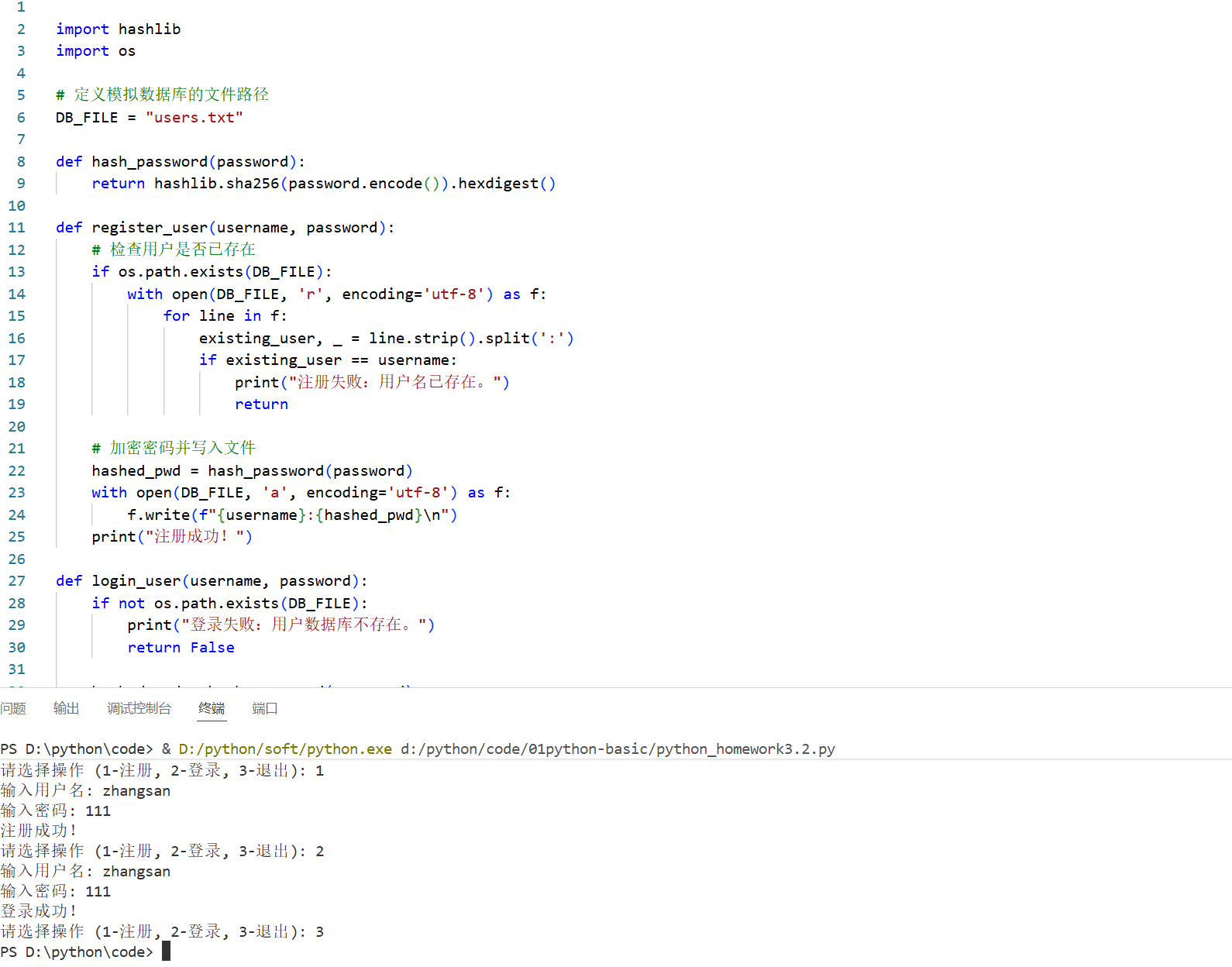
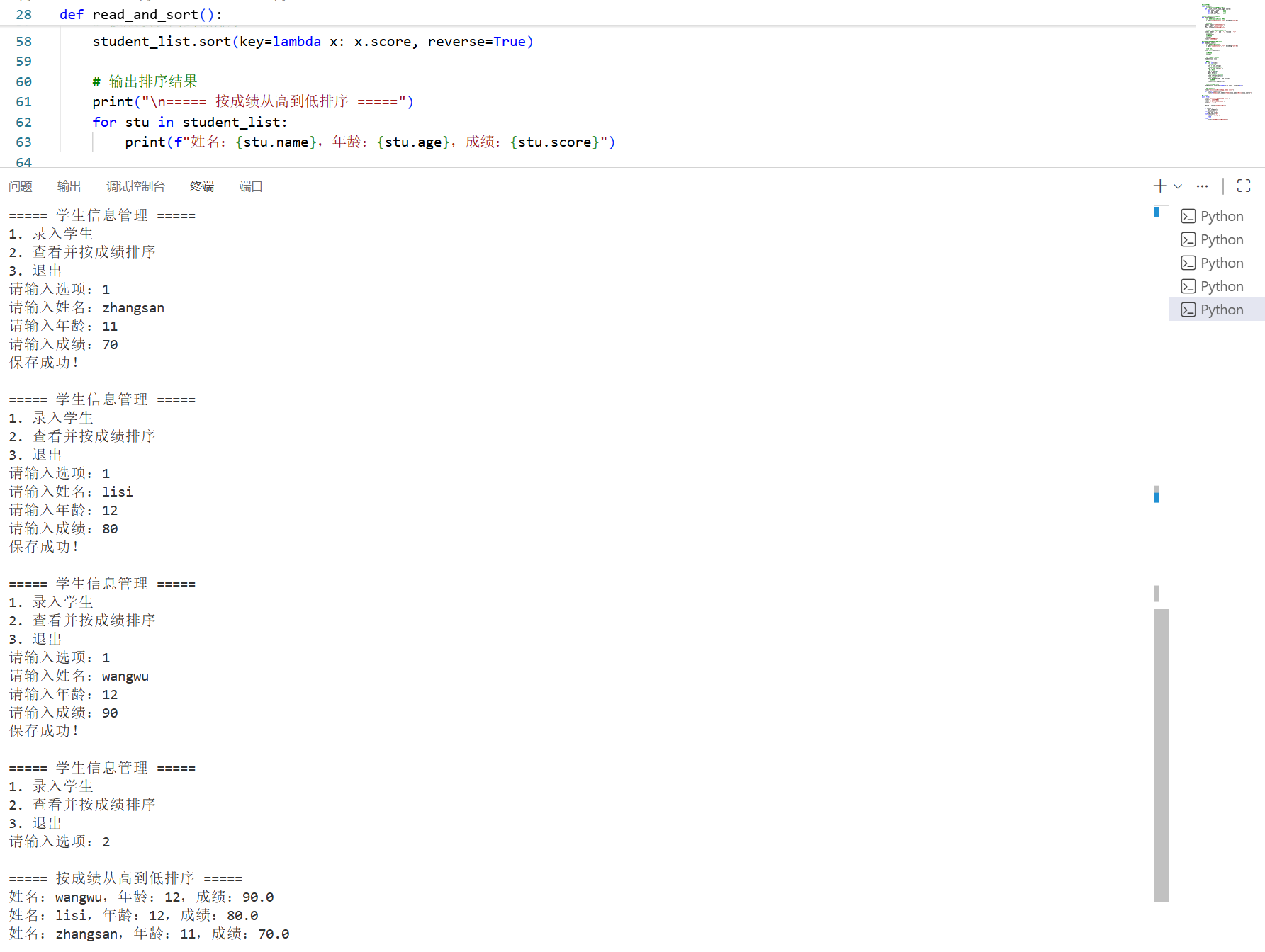
3.使用面向对象编程完成学生信息录入功能,数据存储在本地文件txt中,并读取学生信息并按照成绩进行排序,学生其他属性自行规划
python
# 定义学生类
class Student:
# 初始化方法:给学生对象赋值
def __init__(self, name, age, score):
self.name = name # 姓名
self.age = age # 年龄
self.score = score # 成绩
# 录入学生信息并保存到文件
def save_student():
# 打开文件,模式a表示追加写入
f = open("students.txt", "a", encoding="utf-8")
# 输入信息
name = input("请输入姓名:")
age = input("请输入年龄:")
score = input("请输入成绩:")
# 拼接成一行字符串,用逗号分隔
line = name + "," + age + "," + score + "\n"
# 写入文件
f.write(line)
# 关闭文件
f.close()
print("保存成功!")
# 从文件读取学生并按成绩排序
def read_and_sort():
# 打开文件,r表示只读
f = open("students.txt", "r", encoding="utf-8")
# 读取所有行
lines = f.readlines()
# 关闭文件
f.close()
# 存放学生对象的列表
student_list = []
# 遍历每一行
for line in lines:
# 去掉换行符
line = line.strip()
# 按逗号切分成三部分
data = line.split(",")
# 取出数据
name = data[0]
age = data[1]
# 成绩转成数字才能排序
score = float(data[2])
# 创建学生对象
stu = Student(name, age, score)
# 加入列表
student_list.append(stu)
# 按成绩从高到低排序
student_list.sort(key=lambda x: x.score, reverse=True)
# 输出排序结果
print("\n===== 按成绩从高到低排序 =====")
for stu in student_list:
print(f"姓名:{stu.name},年龄:{stu.age},成绩:{stu.score}")
# 主菜单
while True:
print("\n===== 学生信息管理 =====")
print("1. 录入学生")
print("2. 查看并按成绩排序")
print("3. 退出")
choice = input("请输入选项:")
if choice == "1":
save_student()
elif choice == "2":
read_and_sort()
elif choice == "3":
print("退出程序")
break
else:
print("输入错误,请重新输入")