前言:我们已经了解了vector的接口用法及空间是如何增长的还有Vector是如何遍历的。那下面我们来了解一下vector程序的结构。
vector的结构
vector<vector<int >>是个二维数组,但是它的结构是啥呢?
我们如何用下标[]的方式进行遍历呢?
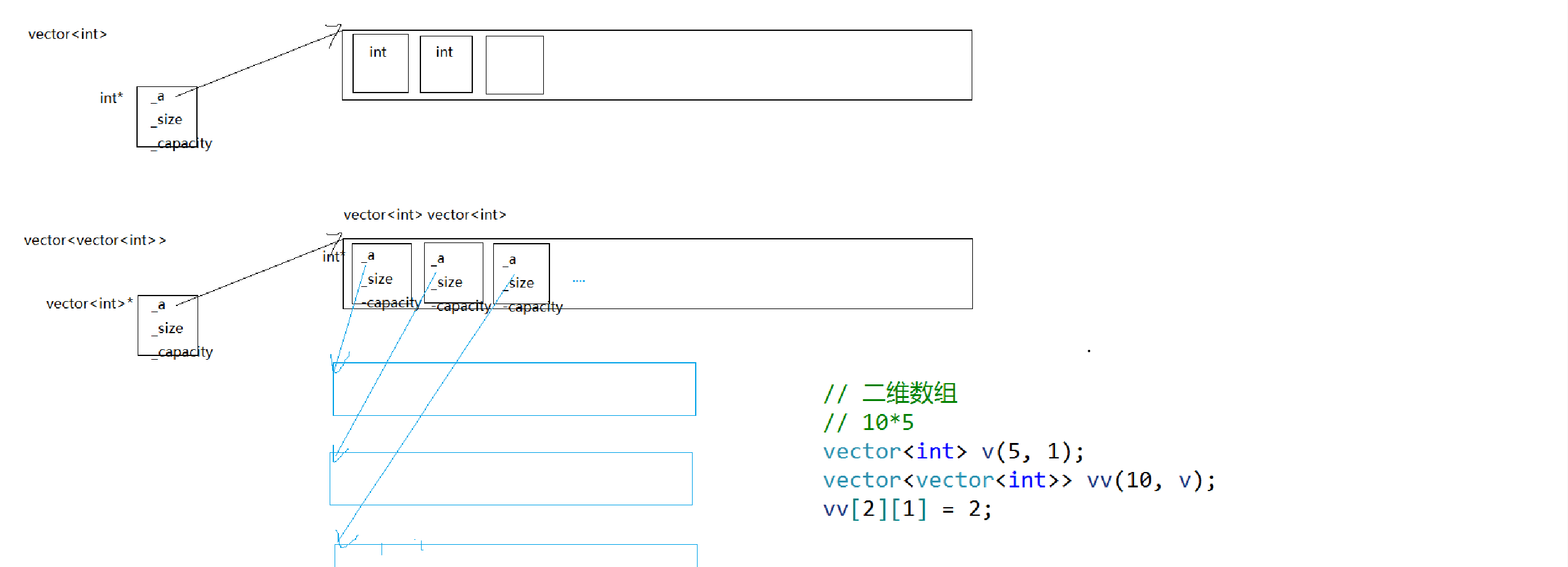
其实内部是由两个类完成的,当我们VV[2][1]的时候,先访问Vector的vector,再访问vector <int> ,这点和二维数组一样的。
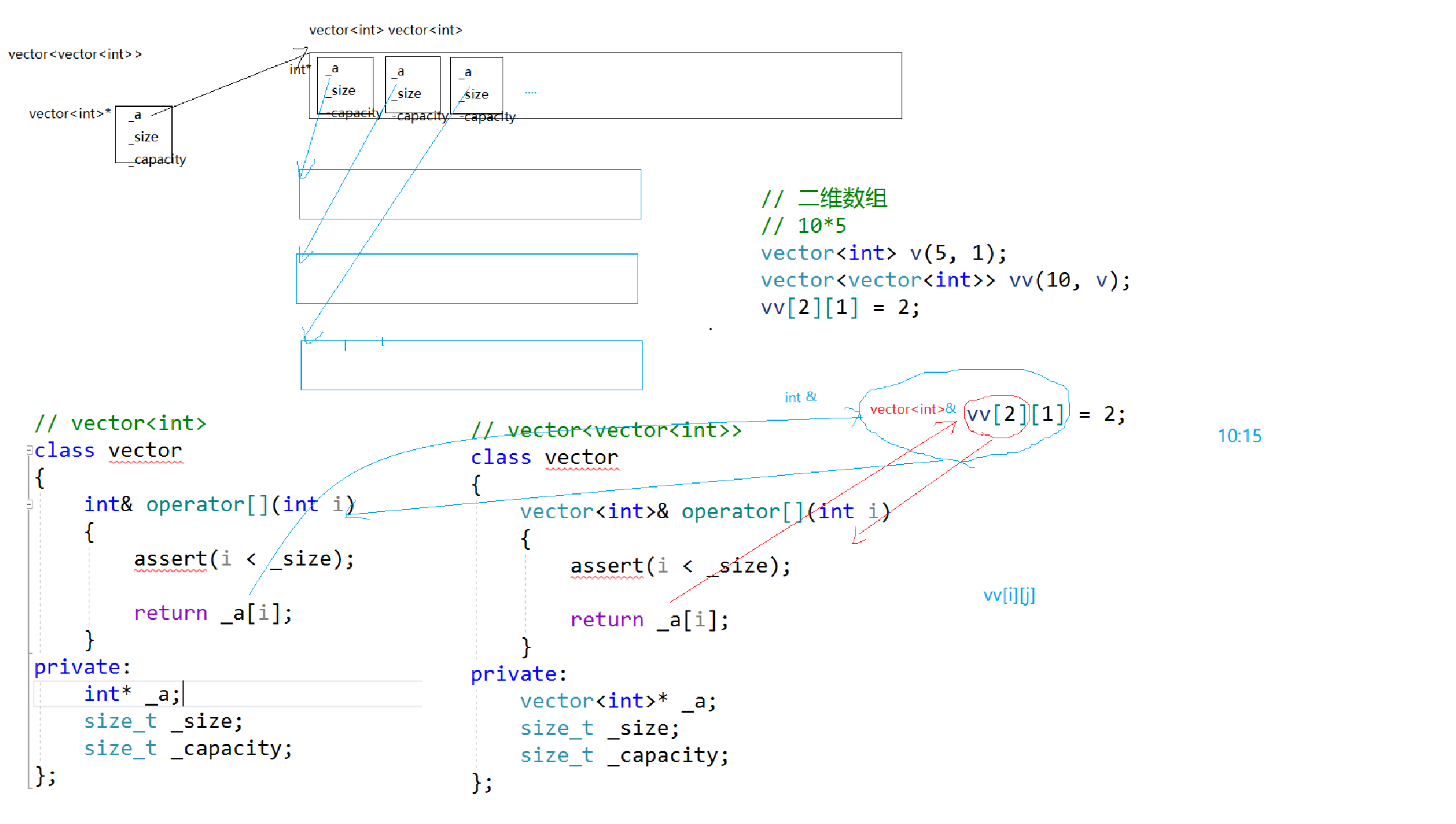
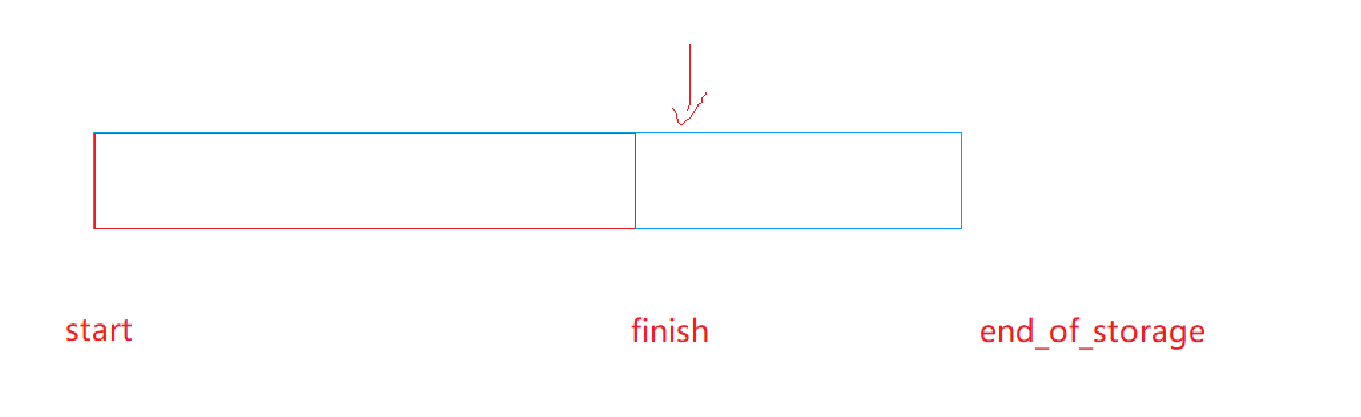
而我们要实现的vector内部是有三个指针,一个指向头部,一个指向最后数据的下一个位置,一个指向空间大小。但是我们这个顺序表必须要考虑能够存任何数据。所以我们要给他搞成自定义成员变量同时也需要模板类的形式来处理。
但是我们存数据的时候要扩容、插入数据,头插、尾插。同时还要注意深浅拷贝(现代写法和传统写法),同时还要考虑迭代器失效等问题。
vector的实现代码
cpp
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<list>
#include<assert.h>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm> // std::find必须的头文件
namespace px
{
template<class T>
class vector
{
public:
// Vector的迭代器是一个原生指针
typedef T* iterator;
typedef const T* const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _start;
}
iterator end()
{
return _finish;
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _start;
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _finish;
}
// construct and destroy
// C++11 前置生成默认构造
vector() = default;
vector(int n, const T& value = T())
{
reserve(n);
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
push_back(value);
}
}
//类模板中的函数模板
template<class InputIterator>
//迭代器构造
vector(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
{
while (first != last)
{
push_back(*first);
++first;
}
}
vector(const vector<T>& v)
{
reserve(v.size());
for (auto& e : v)
{
push_back(e);
}
}
void clear()
{
_finish = _start;
}
vector<T>& operator= (vector<T> v)
{
if (this != &v)
{
clear();
reserve(v.size());
for (auto& e : v)
{
push_back(e);
}
}
return *this;
}
~vector()
{
if (_start)
{
delete[] _start;
_start = _finish = _endOfStorage = nullptr;
}
}
// capacity
size_t size() const
{
return _finish - _start;
}
size_t capacity() const
{
return _endOfStorage - _start;
}
void reserve(size_t n)
{
if (n > capacity())
{
size_t old_size = size();
T* tmp = new T[n];
// memcopy(tmp, _start, sizeof(T) * size());
for (size_t i = 0;i < old_size;i++)
{
tmp[i] = _start[i];
}
delete[] _start;
_start = tmp;
_finish = tmp + old_size;
_endOfStorage = tmp + n;
}
}
bool empty() const
{
return _start == _finish;
}
void resize(size_t n, const T& value = T())
{
if (n < size())
{
_finish = _start + n;
}
else if (n > size())
{
reserve(n);
while (_finish < _start + n)
{
*_finish = value;
++_finish;
}
}
}
T& operator[](size_t pos)
{
assert(pos < size());
return _start[pos];
}
const T& operator[](size_t pos)const
{
assert(pos < size());
return _start[pos];
}
void push_back(const T& x)
{
if (_finish == _endOfStorage)
{
reserve(capacity() == 0 ? 4 : capacity() * 2);
}
*_finish = x;
++_finish;
}
void pop_back()
{
assert(!empty());
--_finish;
}
void swap(vector<T>& v)
{
std::swap(_start, v._start);
std::swap(_finish, v._finish);
std::swap(_endOfStorage, v._endOfStorage);
}
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x)
{
if (_finish == _endOfStorage)
{
size_t len = pos - _start;
reserve(capacity() == 0 ? 4 : capacity() * 2);
pos = _start + len;
}
iterator end = _finish - 1;
while (end >= pos)
{
*(end + 1) = *end;
--end;
}
*pos = x;
++_finish;
return pos;
}
void erase(iterator pos)
{
assert(pos >= _start);
assert(pos < _finish);
iterator it = pos + 1;
while (it != end())
{
*(it - 1) = *it;
++it;
}
--_finish;
}
private:
iterator _start = nullptr; // 指向数据块的开始
iterator _finish = nullptr; // 指向有效数据的尾
iterator _endOfStorage = nullptr; // 指向存储容量的尾
};
template<class T>
void print_vector(const px::vector<T>& v)
{
auto it = v.begin();
while (it != v.end())
{
std::cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
for (auto e : v)
{
std::cout << e << " ";
++it;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
template<class Container>
void print_container(const Container& v)
{
for (auto e : v)
{
std::cout << e << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
void test_vector1()
{
px::vector<int> v;
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(4);
v.push_back(5);
for (size_t i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
{
std::cout << v[i] << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
px::vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin();
while (it != v.end())
{
std::cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
for (auto e : v)
{
std::cout << e << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
print_vector(v);
vector<double> vd;
vd.push_back(1.1);
vd.push_back(2.1);
vd.push_back(3.1);
vd.push_back(4.1);
vd.push_back(5.1);
print_vector(vd);
}
/*void test_vector2()
{
std::vector<int> v;
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(4);
v.push_back(5);
print_container(v);
int x;
std::cin >> x;
auto p = std::find(v.begin(), v.end(), x);
if (p != v.end())
{
p = v.insert(p, 40);
(*(p + 1)) *= 10;
}
print_container(v);
}*/
/*void test_vector3()
{
std::vector<int> v;
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(4);
print_container(v);
auto it = v.begin();
while (it != v.end())
{
if (*it % 2 == 0)
{
it = v.erase(it);
}
else
{
++it;
}
}
print_container(v);
}*/
void test_vector4()
{
int i = int();
int j = int(1);
int k(2);
vector<int> v;
v.resize(10, 1);
v.reserve(20);
print_container(v);
std::cout << v.size() << std::endl;
std::cout << v.capacity() << std::endl;
v.resize(15, 2);
print_container(v);
v.resize(25, 3);
print_container(v);
v.resize(5);
print_container(v);
}
void test_vector5()
{
vector<int> v1;
v1.push_back(1);
v1.push_back(2);
v1.push_back(3);
v1.push_back(4);
print_container(v1);
px::vector<int> v2 = v1;
print_container(v2);
px::vector<int> v3;
v3.push_back(10);
v3.push_back(20);
v3.push_back(30);
v1 = v3;
print_container(v1);
print_container(v3);
}
void test_vector6()
{
vector<int> v1;
v1.push_back(1);
v1.push_back(2);
v1.push_back(3);
v1.push_back(4);
v1.push_back(4);
v1.push_back(4);
px::vector<int> v2(v1.begin(), v1.begin() + 3);
print_container(v1);
print_container(v2);
std::list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(10);
lt.push_back(20);
lt.push_back(30);
lt.push_back(40);
px::vector<int> v3(lt.begin(), lt.end());
print_container(lt);
print_container(v3);
px::vector<std::string> v4(10, "1111111");
print_container(v4);
px::vector<int> v5(10);
print_container(v5);
px::vector<int> v6(10u, 1);
print_container(v6);
px::vector<int> v7(10, 1);
print_container(v7);
}
void test_vector7()
{
px::vector<std::string> v;
v.push_back("11111111111111111111");
v.push_back("11111111111111111111");
v.push_back("11111111111111111111");
v.push_back("11111111111111111111");
print_container(v);
v.push_back("11111111111111111111");
print_container(v);
}
}测试
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Vector.h"
int main()
{
//px::test_vector4();
return 0;
}