Redis-SDK 介绍及使用
- [一. Redis 介绍](#一. Redis 介绍)
- [二. Redis 安装](#二. Redis 安装)
- [三. redis-plus-plus SDK 介绍](#三. redis-plus-plus SDK 介绍)
- [四. redis-plus-plus SDK 安装](#四. redis-plus-plus SDK 安装)
- [五. redis-plus-plus 类与接口](#五. redis-plus-plus 类与接口)
-
- [1. 异常、客户端配置、常规操作](#1. 异常、客户端配置、常规操作)
- [2. 字符串、列表、哈希、无序集合、有序集合](#2. 字符串、列表、哈希、无序集合、有序集合)
- [3. transaction、pipeline、watch](#3. transaction、pipeline、watch)
- [六. redis-plus-plus 使用样例](#六. redis-plus-plus 使用样例)
-
- [1. 目录结构](#1. 目录结构)
- [2. 项目构建](#2. 项目构建)
- [3. 代码实现](#3. 代码实现)
-
- [3.1 字符串、列表、哈希、无序集合、有序集合操作](#3.1 字符串、列表、哈希、无序集合、有序集合操作)
- [3.2 transaction、pipeline、watch 操作](#3.2 transaction、pipeline、watch 操作)
- [七. redis-plus-plus 封装](#七. redis-plus-plus 封装)
-
- [1. 设计与实现](#1. 设计与实现)
-
- [1.1 目录结构](#1.1 目录结构)
- [1.2 代码实现](#1.2 代码实现)
- [2. 使用样例](#2. 使用样例)
-
- [1.1 目录结构](#1.1 目录结构)
- [1.2 项目构建](#1.2 项目构建)
- [1.3 代码实现](#1.3 代码实现)
一. Redis 介绍
- Redis 是一种高性能的内存键值数据库,常用于缓存、消息队列和实时数据处理等场景。它将数据主要存储在内存中,读写速度非常快,同时支持将数据持久化到磁盘,保证数据在重启后的安全性。
- Redis 提供了丰富的数据结构,如字符串、哈希、列表、集合、有序集合等,能够满足多种业务需求。它支持主从复制、哨兵机制和集群模式,具备良好的高可用性和横向扩展能力。凭借简单易用的命令、优秀的性能和稳定性,Redis 被广泛应用于互联网系统中,如用户会话管理、排行榜、计数器和分布式锁等,是现代分布式架构中的重要基础组件。
Redis 的主要特性:
- 高性能:数据主要存储在内存中,读写操作通常在微秒级完成,非常适合高并发、低延迟的业务场景。
- 支持多种数据结构:包括字符串、哈希、列表、集合和有序集合等,能够直接在服务端完成复杂的数据操作,减少应用层逻辑负担。
- 支持数据持久化:提供 RDB 和 AOF 两种方式,在保证高性能的同时,能够在系统重启后恢复数据。
- 高可用与扩展能力:支持主从复制、哨兵模式和集群模式,满足分布式系统的需求。
- 功能丰富且易用:支持事务、发布订阅、Lua 脚本等特性,被广泛应用于缓存、消息队列、排行榜和分布式锁等场景。
二. Redis 安装
bash
# 安装 Redis 服务端
sudo apt install redis -y
# 安装 Redis 客户端工具
sudo apt install redis-tools
# 启动 Redis 服务
service redis-server start
# 停止 Redis 服务
service redis-server stop
# 重启 Redis 服务
service redis-server restart修改 /etc/redis/redis.conf 支持远程连接。
- 修改 bind 127.0.0.1 为 bind 0.0.0.0
- 修改 protected-mode yes 为 protected-mode no
由于在环境搭建中已经安装了 Redis 服务器,并且启动了,我们不需要再次安装:
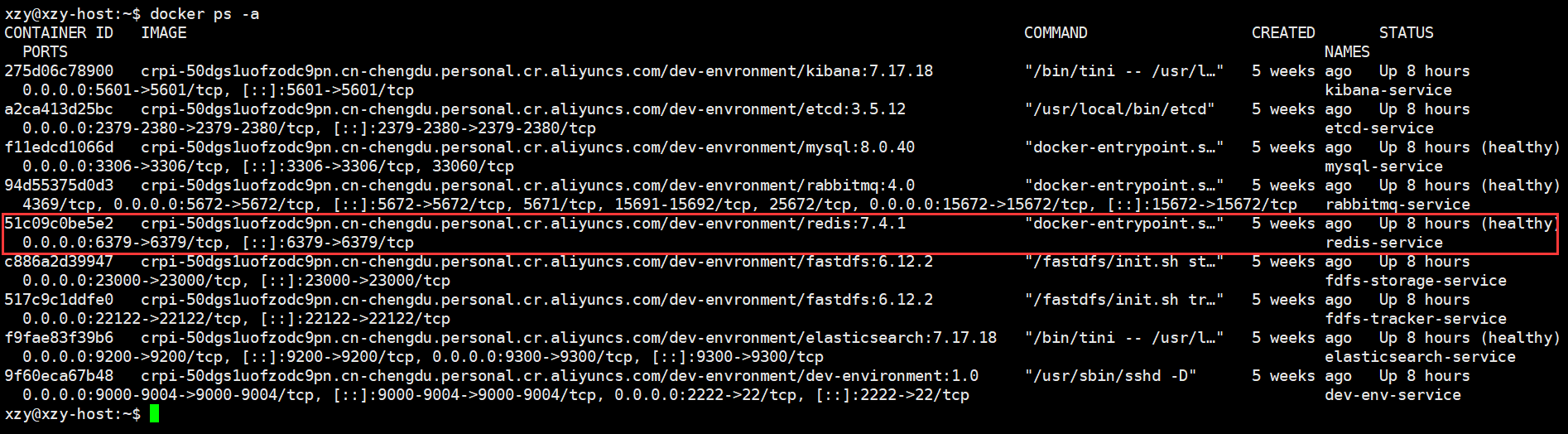
但是需要手动安装 redis-tools 客户端:
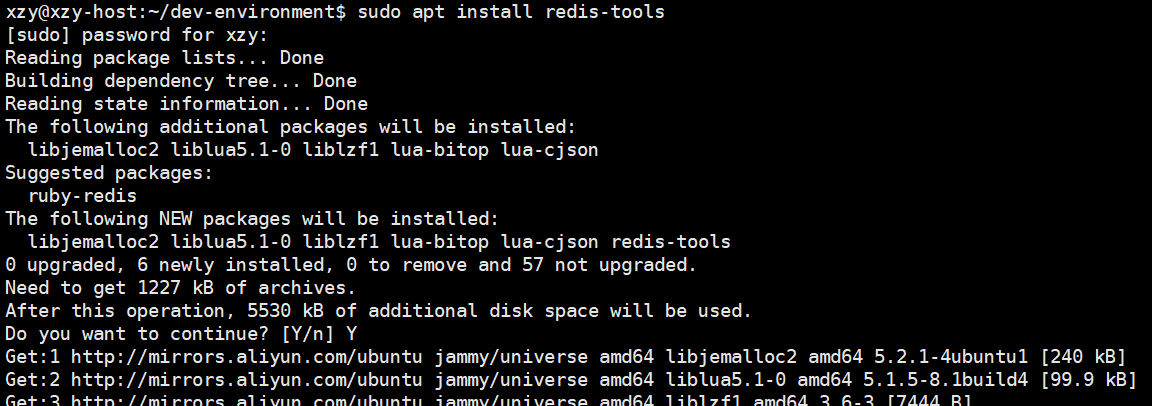
使用客户端连接 Reids 服务器:
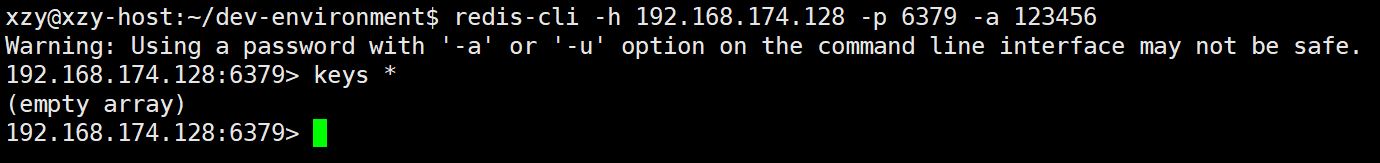
容器内运行 redis 服务器,可根据需要在配置文件 (./redis/redis.conf 该配置文件所在目录与 docker-compsoe.yml 同级) 中设置 redis 的 default 用户默认密码 (在文件1037行)
三. redis-plus-plus SDK 介绍
- redis-plus-plus (又称 redis++) 是一个基于 C++ 的 Redis 客户端库,对 Redis 官方 C 客户端 hiredis 进行了现代 C++ 风格的封装。它遵循 C++11 及以上标准,提供类型安全、接口清晰的 API,使开发者能够更加方便地在 C++ 项目中使用 Redis。
- redis-plus-plus 支持字符串、哈希、列表、集合、有序集合等 Redis 常用数据结构,并对事务、流水线 (Pipeline)、发布订阅、Lua 脚本等高级功能提供良好支持。同时,该库内置连接池机制,支持同步和异步操作,能够适应高并发场景。
- 凭借良好的性能、易用性和完善的文档,redis-plus-plus 被广泛应用于高性能服务器和分布式系统中,是 C++ 访问 Redis 的主流选择之一。
四. redis-plus-plus SDK 安装
Github 地址:https://github.com/sewenew/redis-plus-plus
bash
# 安装 hiredis 开发库(依赖)
apt install libhiredis-dev
# 克隆 redis-plus-plus 源码
git clone https://github.com/sewenew/redis-plus-plus.git
# 进入源码目录
cd redis-plus-plus
# 创建并进入构建目录
mkdir build && cd build
# 生成构建文件
cmake ..
# 编译并安装
make && sudo make install 由于在环境搭建中已经安装了 redis-plus-plus,这里不需要再次安装了。
五. redis-plus-plus 类与接口
1. 异常、客户端配置、常规操作
异常类与接口:
cpp
namespace sw {
namespace redis {
// 错误类型枚举
enum ReplyErrorType {
ERR, // 错误类型
MOVED, // 迁移类型
ASK // 询问类型
};
// 错误类
class Error : public std::exception {
public:
explicit Error(const std::string &msg) : _msg(msg) {}
Error(const Error &) = default;
Error& operator=(const Error &) = default;
Error(Error &&) = default;
Error& operator=(Error &&) = default;
virtual ~Error() override = default;
// 获取错误信息
virtual const char* what() const noexcept override {
return _msg.data();
}
private:
std::string _msg;
};
// 监控键被修改错误类
class WatchError : public Error {
public:
explicit WatchError() : Error("Watched key has been modified") {}
WatchError(const WatchError &) = default;
WatchError& operator=(const WatchError &) = default;
WatchError(WatchError &&) = default;
WatchError& operator=(WatchError &&) = default;
virtual ~WatchError() override = default;
};
}
}客户端配置类与接口:
cpp
namespace sw {
namespace redis {
// 连接选项结构体
struct ConnectionOptions {
std::string host; // 主机地址
int port = 6379; // 端口号
std::string path; // 路径
std::string user = "default"; // 用户
std::string password; // 密码
int db = 0; // 数据库索引
bool keep_alive = false; // 是否保持长连接
}
// 连接池选项结构体
struct ConnectionPoolOptions {
std::size_t size = 1; // 连接池大小
std::chrono::milliseconds wait_timeout{0}; // 等待超时时间
std::chrono::milliseconds connection_lifetime{0}; // 连接生命周期
std::chrono::milliseconds connection_idle_time{0}; // 连接空闲时间
}
// Redis 客户端类
class Redis {
public:
explicit Redis(const std::string &uri)
explicit Redis(const ConnectionOptions &connection_opts, const ConnectionPoolOptions &pool_opts = {})
};
}
}客户端常规操作接口:
cpp
namespace sw {
namespace redis {
class Redis {
// 删除所有库中的数据
void flushall(bool async = false);
// 删除当前库中所有数据
void flushdb(bool async = false);
// 删除指定键值对
long long del(const StringView &key);
// 删除多个键值对
template <typename Input>
long long del(Input first, Input last);
// 判断指定键值对是否存在
long long exists(const StringView &key);
// 判断多个键值对是否存在
template <typename Input>
long long exists(Input first, Input last);
// 为key设置一个过期时间
bool expire(const StringView &key, const std::chrono::seconds &timeout);
// 移除key的过期时间,将key设置为永久有效
bool persist(const StringView &key);
// 对指定数字字段进行数值增加
long long incrby(const StringView &key, long long increment);
// 对指定数字字段进行数值减少
long long decrby(const StringView &key, long long decrement);
}
}
}2. 字符串、列表、哈希、无序集合、有序集合
字符串操作接口:
cpp
namespace sw {
namespace redis {
class Redis {
// 获取string键值对
OptionalString get(const StringView &key);
// 新增string键值对,且设置过期时间-毫秒,0表示不设置超时
// 标志位:EXIST/NOT_EXIST/ALWAYS 表示什么情况新增、更新键值对
bool set(const StringView &key, const StringView &val,
const std::chrono::milliseconds &ttl = std::chrono::milliseconds(0),
UpdateType type = UpdateType::ALWAYS);
// 更新string键值对,并返回旧值
OptionalString getset(const StringView &key, const StringView &val);
// 批量获取string键值对
template <typename Input, typename Output>
void mget(Input first, Input last, Output output);
// 批量新增string键值对
template <typename Input>
void mset(Input first, Input last);
}
}
}列表操作接口:
cpp
namespace sw {
namespace redis {
class Redis {
// 往右新增string键值对
long long rpush(const StringView &key, const StringView &val);
// 往左新增string键值对
long long lpush(const StringView &key, const StringView &val);
// 获取元素数量
long long llen(const StringView &key);
// 往右新增多个string键值对
template <typename Input>
long long rpush(const StringView &key, Input first, Input last);
// 往左新增多个string键值对
template <typename Input>
long long lpush(const StringView &key, Input first, Input last);
// 获取指定索引位置的string键值对
OptionalString lindex(const StringView &key, long long index);
// 从左边弹出一个string键值对
OptionalString lpop(const StringView &key);
// 从右边弹出一个string键值对
OptionalString rpop(const StringView &key);
// 获取指定范围的string键值对
template <typename Output>
void lrange(const StringView &key, long long start, long long stop, Output output);
}
}
}哈希操作接口:
cpp
namespace sw {
namespace redis {
class Redis {
// 判断哈希表中是否存在指定字段
bool hexists(const StringView &key, const StringView &field);
// 删除哈希表中指定字段
long long hdel(const StringView &key, const StringView &field);
// 批量删除哈希表中指定字段
template <typename Input>
long long hdel(const StringView &key, Input first, Input last);
// 获取哈希表中所有字段和值
template <typename Output>
void hgetall(const StringView &key, Output output);
// 获取哈希表中指定字段的值
OptionalString hget(const StringView &key, const StringView &field);
// 批量获取哈希表中指定字段的值
template <typename Input, typename Output>
void hmget(const StringView &key, Input first, Input last, Output output);
// 批量设置哈希表中指定字段的值
template <typename Input>
void hmset(const StringView &key, Input first, Input last);
// 设置哈希表中指定字段的值
long long hset(const StringView &key, const StringView &field, const StringView &val);
// 哈希表中指定字段的值增加指定增量
long long hincrby(const StringView &key, const StringView &field, long long increment);
};
}
}无序集合操作接口:
cpp
namespace sw {
namespace redis {
class Redis {
// 添加集合元素
long long sadd(const StringView &key, const StringView &member);
// 批量添加集合元素
template <typename Input>
long long sadd(const StringView &key, Input first, Input last);
// 获取集合元素数量
long long scard(const StringView &key);
// 判断集合元素是否存在
bool sismember(const StringView &key, const StringView &member);
// 获取集合所有元素
template <typename Output>
void smembers(const StringView &key, Output output);
};
}
}有序集合操作接口:
cpp
namespace sw {
namespace redis {
class Redis {
// 添加有序集合元素
long long zadd(const StringView &key, const StringView &member,
double score, UpdateType type = UpdateType::ALWAYS, bool changed = false);
// 批量添加有序集合元素
template <typename Input>
long long zadd(const StringView &key, Input first, Input last,
UpdateType type = UpdateType::ALWAYS, bool changed = false);
// 获取有序集合元素数量
long long zcard(const StringView &key);
// 有序集合元素分数增加
double zincrby(const StringView &key, double increment, const StringView &member);
// 获取有序集合排名区间元素
template <typename Output>
void zrange(const StringView &key, long long start, long long stop, Output output);
// 获取有序集合分数区间元素
template <typename Interval, typename Output>
void zrangebyscore(const StringView &key, const Interval &interval, Output output);
// 获取有序集合排名区间元素(带偏移量和数量限制)
template <typename Interval, typename Output>
void zrangebyscore(const StringView &key, const Interval &interval,
const LimitOptions &opts, Output output);
// 获取有序集合元素排名
OptionalLongLong zrank(const StringView &key, const StringView &member);
// 获取有序集合字典序区间元素
template <typename Interval, typename Output>
void zrangebylex(const StringView &key, const Interval &interval, Output output);
// 获取有序集合字典序区间元素(带偏移量和数量限制)
template <typename Interval, typename Output>
void zrangebylex(const StringView &key, const Interval &interval,
const LimitOptions &opts, Output output);
// 获取有序集合排名区间元素(降序)
template <typename Output>
void zrevrange(const StringView &key, long long start, long long stop, Output output);
// 获取有序集合分数区间元素(降序)
template <typename Interval, typename Output>
void zrevrangebyscore(const StringView &key, const Interval &interval, Output output);
// 获取有序集合排名区间元素(降序,带偏移量和数量限制)
template <typename Interval, typename Output>
void zrevrangebyscore(const StringView &key, const Interval &interval,
const LimitOptions &opts, Output output);
// 获取有序集合元素排名(降序)
OptionalLongLong zrevrank(const StringView &key, const StringView &member);
// 获取有序集合字典序区间元素(降序)
template <typename Interval, typename Output>
void zrevrangebylex(const StringView &key, const Interval &interval, Output output);
// 获取有序集合字典序区间元素(降序,带偏移量和数量限制)
template <typename Interval, typename Output>
void zrevrangebylex(const StringView &key, const Interval &interval,
const LimitOptions &opts, Output output);
// 获取有序集合元素分数
OptionalDouble zscore(const StringView &key, const StringView &member);
// 有序集合元素扫描
template <typename Output>
Cursor zscan(const StringView &key, Cursor cursor, const StringView &pattern,
long long count, Output output);
// 删除有序集合元素
long long zrem(const StringView &key, const StringView &member);
// 弹出有序集合最大分数元素
Optional<std::pair<std::string, double>> zpopmax(const StringView &key);
// 弹出有序集合最小分数元素
Optional<std::pair<std::string, double>> zpopmin(const StringView &key);
// 删除有序集合分数区间元素
template <typename Interval>
long long zremrangebyscore(const StringView &key, const Interval &interval);
// 删除有序集合排名区间元素
long long zremrangebyrank(const StringView &key, long long start, long long stop);
// 删除有序集合字典序区间元素
template <typename Interval>
long long zremrangebylex(const StringView &key, const Interval &interval);
};
}
}3. transaction、pipeline、watch
- 默认情况下,创建一个 transaction、pipeline 对象是比较昂贵的,因为会新建连接实例化对象,建议尽可能重复使用。
- 因此为了减低使用成本,建议使用连接池,并且连接池中最大的连接数量必须大于1,创建transaction、pipeline 对象的时候,设置不创建新连接,而是从连接池中获取。
- transaction、pipeline 对象的常规数据操作,无法直接获取到结果,必须执行 .exec() 来获取结果。它们的使用方式基本一致,但是使用目标不同。
- transaction 为了能够让多个操作成为一个原子操作来执行;pipeline 为了能够实现网络通信的管线话传输来提高效率。
注意:transaction、pipeline 对象的操作不是线程安全的,析构时会将连接返回给连接池。
cpp
namespace sw {
namespace redis {
// Redis 客户端操作类
class Redis {
// 1.从连接池获取连接,创建Transaction对象
// pipe: 若为 true 表示开启管道模式,所有操作都在一个事务中执行,若为 false 表示不开启管道模式
// new_connection: 若为 true 表示新创建连接,若为 false 表示从连接池获取连接
Transaction transaction(bool piped = false, bool new_connection = true);
// 2.从连接池获取连接,创建Pipeline对象
// new_connection: 若为 true 表示新创建连接,若为 false 表示从连接池获取连接
Pipeline pipeline(bool new_connection = true);
};
using Transaction = QueuedRedis<TransactionImpl>;
using Pipeline = QueuedRedis<PipelineImpl>;
// 队列式Redis操作类
template <typename Impl>
class QueuedRedis {
// 返回底层的 Redis 客户端对象
Redis redis();
// 执行队列中的所有操作,返回结果队列
QueuedReplies exec();
// 清空队列中的所有操作
void discard();
// 3.清空数据库中的所有键值对
QueuedRedis& flushall(bool async = false);
// 4.删除指定键值对
QueuedRedis& del(const StringView &key);
// 5.检查指定键是否存在
QueuedRedis& exists(const StringView &key);
// 6.设置键的过期时间
QueuedRedis& expire(const StringView &key, const std::chrono::seconds &timeout);
// 7.获取指定键的值
QueuedRedis& get(const StringView &key);
// 8.获取指定键的子字符串
QueuedRedis& getrange(const StringView &key, long long start, long long end);
// 9.设置指定键的值,并返回旧值
QueuedRedis& getset(const StringView &key, const StringView &val);
// 10.批量获取多个键的值
template <typename Input>
QueuedRedis& mget(Input first, Input last);
//......
// 11.检查哈希表中指定字段是否存在
QueuedRedis& hexists(const StringView &key, const StringView &field);
// 12.获取哈希表中指定字段的值
QueuedRedis& hget(const StringView &key, const StringView &field);
// 13.获取哈希表中所有字段和值
QueuedRedis& hgetall(const StringView &key);
// 14.获取列表中指定范围的元素
QueuedRedis& lrange(const StringView &key, long long start, long long stop);
};
// 队列式Redis操作结果类
class QueuedReplies {
// 返回结果队列的大小
std::size_t size();
// 获取指定索引位置的操作结果
template <typename Result>
auto get(std::size_t idx) -> typename std::enable_if<!std::is_same<Result, bool>::value, Result>::type
// 将指定索引位置的操作结果写入输出迭代器
template <typename Output>
void get(std::size_t idx, Output output);
// 返回指定索引位置的原始 redisReply 对象
redisReply& get(std::size_t idx);
};
}
}transaction 事务操作主要目的是,将多个操作当做一个原子操作执行。但是事务操作虽然是原子操作,但不代表不会出现错误,因为 redis 事务操作中,无法感知数据变化,有可能数据被修改了会导致一些错误。
因此,事务操作之前,最好对 key 进行监控,若 key 的 val 发生改变,则事务抛出异常 (在异常处理中,可以重新针对新的数据做出新的操作),因此 transaction 通常是和 watch 一起搭配使用的。也就是说只要在你提交事务前它被别人改过,当前事务就会失败。
cpp
class sw {
class redis {
class Redis {
// 监控一个key
void watch(const StringView &key);
// 监控多个key
template <typename Input>
void watch(Input first, Input last);
}
}
}六. redis-plus-plus 使用样例
1. 目录结构
bash
example/
|-- redis
| |-- complement.cc
| |-- hash.cc
| |-- list.cc
| |-- makefile
| |-- pipeline.cc
| |-- set.cc
| |-- string.cc
| |-- transaction.cc
| |-- watch.cc
| |-- zset.cc2. 项目构建
bash
# makefile
all: string list hash set zset complement pipeline transaction watch
string: string.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++17 -lhiredis -lredis++ -lpthread
list: list.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++17 -lhiredis -lredis++ -lpthread
hash: hash.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++17 -lhiredis -lredis++ -lpthread
set: set.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++17 -lhiredis -lredis++ -lpthread
zset: zset.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++17 -lhiredis -lredis++ -lpthread
complement: complement.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++17 -lhiredis -lredis++ -lpthread
pipeline: pipeline.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++17 -lhiredis -lredis++ -lpthread
transaction: transaction.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++17 -lhiredis -lredis++ -lpthread
watch: watch.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++17 -lhiredis -lredis++ -lpthread
.PHONY: clean
clean:
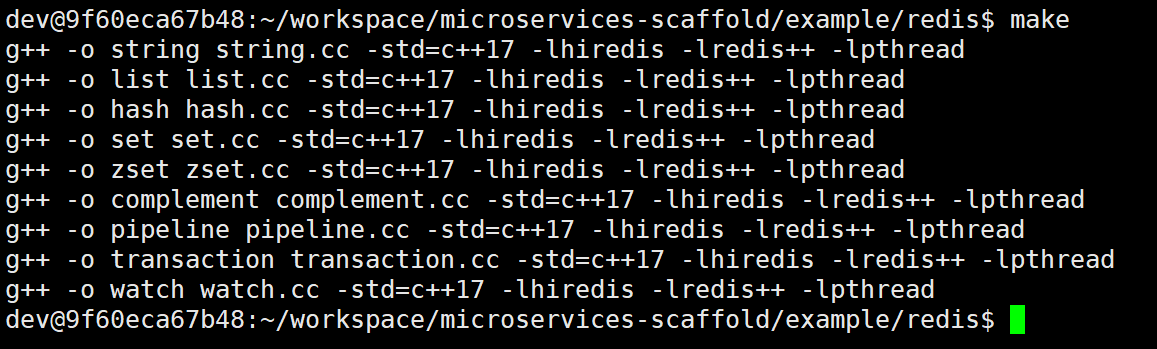
rm -f string list hash set zset complement pipeline transaction watch编译生成可执行程序:
3. 代码实现
3.1 字符串、列表、哈希、无序集合、有序集合操作
cpp
// string.cc
#include <iostream>
#include <chrono>
#include <sw/redis++/redis.h>
int main()
{
// 创建连接选项、连接池选项配置对象、并实例化 Redis 客户端对象
sw::redis::ConnectionOptions conn_opts = {
.host = "192.168.174.128",
.port = 6379,
.password = "123456"
};
sw::redis::ConnectionPoolOptions pool_opts = {
.size = 10,
.connection_idle_time = std::chrono::milliseconds(600)
};
sw::redis::Redis redis(conn_opts, pool_opts);
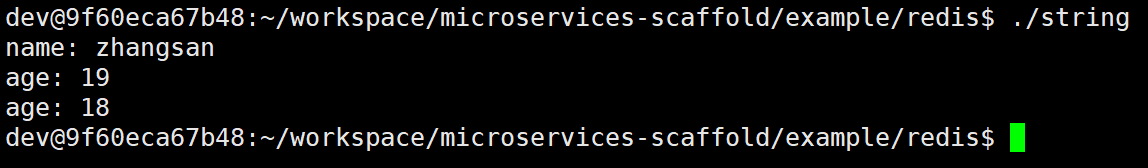
// 1.添加一个键值对
redis.set("name", "zhangsan");
// 2.获取一个键值对
sw::redis::OptionalString val = redis.get("name");
std::cout << "name: " << *val << std::endl;
// 3.删除键值对
redis.del("name");
// 4.对键值对中的数据进行自增/自减
redis.set("age", "18");
redis.incrby("age", 1);
std::cout << "age: " << *redis.get("age") << std::endl;
redis.decrby("age", 1);
std::cout << "age: " << *redis.get("age") << std::endl;
// 5.删除字符串
redis.del("age");
return 0;
}
cpp
// list.cc
#include <iostream>
#include <chrono>
#include <sw/redis++/redis.h>
int main()
{
// 创建连接选项、连接池选项配置对象、并实例化 Redis 客户端对象
sw::redis::ConnectionOptions conn_opts = {
.host = "192.168.174.128",
.port = 6379,
.password = "123456"
};
sw::redis::ConnectionPoolOptions pool_opts = {
.size = 10,
.connection_idle_time = std::chrono::milliseconds(600)
};
sw::redis::Redis redis(conn_opts, pool_opts);
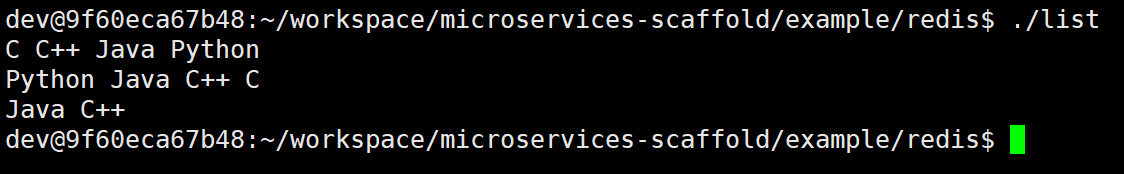
// 1.从左侧插入数据
redis.lpush("skills", "C");
std::vector<std::string> arr = {"C++", "Java", "Python"};
redis.lpush("skills", arr.begin(), arr.end());
// 2.从右侧获取数据
int len = redis.llen("skills");
for (int i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
// 3.获取指定下标的数据
sw::redis::OptionalString val = redis.lindex("skills", i);
std::cout << *val << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
// 4.获取所有的数据
std::vector<std::string> skills;
redis.lrange("skills", 0, -1, std::back_inserter(skills));
for (auto& val : skills) {
std::cout << val << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
// 5.删除左右两侧的数据
redis.lpop("skills");
redis.rpop("skills");
// 6.输出最终的数据
skills.clear();
redis.lrange("skills", 0, -1, std::back_inserter(skills));
for (auto& val : skills) {
std::cout << val << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
// 7.删除列表
redis.del("skills");
return 0;
}
cpp
// hash.cc
#include <iostream>
#include <chrono>
#include <sw/redis++/redis.h>
int main()
{
// 创建连接选项、连接池选项配置对象、并实例化 Redis 客户端对象
sw::redis::ConnectionOptions conn_opts = {
.host = "192.168.174.128",
.port = 6379,
.password = "123456"
};
sw::redis::ConnectionPoolOptions pool_opts = {
.size = 10,
.connection_idle_time = std::chrono::milliseconds(600)
};
sw::redis::Redis redis(conn_opts, pool_opts);
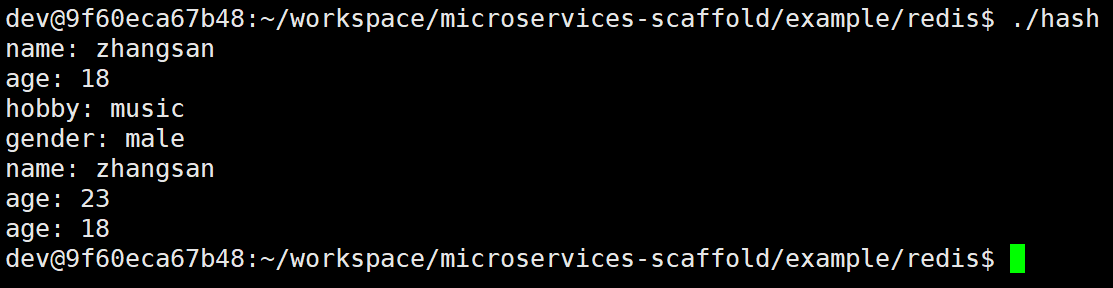
// 1.插入一个哈希键值对
redis.hset("user", "name", "zhangsan");
// 2.批量插入哈希键值对
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> userinfo = {
{"age", "18"},
{"gender", "male"},
{"hobby", "music"}
};
redis.hmset("user", userinfo.begin(), userinfo.end());
// 3.获取一个哈希键值对
sw::redis::OptionalString val = redis.hget("user", "name");
std::cout << "name: " << *val << std::endl;
// 4.获取所有哈希键值对
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> results;
redis.hgetall("user", std::inserter(results, results.begin()));
for (auto& val : results) {
std::cout << val.first << ": " << val.second << std::endl;
}
// 5.对键值对中的值进行自增/自减
redis.hincrby("user", "age", 5);
std::cout << "age: " << *redis.hget("user", "age") << std::endl;
redis.hincrby("user", "age", -5);
std::cout << "age: " << *redis.hget("user", "age") << std::endl;
// 6.删除哈希
redis.del("user");
return 0;
}
cpp
// set.cc
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <chrono>
#include <sw/redis++/redis.h>
int main()
{
// 创建连接选项、连接池选项配置对象、并实例化 Redis 客户端对象
sw::redis::ConnectionOptions conn_opts = {
.host = "192.168.174.128",
.port = 6379,
.password = "123456"
};
sw::redis::ConnectionPoolOptions pool_opts = {
.size = 10,
.connection_idle_time = std::chrono::milliseconds(600)
};
sw::redis::Redis redis(conn_opts, pool_opts);
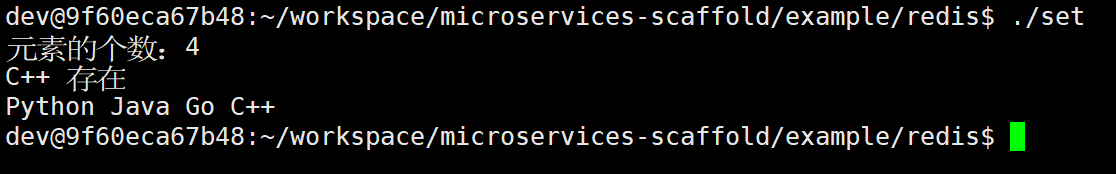
// 1.向集合中添加一个元素
redis.sadd("skills", "C++");
// 2.批量向集合中添加多个元素
std::unordered_set<std::string> skills = {"Python", "Java", "Go"};
redis.sadd("skills", skills.begin(), skills.end());
// 3.获取集合中元素的个数
long long size = redis.scard("skills");
std::cout << "元素的个数:" << size << std::endl;
// 4.判断集合中是否包含某个元素
bool ret = redis.sismember("skills", "C++");
if (ret) {
std::cout << "C++ 存在" << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "C++ 不存在" << std::endl;
}
// 5.获取集合中所有元素
std::unordered_set<std::string> skills2;
redis.smembers("skills", std::inserter(skills2, skills2.begin()));
for (auto& val : skills2) {
std::cout << val << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
// 6.删除无序集合
redis.del("skills");
return 0;
}
cpp
// zset.cc
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <chrono>
#include <sw/redis++/redis.h>
// 打印有序集合中的所有元素
void print(sw::redis::Redis& redis, const std::string& key) {
sw::redis::Cursor cursor = 0; // 定义游标变量
std::vector<std::pair<std::string, double>> memers; // 删除集合
while (true) {
// 扫描有序集合中的元素
cursor = redis.zscan(key, cursor, "*", 10, std::back_inserter(memers));
if (cursor == 0) {
break;
}
}
// 打印有序集合中的所有元素
for (auto& val : memers) {
std::cout << val.first << " " << val.second << std::endl;
}
}
int main()
{
// 创建连接选项、连接池选项配置对象、并实例化 Redis 客户端对象
sw::redis::ConnectionOptions conn_opts = {
.host = "192.168.174.128",
.port = 6379,
.password = "123456"
};
sw::redis::ConnectionPoolOptions pool_opts = {
.size = 10,
.connection_idle_time = std::chrono::milliseconds(600)
};
sw::redis::Redis redis(conn_opts, pool_opts);
// 1.向有序集合中添加元素:单个/批量添加
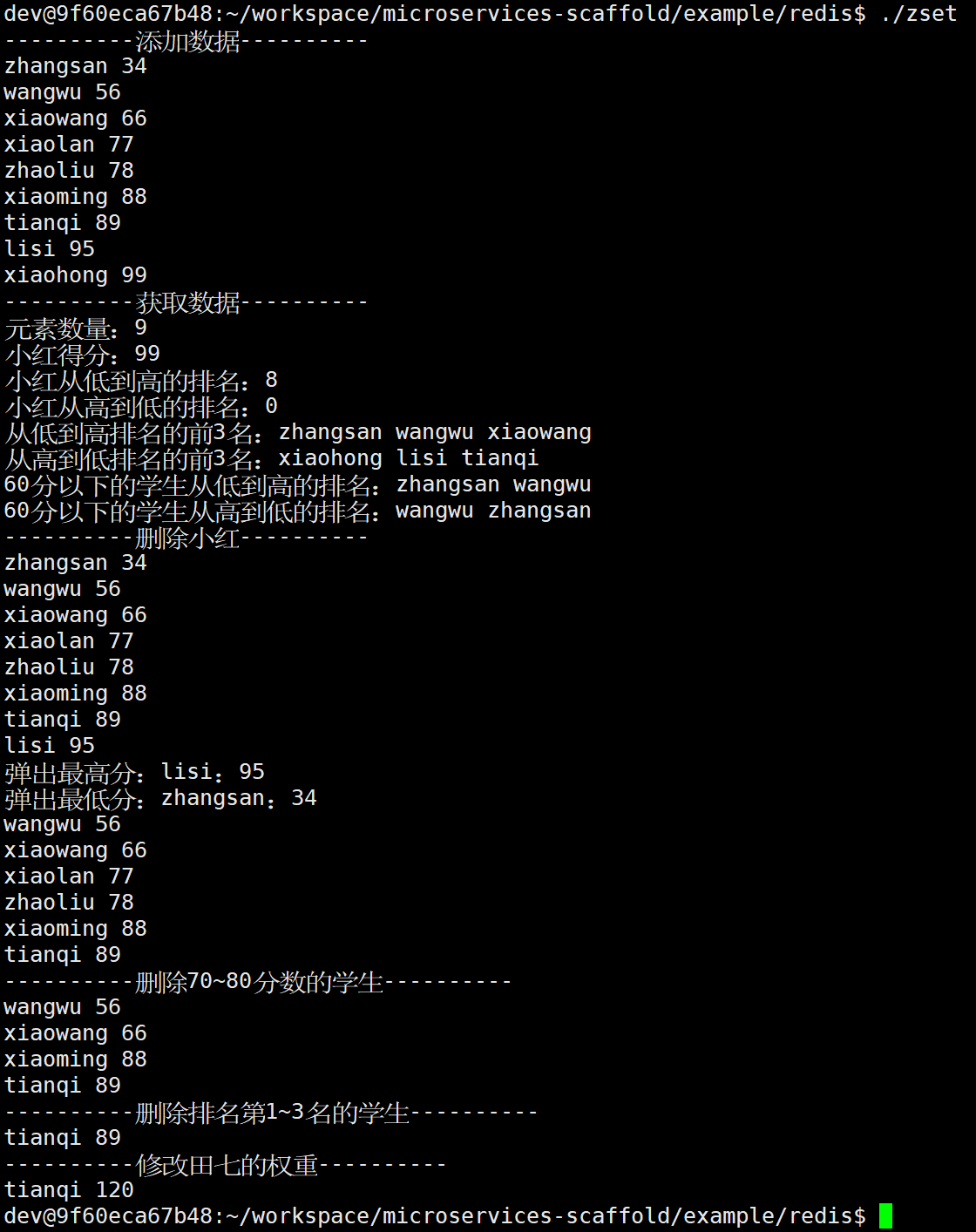
std::cout << "----------添加数据----------" << std::endl;
redis.zadd("score", "zhangsan", 34);
std::unordered_map<std::string, double> scores = {
{"lisi", 95},
{"wangwu", 56},
{"zhaoliu", 78},
{"tianqi", 89},
{"xiaohong", 99},
{"xiaoming", 88},
{"xiaolan", 77},
{"xiaowang", 66}
};
redis.zadd("score", scores.begin(), scores.end());
print(redis, "score");
// 2.获取集合中元素的数量
std::cout << "----------获取数据----------" << std::endl;
std::cout << "元素数量:" << redis.zcard("score") << std::endl;
// 3.获取指定元素权重得分
std::cout << "小红得分:" << *redis.zscore("score", "xiaohong") << std::endl;
// 4.获取指定元素的权重排名
std::cout << "小红从低到高的排名:" << *redis.zrank("score", "xiaohong") << std::endl;
std::cout << "小红从高到低的排名:" << *redis.zrevrank("score", "xiaohong") << std::endl;
// 5.获取集合数据
std::vector<std::string> results;
redis.zrange("score", 0, 2, std::back_inserter(results));
std::cout << "从低到高排名的前3名:";
for (auto& val : results) {
std::cout << val << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
results.clear();
redis.zrevrange("score", 0, 2, std::back_inserter(results));
std::cout << "从高到低排名的前3名:";
for (auto& val : results) {
std::cout << val << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
results.clear();
sw::redis::BoundedInterval<double> interval(0, 60, sw::redis::BoundType::RIGHT_OPEN);
redis.zrangebyscore("score", interval, std::back_inserter(results));
std::cout << "60分以下的学生从低到高的排名:";
for (auto& val : results) {
std::cout << val << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
results.clear();
redis.zrevrangebyscore("score", interval, std::back_inserter(results));
std::cout << "60分以下的学生从高到低的排名:";
for (auto& val : results) {
std::cout << val << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
// 6.删除指定元素
std::cout << "----------删除小红----------" << std::endl;
redis.zrem("score", "xiaohong");
print(redis, "score");
// 7.弹出一个最高分和最低分
sw::redis::Optional<std::pair<std::string, double>> max = redis.zpopmax("score");
if (max) {
std::cout << "弹出最高分:" << max->first << ":" << max->second << std::endl;
}
sw::redis::Optional<std::pair<std::string, double>> min = redis.zpopmin("score");
if (min) {
std::cout << "弹出最低分:" << min->first << ":" << min->second << std::endl;
}
print(redis, "score");
// 8.以权重得分删除指定区间的数据
std::cout << "----------删除70~80分数的学生----------" << std::endl;
sw::redis::BoundedInterval<double> interval1(70, 80, sw::redis::BoundType::OPEN);
redis.zremrangebyscore("score", interval1);
print(redis, "score");
// 9.以权重排名删除指定区间的数据
std::cout << "----------删除排名第1~3名的学生----------" << std::endl;
redis.zremrangebyrank("score", 0, 2);
print(redis, "score");
// 10.修改元素权重
std::cout << "----------修改田七的权重----------" << std::endl;
redis.zincrby("score", 31, "tianqi");
print(redis, "score");
// 11.删除有序集合
redis.del("score");
return 0;
}
cpp
// cpmplement.cc
#include <iostream>
#include <chrono>
#include <sw/redis++/redis.h>
int main()
{
// 创建连接选项、连接池选项配置对象、并实例化 Redis 客户端对象
sw::redis::ConnectionOptions conn_opts = {
.host = "192.168.174.128",
.port = 6379,
.password = "123456"
};
sw::redis::ConnectionPoolOptions pool_opts = {
.size = 10,
.connection_idle_time = std::chrono::milliseconds(600)
};
sw::redis::Redis redis(conn_opts, pool_opts);
// 1.字段生命周期控制(设置过期时间/移除过期时间)
redis.set("name", "zhangsan");
redis.expire("name", std::chrono::seconds(5));
redis.persist("name");
// 2.判断字段是否存在
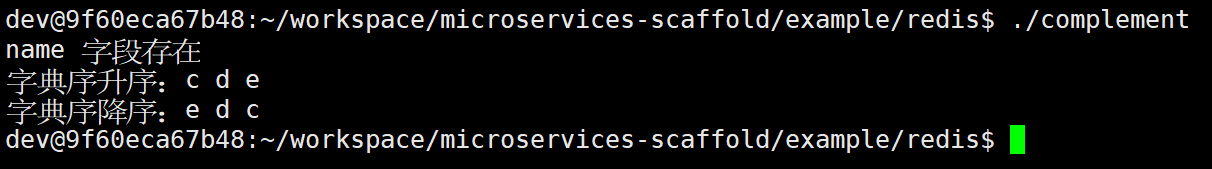
bool ret = redis.exists("name");
if (ret == true) {
std::cout << "name 字段存在" << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "name 字段不存在" << std::endl;
}
// 3.有序集合字典序操作
redis.zadd("score", "a", 100);
redis.zadd("score", "d", 100);
redis.zadd("score", "c", 100);
redis.zadd("score", "b", 100);
redis.zadd("score", "e", 100);
redis.zadd("score", "f", 100);
sw::redis::LimitOptions limit; // 偏移量为1,获取3个元素
limit.offset = 1;
limit.count = 3;
sw::redis::BoundedInterval<std::string> interval("b", "f", sw::redis::BoundType::CLOSED); // 包含b和f
std::vector<std::string> results;
std::cout << "字典序升序:";
redis.zrangebylex("score", interval, limit, std::back_inserter(results));
for (auto& val : results) {
std::cout << val << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
results.clear();
std::cout << "字典序降序:";
redis.zrevrangebylex("score", interval, limit, std::back_inserter(results));
for (auto& val : results) {
std::cout << val << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
// 4.库的清理操作
redis.flushall();
return 0;
}
3.2 transaction、pipeline、watch 操作
cpp
// transaction.cc
#include <iostream>
#include <chrono>
#include <sw/redis++/redis.h>
#include <sw/redis++/queued_redis.h>
int main()
{
// 创建连接选项、连接池选项配置对象、并实例化 Redis 客户端对象
sw::redis::ConnectionOptions conn_opts = {
.host = "192.168.174.128",
.port = 6379,
.password = "123456"
};
sw::redis::ConnectionPoolOptions pool_opts = {
.size = 10,
.connection_idle_time = std::chrono::milliseconds(600)
};
sw::redis::Redis redis(conn_opts, pool_opts);
{
// 1.从连接池获取连接,创建Transaction对象,需要注意的是,transaction对象的生命周期必须要在连接池的生命周期内
sw::redis::Transaction transaction = redis.transaction(false, false);
// 2.使用transaction对象进行批量操作
transaction.set("key1", "value1");
transaction.set("key2", "value2");
transaction.get("key1");
transaction.get("key2");
// 3.执行批量操作
sw::redis::QueuedReplies replies = transaction.exec();
// 4.处理批量操作的结果:需要根据操作的顺序来获取结果
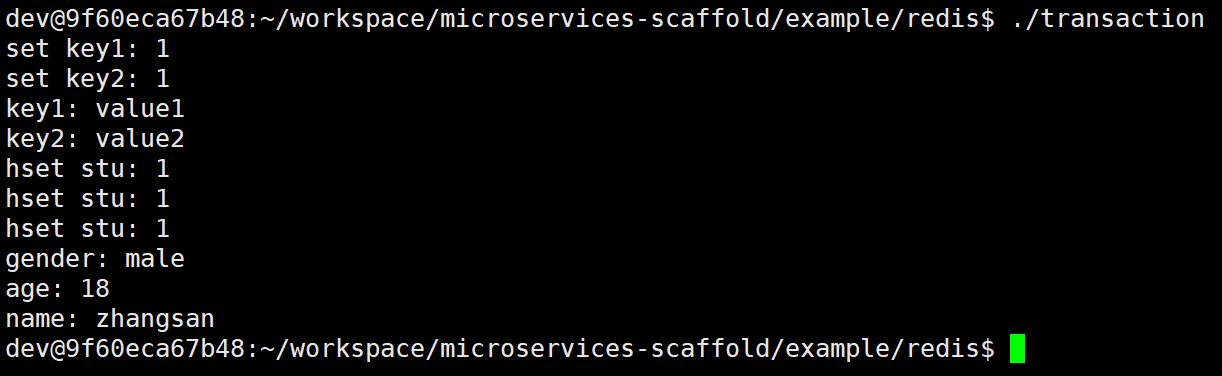
std::cout << "set key1: " << replies.get<bool>(0) << std::endl;
std::cout << "set key2: " << replies.get<bool>(1) << std::endl;
std::cout << "key1: " << replies.get<std::string>(2) << std::endl;
std::cout << "key2: " << replies.get<std::string>(3) << std::endl;
}
{
// 1.从连接池获取连接,创建Transaction对象
sw::redis::Transaction transaction = redis.transaction(false, false);
// 2.使用transaction对象进行批量操作
transaction.hset("stu", "name", "zhangsan");
transaction.hset("stu", "age", "18");
transaction.hset("stu", "gender", "male");
transaction.hgetall("stu");
// 3.执行批量操作
sw::redis::QueuedReplies replies = transaction.exec();
// 4.处理批量操作的结果:需要根据操作的顺序来获取结果
std::cout << "hset stu: " << replies.get<bool>(0) << std::endl;
std::cout << "hset stu: " << replies.get<bool>(1) << std::endl;
std::cout << "hset stu: " << replies.get<bool>(2) << std::endl;
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> stu;
replies.get(3, std::inserter(stu, stu.end()));
for (auto &val : stu) {
std::cout << val.first << ": " << val.second << std::endl;
}
}
// 删除key1键、key2键、stu哈希表
redis.del("key1");
redis.del("key2");
redis.del("stu");
return 0;
}
cpp
// pipeline.cc
#include <iostream>
#include <chrono>
#include <sw/redis++/redis.h>
#include <sw/redis++/queued_redis.h>
int main()
{
// 创建连接选项、连接池选项配置对象、并实例化 Redis 客户端对象
sw::redis::ConnectionOptions conn_opts = {
.host = "192.168.174.128",
.port = 6379,
.password = "123456"
};
sw::redis::ConnectionPoolOptions pool_opts = {
.size = 10,
.connection_idle_time = std::chrono::milliseconds(600)
};
sw::redis::Redis redis(conn_opts, pool_opts);
{
// 1.从连接池获取连接,创建Pipeline对象,需要注意的是,pipeline对象的生命周期必须要在连接池的生命周期内
sw::redis::Pipeline pipeline = redis.pipeline(false);
// 2.使用pipeline对象进行批量操作
pipeline.set("key1", "value1");
pipeline.set("key2", "value2");
pipeline.get("key1");
pipeline.get("key2");
// 3.执行批量操作
sw::redis::QueuedReplies replies = pipeline.exec();
// 4.处理批量操作的结果:需要根据操作的顺序来获取结果
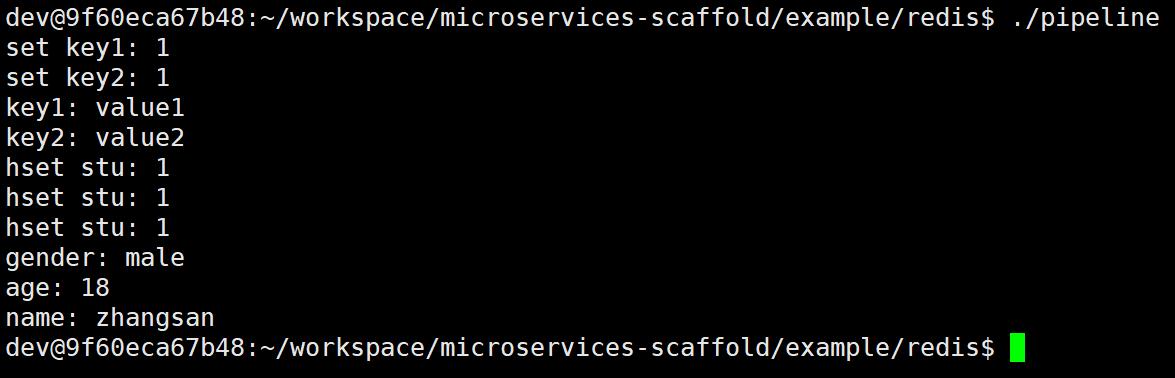
std::cout << "set key1: " << replies.get<bool>(0) << std::endl;
std::cout << "set key2: " << replies.get<bool>(1) << std::endl;
std::cout << "key1: " << replies.get<std::string>(2) << std::endl;
std::cout << "key2: " << replies.get<std::string>(3) << std::endl;
}
{
// 1.从连接池获取连接,创建Pipeline对象
sw::redis::Pipeline pipeline = redis.pipeline(false);
// 2.使用pipeline对象进行批量操作
pipeline.hset("stu", "name", "zhangsan");
pipeline.hset("stu", "age", "18");
pipeline.hset("stu", "gender", "male");
pipeline.hgetall("stu");
// 3.执行批量操作
sw::redis::QueuedReplies replies = pipeline.exec();
// 4.处理批量操作的结果:需要根据操作的顺序来获取结果
std::cout << "hset stu: " << replies.get<bool>(0) << std::endl;
std::cout << "hset stu: " << replies.get<bool>(1) << std::endl;
std::cout << "hset stu: " << replies.get<bool>(2) << std::endl;
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> stu;
replies.get(3, std::inserter(stu, stu.end()));
for (auto &val : stu) {
std::cout << val.first << ": " << val.second << std::endl;
}
}
// 删除key1键、key2键、stu哈希表
redis.del("key1");
redis.del("key2");
redis.del("stu");
return 0;
}
cpp
// watch.cc
#include <iostream>
#include <chrono>
#include <sw/redis++/redis.h>
#include <sw/redis++/queued_redis.h>
int main()
{
// 创建连接选项、连接池选项配置对象、并实例化 Redis 客户端对象
sw::redis::ConnectionOptions conn_opts = {
.host = "192.168.174.128",
.port = 6379,
.password = "123456"
};
sw::redis::ConnectionPoolOptions pool_opts = {
.size = 10,
.connection_idle_time = std::chrono::milliseconds(600)
};
sw::redis::Redis redis(conn_opts, pool_opts);
// 1.添加初始值
redis.set("score", "100");
{
// 2.通过redis对象创建transaction对象
sw::redis::Transaction transaction = redis.transaction(false, false);
// 3.通过transaction对象获取redis对象(redis对象与transaction对象共享连接)
sw::redis::Redis redis = transaction.redis();
while (true) {
try {
// 4.通过redis对象执行watch操作(transaction对象中没有watch操作、transaction操作无法获取结果,但是redis操作可以获取结果)
redis.watch("score");
bool ret = redis.exists("score");
if (!ret) {
break; // 不存在时跳出循环
}
// 5.通过transaction对象执行
transaction.incrby("score", 20);
transaction.exec();
break; // 事务执行成功时跳出循环
} catch (const sw::redis::WatchError &e) {
std::cout << "transaction watch error: " << e.what() << std::endl;
continue;
} catch (const sw::redis::Error &e) {
std::cout << "transaction exec error: " << e.what() << std::endl;
throw;
}
}
}
// 6.删除score键
redis.del("score");
return 0;
}
七. redis-plus-plus 封装
1. 设计与实现
只需要创建 redis 服务器配置结构即可。
1.1 目录结构
bash
source/
|-- redis.cc
|-- redis.h1.2 代码实现
cpp
// redis.h
#include <iostream>
#include <chrono>
#include <sw/redis++/redis.h>
#include <sw/redis++/queued_redis.h>
namespace xzyredis {
// Redis 客户端配置选项
struct redis_settings {
int db = 0; // 数据库编号
int port = 6379; // 端口号
std::string host; // 主机地址
std::string user = "default"; // 默认用户
std::string passwd; // 密码
size_t connection_pool_size = 3; // 连接池大小
};
// 创建 Redis 客户端对象工厂类
class RedisFactory {
public:
static std::shared_ptr<sw::redis::Redis> create(const redis_settings& settings);
};
}
cpp
// redis.cc
#include "redis.h"
namespace xzyredis {
// 创建 Redis 客户端对象
std::shared_ptr<sw::redis::Redis> RedisFactory::create(const redis_settings& settings) {
// 1.创建连接选项
sw::redis::ConnectionOptions conn_opts = {
.host = settings.host,
.port = settings.port,
.user = settings.user,
.password = settings.passwd,
.db = settings.db
};
// 2.连接池选项配置对象
sw::redis::ConnectionPoolOptions pool_opts = {
.size = settings.connection_pool_size
};
// 3.实例化 Redis 客户端对象
return std::make_shared<sw::redis::Redis>(conn_opts, pool_opts);
}
}2. 使用样例
1.1 目录结构
bash
test/
|-- redis
|-- makefile
|-- redis_test.cc1.2 项目构建
bash
# makefile
redis_test: redis_test.cc ../../source/redis.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++17 -lhiredis -lredis++ -pthread
.PHONY: clean
clean:
rm -f redis_test编译生成可执行程序:

1.3 代码实现
cpp
// redis_test.cc
#include "../../source/redis.h"
int main()
{
try {
// 1.创建 Redis 客户端配置选项
xzyredis::redis_settings settings = {
.host = "192.168.174.128",
.passwd = "123456",
.connection_pool_size = 3
};
// 2.创建 Redis 客户端对象
std::shared_ptr<sw::redis::Redis> redis = xzyredis::RedisFactory::create(settings);
{
// 3.创建事务对象
sw::redis::Transaction transaction = redis->transaction(false, false);
// 4.获取事务对象的 Redis 客户端对象
sw::redis::Redis redis = transaction.redis();
// 5.添加一个键值对
redis.set("name", "zhangsan");
// 6.获取一个键值对
sw::redis::OptionalString val = redis.get("name");
std::cout << "name: " << *val << std::endl;
// 7.删除所有键值对
redis.flushall();
}
}
catch (const sw::redis::Error& e) {
std::cerr << "Redis connection failed: " << e.what() << std::endl;
}
}