目录
[1 构造函数](#1 构造函数)
[1.1 空字符](#1.1 空字符)
[1.2 C语言字符串](#1.2 C语言字符串)
[1.3 取子串](#1.3 取子串)
[1.4 拷贝构造](#1.4 拷贝构造)
[1.5 取前n个字母](#1.5 取前n个字母)
[2 赋值运算符重载](#2 赋值运算符重载)
[2.1 string对象](#2.1 string对象)
[2.2 C语言字符串](#2.2 C语言字符串)
[3 遍历](#3 遍历)
[3.1 [下标]](#3.1 [下标])
[3.2 迭代器](#3.2 迭代器)
[3.2.2 反向遍历](#3.2.2 反向遍历)
[3.2.3 cosnt正向迭代器](#3.2.3 cosnt正向迭代器)
[3.2.4 const反向迭代器](#3.2.4 const反向迭代器)
[3.3 范围for](#3.3 范围for)
[3.3.1 auto关键字](#3.3.1 auto关键字)
[3.3.2 范围for](#3.3.2 范围for)
[4 常用接口](#4 常用接口)
[4.1 容量操作](#4.1 容量操作)
[4.1.1 size(推荐)](#4.1.1 size(推荐))
[4.1.2 length(不推荐)](#4.1.2 length(不推荐))
[4.1.3 max_size](#4.1.3 max_size)
[4.1.4 capacity](#4.1.4 capacity)
[4.1.5 empty](#4.1.5 empty)
[4.1.6 clear](#4.1.6 clear)
[4.1.7 shrink_to_fit](#4.1.7 shrink_to_fit)
[4.1.8 reserve](#4.1.8 reserve)
[4.1.9 resize](#4.1.9 resize)
[4.2 访问元素](#4.2 访问元素)
[4.2.1 [ ]](#4.2.1 [ ])
[4.2.2 at](#4.2.2 at)
[4.3 修改string](#4.3 修改string)
[4.3.1 +=](#4.3.1 +=)
[4.3.2 apppend](#4.3.2 apppend)
[4.3.3 push_back](#4.3.3 push_back)
[4.3.4 pop_back](#4.3.4 pop_back)
[4.3.5 insert](#4.3.5 insert)
[4.3.6 erase](#4.3.6 erase)
[4.3.7 assign](#4.3.7 assign)
[4.3.8 replace](#4.3.8 replace)
[4.4 string 操作](#4.4 string 操作)
[4.4.1 c_str](#4.4.1 c_str)
[4.4.2 data](#4.4.2 data)
[4.4.3 find](#4.4.3 find)
[4.4.4 substr](#4.4.4 substr)
[4.4.5 find_first_of](#4.4.5 find_first_of)
[4.4.6 find_first_not_of](#4.4.6 find_first_not_of)
[4.4.7 compare](#4.4.7 compare)
[4.5 全局函数](#4.5 全局函数)
[4.5.1 operator==](#4.5.1 operator==)
[4.5.2 getline](#4.5.2 getline)
[4.6 类型转换](#4.6 类型转换)
[4.6.1 string转数字](#4.6.1 string转数字)
[4.6.2 to_string](#4.6.2 to_string)
[5 题目](#5 题目)
[5.2 字符串中的第一个唯一字符](#5.2 字符串中的第一个唯一字符)
[5.3 验证回文串](#5.3 验证回文串)
[5.4 字符串相加](#5.4 字符串相加)
[5.5 最后一个单词的长度](#5.5 最后一个单词的长度)
1 构造函数
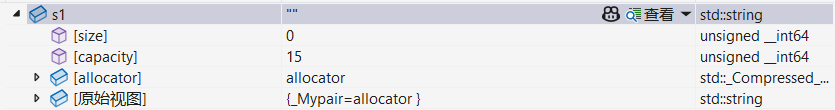
1.1 空字符
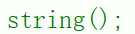

cpp
string s1;调试:
1.2 C语言字符串
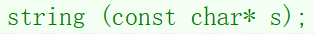

cpp
string s2("hello");调试:

1.3 取子串
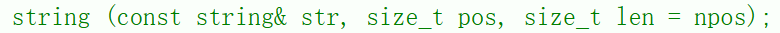

cpp
string s3(s2, 1, 1);调试:
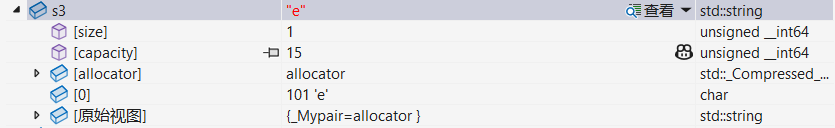
1.4 拷贝构造


cpp
string s4(s2);调试:

1.5 取前n个字母
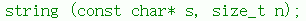

cpp
string s5("hello",1);调试:
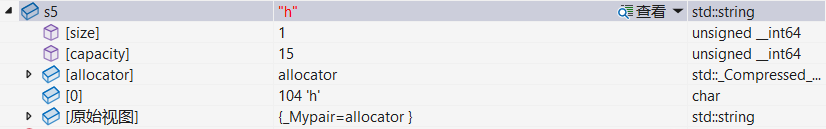
2 赋值运算符重载
2.1 string对象


cpp
string s1("hello");
string s2;
s2 = s1;调试:

2.2 C语言字符串
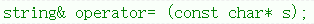

cpp
s2 = "nihao";调试:

3 遍历
3.1 [下标]
cpp
string s("hello");
for (int i = 0;i < s.size();++i) {
cout << s[i] ;
}
cout << endl;运行:
3.2 迭代器
通用的遍历方法。
3.2.1正向遍历
cpp
string::iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end()) {
cout << *it;
++it;
}
cout << endl;这里的 it 类似于一个指针。
运行:
3.2.2 反向遍历
cpp
string::reverse_iterator rit = s.begin();
while (rit != s.end()) {
cout << *it;
++it;
}
cout << endl;运行结果:
3.2.3 cosnt正向迭代器
遍历的对象不能改变。
cpp
string::const_iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end()) {
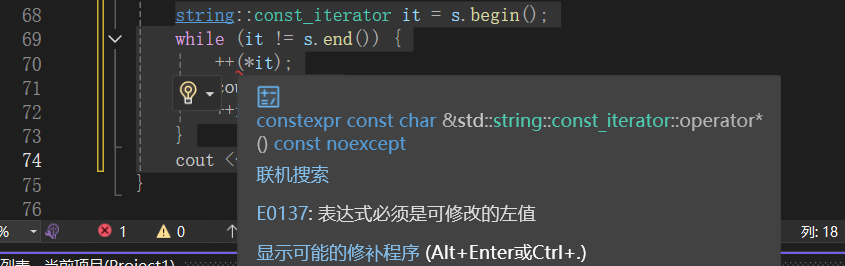
++(*it); // 报错
cout << *it;
++it;
}
cout << endl;编译器报错:
3.2.4 const反向迭代器
cpp
string::const_reverse_iterator rit = s.rbegin();
while (rit != s.rend()) {
//++(*rit);
cout << *rit;
++rit;
}
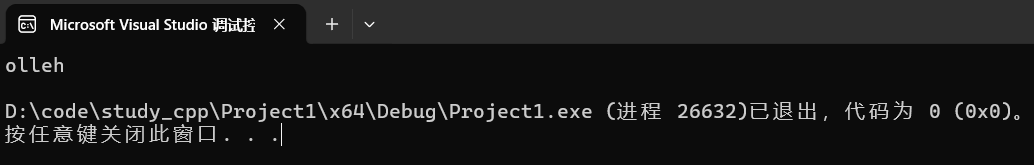
cout << endl;运行结果:
3.3 范围for
首先介绍一下auto关键字。
3.3.1 auto关键字
auto可根据右值推断出左值类型。
(1)替换长类型
假如根据右值,我们判断左值的类型很长,这时就能用auto代替那一串类型。
cpp
string::iterator it = s.begin();这是上面我们迭代器遍历的代码第一行,可以用auto替代string::iterator:
cpp
auto it = s.begin();(2)做参数or返回值(不推荐)
如果要用需要调设置:
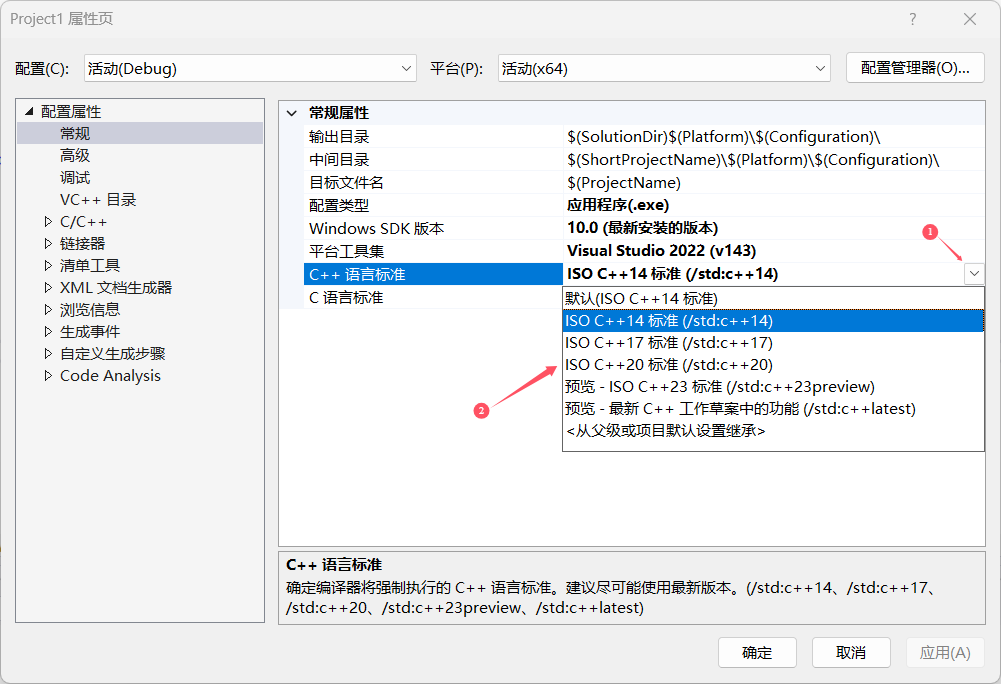
改到20标准。
cpp
auto test_auto(auto n) {
return n;
}我随便写一个函数,测试:
cpp
cout << test_auto(1) << endl;运行结果符合预期:
3.3.2 范围for
自动取容器数据依次赋值给对象,自动判断结束。
(1)可使用auto(推荐)
cpp
for (auto e:s) {
cout << e;
}
cout << endl;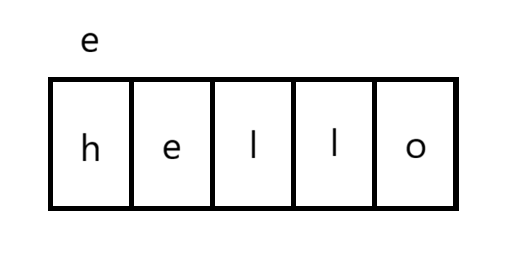
运行结果:
(2)也可不使用auto
cpp
for (char c:s) {
cout << c;
}
cout << endl;运行结果:
(3)如果需要修改容器里的元素
可使用引用,&需要显式编写。
cpp
for (auto& c : s) {
c = 'a';
}
for (auto c : s) {
cout << c;
}
cout << endl;运行结果:
(4)原理
基于迭代器(iterator)实现,底层完全由 begin() 和 end() 迭代器驱动。

4 常用接口
4.1 容量操作
4.1.1 size(推荐)
相对来说更通用。
cpp
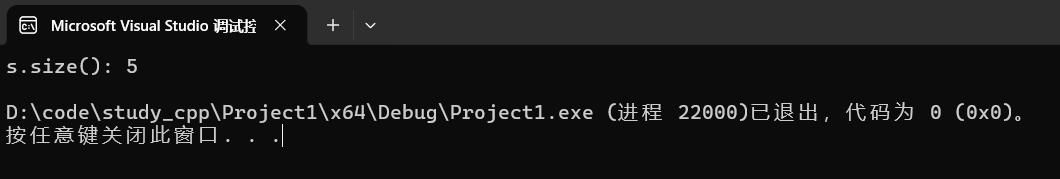
string s("hello");
cout << "s.size():" << s.size() << endl;运行结果:
4.1.2 length(不推荐)
cpp
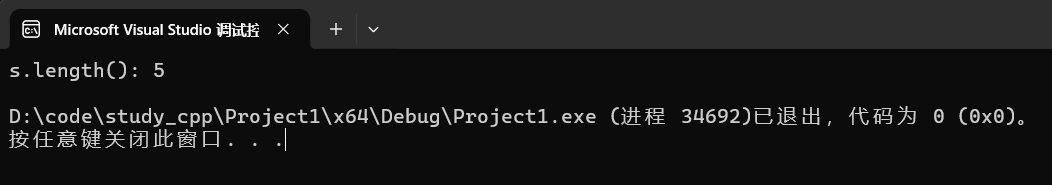
string s("hello");
cout << "s.length(): " << s.length() << endl;运行结果:
4.1.3 max_size
理想设计。

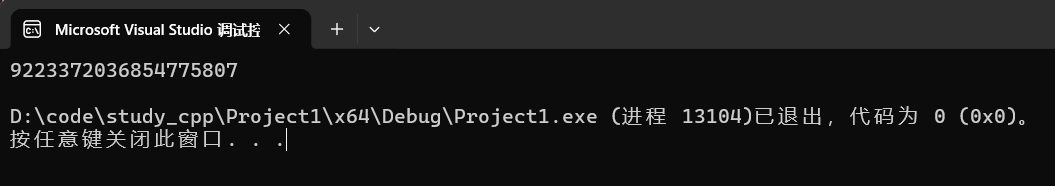
cpp
cout << s.max_size() << endl;运行结果:
4.1.4 capacity
返回容量(可存储有效字符)大小。
cpp
cout << s.capacity() << endl;运行结果:
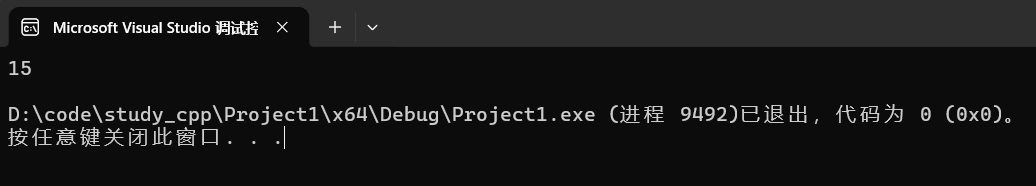
调试:

4.1.5 empty
判空。
cpp
string s1;
cout << s1.empty() << endl;运行结果:
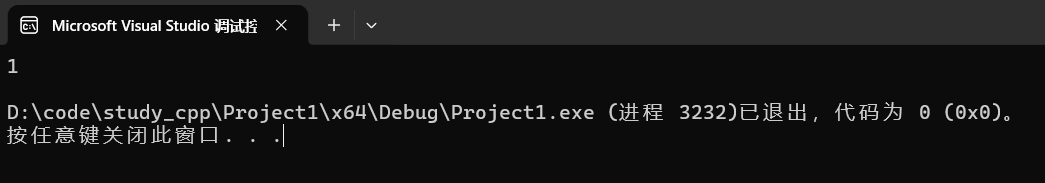
4.1.6 clear
清数据,容量空间不变。
cpp
string s("hello");
s.clear();调试:

4.1.7 shrink_to_fit
缩容,不常用。
4.1.8 reserve
申请空间,可扩容,可缩容。
(1)扩容
cpp
string s("hello");
s.reserve(20);调试:

至于为什么capacity不是20(至少有20),这里涉及到C++ 标准库中std::string的内存分配策略(特别是libc++ 和 libstdc++ 的实现差异)。
(2)缩容(不推荐)
不推荐,因为不同情况下不同平台实现不同。
4.1.9 resize
用法有三。
(1)插入数据
cpp
string s("hello");
s.resize(10,'~');
cout << s << endl;运行结果:
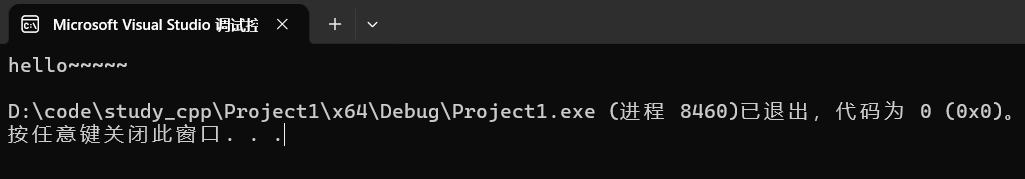
调试:

(2)扩容+插入数据
cpp
string s("hello");
s.resize(20,'~');
cout << s << endl;运行结果:
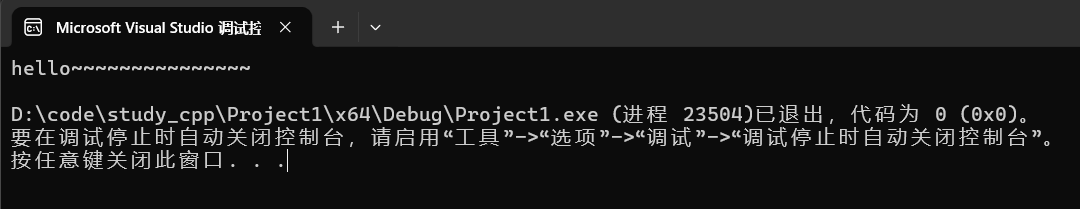
调试:

(3)删除数据
cpp
string s("hello");
s.resize(4);调试:

4.2 访问元素
4.2.1 [ ]
我们观察越界访问:
cpp
string s("hello");
cout << s[15] << endl;运行:
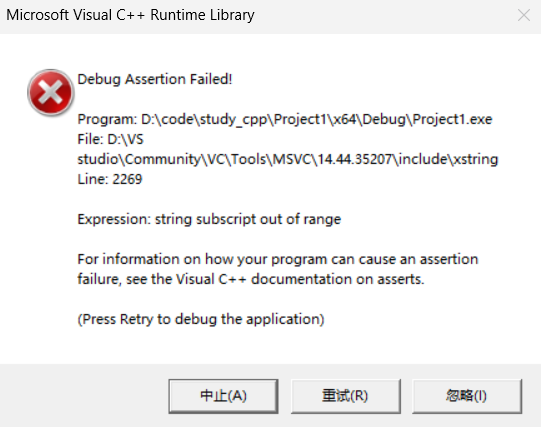
可以看到越界,assert报错。
4.2.2 at
同样观察越界访问:
cpp
cout << s.at(15) << endl;运行:
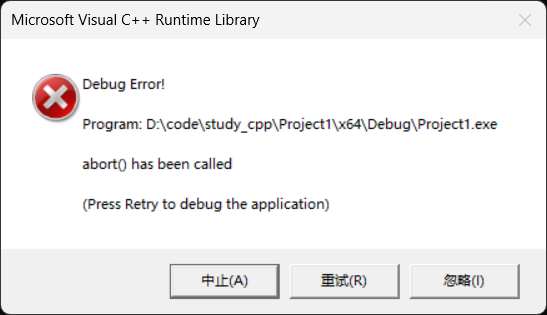
可以看到越界抛异常(意味着我们可以捕获),具体要等后面学。
4.3 修改string
4.3.1 +=
同效果函数里好用,推荐用这个。
cpp
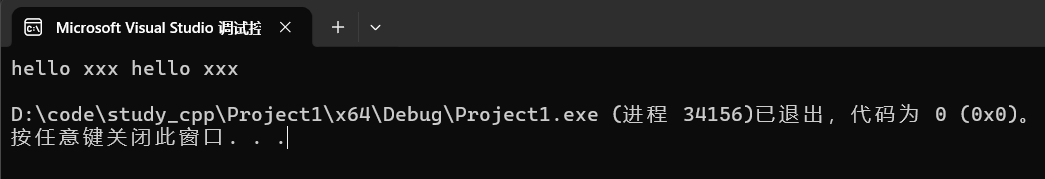
string s("hello");
s += ' ';
s += "xxx ";
s += s;
cout << s << endl;运行结果:
4.3.2 apppend
(1)追加c_string
cpp
string s("hello");
s.append(":)");
cout << s << endl;运行:
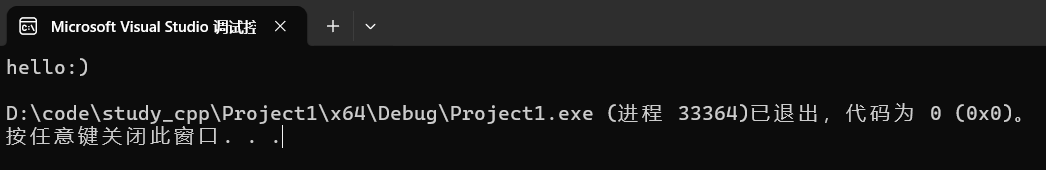
(2)追加string
cpp
string s("hello");
string s1(":>");
s.append(s1);
cout << s << endl;运行:
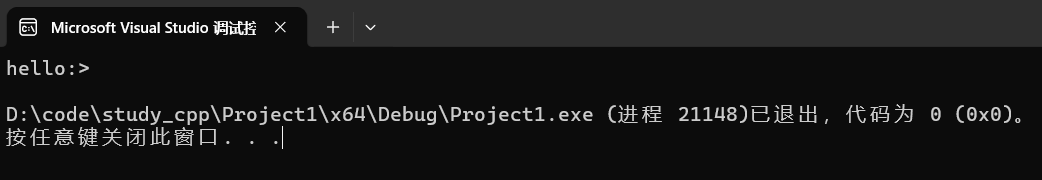
(3)迭代区间
cpp
string s("hello");
s.append(s.begin(),s.end());
cout << s << endl;运行结果:
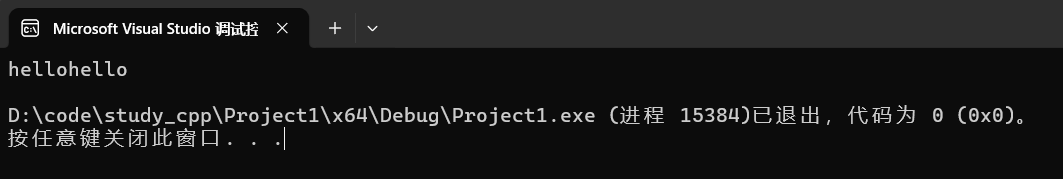
4.3.3 push_back
尾插。
cpp
s.push_back('~');运行:
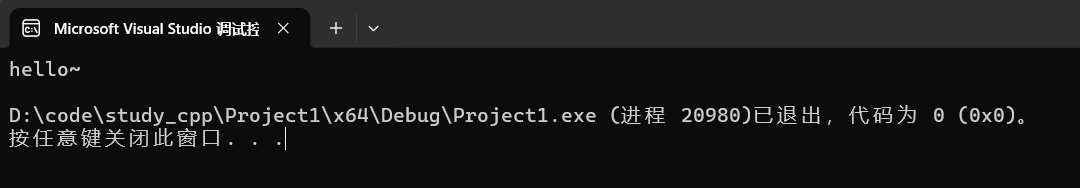
4.3.4 pop_back
尾删。
cpp
string s("hello");
s.push_back('~');
s.pop_back();
cout << s << endl;运行:
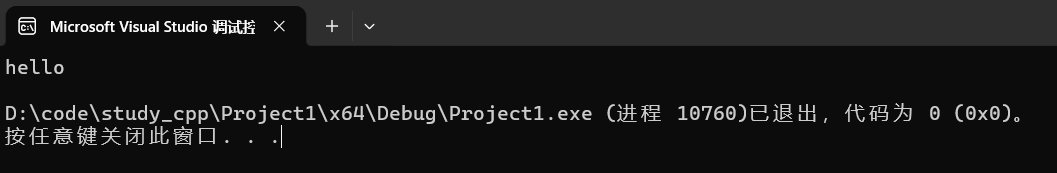
4.3.5 insert
插入数据。
cpp
string s("hello");
s.insert(0, "xxx ");
cout << s << endl;运行:
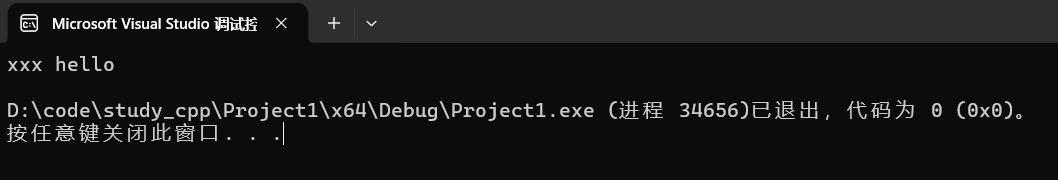
谨慎使用,因为底层时间复杂度为O(N),效率不高。
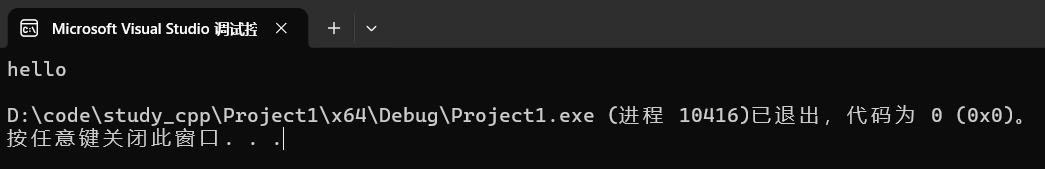
4.3.6 erase
删除数据。
cpp
string s("hello");
s.insert(0, "xxx ");
s.erase(0,4);
cout << s << endl;运行:
有多少删多少,不会报错:
cpp
string s("hello");
s.erase(0,10);调试:

这个也是谨慎使用,底层涉及挪动覆盖。
4.3.7 assign
覆盖,很少使用。
4.3.8 replace
替换。
cpp
string s("hello");
s.replace(0,5,"hi");调试:

谨慎使用,底层涉及挪动覆盖。
4.4 string 操作
4.4.1 c_str
把string转换成c_string,主要为了兼容C语言。
cpp
string s("hello");
const char* cstr = s.c_str();调试:

4.4.2 data
一般用c_str就行。
4.4.3 find
查找。
以网址分割举例:
cpp
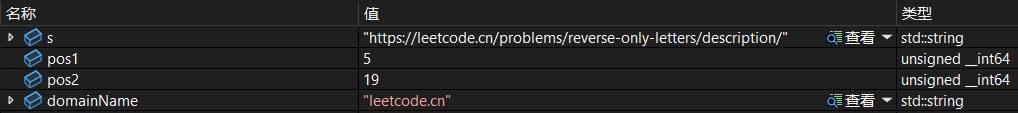
string s("https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-only-letters/description/");
cout << s.find(":") << endl;运行:
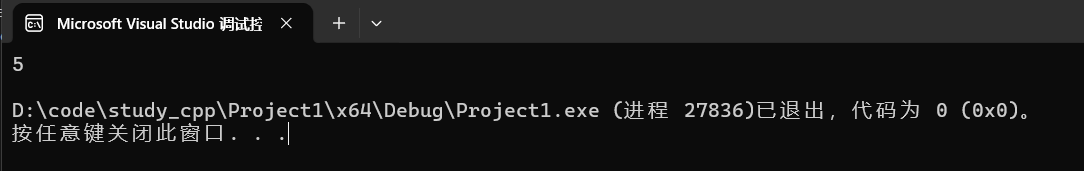
4.4.4 substr
从指定位置构造。
同样以网址分割举例:
cpp
string s("https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-only-letters/description/");先用find找出我们要的点位:
cpp
size_t pos1 = s.find(":");
size_t pos2 = s.find("/",pos1 + 3);再用substr构造:
cpp
string domainName = s.substr(pos1 + 3,pos2 - pos1 - 3);调试:
- 比copy好用一些。
4.4.5 find_first_of
找指定的一些字符。
cpp
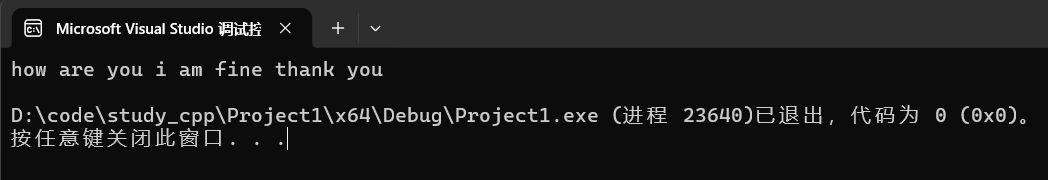
string s("how are you?i am fine,thank you.");
size_t pos = s.find_first_of("?!,.");
while (pos != s.npos) {
s[pos] = ' ';
pos = s.find_first_of("?!,.",pos + 1);
}
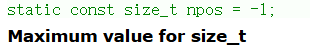
cout << s << endl;s.npos:
运行:
find_last_of倒着找。
4.4.6 find_first_not_of
找除 指定的一些字符 外的其他字符。
4.4.7 compare
比较两个string,一般不用这个函数,用(重载的)比较操作符比较。
4.5 全局函数
4.5.1 operator==
支持string和string,string和c_string,c_string和string。
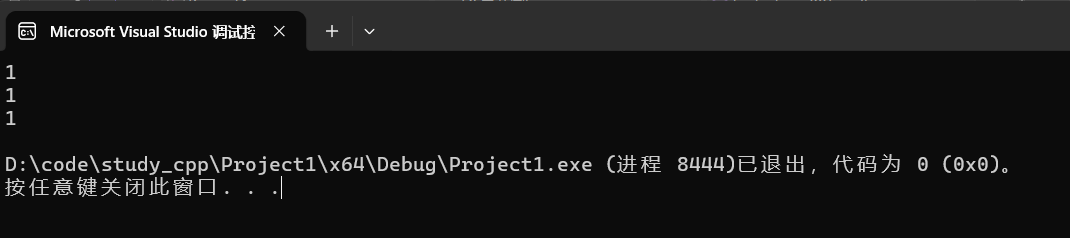
cpp
string s1("hello");
string s2("hello");
char str[] = "hello";
cout << (s1 == s2) << endl;
cout << (str == s1) << endl;
cout << (s1 == str) << endl;运行:
4.5.2 getline
我们原先使用>>输入。
cpp
string s;
cout << "please enter:";
cin >> s;
cout << s << endl;运行:
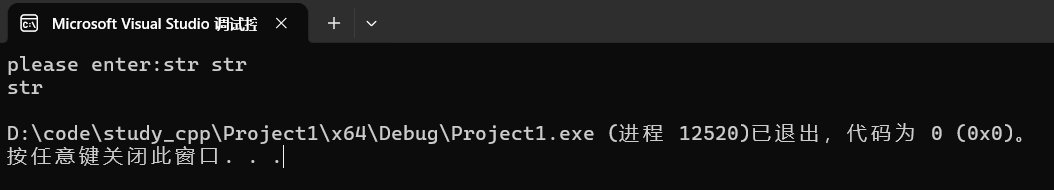
可以看到我们输入了俩str,但是空格是默认结束符,>> 遇到空格就停止输入了。
(1)获取一行
那我们这里的俩str怎么输入呢?
cpp
string s;
cout << "please enter:";
getline(cin,s);
cout << s << endl;运行:
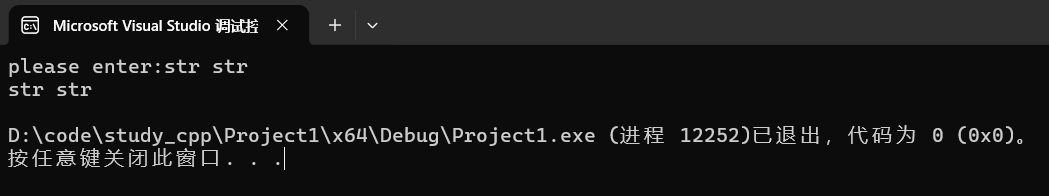
这里getline遇到换行符停止输入。
(2)自定义结束符
我们也可以自定义结束符。
cpp
string s;
cout << "please enter:";
getline(cin,s,'#');
cout << s << endl;这里我们设置 '#' 为结束符。
运行:
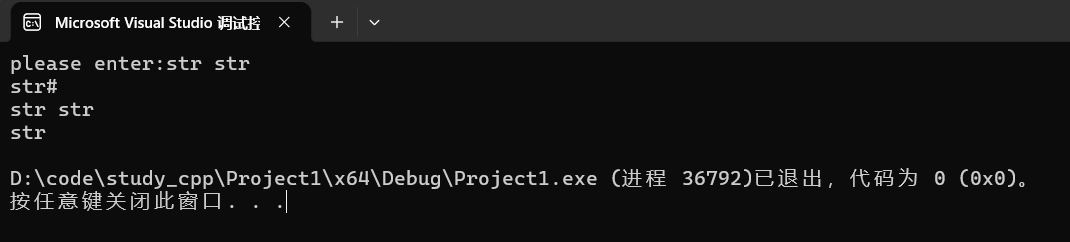
调试:

4.6 类型转换
4.6.1 string转数字

cpp
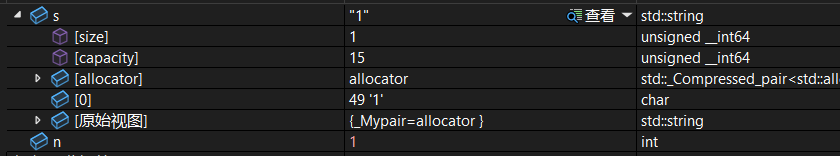
string s("1");
int n = stoi(s);调试:
4.6.2 to_string

cpp
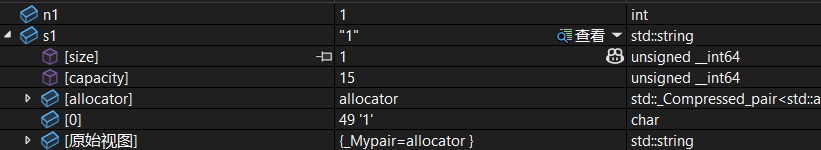
int n1 = 1;
string s1(to_string(n1));
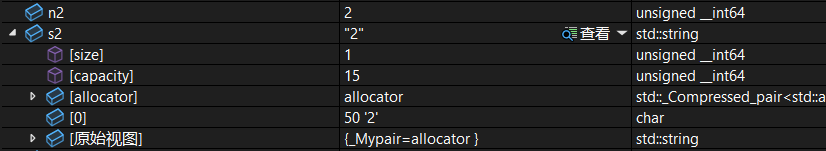
size_t n2 = 2;
string s2(to_string(n2));
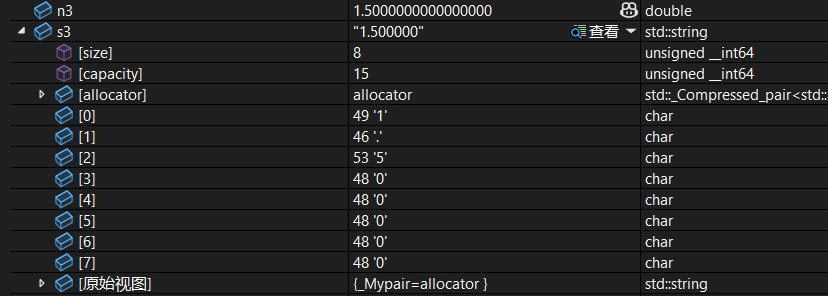
double n3 = 1.5;
string s3(to_string(n3));调试:
5 题目
整点题目练练手。
5.1反转字母
cpp
string reverseOnlyLetters(string s) {
auto left = s.begin();
auto right = s.end();
while(left < right){
while(left < right && !isalpha(*left)){
++left;
}
while(left < right && !isalpha(*right)){
--right;
}
if(left >= right){
break;
}
char c = *left;
*left = *right;
*right = c;
++left;
--right;
}
return s;
}-
left自左向右,right自右向左遍历。
-
如果这两遇到非字母就继续向前走。
-
如果这两都是字母就交换位置。
-
直到 left 和 right 的轨迹重叠。
isalpha是cctype头文件里的函数。
5.2 字符串中的第一个唯一字符
387. 字符串中的第一个唯一字符 - 力扣(LeetCode)
cpp
int firstUniqChar(string s) {
int cnt[26];
for(auto c:s){
++cnt[c - 'a'];
}
for(int i = 0;i < s.size();++i){
if(cnt[s[i] - 'a'] == 1){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}-
cnt数组用来存储字母出现次数,下标即为 各字母 相对于 'a' 字符的偏移量。
-
先遍历s,记录各字母出现次数。
-
再遍历一遍s,找出第一个出现了一次的字母。
5.3 验证回文串
cpp
bool isPalindrome(string s) {
auto left = s.begin();
auto right = s.end() - 1;
while(left < right){
while(left < right && !(isalpha(*left) || isdigit(*left)) ){
++left;
}
while(left < right && !(isalpha(*right) || isdigit(*right)) ){
--right;
}
if(left == right){
return true;
}
if(isupper(*left)){
*left+=32;
}
if(isupper(*right)){
*right+=32;
}
if(*left != *right){
return false;
}
++left;
--right;
}
return true;
}-
同样left,right遍历s。
-
left,right不能指向非字母数字,要判断。
-
这里判断回文串无关字母大小写,判断处理一下。
-
最后比较left,right是否是同一个字母数字。
-
不是同一个字母数字就直接返回 false,判断到最后都没返回false就返回true。
isdigit也是cctype头文件里的函数。
5.4 字符串相加
cpp
string addStrings(string num1, string num2) {
string ret;
ret.reserve(max(num1.size(),num2.size()) + 1);
int end1 = num1.size() - 1;
int end2 = num2.size() - 1;
int add = 0;
while(end1 >= 0 || end2 >= 0){
int n1 = end1 < 0?0:(num1[end1--] - '0');
int n2 = end2 < 0?0:(num2[end2--] - '0');
add += (n1 + n2);
ret += (add % 10 + '0');
add /= 10;
}
if(add == 1){
ret += '1';
}
reverse(ret.begin(),ret.end());
return ret;
}-
ret为要返回的相加后string,先提前reserve好所需空间。
-
end1,end2从后往前遍历num1,num2。
-
add为某数位相加后的中间值。
-
n1,n2为num1,num2各自某一数位的值。
-
给 n 值时要考虑到 end 是否已经遍历完num,这里给了一个三目运算符判断赋值。
-
最后算出的add的个位才是我们要拼接到ret上的值。
-
留下add十位上的数,我们进入下一位运算。
-
直到两个num都遍历完,反转ret后返回。
5.5 最后一个单词的长度
cpp
int main() {
string s;
while (getline(cin,s)) {
int pos = s.find_last_of(' ');
string s1 = s.substr(pos + 1);
cout << s1.size() << endl;
}
}-
牛客网上的题,需要处理多输入。
-
while循环中从后往前找最后一个空格。
-
找到后即可取出最后一个单词。
-
返回其size。

