文章目录
- 引言
- 一、项目搭建与依赖选择
-
- [1.1 Maven项目结构](#1.1 Maven项目结构)
- [1.2 最小化依赖](#1.2 最小化依赖)
- 二、消息模型:对话的基石
-
- [2.1 角色定义](#2.1 角色定义)
- [2.2 消息模型](#2.2 消息模型)
- [2.3 工具调用相关模型](#2.3 工具调用相关模型)
- [2.4 记忆管理](#2.4 记忆管理)
- 三、LLM客户端:对接大模型API
- 四、Agent核心:ReAct循环实现
-
- [4.1 BaseAgent:循环骨架](#4.1 BaseAgent:循环骨架)
- [4.2 ToolCallAgent:ReAct核心引擎](#4.2 ToolCallAgent:ReAct核心引擎)
- 五、工具系统:可插拔的能力扩展
-
- [5.1 工具接口](#5.1 工具接口)
- [5.2 工具基类](#5.2 工具基类)
- [5.3 工具注册中心](#5.3 工具注册中心)
- [5.4 首批工具:文件读写](#5.4 首批工具:文件读写)
- 六、ManusAgent:组装一切
- 七、启动入口
- 八、执行流程图
- 总结
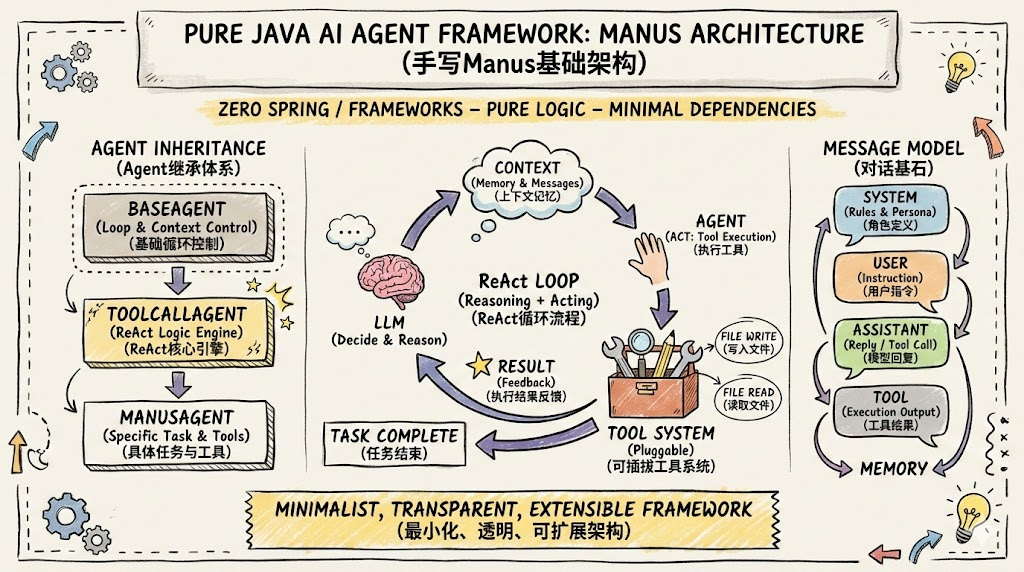
引言
当我们谈论AI Agent时,最核心的问题是:一个Agent到底是怎么运转的? 它如何接收用户指令?如何决定调用哪个工具?如何在多轮交互中保持上下文?
接下来我将从零开始,用纯Java(不依赖Spring框架)搭建一个完整的AI Agent基础架构。我们将实现:
- 三层Agent继承体系(BaseAgent → ToolCallAgent → ManusAgent)
- OpenAI兼容的LLM客户端
- 消息模型与记忆管理
- 可插拔的工具系统
- 文件读写工具作为首批能力
完成后,这个Agent就能接收用户指令,调用大模型进行推理,选择合适的工具执行任务,并将结果反馈给大模型继续决策------这就是经典的ReAct(Reasoning + Acting)模式。
一、项目搭建与依赖选择
1.1 Maven项目结构
java
ai-manus/
├── pom.xml
└── src/main/java/com/zhouyu/
├── ManusApplication.java # 启动入口
├── agent/
│ ├── BaseAgent.java # Agent基类
│ ├── ToolCallAgent.java # 工具调用Agent
│ └── ManusAgent.java # 具体Agent实现
├── model/
│ ├── ModelConfig.java # 模型配置
│ ├── OpenAIClient.java # LLM API客户端
│ ├── Message.java # 消息模型
│ ├── Memory.java # 记忆管理
│ ├── ModelResponse.java # 模型响应
│ ├── Role.java # 角色枚举
│ ├── ToolCall.java # 工具调用模型
│ ├── ToolDefinition.java # 工具定义
│ └── Function.java # 函数模型
└── tools/
├── Tool.java # 工具接口
├── BaseTool.java # 工具基类
├── ToolCollection.java # 工具注册中心
├── ToolResult.java # 工具执行结果
└── impl/
├── FileWriterTool.java # 文件写入工具
└── FileReaderTool.java # 文件读取工具1.2 最小化依赖
项目刻意选择"最小依赖"原则,不使用Spring等重型框架:
xml
<dependencies>
<!-- HTTP客户端:调用LLM API -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.squareup.okhttp3</groupId>
<artifactId>okhttp</artifactId>
<version>4.12.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- JSON处理 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.16.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 日志 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>2.0.12</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.4.14</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 减少样板代码 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.26</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>这样做的好处是:你看到的每一行代码都是Agent逻辑本身,没有框架魔法的干扰。
二、消息模型:对话的基石
2.1 角色定义
OpenAI Chat API定义了四种消息角色,我们用枚举来表示:
java
public enum Role {
SYSTEM("system"), // 系统提示词,定义Agent行为
USER("user"), // 用户输入
ASSISTANT("assistant"), // 大模型回复(可能包含tool_calls)
TOOL("tool"); // 工具执行结果
private final String value;
Role(String value) { this.value = value; }
public String getValue() { return value; }
}2.2 消息模型
Message类需要兼容OpenAI Chat Completions API的消息格式,同时支持多模态(文本+图片):
java
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Message {
private Role role;
private String content;
private List<ToolCall> toolCalls; // assistant消息携带的工具调用请求
private String name; // tool消息的工具名
private String toolCallId; // tool消息关联的调用ID
private String base64Image; // 多模态图片数据(Base64编码)
// 静态工厂方法,创建不同角色的消息
public static Message userMessage(String content) {
return new Message(Role.USER, content);
}
public static Message systemMessage(String content) {
return new Message(Role.SYSTEM, content);
}
public static Message assistantMessage(String content) {
return new Message(Role.ASSISTANT, content);
}
public static Message toolMessage(String content, String name,
String toolCallId, String base64Image) {
Message msg = new Message(Role.TOOL, content);
msg.setName(name);
msg.setToolCallId(toolCallId);
msg.setBase64Image(base64Image);
return msg;
}
}关键设计点:
toolCalls字段:当大模型决定调用工具时,返回的assistant消息会包含tool_calls列表toolCallId字段:工具执行结果必须通过toolCallId与对应的调用请求关联,这是OpenAI协议要求base64Image字段:预留多模态支持,后续浏览器截图等功能会用到
2.3 工具调用相关模型
java
// 工具调用请求
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class ToolCall {
private String id;
private String type = "function";
private Function function;
}
// 函数信息
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Function {
private String name; // 函数名
private String arguments; // 参数(JSON字符串)
}
// 工具定义(传给LLM的元信息)
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Builder
public class ToolDefinition {
private String name;
private String description;
private Map<String, Object> parameters; // JSON Schema格式
}2.4 记忆管理
初始版本的Memory非常简洁------一个消息列表:
java
@Data
public class Memory {
private List<Message> messages;
public Memory() {
this.messages = new ArrayList<>();
}
public void addMessage(Message message) {
messages.add(message);
}
}所有消息(系统提示、用户输入、模型回复、工具结果)都存入Memory,保证上下文的完整性。
三、LLM客户端:对接大模型API
OpenAIClient负责与大模型API通信。它使用OkHttp3发送HTTP请求,兼容OpenAI Chat Completions API格式:
java
public class OpenAIClient {
private final ModelConfig modelConfig;
private final OkHttpClient httpClient;
private final ObjectMapper objectMapper;
public OpenAIClient(ModelConfig modelConfig) {
this.modelConfig = modelConfig;
this.objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
this.httpClient = new OkHttpClient.Builder()
.connectTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(30))
.readTimeout(Duration.ofMinutes(5)) // 大模型推理需要较长时间
.writeTimeout(Duration.ofMinutes(5))
.build();
}
public ModelResponse chat(List<Message> messages, List<ToolDefinition> tools) {
Map<String, Object> requestBody = new HashMap<>();
requestBody.put("model", modelConfig.getModel());
requestBody.put("messages", convertMessagesToApiFormat(messages));
// 仅在有工具时传入tools参数
if (tools != null && !tools.isEmpty()) {
requestBody.put("tools", convertToolsToApiFormat(tools));
}
String jsonBody = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(requestBody);
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url(modelConfig.getBaseUrl() + "/chat/completions")
.post(RequestBody.create(jsonBody, JSON))
.addHeader("Authorization", "Bearer " + modelConfig.getApiKey())
.build();
try (Response response = httpClient.newCall(request).execute()) {
return parseResponse(response.body().string());
}
}
}多模态消息转换
客户端自动处理含图片的消息,转为OpenAI多模态格式:
java
private List<Map<String, Object>> convertMessagesToApiFormat(List<Message> messages) {
List<Map<String, Object>> apiMessages = new ArrayList<>();
for (Message message : messages) {
Map<String, Object> apiMessage = new HashMap<>();
apiMessage.put("role", message.getRole().getValue());
if (message.getContent() != null) {
if (message.getBase64Image() != null) {
// 多模态content数组
List<Map<String, Object>> content = new ArrayList<>();
content.add(Map.of("type", "text", "text", message.getContent()));
content.add(Map.of("type", "image_url",
"image_url", Map.of("url",
"data:image/jpeg;base64," + message.getBase64Image())));
apiMessage.put("content", content);
} else {
apiMessage.put("content", message.getContent());
}
}
// ... 处理toolCalls、name、toolCallId等字段
apiMessages.add(apiMessage);
}
return apiMessages;
}工具定义转换
遵循OpenAI Function Calling标准格式:
java
private List<Map<String, Object>> convertToolsToApiFormat(List<ToolDefinition> tools) {
List<Map<String, Object>> apiTools = new ArrayList<>();
for (ToolDefinition tool : tools) {
apiTools.add(Map.of(
"type", "function",
"function", Map.of(
"name", tool.getName(),
"description", tool.getDescription(),
"parameters", tool.getParameters()
)
));
}
return apiTools;
}四、Agent核心:ReAct循环实现
4.1 BaseAgent:循环骨架
BaseAgent定义了Agent执行的基本骨架------一个有限步数的循环:
java
public abstract class BaseAgent {
protected final Memory memory;
private final int maxStep;
protected String systemPrompt;
public BaseAgent(String systemPrompt) {
this.memory = new Memory();
this.maxStep = 10; // 安全阀:防止无限循环
this.systemPrompt = systemPrompt;
}
public String run(String prompt) {
// 1. 初始化上下文
memory.addMessage(Message.systemMessage(systemPrompt));
memory.addMessage(Message.userMessage(prompt));
int currentStep = 0;
StringBuilder allStepResult = new StringBuilder();
// 2. ReAct循环
while (currentStep < maxStep) {
StepResult stepResult = step(); // 子类实现单步逻辑
allStepResult.append(stepResult.output).append("/n");
if (!stepResult.isShouldContinue()) {
break; // 大模型认为任务完成
}
currentStep++;
}
return allStepResult.toString();
}
protected abstract StepResult step();
@Data @Builder
public static class StepResult {
private final String output; // 当前步的输出
private final boolean shouldContinue; // 是否继续执行
}
}4.2 ToolCallAgent:ReAct核心引擎
ToolCallAgent实现了ReAct循环的单步逻辑------这是整个系统的灵魂:
java
public class ToolCallAgent extends BaseAgent {
protected ToolCollection toolCollection;
protected OpenAIClient openAIClient;
private ObjectMapper objectMapper;
@Override
protected StepResult step() {
// 1. 获取全部上下文消息和工具定义
List<Message> contextMessages = memory.getMessages();
List<ToolDefinition> toolDefinitions = toolCollection.getToolDefinitions();
// 2. 调用大模型
ModelResponse modelResponse = openAIClient.chat(contextMessages, toolDefinitions);
// 3. 大模型决定调用工具
if (modelResponse.hasToolCalls()) {
Message assistantMessage = Message.assistantMessage(modelResponse.getContent());
assistantMessage.setToolCalls(convertToToolCalls(modelResponse.getToolCalls()));
memory.addMessage(assistantMessage);
return handleToolCalls(modelResponse.getToolCalls());
}
// 4. 大模型直接回复文本
if (modelResponse.getContent() != null && !modelResponse.getContent().isBlank()) {
memory.addMessage(Message.assistantMessage(modelResponse.getContent()));
}
// 5. 判断是否结束(finish_reason == "stop")
if (modelResponse.getFinishReason().equals("stop")) {
return StepResult.builder()
.shouldContinue(false)
.output("大模型认为任务已经执行结束").build();
}
return StepResult.builder()
.shouldContinue(true)
.output(modelResponse.getContent()).build();
}
}核心设计决策:
- 工具执行后
shouldContinue始终为true------工具只是中间步骤,执行结果需要反馈给大模型做下一步决策 - 严格维护消息链------先存assistant的tool_calls消息,再存tool的执行结果消息,这个顺序不能乱
- 错误也要存入Memory------让大模型知道工具执行失败了,它可以调整策略
工具执行的实现:
java
private StepResult handleToolCalls(List<Object> toolCalls) {
StringBuilder allResults = new StringBuilder();
for (Object toolCallObj : toolCalls) {
try {
JsonNode toolCallNode = objectMapper.valueToTree(toolCallObj);
String toolCallId = toolCallNode.get("id").asText();
String toolName = toolCallNode.get("function").get("name").asText();
String argumentsJson = toolCallNode.get("function").get("arguments").asText();
// 解析参数并执行工具
Map<String, Object> arguments = objectMapper.readValue(argumentsJson, Map.class);
ToolResult result = toolCollection.executeTool(toolName, arguments);
// 将结果封装为toolMessage
String resultContent = result.hasError()
? "Error: " + result.getError()
: result.getOutput().toString();
Message toolMessage = Message.toolMessage(
resultContent, toolName, toolCallId, result.getBase64Image());
memory.addMessage(toolMessage);
} catch (Exception e) {
// 错误也存入Memory
Message errorMessage = Message.toolMessage(
"工具执行失败: " + e.getMessage(), "unknown",
UUID.randomUUID().toString());
memory.addMessage(errorMessage);
}
}
return StepResult.builder().shouldContinue(true).output(allResults.toString()).build();
}五、工具系统:可插拔的能力扩展
5.1 工具接口
java
public interface Tool {
String getName();
String getDescription();
Map<String, Object> getParametersSchema(); // JSON Schema
ToolResult execute(Map<String, Object> parameters);
default ToolDefinition toDefinition() {
return new ToolDefinition(getName(), getDescription(), getParametersSchema());
}
}5.2 工具基类
BaseTool提供构建JSON Schema和安全提取参数的辅助方法:
java
public abstract class BaseTool implements Tool {
protected final String name;
protected final String description;
// JSON Schema构建辅助
protected Map<String, Object> stringParam(String description) {
return Map.of("type", "string", "description", description);
}
protected Map<String, Object> boolParam(String description) {
return Map.of("type", "boolean", "description", description);
}
// 安全的参数提取
protected String getString(Map<String, Object> parameters, String key) {
Object value = parameters.get(key);
return value != null ? value.toString() : null;
}
// Schema组装
protected Map<String, Object> buildSchema(
Map<String, Map<String, Object>> properties, List<String> required) {
Map<String, Object> schema = new HashMap<>();
schema.put("type", "object");
schema.put("properties", properties);
if (required != null && !required.isEmpty()) {
schema.put("required", required);
}
return schema;
}
}5.3 工具注册中心
java
public class ToolCollection {
private final Map<String, Tool> tools = new HashMap<>();
public void addTool(Tool tool) {
tools.put(tool.getName(), tool);
}
public List<ToolDefinition> getToolDefinitions() {
List<ToolDefinition> definitions = new ArrayList<>();
for (Tool tool : tools.values()) {
definitions.add(tool.toDefinition());
}
return definitions;
}
public ToolResult executeTool(String toolName, Map<String, Object> parameters) {
Tool tool = tools.get(toolName);
if (tool == null) {
return ToolResult.error("Tool not found: " + toolName);
}
return tool.execute(parameters);
}
}5.4 首批工具:文件读写
FileWriterTool------支持写入和追加模式:
java
public class FileWriterTool extends BaseTool {
public FileWriterTool() {
super("write_file", "写入内容到文件");
}
@Override
public Map<String, Object> getParametersSchema() {
return buildSchema(
Map.of(
"file_path", stringParam("要写入的文件路径"),
"content", stringParam("要写入文件的内容"),
"append", boolParam("追加到文件而不是覆盖(默认:false)")
),
List.of("file_path", "content")
);
}
@Override
public ToolResult execute(Map<String, Object> parameters) {
try {
String filePath = getString(parameters, "file_path");
String content = getString(parameters, "content");
boolean append = getBoolean(parameters, "append", false);
Path path = Paths.get(filePath);
if (path.getParent() != null) {
Files.createDirectories(path.getParent());
}
if (append) {
Files.writeString(path, content, StandardOpenOption.CREATE, StandardOpenOption.APPEND);
} else {
Files.writeString(path, content, StandardOpenOption.CREATE, StandardOpenOption.TRUNCATE_EXISTING);
}
return ToolResult.success("成功写入文件:" + filePath);
} catch (IOException e) {
return ToolResult.error("写入文件失败:" + e.getMessage());
}
}
}FileReaderTool:
java
public class FileReaderTool extends BaseTool {
public FileReaderTool() {
super("read_file", "读取文件内容");
}
@Override
public ToolResult execute(Map<String, Object> parameters) {
try {
String filePath = getString(parameters, "file_path");
Path path = Paths.get(filePath);
if (!Files.exists(path)) {
return ToolResult.error("文件不存在:" + filePath);
}
return ToolResult.success(Files.readString(path));
} catch (IOException e) {
return ToolResult.error("读取文件失败:" + e.getMessage());
}
}
}六、ManusAgent:组装一切
ManusAgent是面向用户的具体Agent,负责注册工具、配置系统提示词、管理工作空间:
java
public class ManusAgent extends ToolCallAgent {
private final static String SYSTEM_PROMPT = """
# 角色定义
你是Manus,一个多功能的AI代理,能够使用可用的工具处理各种任务。
# 规则
- 工作目录:{workspace}
- 一次只能执行一个工具
""";
public ManusAgent(OpenAIClient openAIClient) {
super(openAIClient, null, null);
// 注册工具
ToolCollection toolCollection = new ToolCollection();
toolCollection.addTool(new FileWriterTool());
toolCollection.addTool(new FileReaderTool());
this.toolCollection = toolCollection;
// 创建workspace工作目录
Path workspaceRoot = getProjectRoot().resolve("workspace");
Files.createDirectories(workspaceRoot);
this.systemPrompt = SYSTEM_PROMPT.replace("{workspace}", workspaceRoot.toString());
}
}七、启动入口
java
public class ManusApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
OpenAIClient openAIClient = new OpenAIClient(ModelConfig.builder()
.baseUrl("https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1")
.apiKey(System.getenv("DASHSCOPE_API_KEY"))
.model("qwen-plus")
.build());
ManusAgent manusAgent = new ManusAgent(openAIClient);
String prompt = "请帮我用HTML、CSS、JS创建一个简单的贪吃蛇游戏,分成三个文件";
manusAgent.run(prompt);
System.exit(0);
}
}八、执行流程图
java
用户输入: "创建贪吃蛇游戏"
▼
┌─ BaseAgent.run() ──────────────────────────┐
│ Memory: [SystemMsg, UserMsg] │
│ ▼ │
│ ┌─ ToolCallAgent.step() ────────────────┐ │
│ │ LLM推理 → 返回 write_file(snake.html)│ │
│ │ 执行工具 → 存入结果 → continue=true │ │
│ └───────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ ▼ │
│ ┌─ step() ──────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ LLM推理 → 返回 write_file(snake.css) │ │
│ │ 执行工具 → 存入结果 → continue=true │ │
│ └───────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ ▼ │
│ ┌─ step() ──────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ LLM推理 → 返回 write_file(snake.js) │ │
│ │ 执行工具 → 存入结果 → continue=true │ │
│ └───────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ ▼ │
│ ┌─ step() ──────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ LLM推理 → finish_reason="stop" │ │
│ │ 任务完成 → continue=false │ │
│ └───────────────────────────────────────┘ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────┘总结
通过这篇文章,我们搭建了一个AI Agent的完整基础架构:
- 三层Agent体系 :
BaseAgent负责循环控制,ToolCallAgent负责ReAct逻辑,ManusAgent负责具体业务 - 消息驱动架构:所有交互通过Message对象流转,严格遵循OpenAI Chat API协议
- 可插拔工具系统 :通过
Tool接口和ToolCollection注册中心,工具的增减不影响Agent核心逻辑 - LLM作为决策引擎:Agent不包含硬编码的决策规则,所有决策由大模型在运行时完成
这个基础架构已经可以通过文件读写工具完成简单任务。在后续文章中,我们将逐步为它添加Docker沙箱、网页搜索、浏览器自动化等更强大的能力。
