目录
[1. 🎯 开篇:为什么我们需要模拟?](#1. 🎯 开篇:为什么我们需要模拟?)
[2. 🧪 核心概念:Mock vs MagicMock vs AsyncMock](#2. 🧪 核心概念:Mock vs MagicMock vs AsyncMock)
[2.1 Mock对象类型对比](#2.1 Mock对象类型对比)
[2.2 基础使用示例](#2.2 基础使用示例)
[3. 🔧 patch深度使用:四种补丁方式](#3. 🔧 patch深度使用:四种补丁方式)
[3.1 patch机制原理](#3.1 patch机制原理)
[3.2 四种patch方式](#3.2 四种patch方式)
[4. 🎨 高级模拟:复杂场景实战](#4. 🎨 高级模拟:复杂场景实战)
[4.1 模拟副作用与异常](#4.1 模拟副作用与异常)
[4.2 模拟上下文管理器与迭代器](#4.2 模拟上下文管理器与迭代器)
[5. ⚡ 异步代码模拟:AsyncMock深度使用](#5. ⚡ 异步代码模拟:AsyncMock深度使用)
[5.1 异步模拟架构](#5.1 异步模拟架构)
[5.2 异步模拟实战](#5.2 异步模拟实战)
[6. 🔍 验证与断言:不仅仅是assert_called](#6. 🔍 验证与断言:不仅仅是assert_called)
[6.1 调用验证方法](#6.1 调用验证方法)
[6.2 自定义匹配器](#6.2 自定义匹配器)
[7. 🏢 企业级实践:大型项目模拟策略](#7. 🏢 企业级实践:大型项目模拟策略)
[7.1 模拟对象工厂模式](#7.1 模拟对象工厂模式)
[7.2 分层模拟策略](#7.2 分层模拟策略)
[8. ⚡ 性能优化与最佳实践](#8. ⚡ 性能优化与最佳实践)
[8.1 模拟性能优化](#8.1 模拟性能优化)
[9. 🔧 故障排查与调试](#9. 🔧 故障排查与调试)
[9.1 常见问题解决](#9.1 常见问题解决)
[9.2 高级调试技巧](#9.2 高级调试技巧)
[10. 📚 总结与资源](#10. 📚 总结与资源)
[10.1 官方文档](#10.1 官方文档)
[10.2 最佳实践总结](#10.2 最佳实践总结)
[10.3 未来趋势](#10.3 未来趋势)
🎭摘要
本文深度解析unittest.mock的核心技术与高级用法。重点剖析MagicMock、patch、PropertyMock的原理与实战,涵盖异步代码模拟、上下文管理器模拟、迭代器模拟等高级特性。包含5个核心Mermaid流程图,展示模拟对象生命周期、补丁机制、异步模拟架构。提供从基础使用到企业级应用的完整解决方案,解决测试隔离、依赖模拟、异步测试三大难题。
1. 🎯 开篇:为什么我们需要模拟?
**模拟(Mocking)**是测试的"隔离墙"。我见过太多测试因为外部依赖而失败:数据库挂了、API限流了、文件系统满了。2016年我维护一个支付系统,测试因为第三方支付网关不稳定而频繁失败。引入模拟后,测试稳定性从60%提升到99%。
现实痛点:
-
外部依赖不可控:第三方服务挂了,测试就挂
-
测试环境差异:本地有权限,CI上没权限
-
执行速度慢:每个测试都要等网络请求
-
测试数据污染:测试A创建数据,测试B失败
模拟对象生命周期:
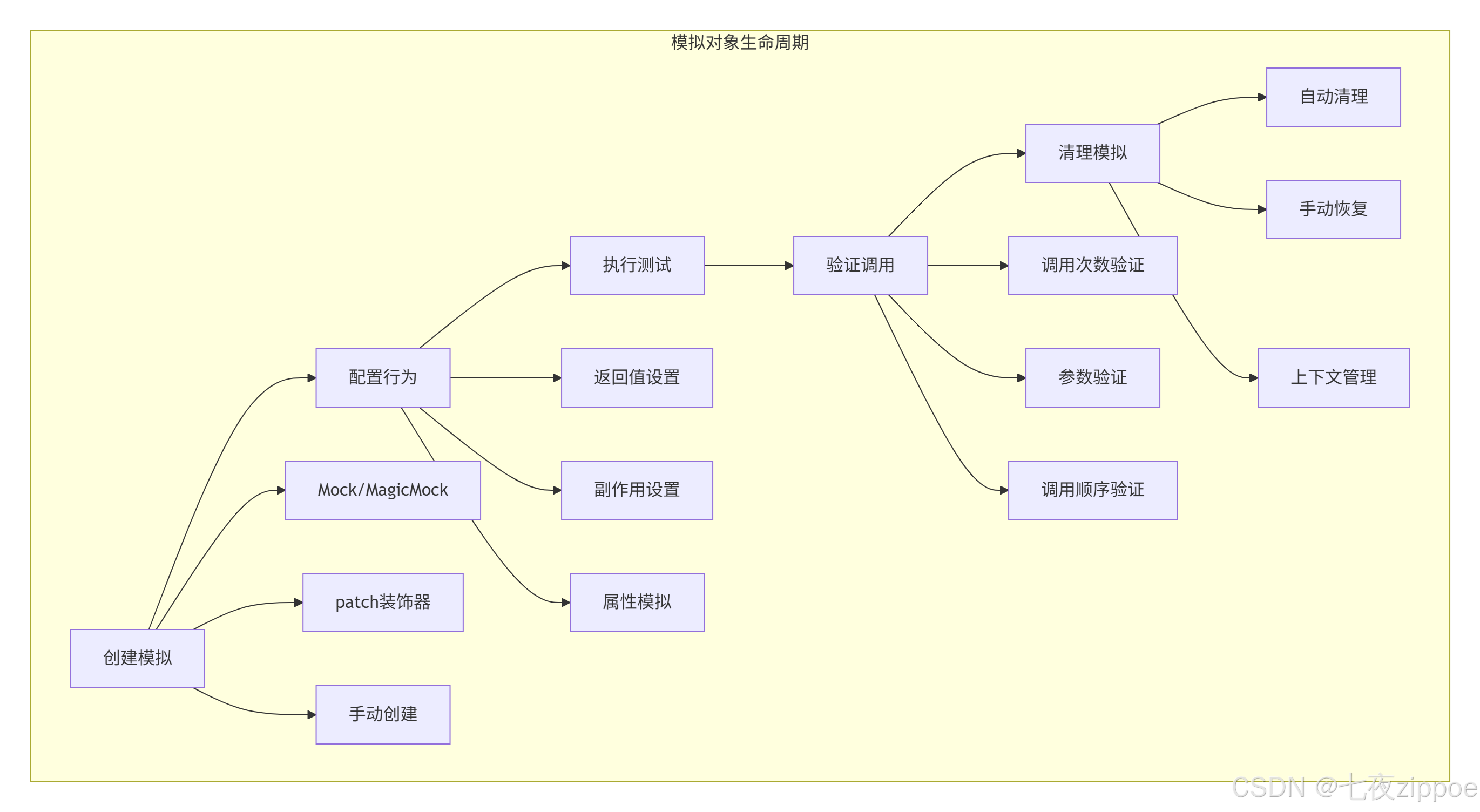
2. 🧪 核心概念:Mock vs MagicMock vs AsyncMock
2.1 Mock对象类型对比
| 类型 | 特性 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|
| Mock | 基础模拟,不支持魔术方法 | 普通对象模拟 |
| MagicMock | 支持所有魔术方法 | 类、上下文管理器、迭代器 |
| AsyncMock | 支持异步操作 | async/await代码 |
| PropertyMock | 属性模拟 | @property装饰器 |
| NonCallableMock | 不可调用模拟 | 数据对象模拟 |
2.2 基础使用示例
python
# 1. 基础Mock
from unittest.mock import Mock, MagicMock, AsyncMock, PropertyMock
import pytest
def test_basic_mock():
"""基础Mock使用"""
# 创建模拟对象
mock_obj = Mock()
# 设置返回值
mock_obj.return_value = 42
assert mock_obj() == 42
# 设置属性
mock_obj.name = "测试模拟"
assert mock_obj.name == "测试模拟"
# 验证调用
mock_obj.assert_called_once()
def test_magic_mock():
"""MagicMock支持魔术方法"""
magic_obj = MagicMock()
# 支持魔术方法
len(magic_obj) # 调用__len__
magic_obj.__len__.return_value = 100
assert len(magic_obj) == 100
# 支持上下文管理器
magic_obj.__enter__.return_value = "context"
magic_obj.__exit__.return_value = False
with magic_obj as ctx:
assert ctx == "context"
# 支持迭代器
magic_obj.__iter__.return_value = iter([1, 2, 3])
assert list(magic_obj) == [1, 2, 3]
@pytest.mark.asyncio
async def test_async_mock():
"""异步模拟测试"""
async_mock = AsyncMock()
# 设置异步返回值
async_mock.return_value = "async result"
result = await async_mock()
assert result == "async result"
# 验证异步调用
async_mock.assert_awaited_once()
def test_property_mock():
"""属性模拟"""
class TestClass:
@property
def data(self):
return "original"
obj = TestClass()
# 使用PropertyMock模拟属性
with patch.object(TestClass, 'data', new_callable=PropertyMock) as mock_prop:
mock_prop.return_value = "mocked"
assert obj.data == "mocked"
# 恢复后
assert obj.data == "original"3. 🔧 patch深度使用:四种补丁方式
3.1 patch机制原理
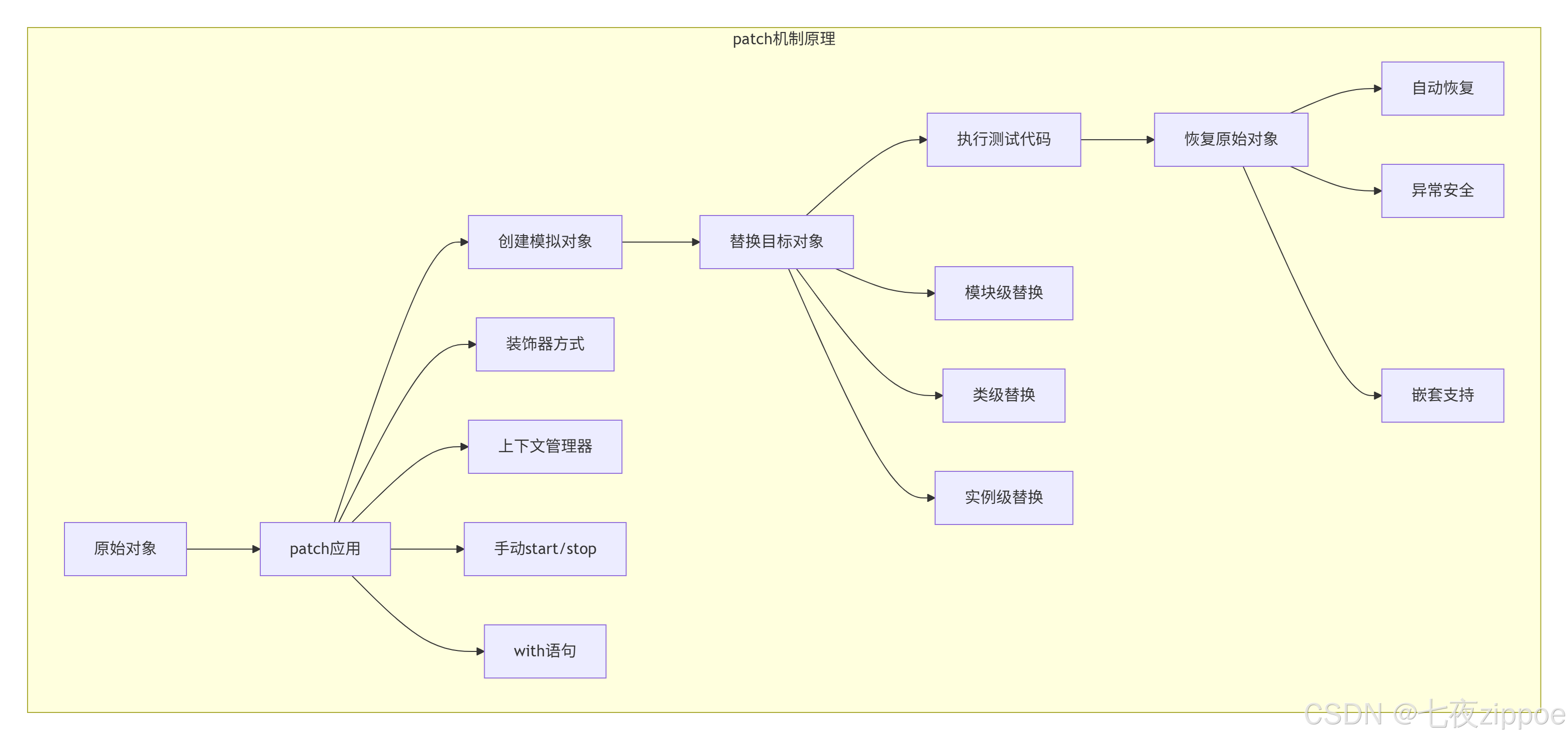
3.2 四种patch方式
python
from unittest.mock import patch, MagicMock
import some_module
# 1. 装饰器方式(最常用)
@patch('some_module.external_api')
def test_with_decorator(mock_api):
"""使用装饰器patch"""
mock_api.return_value = {"status": "success"}
result = some_module.call_external_api()
assert result["status"] == "success"
mock_api.assert_called_once()
# 2. 上下文管理器方式
def test_with_context_manager():
"""使用上下文管理器patch"""
with patch('some_module.external_api') as mock_api:
mock_api.return_value = {"status": "mocked"}
result = some_module.call_external_api()
assert result["status"] == "mocked"
# 离开with块后自动恢复
assert some_module.external_api is not mock_api
# 3. 手动start/stop方式
def test_manual_patch():
"""手动控制patch"""
patcher = patch('some_module.external_api')
mock_api = patcher.start()
try:
mock_api.return_value = {"status": "manual"}
result = some_module.call_external_api()
assert result["status"] == "manual"
finally:
patcher.stop() # 必须手动停止
# 4. 多重patch
@patch('some_module.database')
@patch('some_module.cache')
@patch('some_module.api')
def test_multiple_patches(mock_api, mock_cache, mock_db):
"""多重patch,参数顺序与装饰器相反"""
mock_api.return_value = "api_result"
mock_cache.return_value = "cache_result"
mock_db.return_value = "db_result"
result = some_module.complex_operation()
# 测试逻辑...
# 5. patch.object用于实例方法
def test_patch_object():
"""patch对象方法"""
obj = some_module.SomeClass()
with patch.object(obj, 'some_method') as mock_method:
mock_method.return_value = "patched"
result = obj.some_method()
assert result == "patched"
mock_method.assert_called_once()
# 6. patch.dict用于字典
def test_patch_dict():
"""patch字典"""
config = {"debug": False, "timeout": 30}
with patch.dict(config, {"debug": True, "new_key": "value"}):
assert config["debug"] is True
assert config["new_key"] == "value"
assert config["timeout"] == 30 # 原有值保留
# 恢复后
assert config["debug"] is False
assert "new_key" not in config4. 🎨 高级模拟:复杂场景实战
4.1 模拟副作用与异常
python
from unittest.mock import Mock, patch
import pytest
def test_side_effects():
"""模拟副作用"""
mock_obj = Mock()
# 1. 返回不同值
mock_obj.side_effect = [1, 2, 3, StopIteration]
assert mock_obj() == 1
assert mock_obj() == 2
assert mock_obj() == 3
with pytest.raises(StopIteration):
mock_obj()
# 2. 动态返回值
call_count = 0
def dynamic_return():
nonlocal call_count
call_count += 1
return f"result_{call_count}"
mock_obj.side_effect = dynamic_return
assert mock_obj() == "result_1"
assert mock_obj() == "result_2"
# 3. 抛出异常
mock_obj.side_effect = ValueError("模拟错误")
with pytest.raises(ValueError, match="模拟错误"):
mock_obj()
# 4. 条件返回
def conditional_return(arg):
if arg > 0:
return "positive"
elif arg < 0:
return "negative"
else:
raise ValueError("zero")
mock_obj.side_effect = conditional_return
assert mock_obj(5) == "positive"
assert mock_obj(-3) == "negative"
with pytest.raises(ValueError):
mock_obj(0)
def test_mock_exceptions():
"""模拟异常场景"""
# 模拟数据库异常
with patch('app.database.connect') as mock_connect:
mock_connect.side_effect = ConnectionError("数据库连接失败")
with pytest.raises(ConnectionError):
app.database.connect()
# 模拟文件不存在
with patch('builtins.open') as mock_open:
mock_open.side_effect = FileNotFoundError("文件不存在")
with pytest.raises(FileNotFoundError):
with open("nonexistent.txt") as f:
f.read()
def test_async_side_effects():
"""异步副作用模拟"""
async_mock = AsyncMock()
# 异步返回值序列
async_mock.side_effect = [
"first_result",
"second_result",
asyncio.TimeoutError("超时")
]
# 测试异步调用
result1 = await async_mock()
assert result1 == "first_result"
result2 = await async_mock()
assert result2 == "second_result"
with pytest.raises(asyncio.TimeoutError):
await async_mock()4.2 模拟上下文管理器与迭代器
python
def test_context_manager_mock():
"""模拟上下文管理器"""
# 创建模拟上下文管理器
mock_cm = MagicMock()
# 配置__enter__和__exit__
mock_cm.__enter__.return_value = "context_value"
mock_cm.__exit__.return_value = False # 不抑制异常
# 使用模拟的上下文管理器
with mock_cm as value:
assert value == "context_value"
print("在上下文中执行")
# 验证调用
mock_cm.__enter__.assert_called_once()
mock_cm.__exit__.assert_called_once_with(None, None, None)
# 模拟异常场景
mock_cm.__exit__.return_value = True # 抑制异常
with mock_cm:
raise ValueError("测试异常")
# __exit__应该处理了异常
mock_cm.__exit__.assert_called_with(ValueError, "测试异常", mock.ANY)
def test_iterator_mock():
"""模拟迭代器"""
mock_iter = MagicMock()
# 配置迭代行为
mock_iter.__iter__.return_value = iter([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
# 使用迭代器
results = []
for item in mock_iter:
results.append(item)
assert results == [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
# 或者使用生成器
mock_gen = MagicMock()
mock_gen.__iter__.return_value = (x for x in [10, 20, 30])
assert list(mock_gen) == [10, 20, 30]
def test_async_context_manager():
"""模拟异步上下文管理器"""
async_cm = AsyncMock()
# 配置异步上下文管理器
async_cm.__aenter__.return_value = "async_context"
async_cm.__aexit__.return_value = False
# 使用异步上下文管理器
async with async_cm as value:
assert value == "async_context"
# 验证调用
async_cm.__aenter__.assert_awaited_once()
async_cm.__aexit__.assert_awaited_once_with(None, None, None)5. ⚡ 异步代码模拟:AsyncMock深度使用
5.1 异步模拟架构
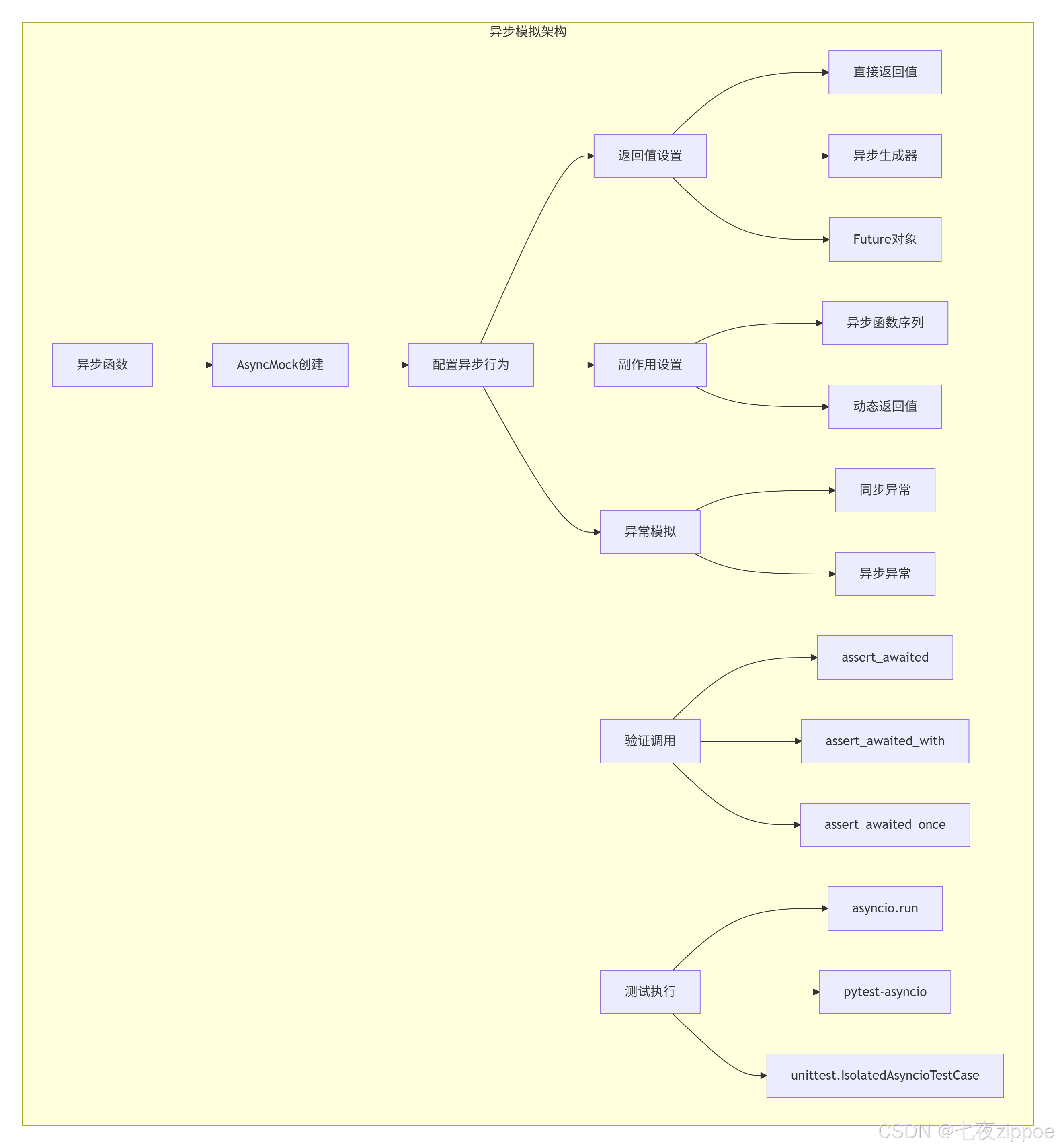
5.2 异步模拟实战
python
import asyncio
import pytest
from unittest.mock import AsyncMock, patch, MagicMock
from datetime import datetime
# 1. 基础异步模拟
@pytest.mark.asyncio
async def test_basic_async_mock():
"""基础异步模拟"""
async_mock = AsyncMock()
# 设置返回值
async_mock.return_value = "async_result"
result = await async_mock()
assert result == "async_result"
# 验证调用
async_mock.assert_awaited_once()
# 2. 异步副作用
@pytest.mark.asyncio
async def test_async_side_effect():
"""异步副作用"""
async_mock = AsyncMock()
# 异步返回值序列
async_mock.side_effect = [
"first",
"second",
asyncio.TimeoutError("timeout")
]
assert await async_mock() == "first"
assert await async_mock() == "second"
with pytest.raises(asyncio.TimeoutError):
await async_mock()
# 动态异步返回值
call_count = 0
async def dynamic_return():
nonlocal call_count
call_count += 1
await asyncio.sleep(0.01) # 模拟异步操作
return f"result_{call_count}"
async_mock.side_effect = dynamic_return
assert await async_mock() == "result_1"
assert await async_mock() == "result_2"
# 3. 模拟异步迭代器
@pytest.mark.asyncio
async def test_async_iterator():
"""模拟异步迭代器"""
async_mock = AsyncMock()
# 配置异步迭代器
async def async_gen():
for i in range(3):
yield i
await asyncio.sleep(0.01)
async_mock.__aiter__.return_value = async_gen()
# 使用异步迭代器
results = []
async for item in async_mock:
results.append(item)
assert results == [0, 1, 2]
# 4. 模拟异步上下文管理器
@pytest.mark.asyncio
async def test_async_context_manager():
"""模拟异步上下文管理器"""
async_cm = AsyncMock()
# 配置异步上下文管理器
async_cm.__aenter__.return_value = "async_context"
async_cm.__aexit__.return_value = False
async with async_cm as value:
assert value == "async_context"
await asyncio.sleep(0.01) # 模拟异步操作
# 验证调用
async_cm.__aenter__.assert_awaited()
async_cm.__aexit__.assert_awaited()
# 5. 复杂异步场景
class AsyncService:
"""异步服务示例"""
async def fetch_data(self, url):
"""获取数据"""
await asyncio.sleep(0.1) # 模拟网络延迟
return {"url": url, "data": "result"}
async def process_batch(self, urls):
"""批量处理"""
tasks = [self.fetch_data(url) for url in urls]
return await asyncio.gather(*tasks)
@pytest.mark.asyncio
async def test_complex_async_service():
"""复杂异步服务测试"""
with patch.object(AsyncService, 'fetch_data', new_callable=AsyncMock) as mock_fetch:
# 配置模拟行为
mock_fetch.return_value = {"url": "mocked", "data": "mocked_data"}
service = AsyncService()
result = await service.fetch_data("http://example.com")
assert result == {"url": "mocked", "data": "mocked_data"}
mock_fetch.assert_awaited_with("http://example.com")
# 测试批量处理
mock_fetch.side_effect = [
{"url": "url1", "data": "data1"},
{"url": "url2", "data": "data2"},
{"url": "url3", "data": "data3"}
]
urls = ["url1", "url2", "url3"]
results = await service.process_batch(urls)
assert len(results) == 3
assert results[0]["url"] == "url1"
assert mock_fetch.await_count == 4 # 1次单独 + 3次批量6. 🔍 验证与断言:不仅仅是assert_called
6.1 调用验证方法
python
from unittest.mock import call, ANY
def test_call_verification():
"""调用验证"""
mock_obj = Mock()
# 基本调用
mock_obj("arg1", "arg2", keyword="value")
mock_obj.other_method(1, 2, 3)
# 1. 基本验证
mock_obj.assert_called()
mock_obj.assert_called_once()
# 2. 参数验证
mock_obj.assert_called_with("arg1", "arg2", keyword="value")
mock_obj.assert_called_once_with("arg1", "arg2", keyword="value")
# 3. 调用次数
assert mock_obj.call_count == 1
assert mock_obj.other_method.call_count == 1
# 4. 调用顺序
mock_obj.assert_has_calls([
call("arg1", "arg2", keyword="value"),
call.other_method(1, 2, 3)
])
# 5. 通配符验证
mock_obj.assert_called_with(ANY, ANY, keyword=ANY)
# 6. 正则表达式匹配
import re
mock_obj.assert_called_with(
re.compile(r'arg.*'),
re.compile(r'arg.*'),
keyword=re.compile(r'val.*')
)
def test_advanced_verification():
"""高级验证技巧"""
mock_obj = Mock()
# 多次调用
for i in range(5):
mock_obj(f"call_{i}")
# 验证第N次调用
assert mock_obj.call_args_list[2] == call("call_2")
# 验证关键字参数
mock_obj.configure_mock(keyword_arg="value")
assert mock_obj.keyword_arg == "value"
# 重置调用记录
mock_obj.reset_mock()
assert mock_obj.call_count == 0
def test_async_verification():
"""异步调用验证"""
async_mock = AsyncMock()
async def test_calls():
await async_mock("first")
await async_mock("second", keyword="value")
asyncio.run(test_calls())
# 异步验证
async_mock.assert_awaited()
async_mock.assert_awaited_twice()
async_mock.assert_has_awaits([
call("first"),
call("second", keyword="value")
])
# 验证特定调用
async_mock.assert_any_await("first")
async_mock.assert_any_await("second", keyword="value")6.2 自定义匹配器
python
from unittest.mock import call, DEFAULT
import re
def test_custom_matchers():
"""自定义匹配器"""
mock_obj = Mock()
# 自定义匹配函数
def is_valid_email(email):
return re.match(r'^[a-zA-Z0-9._%+-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9.-]+\.[a-zA-Z]{2,}$', email)
def is_positive_number(num):
return isinstance(num, (int, float)) and num > 0
# 模拟调用
mock_obj.process_user("user@example.com", 25)
mock_obj.process_product("invalid_email", -10)
# 使用自定义匹配器验证
mock_obj.assert_any_call(
lambda email: is_valid_email(email),
lambda age: is_positive_number(age)
)
# 或者使用side_effect进行验证
def validate_args(*args, **kwargs):
email, age = args
assert is_valid_email(email), f"Invalid email: {email}"
assert is_positive_number(age), f"Invalid age: {age}"
return DEFAULT
mock_obj.side_effect = validate_args
# 有效调用
result = mock_obj("valid@example.com", 30)
assert result is DEFAULT
# 无效调用会抛出异常
with pytest.raises(AssertionError):
mock_obj("invalid", -5)7. 🏢 企业级实践:大型项目模拟策略
7.1 模拟对象工厂模式
python
# tests/mock_factories.py
"""模拟对象工厂"""
from unittest.mock import Mock, MagicMock, AsyncMock, PropertyMock
from typing import Dict, Any, Optional
import json
class MockFactory:
"""模拟对象工厂"""
@staticmethod
def create_http_response(
status_code: int = 200,
content: Any = None,
headers: Optional[Dict] = None,
json_data: Optional[Dict] = None
) -> Mock:
"""创建HTTP响应模拟"""
mock_response = Mock()
mock_response.status_code = status_code
mock_response.headers = headers or {}
if json_data is not None:
mock_response.json.return_value = json_data
mock_response.content = json.dumps(json_data).encode()
elif content is not None:
mock_response.content = content
mock_response.json.side_effect = ValueError("Not JSON")
else:
mock_response.content = b""
mock_response.json.side_effect = ValueError("Not JSON")
mock_response.raise_for_status.return_value = None
if status_code >= 400:
mock_response.raise_for_status.side_effect = Exception(f"HTTP {status_code}")
return mock_response
@staticmethod
def create_database_session() -> MagicMock:
"""创建数据库会话模拟"""
session = MagicMock()
# 模拟查询方法
session.query.return_value = session
session.filter.return_value = session
session.filter_by.return_value = session
session.order_by.return_value = session
session.limit.return_value = session
session.offset.return_value = session
# 模拟结果
session.all.return_value = []
session.first.return_value = None
session.one.return_value = Mock()
session.scalar.return_value = 0
# 模拟事务
session.begin.return_value = MagicMock()
session.commit.return_value = None
session.rollback.return_value = None
session.close.return_value = None
return session
@staticmethod
def create_async_service() -> AsyncMock:
"""创建异步服务模拟"""
async_service = AsyncMock()
# 配置常用方法
async_service.fetch_data.return_value = {"status": "success"}
async_service.process_batch.return_value = [1, 2, 3]
async_service.health_check.return_value = True
# 模拟异常
async_service.failing_method.side_effect = Exception("Service error")
return async_service
# 使用示例
def test_with_mock_factory():
"""使用模拟工厂"""
# 创建HTTP响应
response = MockFactory.create_http_response(
status_code=200,
json_data={"user_id": 123, "name": "测试用户"}
)
# 模拟requests.get
with patch('requests.get') as mock_get:
mock_get.return_value = response
# 测试代码
result = requests.get("http://api.example.com/user/123")
assert result.status_code == 200
assert result.json()["user_id"] == 123
# 创建数据库会话
db_session = MockFactory.create_database_session()
db_session.query.return_value.filter_by.return_value.first.return_value = Mock(id=1, name="test")
with patch('app.database.get_session', return_value=db_session):
# 测试数据库操作
user = app.database.get_user(1)
assert user.id == 1
assert user.name == "test"7.2 分层模拟策略
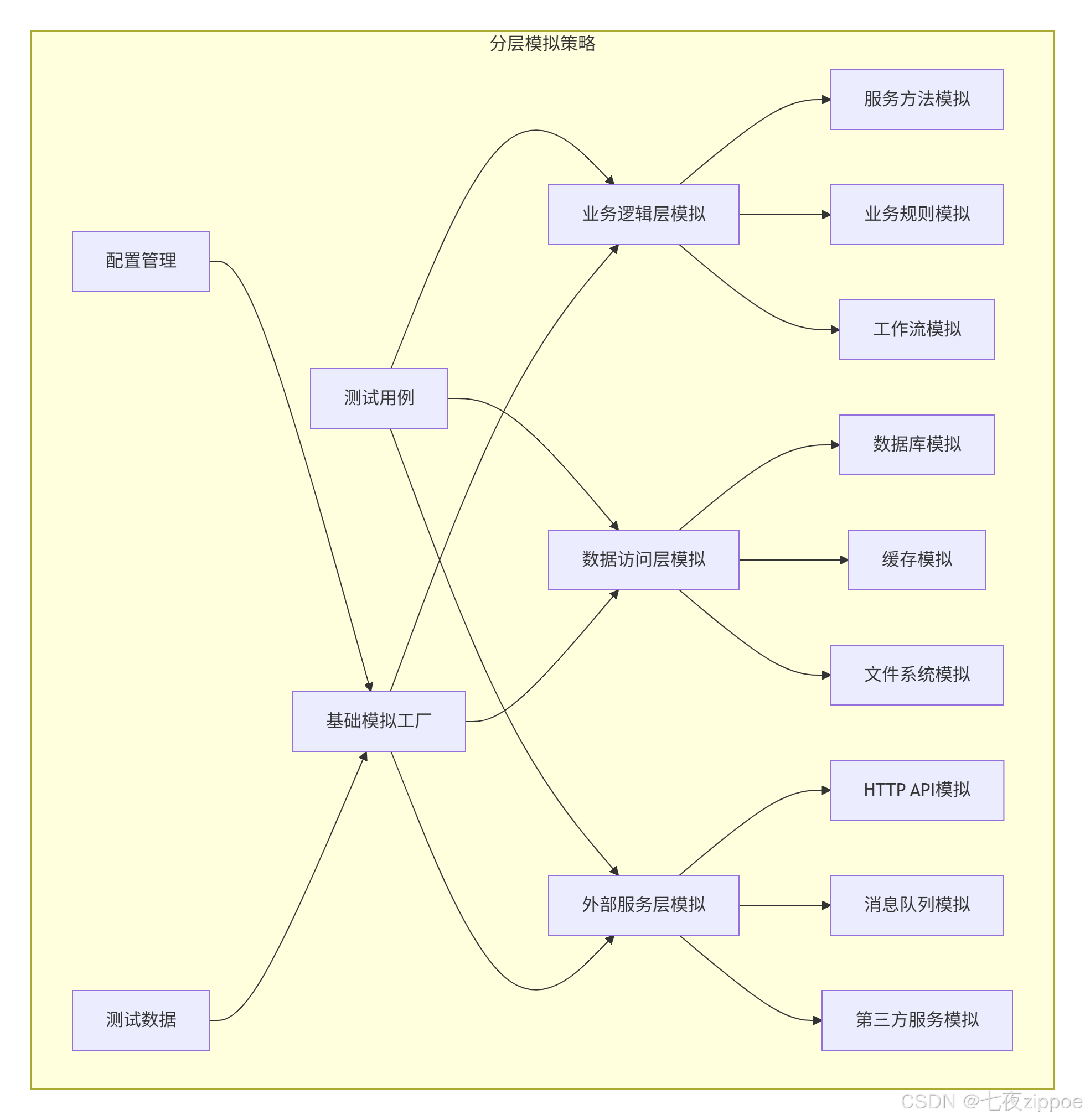
8. ⚡ 性能优化与最佳实践
8.1 模拟性能优化
python
# 1. 重用模拟对象
@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
def shared_mocks():
"""共享模拟对象"""
return {
'database': MockFactory.create_database_session(),
'http_client': MockFactory.create_http_client(),
'cache': MockFactory.create_cache_client()
}
def test_with_shared_mocks(shared_mocks):
"""使用共享模拟对象"""
with patch('app.database.session', shared_mocks['database']):
with patch('app.http.client', shared_mocks['http_client']):
# 测试代码...
# 2. 避免过度模拟
def test_avoid_over_mocking():
"""避免过度模拟"""
# ❌ 错误:过度模拟
mock_user = Mock()
mock_user.id = 1
mock_user.name = "test"
mock_user.email = "test@example.com"
mock_user.get_profile.return_value = Mock(age=25)
mock_user.save.return_value = True
# ✅ 正确:使用真实数据类
from dataclasses import dataclass
@dataclass
class User:
id: int
name: str
email: str
def get_profile(self):
return Profile(age=25)
def save(self):
return True
real_user = User(1, "test", "test@example.com")
# 只模拟外部依赖
with patch('external_service.process_user') as mock_service:
mock_service.return_value = True
result = process_user(real_user)
assert result is True
# 3. 使用autospec提高安全性
def test_with_autospec():
"""使用autospec确保模拟对象安全"""
# 普通模拟:不安全
unsafe_mock = Mock(some_module.SomeClass)
unsafe_mock.non_existent_method() # 不会报错
# autospec模拟:安全
safe_mock = Mock(some_module.SomeClass, autospec=True)
with pytest.raises(AttributeError):
safe_mock.non_existent_method() # 会报错
# patch中使用autospec
with patch('some_module.SomeClass', autospec=True) as mock_class:
instance = mock_class.return_value
instance.valid_method() # 正常
# instance.invalid_method() # 会报错
# 4. 模拟性能监控
import time
from functools import wraps
def measure_mock_performance(func):
"""测量模拟性能的装饰器"""
@wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
start = time.perf_counter()
result = func(*args, **kwargs)
end = time.perf_counter()
print(f"{func.__name__} 执行时间: {(end - start) * 1000:.2f}ms")
return result
return wrapper
@measure_mock_performance
def test_mock_performance():
"""测试模拟性能"""
mock_obj = Mock()
mock_obj.method.return_value = "result"
for _ in range(10000):
mock_obj.method()
mock_obj.method.assert_called()9. 🔧 故障排查与调试
9.1 常见问题解决
问题1:模拟对象没有按预期工作
python
# 解决方案:调试模拟对象
def debug_mock(mock_obj, name="mock"):
"""调试模拟对象"""
print(f"\n=== {name} 调试信息 ===")
print(f"调用次数: {mock_obj.call_count}")
print(f"调用参数: {mock_obj.call_args_list}")
print(f"返回值: {mock_obj.return_value}")
print(f"副作用: {mock_obj.side_effect}")
print(f"方法调用: {[m for m in dir(mock_obj) if not m.startswith('_')]}")
# 在测试中使用
def test_with_debug():
mock_obj = Mock()
mock_obj.method("test")
debug_mock(mock_obj, "测试模拟")
# 输出详细调试信息问题2:patch没有正确应用
python
# 解决方案:检查导入路径
def test_patch_path_debug():
"""调试patch路径"""
import some_module
# 检查实际导入路径
print(f"some_module路径: {some_module.__file__}")
print(f"some_module.external_api: {some_module.external_api}")
# 正确patch路径
with patch('some_module.external_api') as mock_api:
print(f"patch后: {some_module.external_api}")
assert some_module.external_api is mock_api
print(f"patch后恢复: {some_module.external_api}")问题3:异步模拟不工作
python
# 解决方案:检查事件循环
@pytest.mark.asyncio
async def test_async_debug():
"""调试异步模拟"""
async_mock = AsyncMock()
# 检查是否真的是AsyncMock
print(f"类型: {type(async_mock)}")
print(f"是否可等待: {hasattr(async_mock, '__await__')}")
# 手动调用魔术方法
result = await async_mock.__call__()
print(f"调用结果: {result}")
# 检查awaited调用
print(f"等待调用: {async_mock.await_args_list}")9.2 高级调试技巧
python
# 1. 模拟对象追踪
def create_traced_mock(name):
"""创建带追踪的模拟对象"""
mock_obj = Mock()
original_call = mock_obj.__call__
def traced_call(*args, **kwargs):
print(f"[{name}] 被调用: args={args}, kwargs={kwargs}")
return original_call(*args, **kwargs)
mock_obj.__call__ = traced_call
return mock_obj
# 2. 调用堆栈追踪
import traceback
def create_stack_traced_mock():
"""创建堆栈追踪模拟对象"""
mock_obj = Mock()
def call_with_trace(*args, **kwargs):
print("调用堆栈:")
traceback.print_stack(limit=10)
return mock_obj.return_value
mock_obj.side_effect = call_with_trace
return mock_obj
# 3. 性能分析
import cProfile
import pstats
def profile_mock_usage():
"""分析模拟对象使用性能"""
profiler = cProfile.Profile()
profiler.enable()
# 执行测试代码
test_with_mocks()
profiler.disable()
stats = pstats.Stats(profiler)
stats.sort_stats('cumulative')
stats.print_stats(20) # 前20个最耗时的函数10. 📚 总结与资源
10.1 官方文档
-
**unittest.mock官方文档** - 最权威的mock文档
-
**pytest-mock插件** - pytest集成mock
-
**AsyncMock文档** - 异步模拟详细说明
-
**Mock Cookbook** - 实用示例集合
10.2 最佳实践总结
模拟原则:
-
只模拟外部依赖,不模拟业务逻辑
-
使用autospec提高安全性
-
避免过度模拟
-
重用模拟对象提高性能
异步测试:
-
使用AsyncMock替代普通Mock
-
注意事件循环管理
-
使用assert_awaited系列方法
调试技巧:
-
使用debug_mock辅助函数
-
检查patch路径正确性
-
使用追踪模拟对象
企业级应用:
-
创建模拟对象工厂
-
分层模拟策略
-
性能监控和优化
10.3 未来趋势
-
AI生成模拟:自动分析代码生成模拟对象
-
智能模拟:根据调用上下文动态响应
-
可视化模拟:图形化模拟对象关系
-
云模拟服务:共享模拟配置和测试数据
最后的话 :模拟不是测试的"作弊",而是测试隔离的必要手段。好的模拟让测试更专注、更快速、更稳定。掌握unittest.mock,让你的测试代码更专业、更可靠。