1. 模块概述
1.1 EventLoop
EventLoop 是一个绑定到特定线程的事件循环,它在一个无限循环中等待 IO 事件,并跨线程任务调度分发处理。
| 原则 | 含义 | 违反后果 |
|---|---|---|
| 线程绑定 | 一个 EventLoop 只能在一个线程中运行 | 多线程操作会导致数据竞争、崩溃 |
| 唯一性 | 一个线程只能有一个 EventLoop | 多个 Loop 会导致事件处理混乱 |
| 非阻塞 | Loop 不能长时间阻塞,否则无法处理其他事件 | 整个网络库卡死 |
跨线程任务调度机制:
- 其他线程可通过 runInLoop() 向 I/O 线程提交任务
- 通过 eventfd 实现无锁唤醒(比 pipe 更高效)
1.2 EventLoopThread
EventLoopThread 是网络库中的 IO 线程封装类,它实现了"One Loop Per Thread"模式。EventLoopThread 的核心设计目标包括:
- 线程创建与管理:创建并管理一个独立的 IO 线程
- EventLoop 生命周期:在线程中创建和销毁 EventLoop
- 线程同步:确保 EventLoop 创建完成后再返回
- 优雅退出:支持线程的优雅退出
cpp
+--------------------------------------------------+
| EventLoopThread |
+--------------------------------------------------+
| |
| +-------------+ +-------------+ |
| | Thread | | EventLoop | |
| | (std::thread) | (线程内创建) | |
| +-------------+ +-------------+ |
| |
| +------------------------------------------+ |
| | 同步机制 | |
| | mutex_ + condition_variable_ | |
| +------------------------------------------+ |
| |
+--------------------------------------------------+启动流程:
+------------------+ +------------------+
| 主线程 | | IO 线程 |
| (startLoop) | | (threadFunc) |
+------------------+ +------------------+
| |
| thread_.start() |
|----------------------->|
| |
| wait(loop_ != nullptr)|
| |
| | 创建 EventLoop
| | loop_ = &loop
| |
| | notify_one()
|<-----------------------|
| |
| return loop_ |
| | loop.loop()
| | (事件循环运行)1.3 EventLoopThreadPool
EventLoopThreadPool 是 mymuduo 网络库中的事件循环线程池,它管理一组 EventLoopThread,实现主从 Reactor模式。EventLoopThreadPool 的核心设计目标包括:
-
线程池管理:创建和管理多个 IO 线程
-
负载均衡:通过轮询策略分发新连接
-
事件循环管理:每个线程运行独立的 EventLoop
-
线程初始化:支持线程初始化回调
+--------------------------------------------------+
| EventLoopThreadPool |
+--------------------------------------------------+
| |
| +-------------+ |
| | baseLoop | (主 Reactor,接受新连接) |
| +-------------+ |
| |
| +-------------+ +-------------+ +-------------+
| | Loop0 | | Loop1 | | Loop2 |
| | (SubReactor)| | (SubReactor)| | (SubReactor)|
| +-------------+ +-------------+ +-------------+
| | | |
| v v v
| +----------+ +----------+ +----------+
| | Conn1 | | Conn3 | | Conn5 |
| | Conn2 | | Conn4 | | Conn6 |
| +----------+ +----------+ +----------+
| |
+--------------------------------------------------+
2. 源码
2.1 EventLoop.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include "NonCopyable.h" // 禁用拷贝构造与赋值
#include "Timestamp.h" // 时间戳工具类
#include "CurrentThread.h" // 线程ID获取模块
#include <functional> // 函数对象支持
#include <vector> // 容器类型
#include <atomic> // 原子操作支持
#include <memory> // 智能指针
#include <mutex> // 互斥锁
// 事件处理流程:
// 1. EventLoop调用Poller的poll()方法等待事件
// 2. Poller通过epoll_wait获取就绪事件,填充activeChannels_
// 3. EventLoop遍历activeChannels_,调用每个Channel的handleEvent()
// 4. Channel根据事件类型调用预先注册的回调函数
namespace mymuduo {
class Channel;
class Poller;
class EventLoop : NonCopyable {
public:
using Functor = std::function<void()>; // 定义任务类型别名,支持任意可调用对象
EventLoop(); // 构造函数(绑定当前线程)
~EventLoop(); // 析构函数(清理资源)
void loop(); // 启动事件循环
void quit(); // 退出事件循环
Timestamp pollReturnTime() const { return pollRetureTime_; } // 获取poll操作的返回时间
void runInLoop(Functor cb); // 在当前loop线程中执行cb
void queueInLoop(Functor cb); // 将任务加入队列,唤醒loop所在的线程执行cb
void wakeup(); // 唤醒loop所在的线程
// 管理Channel的生命周期 => poller的方法
void updateChannel(Channel* channel);
void removeChannel(Channel* channel);
bool hasChannel(Channel* channel);
bool isInLoopThread() const { return threadId_ == CurrentThread::tid(); } // 判断Eventloop是否在当前线程
private:
void handleRead(); // 处理唤醒事件的回调函数
void doPendingFunctors(); // 执行回调
using ChannelList = std::vector<Channel*>; // 活跃Channel列表类型定义
std::atomic_bool looping_; // 循环标志
std::atomic_bool quit_; // 退出标志
const pid_t threadId_; // 所属线程ID
Timestamp pollRetureTime_; // poll返回时间
std::unique_ptr<Poller> poller_; // I/O多路复用器
int wakeupFd_; // 唤醒用文件描述符
std::unique_ptr<Channel> wakeupChannel_; // 唤醒通道
ChannelList activeChannels_; // 活跃Channel列表
std::atomic_bool callingPendingFunctors_;// 任务执行中标志
std::vector<Functor> pendingFunctors_; // 待执行任务队列
std::mutex mutex_; // 互斥锁保护共享数据
};
}2.2 EventLoop.cpp
cpp
#include "EventLoop.h"
#include "LogStream.h" // 日志模块
#include "Channel.h" // 通道抽象
#include "Poller.h" // 多路复用器
#include <sys/eventfd.h> // eventfd系统调用
#include <unistd.h> // 基础IO操作
#include <fcntl.h> // 文件控制
#include <errno.h> // 错误处理
#include <memory> // 智能指针
namespace mymuduo {
// 线程局部变量,每个线程唯一的EventLoop实例指针,防止一个线程创建多个EventLoop
__thread EventLoop* t_loopInThisThread = nullptr;
// 定义poll超时时间(10秒)
const int kPollTimeMs = 10000;
// 创建eventfd文件描述符,用来唤醒subReactor处理新来的channel
int createEventfd() {
// 创建非阻塞且close-on-exec的eventfd
int evtfd = ::eventfd(0, EFD_NONBLOCK | EFD_CLOEXEC);
if (evtfd < 0) {
LOG_ERROR << "eventfd creation failed: " << errno;
exit(-1);
}
return evtfd;
}
// EventLoop构造函数
EventLoop::EventLoop()
: looping_(false) // 初始未启动循环
, quit_(false) // 初始不退出
, callingPendingFunctors_(false) // 初始无任务执行
, threadId_(CurrentThread::tid()) // 绑定当前线程ID
, poller_(Poller::newDefaultPoller(this)) // 创建默认Poller
, wakeupFd_(createEventfd()) // 创建唤醒用fd
, wakeupChannel_(new Channel(this, wakeupFd_)) // 绑定唤醒通道
{
LOG_DEBUG << "EventLoop created: " << this << " in thread " << threadId_;
// 确保当前线程唯一绑定一个EventLoop
if (t_loopInThisThread) {
LOG_ERROR << "Another EventLoop exists in this thread!";
exit(-1);
} else {
t_loopInThisThread = this;
}
// 设置唤醒事件的读回调函数
wakeupChannel_->setReadCallback(std::bind(&EventLoop::handleRead, this));
// 每个EventLoop都监听wakeupFd_的读事件
wakeupChannel_->enableReading(); // channel::enableReading() -> EventLoop::updateChannel() -> Poller::updateChannel()
}
// EventLoop析构函数
EventLoop::~EventLoop() {
wakeupChannel_->disableAll(); // 禁用所有事件监听
wakeupChannel_->remove(); // 从Poller中移除通道
::close(wakeupFd_); // 关闭文件描述符
t_loopInThisThread = nullptr; // 清除线程局部变量
}
// 事件循环主函数
void EventLoop::loop() {
looping_ = true;
quit_ = false;
LOG_INFO << "EventLoop started: " << this;
// 主循环 I/O 线程,唯一有权操作 EventLoop、Poller、Channel的线程
while (!quit_) {
activeChannels_.clear(); // 清空活跃通道列表
pollRetureTime_ = poller_->poll(kPollTimeMs, &activeChannels_);
for (Channel* channel : activeChannels_) {
// Poller监听事件,上报eventloop,通知channel处理相应事件
channel->handleEvent(pollRetureTime_);
}
// 执行当前EventLoop需要处理的回调
/**
* IO线程 mainloop accept fd打包为channel分发给subloop
* mainloop 注册一个cb,由subloop在这里执行(需要先用weakupfd唤醒subloop)
*/
doPendingFunctors();
}
LOG_INFO << "EventLoop stopped: " << this;
looping_ = false;
}
// 退出事件循环
// 1.loop在自己的线程中调用quit,直接设置quit_为true,循环会自然退出
// 2.在非loop的线程中,调用quit,需要先唤醒事件循环不让poll阻塞,才能让循环退出
void EventLoop::quit() {
quit_ = true;
// 如果在非EventLoop线程调用quit,需要唤醒事件循环
if (!isInLoopThread()) wakeup();
}
// 在事件循环线程中执行任务
void EventLoop::runInLoop(Functor cb) {
if (isInLoopThread())
cb(); // 当前线程即事件循环线程,直接执行任务
else
queueInLoop(cb); // 跨线程调用,将任务加入队列
}
// 将任务加入队列(跨线程安全)
void EventLoop::queueInLoop(Functor cb) {
{
// 加锁保护任务队列
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
pendingFunctors_.emplace_back(cb);
}
// 需要唤醒的情况:非当前loop的线程 或 正在执行回调但又有了新回调(不唤醒则执行完后又阻塞在poll)
if (!isInLoopThread() || callingPendingFunctors_) {
wakeup();
}
}
// 处理唤醒事件(读取eventfd)
void EventLoop::handleRead() {
uint64_t one = 1;
ssize_t n = read(wakeupFd_, &one, sizeof(one));
if (n != sizeof(one)) {
LOG_ERROR << "EventLoop::handleRead() read " << n << " bytes instead of 8";
}
}
// 唤醒事件循环(发生写入eventfd,epoll_wait被唤醒,处理wakeupchannel的读回调,并顺序执行到doPendingFunctors();)
void EventLoop::wakeup() {
uint64_t one = 1;
ssize_t n = write(wakeupFd_, &one, sizeof(one));
if (n != sizeof(one)) {
LOG_ERROR << "EventLoop::wakeup() wrote " << n << " bytes instead of 8";
}
}
// 更新Channel(调用Poller的更新接口)
void EventLoop::updateChannel(Channel* channel) {
poller_->updateChannel(channel);
}
// 移除Channel(调用Poller的移除接口)
void EventLoop::removeChannel(Channel* channel) {
poller_->removeChannel(channel);
}
// 检查Channel是否存在(调用Poller的检查接口)
bool EventLoop::hasChannel(Channel* channel) {
return poller_->hasChannel(channel);
}
// 执行待处理任务
void EventLoop::doPendingFunctors() {
// 临时容器,用于批量取出任务
std::vector<Functor> functors;
// 标记当前正在执行任务(防止重复唤醒)
callingPendingFunctors_ = true;
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
functors.swap(pendingFunctors_); // 把pendingFunctors_的任务全部取出到局部的functors
// 防止在执行任务时,有其他loop调用queueInLoop()加入任务而阻塞
}
// 执行所有任务(此时已释放锁)
for (const Functor& functor : functors) {
functor(); // 执行回调函数
}
// 恢复状态
callingPendingFunctors_ = false;
}
}2.3 EventLoopThread.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include "NonCopyable.h"
#include "Thread.h"
#include <functional>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>
#include <string>
namespace mymuduo
{
class EventLoop;
class EventLoopThread : NonCopyable
{
public:
// 定义线程初始化回调函数的类型,接收一个EventLoop指针
using ThreadInitCallback = std::function<void(EventLoop *)>;
// 构造函数,接收线程初始化回调函数和线程名称(默认为空字符串)
EventLoopThread(const ThreadInitCallback &cb = ThreadInitCallback(), const std::string &name = std::string());
~EventLoopThread(); // 析构函数
EventLoop *startLoop(); // 启动事件循环并返回EventLoop指针
private:
void threadFunc(); // 线程执行的函数,在新线程中运行
EventLoop *loop_; // 指向EventLoop的指针
bool exiting_; // 退出标志
Thread thread_; // 封装的Thread对象
std::mutex mutex_; // 互斥锁,用于线程同步
std::condition_variable cond_; // 条件变量,用于线程同步
ThreadInitCallback callback_; // 线程初始化回调函数,在threadFunc中调用
};
}2.4 EventLoopThread.cpp
cpp
#include "EventLoopThread.h"
#include "EventLoop.h"
using namespace mymuduo;
// 构造函数实现
EventLoopThread::EventLoopThread(const ThreadInitCallback &cb,
const std::string &name)
: loop_(nullptr) // 初始时EventLoop指针为空
, exiting_(false) // 初始退出标志为false
, thread_(std::bind(&EventLoopThread::threadFunc, this), name) // 创建Thread对象,绑定threadFunc方法
, mutex_()
, cond_()
, callback_(cb) {}
// 析构函数实现
EventLoopThread::~EventLoopThread(){
exiting_ = true;
if (loop_ != nullptr){
// 退出EventLoop
loop_->quit();
// 等待线程结束
thread_.join();
}
}
// 启动事件循环并返回EventLoop指针的方法实现
EventLoop *EventLoopThread::startLoop(){
// 启动线程
thread_.start();
EventLoop *loop = nullptr;
{
// 加锁,确保线程安全
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
// 等待EventLoop指针不为空,即新线程thread_中EventLoop已创建
cond_.wait(lock, [this](){return loop_ != nullptr;});
loop = loop_;
}
return loop;
}
// 线程执行的函数,在新线程中运行
void EventLoopThread::threadFunc(){
// 创建一个EventLoop对象,one loop per thread,在线程中创建loop对象,线程关闭loop销毁,不用再外部管理loop
EventLoop loop;
if (callback_) callback_(&loop); // 执行线程初始化回调函数
{
// 加锁,确保线程安全
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
// 将EventLoop指针赋值给loop_
loop_ = &loop;
// 通知等待的线程,EventLoop已创建
cond_.notify_one();
}
// 启动EventLoop的事件循环
loop.loop();
{
// 加锁,确保线程安全
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
// 事件循环结束,将EventLoop指针置为空
loop_ = nullptr;
}
}2.5 EventLoopThreadPool.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include "NonCopyable.h"
#include <functional>
#include <memory>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
namespace mymuduo
{
class EventLoop;
class EventLoopThread;
class EventLoopThreadPool : NonCopyable
{
public:
// 定义线程初始化回调函数的类型,接收一个EventLoop指针
using ThreadInitCallback = std::function<void(EventLoop *)>;
EventLoopThreadPool(EventLoop *baseLoop, const std::string &nameArg);
~EventLoopThreadPool();
void setThreadNum(int numThreads); // 设置线程池中线程数量
void start(const ThreadInitCallback &cb); // 启动线程池,cb为每个线程初始化时调用的回调函数
EventLoop *getNextLoop(); // 获取下一个事件循环,采用轮询策略
std::vector<EventLoop *> getAllLoops(); // 获取所有事件循环的指针
private:
EventLoop *baseLoop_; // 基础事件循环(通常是主线程的事件循环)
std::string name_; // 线程池名称
bool started_; // 线程池是否已启动
int numThreads_; // 线程池中线程数量
int next_; // 轮询索引,用于选择下一个事件循环
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<EventLoopThread>> threads_; // 线程池中的线程对象
std::vector<EventLoop *> loops_; // 线程池中所有事件循环的指针
};
} // namespace mymuduo2.6 EventLoopThreadPool.cpp
cpp
#include "EventLoopThreadPool.h"
#include "EventLoopThread.h"
using namespace mymuduo;
/**
* @brief 构造函数,初始化事件循环线程池
* @param baseLoop 主事件循环(通常由主线程运行)
* @param nameArg 线程池名称
*/
EventLoopThreadPool::EventLoopThreadPool(EventLoop *baseLoop, const std::string &nameArg)
: baseLoop_(baseLoop) // 主事件循环
, name_(nameArg) // 线程池名称
, started_(false) // 是否已启动标志
, numThreads_(0) // 线程数量初始化为0
, next_(0){} // 下一个选择的事件循环索引初始化为0
EventLoopThreadPool::~EventLoopThreadPool() {}
/**
* @brief 设置线程池中线程的数量
* @param numThreads 要设置的线程数量
*/
void EventLoopThreadPool::setThreadNum(int numThreads) {
numThreads_ = numThreads;
}
/**
* @brief 启动线程池
* @param cb 线程初始化回调函数
*/
void EventLoopThreadPool::start(const ThreadInitCallback &cb){
started_ = true; // 标记线程池已启动
// 创建并启动指定数量的线程
for (int i = 0; i < numThreads_; ++i){
// 为每个线程创建唯一的名称,char数组大小需要在编译时确定,故使用std::string
std::string threadName = name_ + std::to_string(i);
// 创建事件循环线程
EventLoopThread *t = new EventLoopThread(cb, threadName);
// 将线程对象存入线程列表
threads_.push_back(std::unique_ptr<EventLoopThread>(t));
// 启动线程的事件循环并保存返回的事件循环指针
loops_.push_back(t->startLoop());
}
// 如果线程数量为0且提供了回调函数,则在主事件循环上执行回调
if (numThreads_ == 0 && cb) {
cb(baseLoop_);
}
}
/**
* @brief 获取下一个事件循环对象(轮询方式)
* @return 返回下一个事件循环指针
*/
EventLoop *EventLoopThreadPool::getNextLoop(){
EventLoop *loop = baseLoop_; // 默认返回主事件循环
// 如果线程池中有事件循环可用,则轮询选择一个
if(!loops_.empty()){
loop = loops_[next_];
++next_;
// 如果到达末尾,从头开始
if(next_ >= loops_.size()) {
next_ = 0;
}
}
return loop;
}
/**
* @brief 获取所有事件循环对象
* @return 包含所有事件循环指针的vector
*/
std::vector<EventLoop *> EventLoopThreadPool::getAllLoops(){
// 如果线程池中没有事件循环,返回只包含主事件循环的vector
if (loops_.empty()) {
return std::vector<EventLoop *>(1, baseLoop_);
}
else {
return loops_;
}
}3. 模块详解
3.1 EvenLoop
3.1.1 事件循环 loop
cpp
void EventLoop::loop() {
looping_ = true;
quit_ = false;
while (!quit_) { // 主循环
activeChannels_.clear(); // 1. 清空上一次的活跃列表
// 2. 等待事件(阻塞在这里)
pollRetureTime_ = poller_->poll(kPollTimeMs, &activeChannels_);
// 3. 处理所有就绪的 Channel
for (Channel* channel : activeChannels_) {
channel->handleEvent(pollRetureTime_);
}
// 4. 执行待处理任务(跨线程任务)
doPendingFunctors();
}
looping_ = false;
}时序:
cpp
时间轴 →
loop() 开始
│
├─> poll() 阻塞等待 ──────────────┐
│ │ (10 秒或事件到达)
│ ▼
│ epoll_wait 返回
│ │
├─> 遍历 activeChannels_ │
│ channel->handleEvent() │
│ │
├─> doPendingFunctors() │
│ 执行任务队列 │
│ │
└─> 检查 quit_ ── 是 ──> 退出 │
└─ 否 ──> 回到 poll() ──┘3.1.2 跨线程无锁唤醒机制
cpp
// 在事件循环线程中执行任务
void EventLoop::runInLoop(Functor cb) {
if (isInLoopThread())
cb(); // 当前线程即事件循环线程,直接执行任务
else
queueInLoop(cb); // 跨线程调用,将任务加入队列
}
// 将任务加入队列(跨线程安全)
void EventLoop::queueInLoop(Functor cb) {
{
// 加锁保护任务队列
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
pendingFunctors_.emplace_back(cb);
}
// 需要唤醒的情况:非当前loop的线程 或 正在执行回调但又有了新回调(不唤醒则执行完后又阻塞在poll)
if (!isInLoopThread() || callingPendingFunctors_) {
wakeup();
}
}
// 唤醒事件循环(发生写入eventfd,epoll_wait被唤醒,处理wakeupchannel的读回调,并顺序执行到doPendingFunctors();)
void EventLoop::wakeup() {
uint64_t one = 1;
ssize_t n = write(wakeupFd_, &one, sizeof(one));
if (n != sizeof(one)) {
LOG_ERROR << "EventLoop::wakeup() wrote " << n << " bytes instead of 8";
}
}
// 事件循环主函数
void EventLoop::loop() {
looping_ = true;
quit_ = false;
LOG_INFO << "EventLoop started: " << this;
// 主循环 I/O 线程,唯一有权操作 EventLoop、Poller、Channel的线程
while (!quit_) {
activeChannels_.clear(); // 清空活跃通道列表
pollRetureTime_ = poller_->poll(kPollTimeMs, &activeChannels_);
for (Channel* channel : activeChannels_) {
// Poller监听事件,上报eventloop,通知channel处理相应事件
channel->handleEvent(pollRetureTime_);
}
// 执行当前EventLoop需要处理的回调
/**
* IO线程 mainloop accept fd打包为channel分发给subloop
* mainloop 注册一个cb,由subloop在这里执行(需要先用weakupfd唤醒subloop)
*/
doPendingFunctors();
}
LOG_INFO << "EventLoop stopped: " << this;
looping_ = false;
}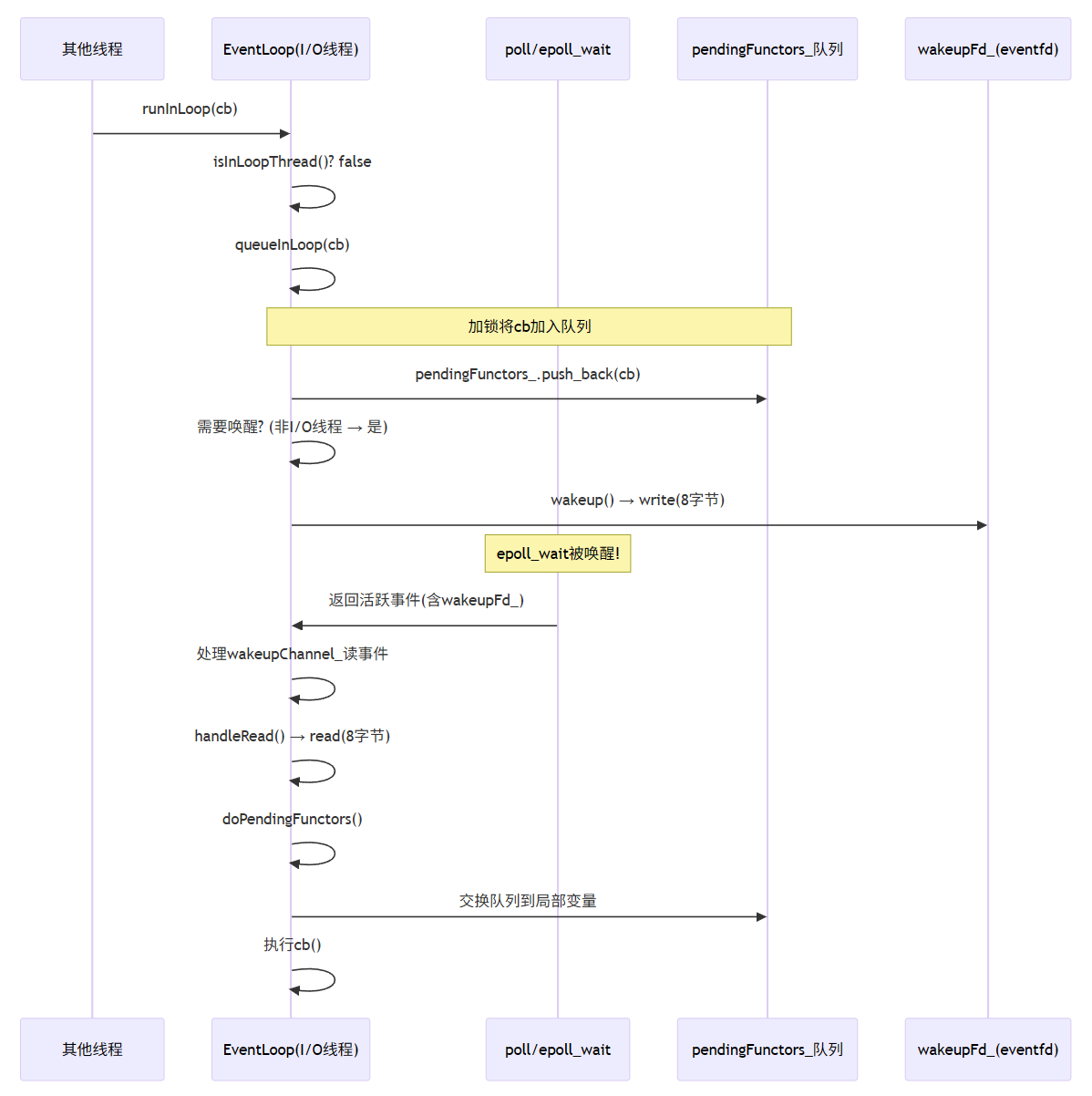
注意:其他线程与 EventLoop 线程操作的都是同一个 EventLoop!
**当其他线程调用 EventLoop::runInLoop(cb) 时,因 当前线程ID ≠ EventLoop.threadId_,自动转入 queueInLoop(cb):**先加锁将任务存入 pendingFunctors_ 队列,再判断"需唤醒"(跨线程调用 或 I/O 线程正执行任务中),随即调用 wakeup() 向 eventfd 写入 8 字节;此操作触发 epoll 事件,使阻塞在 poll() 的 EventLoop 线程立即返回,循环中先处理 wakeupChannel_ 的读事件(handleRead() 清空 eventfd),继而调用 doPendingFunctors():交换队列至局部变量(释放锁后无锁执行),逐个运行回调。全程仅入队时短暂加锁,任务执行完全串行化于 I/O 线程,既避免并发竞争,又确保新任务零延迟触发。
3.2 EventLoopThread 的生命周期管理
1. 创建阶段(构造函数)
cpp
EventLoopThread thread(callback, "SubReactor-1");- 内部状态 :
- loop_ = nullptr(EventLoop 尚未创建)
- exiting_ = false(未标记退出)
- thread_ 对象已构造但线程未启动(仅绑定 threadFunc)
2. 启动阶段(startLoop())
cpp
EventLoop* loop = thread.startLoop();| 主线程(调用者) | 新线程(worker) |
|---|---|
| 1. 调用 thread_.start() 启动新线程 | → |
| 2. 加锁 + cond_.wait() 阻塞等待 | 3. 执行 threadFunc() |
| 4. 栈上创建执行 threadFunc() | |
| 5. 执行初始化回调 callback_(&loop) | |
| 6. 加锁设置 loop_ = &loop | |
| 7. cond_.notify_one() 唤醒主线程 | |
| 8. 被唤醒,获取 loop_ 指针 | 9. 进入 loop.loop() 事件循环 |
| 10. 返回 loop 指针 | → 持续运行事件循环 |
- 生命周期绑定 :栈上创建 EventLoop(非堆分配),EventLoop 与线程栈帧同生共死,无需手动 delete
- 安全同步 :条件变量确保返回的指针必定有效(避免返回 nullptr)
3. 运行阶段(事件循环)
- 新线程持续执行 loop.loop()
- 所有 Channel 事件、跨线程任务均在此线程串行处理
- 外部通过返回的 loop 指针提交任务(如 loop->runInLoop(cb))
4. 退出阶段(析构函数)
cpp
// EventLoopThread 对象析构时
~EventLoopThread() {
exiting_ = true;
if (loop_ != nullptr) {
loop_->quit(); // 1. 设置退出标志
thread_.join(); // 2. 等待线程结束
}
}退出流程:
- 主线程调用 loop_->quit() → 设置 quit_ = true
- 若在非 I/O 线程调用 → 自动 wakeup() 唤醒阻塞的 poll()
- 新线程中 loop.loop() 检测到 quit_ == true → 退出 while 循环
- threadFunc() 执行完毕:
- 加锁设置 loop_ = nullptr
- 栈上 EventLoop 对象自动析构(~EventLoop())
- thread_.join() 返回 → 析构完成
3.3 EventLoopThreadPool 负载均衡
cpp
/**
* @brief 获取下一个事件循环对象(轮询方式)
* @return 返回下一个事件循环指针
*/
EventLoop *EventLoopThreadPool::getNextLoop(){
EventLoop *loop = baseLoop_; // 默认返回主事件循环
// 如果线程池中有事件循环可用,则轮询选择一个
if(!loops_.empty()){
loop = loops_[next_];
++next_;
// 如果到达末尾,从头开始
if(next_ >= loops_.size()) {
next_ = 0;
}
}
return loop;
}