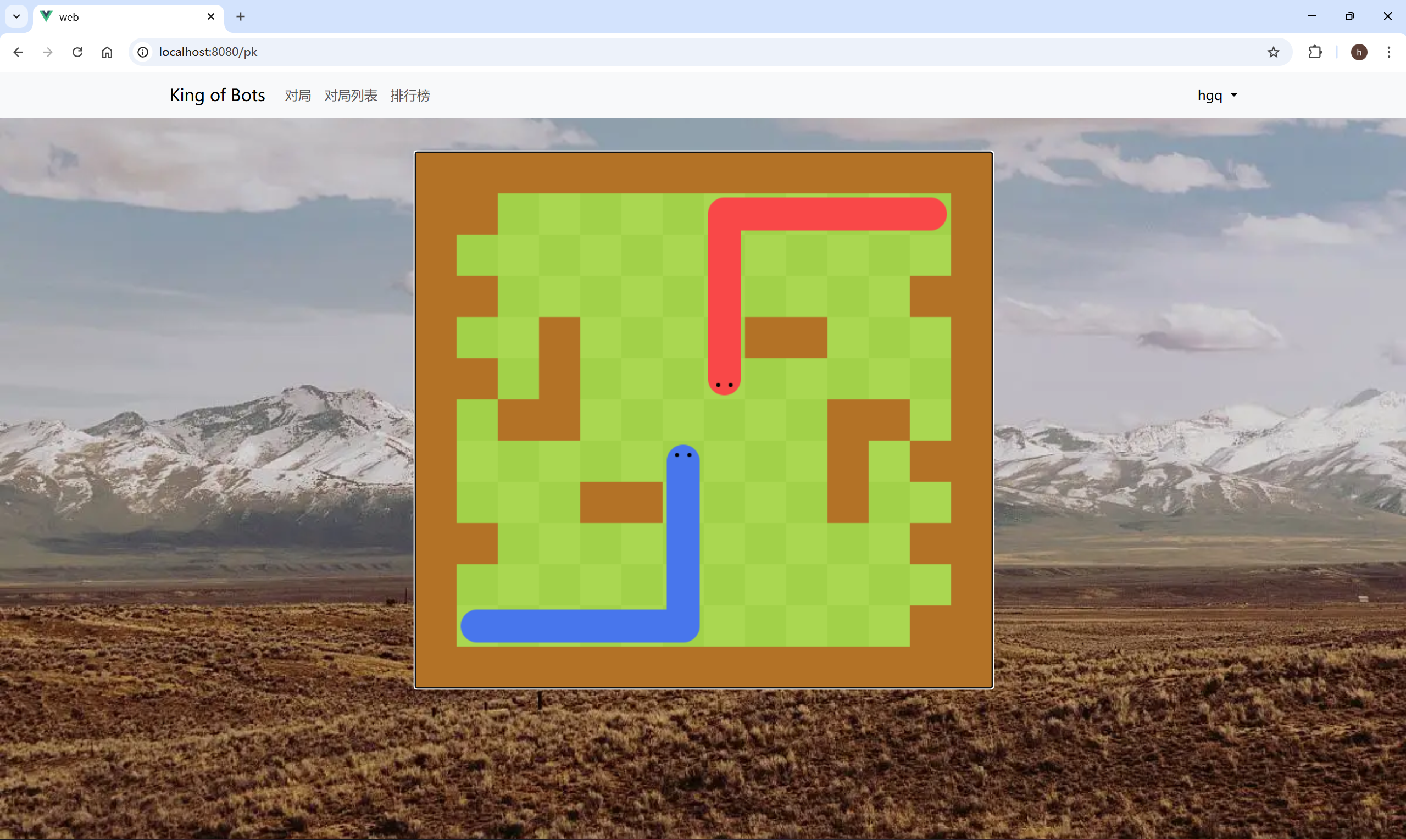
基本的移动
在 Snake.js 中添加代码,实现蛇头的向右移动。
js
import { AcGameObject } from "./AcGameObject";
import { Cell } from "./Cell";
export class Snake extends AcGameObject {
constructor(info, gamemap) {
super(); // 继承AcGameObject的方法
this.id = info.id;
this.color = info.color;
this.gamemap = gamemap;
this.cells = [new Cell(info.r, info.c)]; // 存放蛇的身体, cell[0] 存放蛇头
// new add
this.speed = 5;
}
update_move() {
// 向右移动
this.cells[0].x += this.speed * this.timedelta / 1000;
//向上移动
//this.cells[0].y -= this.speed * this.timedelta / 1000;
}
update() {
this.update_move();
this.render();
}this.speed:蛇的移动速度,设定为 5。这是在更新运动时用到的一个重要参数。
update_move() 方法负责更新蛇头的位置。根据当前的时间增量 this.timedelta,计算出蛇头的新位置。
- 在这个例子中,蛇头向右移动,this.cells[0].x 增加,移动的距离是 speed * timedelta / 1000,其中 this.timedelta 是每帧持续的时间(以毫秒为单位),将其转换为秒以计算实际移动距离。
- 注释掉的部分 (this.cells[0].y -= this.speed * this.timedelta / 1000;) 表示可以向上移动,但在当前实现中并未启用。
update() 方法是游戏的主要更新循环,会调用 update_move() 方法更新蛇的位置,并调用 render() 方法绘制当前状态。
连贯的移动
修改 Snake.js
js
import { AcGameObject } from "./AcGameObject";
import { Cell } from "./Cell";
export class Snake extends AcGameObject {
constructor(info, gamemap) {
super();
this.id = info.id;
this.color = info.color;
this.gamemap = gamemap;
//存放蛇的身体;
this.cells = [new Cell(info.r, info.c)];
this.speed = 5; // 蛇每秒走5格
// new add
this.direction = -1; // -1表示没有指令 0 1 2 3
this.status = "idle"; // 静止, move 移动 die 死亡
}
}this.direction:
-
该属性用于表示蛇的移动方向。
-
初始值设为 -1,表示没有移动指令。可以使用不同的数值来表示不同的方向:
- 0:向上
- 1:向右
- 2:向下
- 3:向左
-
这个设计允许你在后续的代码中根据用户输入或游戏逻辑来更新蛇的移动方向。
this.status:
- 该属性用来表示蛇的当前状态。
- 初始值设为 "idle",表示蛇处于静止状态。
- 可能的状态包括:
- "idle":静止状态
- "move":移动状态
- "die":死亡状态
- 通过这一状态管理,可以在游戏逻辑中更容易地处理不同的行为(例如,只有在状态为 "move" 时才更新蛇的位置)。
check_ready() 方法的主要功能是检查游戏中的两条蛇是否准备好进入下一回合,放在 GameMap.js 中。
js
check_ready() { // 判断两条蛇是否准备下一回合了
for (const snake of this.snakes) {
if (snake.status !== "idle") return false;
if (snake.direction === -1) return false;
}
return true;
}遍历蛇的数组,检查每条蛇的状态属性 (status) 是否为 "idle"。如果有任意一条蛇的状态不是 "idle",即表示它正在移动或执行其他操作,那么方法就会返回 false,表明不可以进入下一回合。
检查蛇的方向属性 (direction) 是否等于 -1。在很多游戏中,-1 通常用来表示蛇处于一种无效或暂停的状态(例如,死亡、暂停或等待输入)。如果任意一条蛇的方向为 -1,则同样返回 false,表示它们不能开始下一回合。
如果所有蛇都处于 "idle" 状态且没有蛇的方向为 -1,那么方法最后会返回 true,表示所有的蛇都准备好进入下一回合。
在 Snake.js 中更新一下蛇的状态
js
this.next_cell = null; //下一步的目标位置
this.dr = [-1, 0, 1, 0]; // 行
this.dc = [0, 1, 0, -1]; //列
this.step = 0;
next_step() {
const d = this.direction;
this.next_cell = new Cell(this.cells[0].r + this.dr[d], this.cells[0].c + this.dc[d]);
this.direction = -1;
this.status = "move";
this.step ++ ;
}next_cell 属性用来存储蛇头下一个要移动到的位置,初始值为 null。
dr 和 dc 数组分别定义了蛇在四个方向(上、右、下、左)的行和列变化。
dr 数组:
- -1: 向上移动一行
- 0: 不移动(列不变)
- 1: 向下移动一行
- 0: 不移动(列不变)
dc 数组:
- 0: 不移动(行不变)
- 1: 向右移动一列
- 0: 不移动(行不变)
- -1: 向左移动一列
step 属性表示蛇当前的移动步骤计数,初始值为 0,用于跟踪蛇已经移动的步数。
根据当前方向 d,利用 dr 和 dc 数组计算出蛇头下一个位置的行 ® 和列 © 坐标,并创建一个新的 Cell 实例 next_cell。这个实例将存储蛇头即将移动到的位置。
将方向设置为 -1,通常用来表示蛇在等待或暂停状态。这意味着在下一次调用 next_step() 方法之前,蛇不会继续移动。
将状态设置为 "move",表示蛇正在移动中。这可以用于游戏逻辑,例如在渲染时决定蛇的动作。
增加 step 计数,每当调用 next_step() 方法时,这个计数就会加一,以便记录蛇移动的总步数。
在 GameMap.js 中更新
js
next_step() {
for (const snake of this.snake) {
snake.next_step();
}
}
update() {
this.update_size();
if (this.check_ready()) {
this.next_step();
}
this.render();
}next_step方法负责处理所有蛇的下一步移动。
使用 for...of 循环遍历 this.snake 数组,假设这个数组包含了游戏中所有的蛇(可能是单条蛇也可能是多条蛇)。
对于每个 snake 对象,调用其 next_step() 方法,这意味着每条蛇都会根据其内部逻辑计算出下一步的位置并更新状态。
update() 方法:
调用 update_size() 方法,可能用于调整游戏界面的大小或更新蛇的某些属性(例如,蛇的长度、蛇身的尺寸等)。具体实现取决于游戏的设计。
调用 check_ready() 方法来检查是否可以进行下一步移动。这个方法可能会检测是否满足一些条件,例如游戏是否正在进行、玩家是否有输入、时间是否到了等等。
如果返回值为 true,则调用 next_step() 方法,更新所有蛇的位置。
最后,调用 render() 方法负责绘制游戏的当前状态。
读取键盘的操作
在 Snake.js 中加入一个辅助函数,用来获取方向。
js
//辅助函数
set_direction(d) {
this.direction = d;
}在 GameMap.js 中修改,添加事件。
js
add_listening_events() {
this.ctx.canvas.focus();
const [snake0, snake1] = this.snakes;
this.ctx.canvas.addEventListener("keydown", e => {
if (e.key === 'w') snake0.set_direction(0);
else if (e.key === 'd') snake0.set_direction(1);
else if (e.key === 's') snake0.set_direction(2);
else if (e.key === 'a') snake0.set_direction(3);
else if (e.key === 'ArrowUp') snake1.set_direction(0);
else if (e.key === 'ArrowRight') snake1.set_direction(1);
else if (e.key === 'ArrowDown') snake1.set_direction(2);
else if (e.key === 'ArrowLeft') snake1.set_direction(3);
});
}add_listening_events()该方法用于添加键盘事件监听器,使得游戏能够响应玩家的输入。
this.ctx.canvas.focus(); 使得游戏画布(canvas)获得焦点,以便能够接收键盘事件。这一步很重要,因为只有获得焦点的元素才能接收到键盘按键事件。
假设 this.snakes 是一个包含两个蛇对象的数组(snake0 和 snake1),通常是两个玩家分别控制的蛇。这种设计允许在同一场景中有两条蛇进行对战。
这部分代码根据用户按下的不同键来设置对应蛇的移动方向:
对于 snake0(第一条蛇),使用 WASD 键来控制:
- W:向上移动(方向 0)。
- D:向右移动(方向 1)。
- S:向下移动(方向 2)。
- A:向左移动(方向 3)。
对于 snake1(第二条蛇),使用箭头键来控制:
- ArrowUp:向上移动(方向 0)。
- ArrowRight:向右移动(方向 1)。
- ArrowDown:向下移动(方向 2)。
- ArrowLeft:向左移动(方向 3)。
每当按下对应的键,就会调用该蛇的 set_direction 方法,传入相应的方向值,以更新蛇的运动方向。
在 Snake.js 中更新状态:
js
update() { // 每一帧执行一次
if (this.status === 'move') {
this.uppdate_move()
}
this.render();
}在每一帧中进行游戏状态的更新和渲染。如果游戏状态允许移动(即状态为 'move'),则调用相应的方法处理移动逻辑。无论状态如何,都会调用 render() 方法来绘制游戏画面,从而确保玩家始终能够看到最新的游戏信息。
实现真正的移动
在 snake.js 中修改 :
js
import { AcGameObject } from "./AcGameObject";
import { Cell } from "./Cell";
export class Snake extends AcGameObject{
constructor(info, gamemap){
super();
this.id = info.id;
this.color = info.color;
this.gamemap = gamemap;
this.cells = [new Cell(info.r, info.c)]; //存放蛇的身体,cell[0]存放蛇头
this.next_cell = null; //下一步的目标位置
this.speed = 5; //蛇的速度
this.direction = -1; //-1表示没有指令,0、1、2、3表示上右下左
this.status = "idle"; //idle表示静止,move表示正在移动,die表示死亡
this.dr = [-1, 0, 1, 0]; //4个方向行的偏移量
this.dc = [0, 1, 0, -1]; //4个方向列的偏移量
this.step = 0; //表示回合数
this.eps = 1e-2; //允许的误差
}
start(){
}
set_direction(d){
this.direction = d;
}
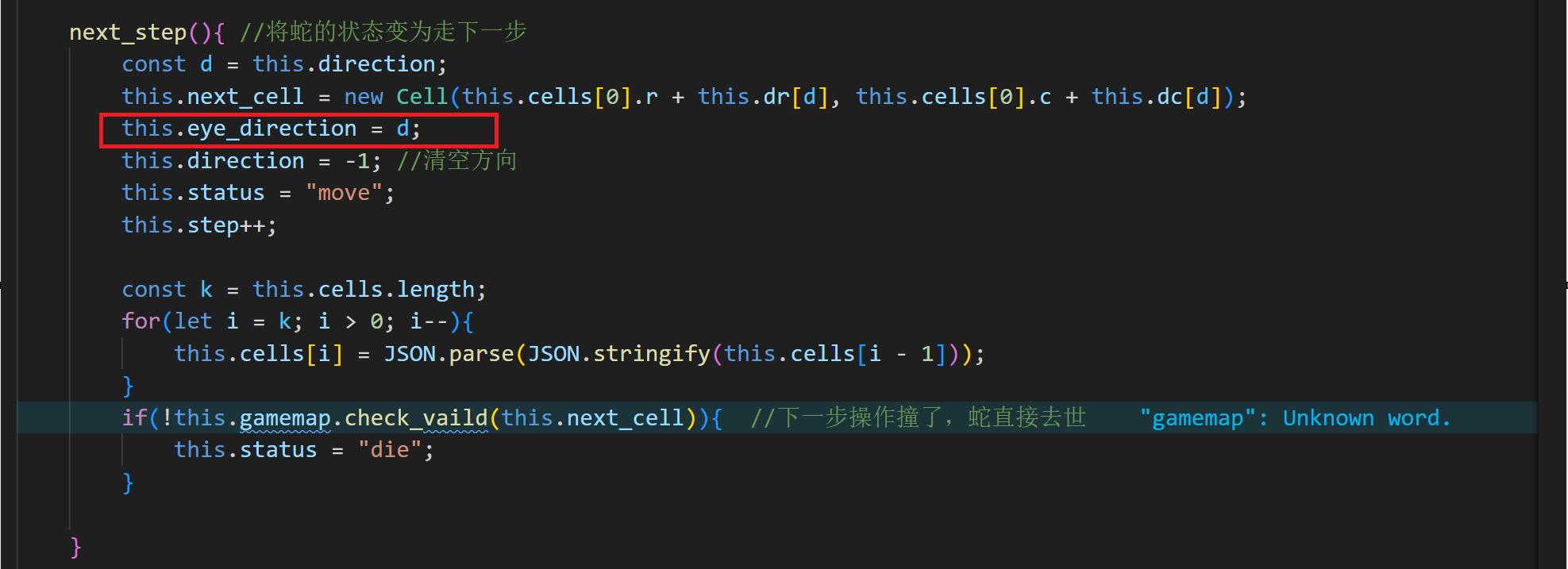
next_step(){ //将蛇的状态变为走下一步
const d = this.direction;
this.next_cell = new Cell(this.cells[0].r + this.dr[d], this.cells[0].c + this.dc[d]);
this.direction = -1; //清空方向
this.status = "move";
this.step++;
const k = this.cells.length;
for(let i = k; i > 0; i--){
this.cells[i] = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(this.cells[i - 1]));
}
}
update_move(){
const dx = this.next_cell.x - this.cells[0].x;
const dy = this.next_cell.y - this.cells[0].y;
const distance = Math.sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
if(distance < this.eps){
this.cells[0] = this.next_cell; //添加一个新蛇头
this.next_cell = null;
this.status = 'idle'; //走完了,停下来
} else {
const move_distance = this.speed * this.timedelta / 1000; //每两帧之间走过的距离
this.cells[0].x += move_distance * dx / distance;
this.cells[0].y += move_distance * dy / distance;
}
}
update(){ //每一帧执行一次
if(this.status === 'move'){
this.update_move();
}
this.render();
}
render() {
const L = this.gamemap.L;
const ctx = this.gamemap.ctx;
ctx.fillStyle = this.color;
for(const cell of this.cells){
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(cell.x * L, cell.y * L, L / 2, 0, Math.PI * 2);
ctx.fill();
}
}
}
蛇尾移动
在 Snake.js 中添加代码,判断蛇尾是否增长
js
check_tail_increasing(){ //检测当前回合,蛇的长度是否会增加
if(this.step <= 10) return true;
if(this.step % 3 === 1) return true;
return false;
}如果当前步骤数小于或等于 10(即游戏的前 10 步),则直接返回 true,表示蛇的长度会增加。
如果当前步骤数除以 3 的余数为 1(即每隔 3 步的第 1 步),则也返回 true,表示蛇的长度会在该步骤中增加。
check_tail_increasing 方法通过逻辑判断确定蛇的长度是否会在当前回合增加。它结合了步骤数的范围和模运算来控制蛇的增长频率。前 10 步始终允许增长,而之后则在每隔 3 步的特定步骤中增加。
修改 Snake.js , 判断蛇尾是否在下一步是否增长
js
this.next_cell = null; //下一步的目标位置
this.dr = [-1, 0, 1, 0]; // 行
this.dc = [0, 1, 0, -1]; //列
this.step = 0;
this.eps = 1e-2 // 允许的误差
next_step() {
const d = this.direction;
this.next_cell = new Cell(this.cells[0].r + this.dr[d], this.cells[0].c + this.dc[d]);
this.direction = -1;
this.status = "move";
this.step ++ ;
// 求长度
const k = this.cells.length;
for (let i = k; i > 0; i -- ) { // 初始元素不变 每一个元素往后移动一位
this.cells[i] = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(this.cells[i - 1]));
}
}
update_move() {
const dx = this.next_cell.x - this.cells[0].x;
const dy = this.next_cell.y - this.cells[0].y;
const distance = Math.sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
if (distance < this.eps) { // 走到目标点了
this.cells[0] = this.next_cell; // 添加一个新蛇头
this.next_cell = null;
this.status = "idle"; // 走完了,停下来
if (!this.check_tail_increasing()) { // 蛇不变长。
this.cells.pop();
}
} else {
const move_distance = this.speed * this.timedelta / 1000;
this.cells[0].x += move_distance * dx / distance;
this.cells[0].y += move_distance * dy / distance;
if (!this.check_tail_increasing()) {
const k = this.cells.length;
const tail = this.cells[k - 1], tail_target = this.cells[k - 2];
const tail_dx = tail_target.x - tail.x;
const tail_dy = tail_target.y - tail.y;
tail.x += move_distance * tail_dx / distance;
tail.y += move_distance * tail_dy / distance;
}
}
}
基本效果:

美化蛇
修改 Snake.js ,让蛇变得连贯、缩小一点。
js
render() {
const L = this.gamemap.L;
const ctx = this.gamemap.ctx;
ctx.fillStyle = this.color;
for(const cell of this.cells){
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(cell.x * L, cell.y * L, L / 2 * 0.8, 0, Math.PI * 2);
ctx.fill();
}
for (let i = 1; i < this.cells.length; i ++ ) {
const a = this.cells[i - 1], b = this.cells[i];
if (Math.abs(a.x - b.x) < this.eps && Math.abs(a.y - b.y) < this.eps)
continue;
if (Math.abs(a.x - b.x) < this.eps) {
ctx.fillRect((a.x - 0.4) * L, Math.min(a.y, b.y) * L, L * 0.8, Math.abs(a.y - b.y) * L);
} else {
ctx.fillRect(Math.min(a.x, b.x) * L, (a.y - 0.4) * L, Math.abs(a.x - b.x) * L, L * 0.8);
}
}
}绘制蛇的连接部分:
循环从第二个单元格开始(i = 1),用于绘制蛇体各部分之间的连接部分。
const a = this.cells[i - 1], b = this.cells[i]; 获取前一个和当前单元格。
第一个 if 语句检查两个单元格是否非常接近,如果是,则跳过当前迭代(不绘制连接部分)。
第二个 if 语句检查两个单元格的 x 坐标是否相等(即它们在垂直方向上对齐)。如果是,则绘制一条垂直矩形,表示蛇的连接部分;ctx.fillRect() 定义了矩形的位置和尺寸。
如果 x 坐标不相等,则绘制水平矩形,连接两部分。
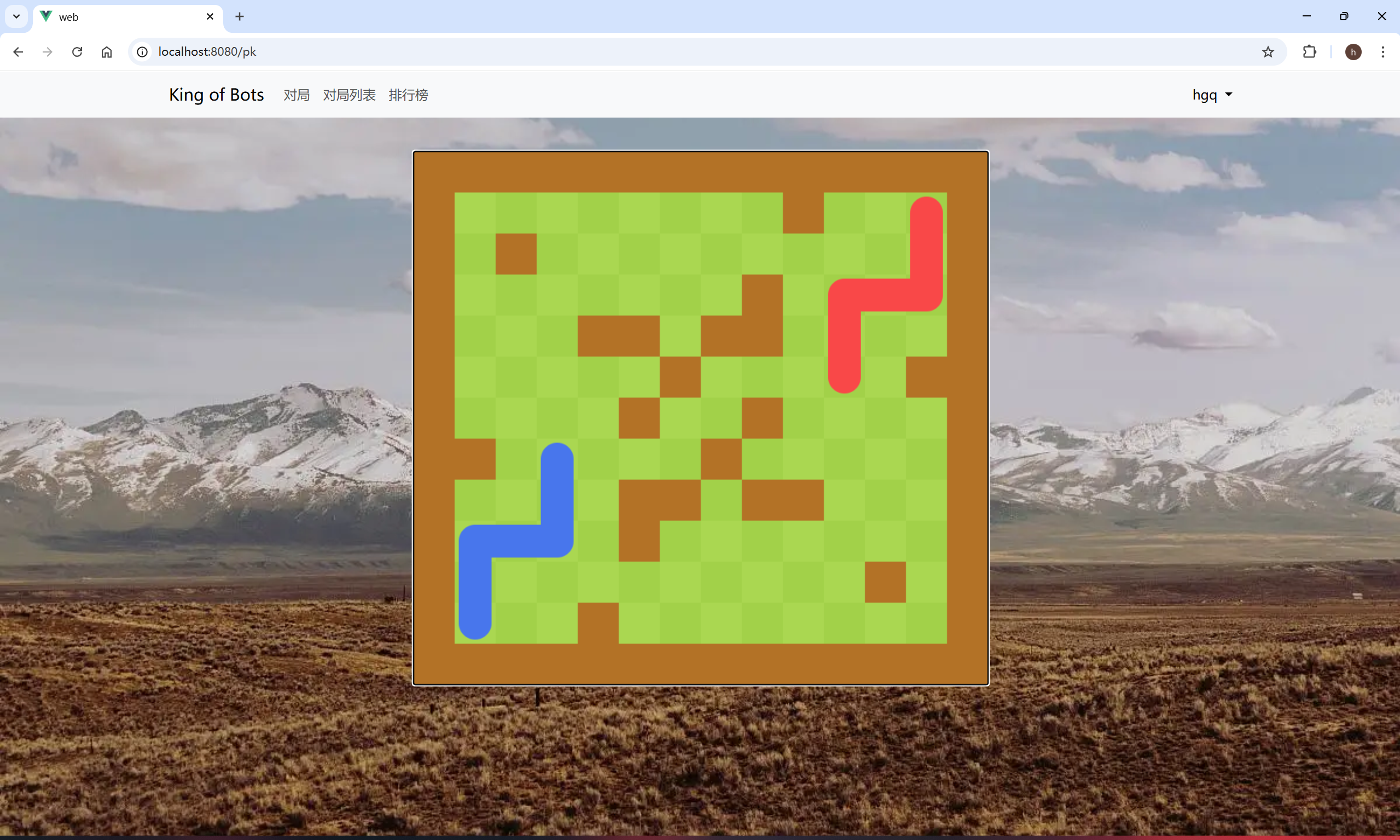
检测非法逻辑
在GameMap.js中更新
js
check_vaild(cell){ //检查目标位置是否合法:没有撞到两条蛇的身体和障碍物
for(const wall of this.walls){
if(wall.r === cell.r && wall.c === cell.c){
return false;
}
}
for(const snake of this.snakes){
let k = snake.cells.length;
if(!snake.check_tail_increasing()){ //当蛇尾会前进的时候,蛇尾不要判断
k--;
}
for(let i = 0; i < k; i++){
if(snake.cells[i].r === cell.r && snake.cells[i].c === cell.c)
return false;
}
}
return true;
}check_vaild 的方法,主要用于检查目标位置是否合法。具体来说,它会验证某个单元格是否可以被蛇移动到,确保该位置没有与墙体或其他蛇的身体发生碰撞。
检查墙体碰撞: 如果目标位置的行 (cell.r) 和列 (cell.c) 与某个墙体的位置相同,则返回 false,表示目标位置是无效的,因为它与墙体重叠。
检查蛇的身体:
使用 for...of 循环遍历所有蛇(this.snakes)。
let k = snake.cells.length; 获取当前蛇的身体单元格数量。
调用 snake.check_tail_increasing() 方法来判断蛇尾是否会在当前回合前进。如果蛇尾会前进,则将 k 减少 1,这意味着在检查时不需要考虑蛇尾,因为它将要在下一步中移动,不应视为障碍。
使用内层循环遍历蛇的身体部分(直到 k),检查每个蛇的单元格位置:如果目标位置的行和列与任何蛇的身体单元格相同,则返回 false,表示目标位置是无效的,因为它与另一条蛇的身体重叠。
如果经过上述所有检查后目标位置没有与墙体或其他蛇的身体发生碰撞,则返回 true,表示该位置是有效的,可以安全地移动到此位置。
在snake.js中更新
js
next_step(){ //将蛇的状态变为走下一步
const d = this.direction;
this.next_cell = new Cell(this.cells[0].r + this.dr[d], this.cells[0].c + this.dc[d]);
this.direction = -1; //清空方向
this.status = "move";
this.step++;
const k = this.cells.length;
for(let i = k; i > 0; i--){
this.cells[i] = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(this.cells[i - 1]));
}
if(!this.gamemap.check_vaild(this.next_cell)){ //下一步操作撞了,蛇直接去世
this.status = "die";
}
}
render() {
const L = this.gamemap.L;
const ctx = this.gamemap.ctx;
ctx.fillStyle = this.color;
if(this.status === "die"){
ctx.fillStyle = "white";
}
for(const cell of this.cells){
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(cell.x * L, cell.y * L, L / 2 * 0.8, 0, Math.PI * 2);
ctx.fill();
}
for (let i = 1; i < this.cells.length; i ++ ) {
const a = this.cells[i - 1], b = this.cells[i];
if (Math.abs(a.x - b.x) < this.eps && Math.abs(a.y - b.y) < this.eps)
continue;
if (Math.abs(a.x - b.x) < this.eps) {
ctx.fillRect((a.x - 0.4) * L, Math.min(a.y, b.y) * L, L * 0.8, Math.abs(a.y - b.y) * L);
} else {
ctx.fillRect(Math.min(a.x, b.x) * L, (a.y - 0.4) * L, Math.abs(a.x - b.x) * L, L * 0.8);
}
}
}next_step 方法:负责更新蛇的状态,包括计算下一步位置、更新身体位置、检查碰撞,并在碰撞时将状态设为"死亡"。
render 方法:在绘制时根据蛇的状态调整颜色,以便在视觉上区分正常状态和死亡状态。
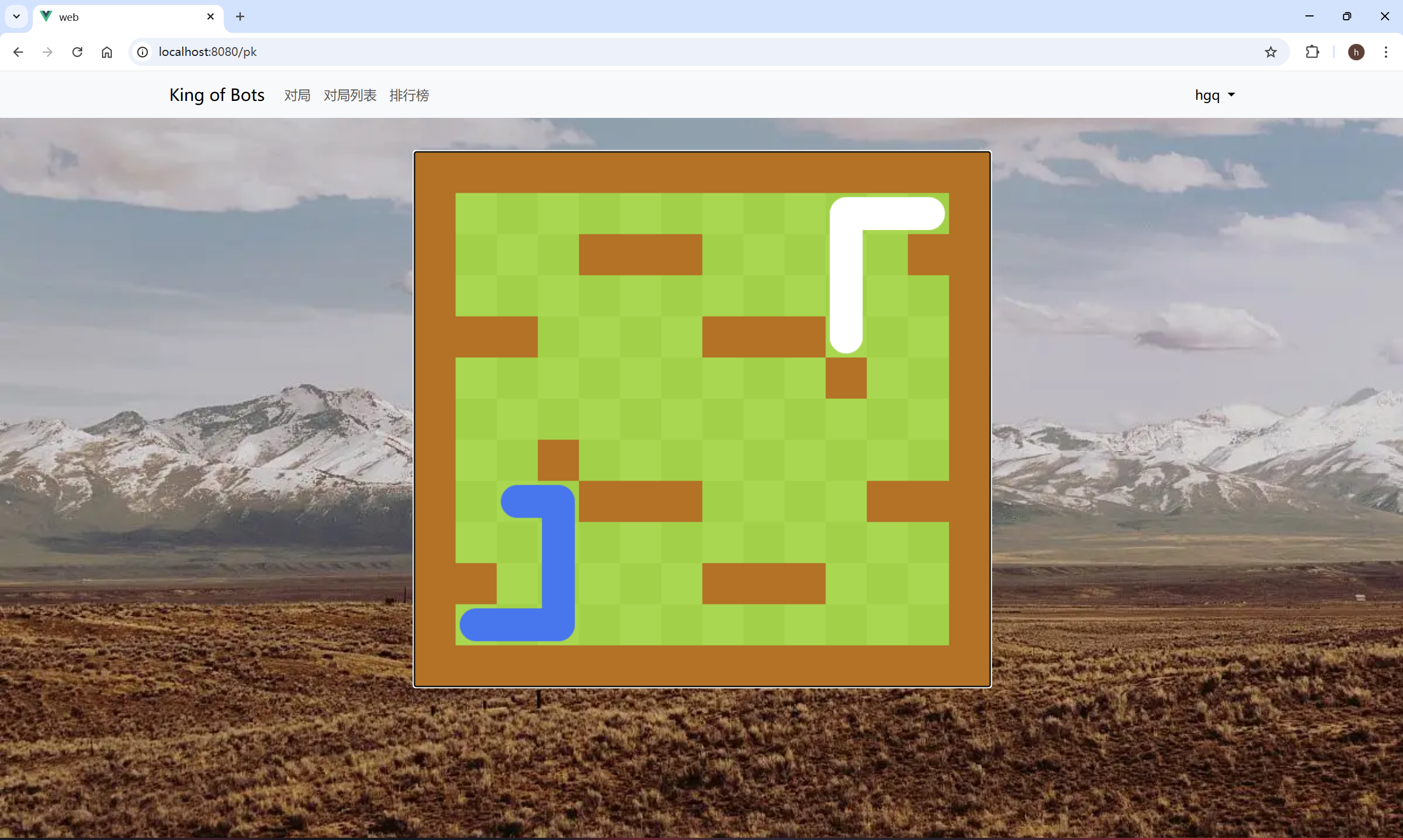
实现眼睛
修改snake.js
js
this.eye_direction = 0;
if(this.id === 1) this.eye_direction = 2; //左下角的蛇初始朝上,右上角的蛇初始朝下
this.eye_dx = [ //蛇眼睛不同方向的x的偏移量
[-1, 1],
[1, 1],
[1, -1],
[-1, -1],
];
this.eye_dy = [ //蛇眼睛不同方向的y的偏移量
[-1, -1],
[-1, 1],
[1, 1],
[1, -1],
];
js
render() {
const L = this.gamemap.L;
const ctx = this.gamemap.ctx;
ctx.fillStyle = this.color;
if(this.status === "die"){
ctx.fillStyle = "white";
}
for(const cell of this.cells){
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(cell.x * L, cell.y * L, L / 2 * 0.8, 0, Math.PI * 2);
ctx.fill();
}
for (let i = 1; i < this.cells.length; i ++ ) {
const a = this.cells[i - 1], b = this.cells[i];
if (Math.abs(a.x - b.x) < this.eps && Math.abs(a.y - b.y) < this.eps)
continue;
if (Math.abs(a.x - b.x) < this.eps) {
ctx.fillRect((a.x - 0.4) * L, Math.min(a.y, b.y) * L, L * 0.8, Math.abs(a.y - b.y) * L);
} else {
ctx.fillRect(Math.min(a.x, b.x) * L, (a.y - 0.4) * L, Math.abs(a.x - b.x) * L, L * 0.8);
}
}
ctx.fillStyle = "black";
for(let i = 0; i < 2; i++){
const eye_x = (this.cells[0].x + this.eye_dx[this.eye_direction][i] * 0.15) * L;
const eye_y = (this.cells[0].y + this.eye_dy[this.eye_direction][i] * 0.15) * L;
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(eye_x, eye_y, L * 0.05, 0, Math.PI * 2);
ctx.fill();
}
}计算眼睛的位置
- eye_x 和 eye_y 是眼睛的坐标。
- this.cells[0].x 和 this.cells[0].y 代表蛇头的中心位置。
- this.eye_dx[this.eye_direction][i] 和 this.eye_dy[this.eye_direction][i] 分别用于获取当前方向下眼睛相对于蛇头的位置偏移量(在 x 和 y 方向上的增量),这种方式支持不同方向的眼睛位置调整。
- *0.15 是一个缩放因子,用于调整眼睛相对于蛇头的位置,使它们在蛇头附近而不是重叠。
- 最后,乘以 L 将这些坐标转换为画布的像素坐标(L 可能代表每个单元格的像素大小)。
ctx.arc(eye_x, eye_y, L * 0.05, 0, Math.PI * 2);:
- 使用 arc 方法绘制一个圆形的眼睛。这里,eye_x 和 eye_y 是眼睛的中心坐标。
- L * 0.05 是眼睛的半径,确保眼睛相对较小。
- 0 到 Math.PI * 2 表示绘制完整的圆(360度)。
在蛇头的位置绘制两个黑色的眼睛。通过使用数组 this.eye_dx 和 this.eye_dy,代码能够根据蛇的当前方向动态调整眼睛的位置,使其在视觉上更符合运动方向,增强游戏的趣味性和表现力。