有效的括号:
题目:
给定一个只包括 '(',')','{','}','[',']' 的字符串 s ,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
每个右括号都有一个对应的相同类型的左括号。
示例 1:
输入:s = "()"
输出:true示例 2:
输入:s = "()[]{}"
输出:true示例 3:
输入:s = "(]"
输出:false提示:
1 <= s.length <= 104s仅由括号'()[]{}'组成
分析:
条件
左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
每个右括号都有一个对应的相同类型的左括号。
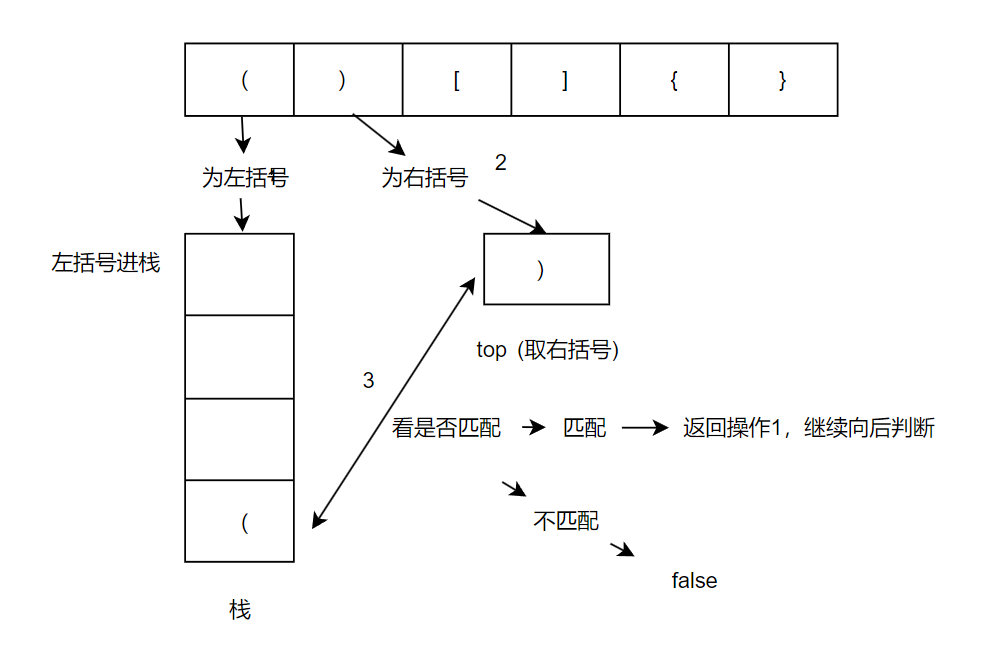
输入: s = "()[]{}"
流程图:
为了方便分析:加大一点点剂量
**输入:**s = "[{}{{(}})"
流程图:逐步分析
第一次
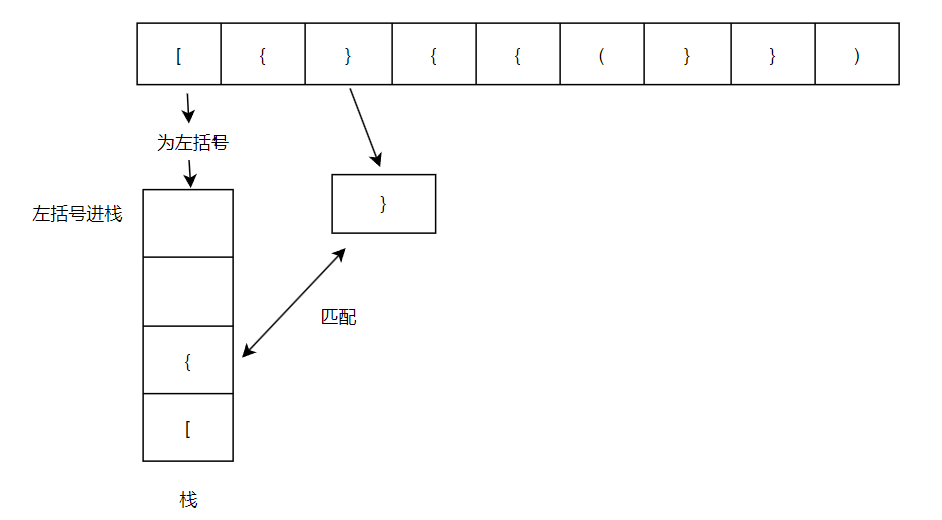
第二次
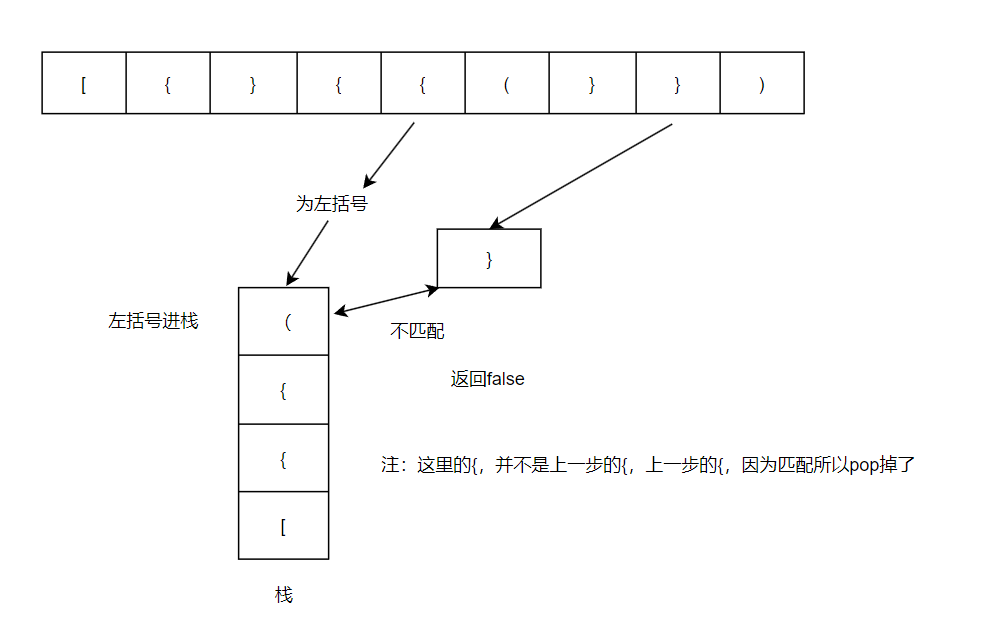
每次取栈顶数据与之匹配
注:这里的{,并不是上一步的{,上一步的{,因为匹配所以pop掉了
实现:
注:实现中的top与图片上top功能不同,请注意辨别
图片中的top是取右括号(因为为数组,所以有括号的值无需变量接收),而下方的top是取栈顶的数据。
这里运用到栈的思想,所以这里先要实现栈
包含栈
// 支持动态增长的栈
typedef char STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top; // 栈顶大小
int capacity; // 容量
}Stack;
// 初始化栈
void StackInit(Stack* ps);
// 入栈
void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDataType data);
// 出栈
void StackPop(Stack* ps);
// 获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps);
// 获取栈中有效元素个数
int StackSize(Stack* ps);
// 检测栈是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果不为空返回0
int StackEmpty(Stack* ps);
// 销毁栈
void StackDestroy(Stack* ps);
void STpop(Stack* ps);
bool stempty(Stack* ps);
// 初始化栈
void StackInit(Stack* ps){
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = 0;
ps->top = 0;
}
bool stempty(Stack* ps);
// 入栈
void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDataType data) {
assert(ps);
//扩容
if (ps->top == ps->capacity) {
int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
STDataType* tmp =(STDataType*) realloc(ps->a, newcapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
if (tmp == NULL) {
perror("realloc fail!");
exit(1);
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
}
ps->a[ps->top] = data;
ps->top++;
}
// 出栈
void StackPop(Stack* ps) {
assert(ps);
while (ps->top > 0) {
STDataType s = StackTop(ps);
printf("%d", s);
}
}
void STpop(Stack*ps) {
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
ps->top--;
}
// 获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps) {
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
// 获取栈中有效元素个数
int StackSize(Stack* ps) {
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
// 检测栈是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果不为空返回0
int StackEmpty(Stack* ps) {
assert(ps);
//return ps->top == 0 ? 1 : 0;
return ps->top == 0;
}
// 销毁栈
void StackDestroy(Stack* ps) {
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}括号匹配
bool isValid(char* s) {
Stack st;
StackInit(&st);
while(*s){
//左括号入栈
if(*s=='{' || *s=='[' || *s=='('){
StackPush(&st,*s);
}
else{
//取栈顶元素,与右括号匹配
char top=StackTop(&st);
STpop(&st);
if((top=='['&&*s!=']')||(top=='{'&&*s!='}')||(top=='('&&*s!=')')){
StackDestroy(&st);
return false;
}
}
++s;
}
return true
}分析问题:
栈剩余
当数组走完,右括号恰好能完全匹配,但是呢,栈却还存留一个
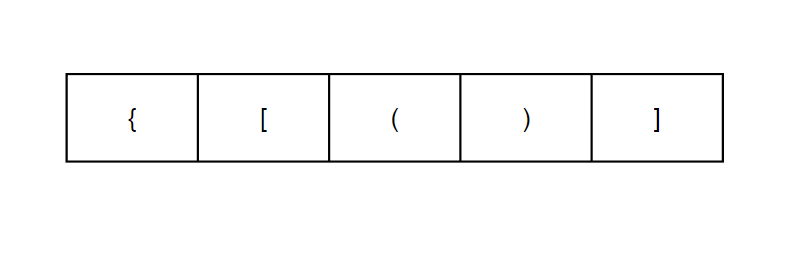
问题解决
为了解决这个问题,我们需要判NULL
bool ret = StackEmpty(&st);
//循环走完,判断栈是否还有剩余
StackDestroy(&st);
return ret;
}访问NULL和首为右括号
对于传址问题,这是很常见的
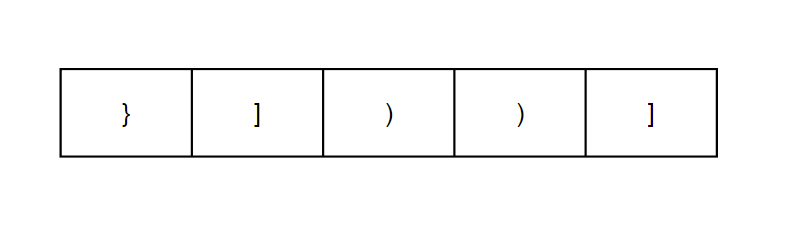
//取栈顶元素,与右括号匹配
char top=StackTop(&st);
//我们会发现,这里对栈的传址
STpop(&st);
if((top=='['&&*s!=']')||(top=='{'&&*s!='}')||(top=='('&&*s!=')')){
StackDestroy(&st);
return false;问题解决
if(StackEmpty(&st)){
StackDestroy(&st);
return false;
}完善代码
// 支持动态增长的栈
typedef char STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top; // 栈顶大小
int capacity; // 容量
}Stack;
// 初始化栈
void StackInit(Stack* ps);
// 入栈
void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDataType data);
// 出栈
void StackPop(Stack* ps);
// 获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps);
// 获取栈中有效元素个数
int StackSize(Stack* ps);
// 检测栈是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果不为空返回0
int StackEmpty(Stack* ps);
// 销毁栈
void StackDestroy(Stack* ps);
void STpop(Stack* ps);
bool stempty(Stack* ps);
// 初始化栈
void StackInit(Stack* ps){
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = 0;
ps->top = 0;
}
bool stempty(Stack* ps);
// 入栈
void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDataType data) {
assert(ps);
//扩容
if (ps->top == ps->capacity) {
int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
STDataType* tmp =(STDataType*) realloc(ps->a, newcapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
if (tmp == NULL) {
perror("realloc fail!");
exit(1);
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
}
ps->a[ps->top] = data;
ps->top++;
}
// 出栈
void StackPop(Stack* ps) {
assert(ps);
while (ps->top > 0) {
STDataType s = StackTop(ps);
printf("%d", s);
}
}
void STpop(Stack*ps) {
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
ps->top--;
}
// 获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps) {
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
// 获取栈中有效元素个数
int StackSize(Stack* ps) {
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
// 检测栈是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果不为空返回0
int StackEmpty(Stack* ps) {
assert(ps);
//return ps->top == 0 ? 1 : 0;
return ps->top == 0;
}
// 销毁栈
void StackDestroy(Stack* ps) {
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}
bool isValid(char* s) {
Stack st;
StackInit(&st);
while(*s){
//左括号入栈
if(*s=='{' || *s=='[' || *s=='('){
StackPush(&st,*s);
}
else{
//取右括号与左括号匹配
//如果左括号为空,则返回false
if(StackEmpty(&st)){
StackDestroy(&st);
return false;
}
//取栈顶元素,与右括号匹配
char top=StackTop(&st);
STpop(&st);
if((top=='['&&*s!=']')||(top=='{'&&*s!='}')||(top=='('&&*s!=')')){
StackDestroy(&st);
return false;
}
}
++s;
}
bool ret = StackEmpty(&st);
StackDestroy(&st);
return ret;
}
