大侠幸会,在下全网同名[算法金] 0 基础转 AI 上岸,多个算法赛 Top [日更万日,让更多人享受智能乐趣]
Sebastian Raschka 2018\] Model Evaluation, Model Selection, and Algorithm Selection in Machine Learning,
摘要:本文主要讨论了模型评估、模型选择和算法选择的重要性,并回顾了解决这些任务的不同技术。文章强调了在小数据集上不推荐使用留出方法,而应使用bootstrap技术来评估性能的不确定性。在讨论偏差-方差权衡时,文章比较了leave-one-out交叉验证和k-折交叉验证,并给出了选择k值的实际建议。文章还展示了用于算法对比的不同统计测试,并讨论了处理多种对比的策略。最后,当数据集较小时,文章推荐使用5×2cv交叉验证和嵌套交叉验证来对比机器学习算法。


## 1. 引言:关于模型评价的基本术语和技术
## 1.1 性能估计:泛化性能与模型选择
在机器学习中,我们通常关心的是模型的泛化性能,也就是模型对未见过的数据的预测能力。为了评估模型的泛化性能,我们需要将数据集划分为训练集和测试集,使用训练集来训练模型,然后使用测试集来评估模型的性能。
此外,模型选择是另一个重要的任务,它涉及到在一组候选模型中选择最优模型。模型选择的目标是找到一个在给定的评价指标下性能最好的模型。
## 1.2 假设和术语
在讨论模型评价时,我们需要定义一些基本的术语。例如,"模型"通常指的是从数据中学习的预测函数;"算法"指的是用于学习模型的过程;"性能度量"指的是用于评价模型的标准,如准确率、召回率等。
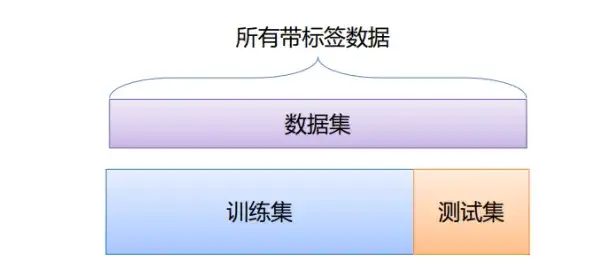
## 1.3 重复验证和保留方法
重复验证和保留方法是两种常用的模型评价方法。
重复验证是指多次使用不同的训练集和测试集来评估模型的性能,然后取平均值作为最终的性能估计。
保留方法是指将数据集划分为训练集和测试集,然后使用训练集来训练模型,使用测试集来评估模型的性能。


## 2. 自举和不确定性
## 2.1 概述
自举是一种强大的统计技术,它可以用来估计一个统计量的抽样分布。在机器学习中,自举方法可以用来估计模型性能的不确定性,从而帮助我们更好地理解模型的稳定性和可靠性。
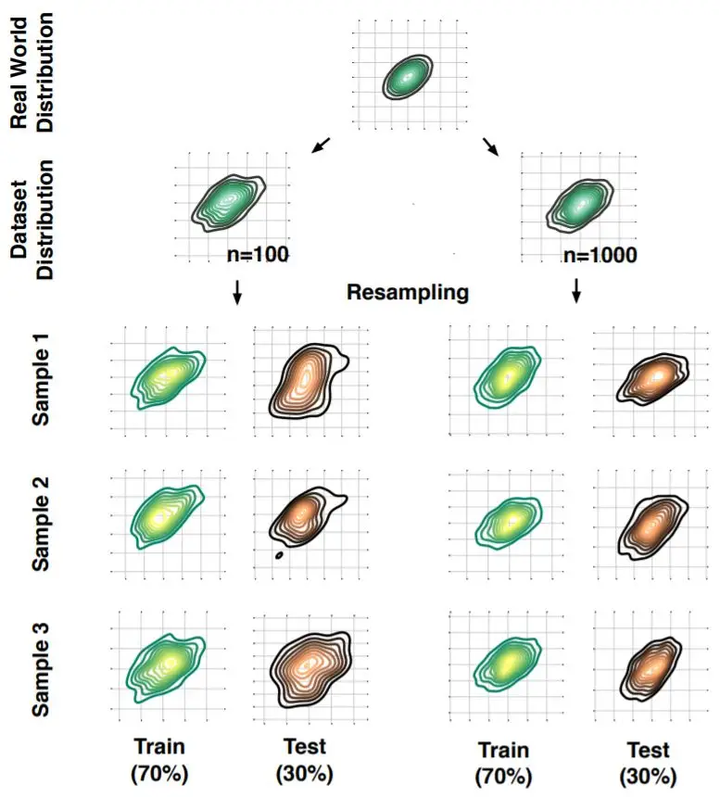
## 2.2 重采样
重采样是自举方法的核心。它是指从原始数据集中随机抽取样本,形成新的数据集。通过重复这个过程,我们可以生成多个不同的数据集,然后在这些数据集上训练和评估模型,从而得到模型性能的多个估计。
## 2.3 重复保留验证
重复保留验证是一种常用的模型评价方法。它是指将数据集划分为训练集和测试集,然后使用训练集来训练模型,使用测试集来评估模型的性能。这个过程会重复多次,每次都使用不同的训练集和测试集,最后将多次评估的结果进行平均,得到模型性能的最终估计。
## 2.4 自举方法和经验置信区间
自举方法可以用来估计模型性能的不确定性,这通常通过计算模型性能的经验置信区间来实现。经验置信区间是指在多次重采样和评估的过程中,模型性能的变化范围。例如,如果我们的模型在100次重采样和评估的过程中,准确率的范围是70%到80%,那么我们就可以说,我们对模型的准确率有70%到80%的信心。


## 3. 交叉验证和超参数优化
## 3.1 概述
交叉验证和超参数优化是机器学习中的两个核心概念。交叉验证是一种评估模型泛化性能的方法,它通过将数据集分割为多个子集,并轮流使用其中一个子集作为测试集,其余子集作为训练集,来评估模型的性能。超参数优化则是在给定的超参数空间中寻找最优超参数的过程,这个过程通常涉及到搜索算法和性能评估。
## 3.2 关于超参数和模型选择
超参数是在训练模型之前就需要确定的参数,比如学习率、正则化参数等。选择合适的超参数对模型的性能有很大影响。模型选择则是在多个模型(可能是不同类型的模型,或者是同一类型模型但具有不同超参数的模型)中选择性能最好的模型。这个过程通常涉及到交叉验证和性能评估。
## 3.3 三路保留方法用于超参数调优
三路保留方法是一种用于超参数调优的方法,它将数据集划分为训练集、验证集和测试集。训练集用于训练模型,验证集用于调整超参数,测试集用于评估最终模型的性能。这种方法可以有效地防止过拟合,并提供了一个公平的性能评估。
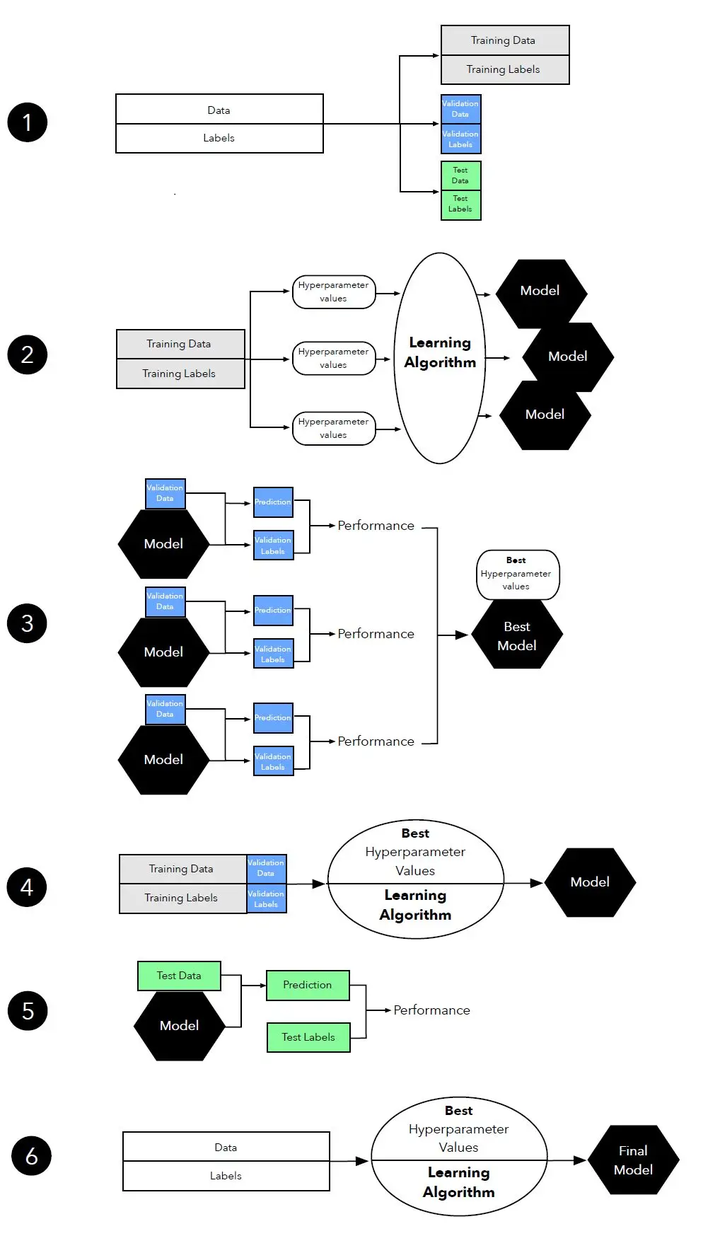
## 3.4 k-折交叉验证简介
k-折交叉验证是一种常用的交叉验证方法,它将数据集划分为k个子集,然后轮流使用其中一个子集作为测试集,其余子集作为训练集,来评估模型的性能。这种方法可以有效地利用有限的数据,并提供了一个公平的性能评估。
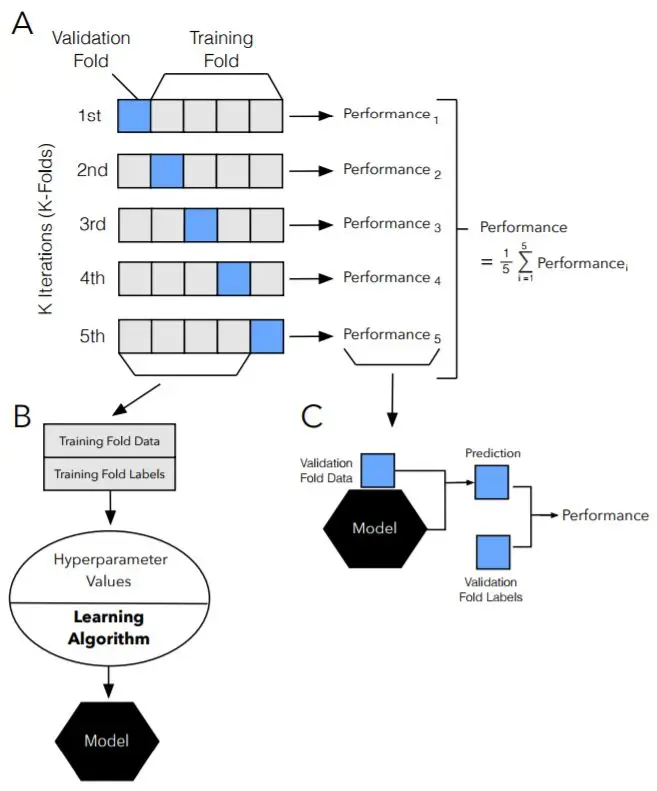
## 3.5 特殊情况:2-折和留一法交叉验证
2-折交叉验证和留一法交叉验证是k-折交叉验证的两种特殊情况。2-折交叉验证将数据集划分为两个子集,留一法交叉验证则将每个样本单独作为测试集,其余样本作为训练集。这两种方法各有优缺点,需要根据具体的应用场景来选择。
## 3.6 k-折交叉验证和偏差-方差权衡
选择合适的k值是k-折交叉验证中的一个重要问题。k值的选择需要在偏差和方差之间找到一个平衡。一般来说,k值越大,偏差越小,方差越大;k值越小,偏差越大,方差越小。因此,选择合适的k值是一个需要权衡的问题。
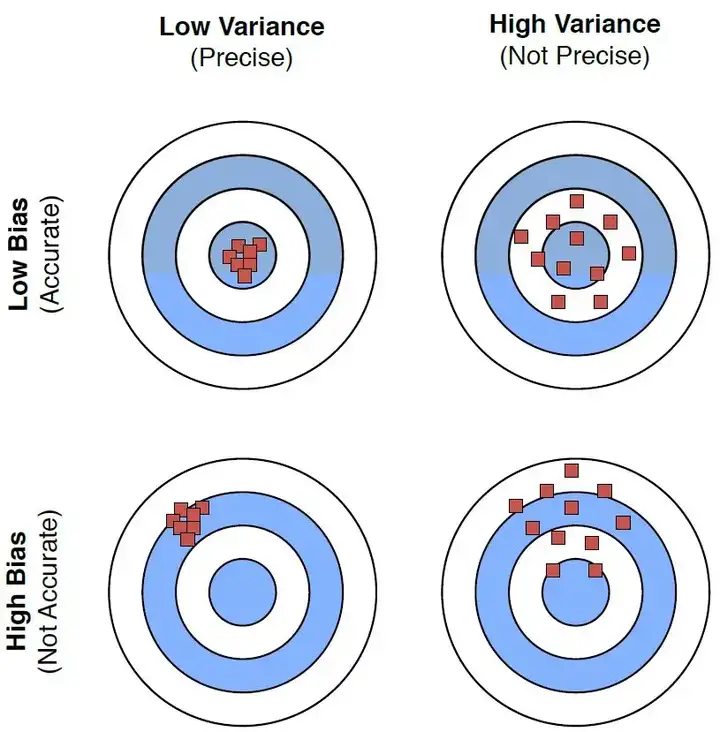
## 3.7 通过k-折交叉验证进行模型选择
k-折交叉验证可以用于模型选择。通过在不同的训练集上训练模型,并在对应的测试集上评估模型的性能,我们可以选择性能最好的模型。这种方法可以有效地利用有限的数据,并提供了一个公平的性能评估。
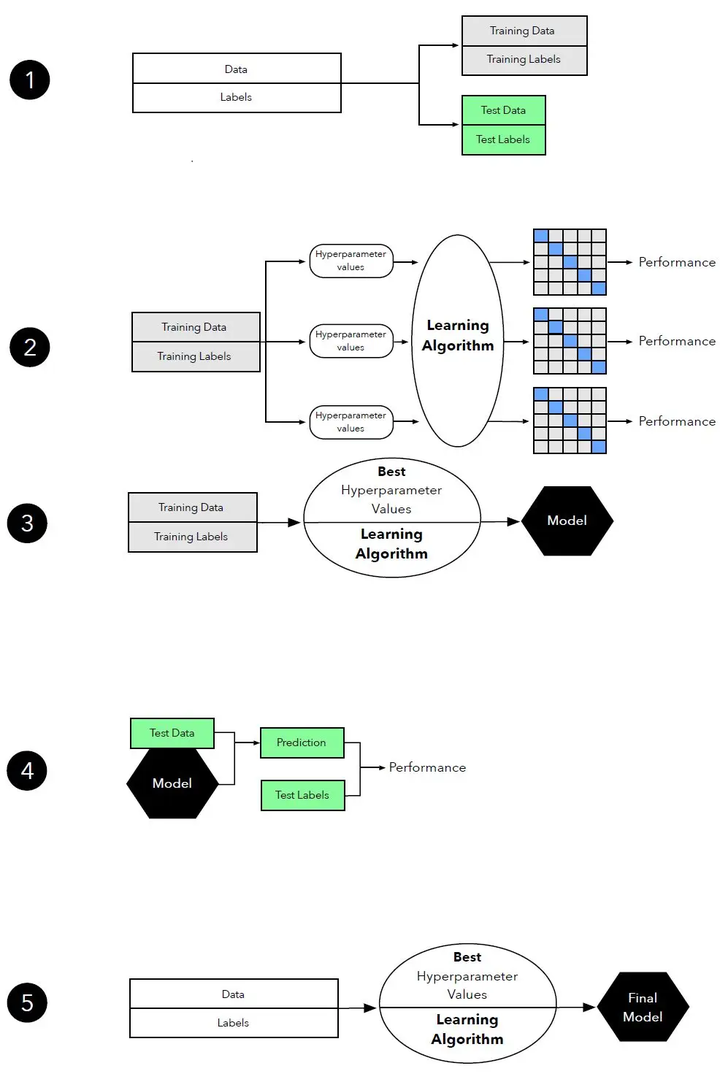


## 4. 算法比较
## 4.1 概述
在机器学习中,我们经常需要比较不同的算法以确定哪种算法在特定任务上的性能更好。这通常涉及到在相同的数据集上训练和评估不同的模型,然后使用某种性能度量来比较它们的性能。
## 4.2 测试比例的差异
在比较两个模型的性能时,我们需要使用统计测试来确定性能差异是否显著。这通常涉及到计算性能度量的差值,并检验这个差值是否显著大于零。如果差值显著大于零,那么我们就可以说一个模型的性能显著优于另一个模型。
## 4.3 使用McNemar测试比较两个模型
McNemar测试是一种用于比较两个模型性能的统计测试。它主要用于比较两个模型在同一数据集上的错误率。McNemar测试的基本思想是比较两个模型在同一数据集上的错误预测的数量,如果一个模型的错误预测数量显著少于另一个模型,那么我们就可以说这个模型的性能优于另一个模型。


### References
\[Sebastian Raschka 2018\] Model Evaluation, Model Selection, and Algorithm Selection in Machine Learning
\[Alpaydin, 1999\]Alpaydin, E. (1999).Combined 5x2cv F test for comparing supervised classification learning algorithms.Neural Computation, 11(8):1885--1892.
\[Bengio and Grandvalet, 2004\]Bengio, Y. and Grandvalet, Y. (2004).No unbiased estimator of the variance of k-fold cross-validation.Journal of Machine Learning Research, 5(Sep):1089--1105.
\[Bonferroni, 1936\]Bonferroni, C. (1936).Teoria statistica delle classi e calcolo delle probabilita.Pubblicazioni del R Istituto Superiore di Scienze Economiche e Commericiali di Firenze, 8:3--62.
\[Breiman et al., 1984\]Breiman, L., Friedman, J., Stone, C. J., and Olshen, R. A. (1984).Classification and regression trees.CRC press. \[Cochran, 1950\]Cochran, W. G. (1950).The comparison of percentages in matched samples.Biometrika, 37(3/4):256--266.
\[Dietterich, 1998\]Dietterich, T. G. (1998).Approximate statistical tests for comparing supervised classification learning algorithms.Neural computation, 10(7):1895--1923.
\[Dunn, 1961\]Dunn, O. J. (1961).Multiple comparisons among means.Journal of the American statistical association, 56(293):52--64.
\[Edwards, 1948\]Edwards, A. L. (1948).Note on the "correction for continuity" in testing the significance of the difference between correlated proportions.Psychometrika, 13(3):185--187.
\[Efron, 1981\]Efron, B. (1981).Nonparametric standard errors and confidence intervals.Canadian Journal of Statistics, 9(2):139--158.
\[Efron, 1983\]Efron, B. (1983).Estimating the error rate of a prediction rule: improvement on cross-validation.Journal of the American Statistical Association, 78(382):316--331.
\[Efron, 1992\]Efron, B. (1992).Bootstrap methods: another look at the Jackknife.In Breakthroughs in Statistics, pages 569--593. Springer.
\[Efron and Tibshirani, 1997\]Efron, B. and Tibshirani, R. (1997).Improvements on cross-validation: the .632+ bootstrap method.Journal of the American Statistical Association, 92(438):548--560.
\[Efron and Tibshirani, 1994\]Efron, B. and Tibshirani, R. J. (1994).An Introduction to the Bootstrap.CRC press.
\[Fleiss et al., 2013\]Fleiss, J. L., Levin, B., and Paik, M. C. (2013).Statistical Methods for Rates and Proportions.John Wiley \& Sons.
\[Hastie et al., 2009\]Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R., and Friedman, J. H. (2009).In The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction.Springer, New York.
\[Hawkins et al., 2003\]Hawkins, D. M., Basak, S. C., and Mills, D. (2003).Assessing model fit by cross-validation.Journal of Chemical Information and Computer Sciences, 43(2):579--586.
\[Iizuka et al., 2003\]Iizuka, N., Oka, M., Yamada-Okabe, H., Nishida, M., Maeda, Y., Mori, N., Takao, T., Tamesa, T., Tangoku, A., Tabuchi, H., et al. (2003).Oligonucleotide microarray for prediction of early intrahepatic recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection.The lancet, 361(9361):923--929.
\[James et al., 2013\]James, G., Witten, D., Hastie, T., and Tibshirani, R. (2013).In An Introduction to Statistical Learning: With Applications in R.Springer, New York.
\[Kim, 2009\]Kim, J.-H. (2009).Estimating classification error rate: Repeated cross-validation, repeated hold-out and bootstrap.Computational Statistics \& Data Analysis, 53(11):3735--3745.
\[Kohavi, 1995\]Kohavi, R. (1995).A study of cross-validation and bootstrap for accuracy estimation and model selection.International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 14(12):1137--1143.
\[Kuncheva, 2004\]Kuncheva, L. I. (2004).Combining Pattern Classifiers: Methods and Algorithms.John Wiley \& Sons.
\[Looney, 1988\]Looney, S. W. (1988).A statistical technique for comparing the accuracies of several classifiers.Pattern Recognition Letters, 8(1):5--9.
\[McNemar, 1947\]McNemar, Q. (1947).Note on the sampling error of the difference between correlated proportions or percentages.Psychometrika, 12(2):153--157.
\[Molinaro et al., 2005\]Molinaro, A. M., Simon, R., and Pfeiffer, R. M. (2005).Prediction error estimation: a comparison of resampling methods.Bioinformatics, 21(15):3301--3307.
\[Pedregosa et al., 2011\]Pedregosa, F., Varoquaux, G., Gramfort, A., Michel, V., Thirion, B., Grisel, O., Blondel, M., Prettenhofer, P., Weiss, R., Dubourg, V., et al. (2011).Scikit-learn: Machine learning in python.Journal of Machine Learning Research, 12(Oct):2825--2830.
\[Perneger, 1998\]Perneger, T. V. (1998).What's wrong with bonferroni adjustments.Bmj, 316(7139):1236--1238.
\[Raschka, 2018\]Raschka, S. (2018).Mlxtend: Providing machine learning and data science utilities and extensions to python's scientific computing stack.The Journal of Open Source Software, 3(24).
\[Refaeilzadeh et al., 2007\]Refaeilzadeh, P., Tang, L., and Liu, H. (2007).On comparison of feature selection algorithms.In Proceedings of AAAI Workshop on Evaluation Methods for Machine Learning II, pages 34--39.
\[Rothman, 1990\]Rothman, K. J. (1990).No adjustments are needed for multiple comparisons.Epidemiology, pages 43--46.
\[Tan et al., 2005\]Tan, P.-N., Steinbach, M., and Kumar, V. (2005).In Introduction to Data Mining.Pearson Addison Wesley, Boston.
\[Varma and Simon, 2006\]Varma, S. and Simon, R. (2006).Bias in error estimation when using cross-validation for model selection.BMC bioinformatics, 7(1):91.
\[Varoquaux, 2017\]Varoquaux, G. (2017).Cross-validation failure: small sample sizes lead to large error bars.Neuroimage.
\[Westfall et al., 2010\]Westfall, P. H., Troendle, J. F., and Pennello, G. (2010).Multiple McNemar tests.Biometrics, 66(4):1185--1191.

## \[ 算法金,碎碎念