搜索二叉树的概念
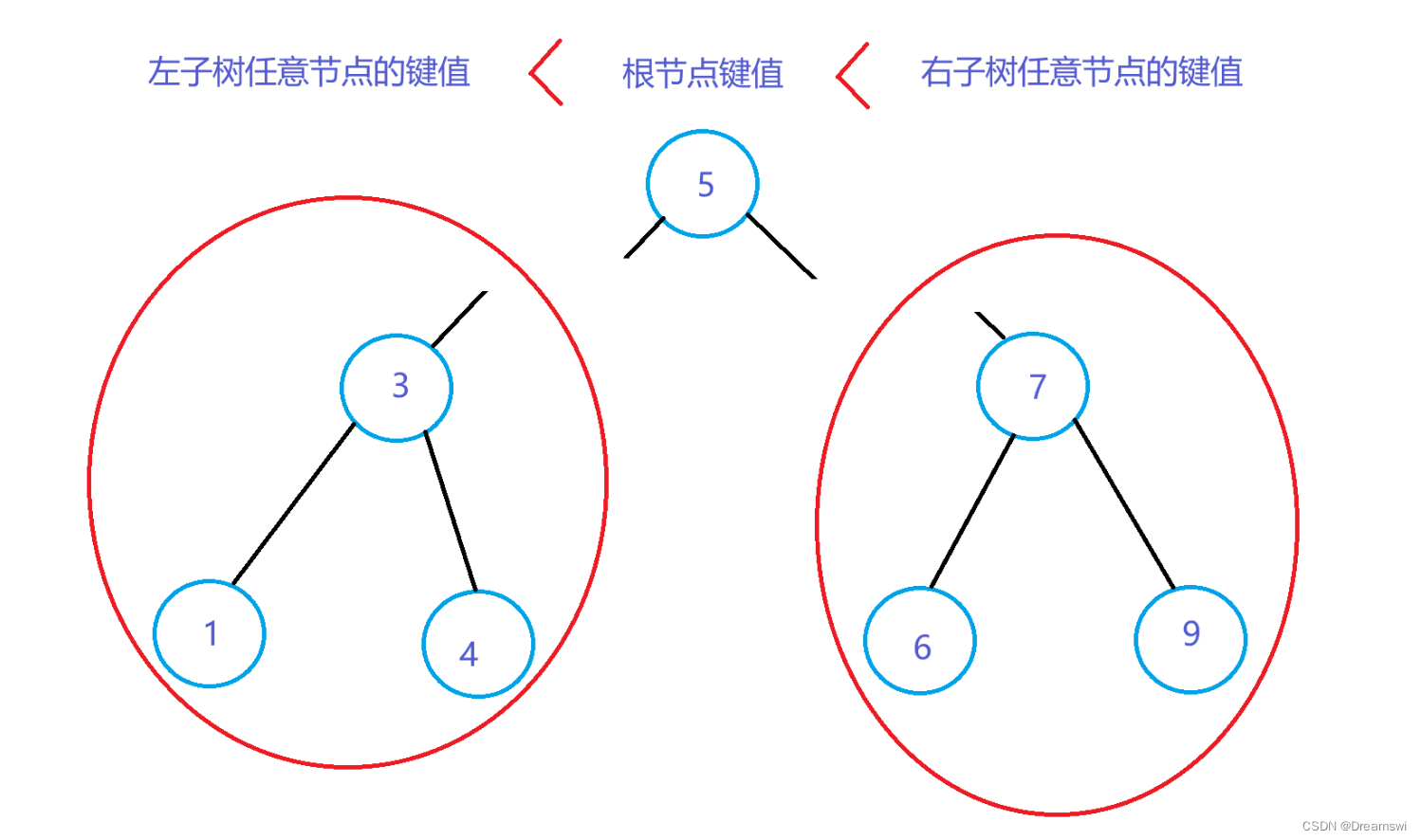
搜索二叉树规则(左小右大):
- 非空左 子树的键值小于其根节点的键值
- 非空右 子树的键值大于其根节点的键值
- 左右子树均为搜索二叉树
如图:
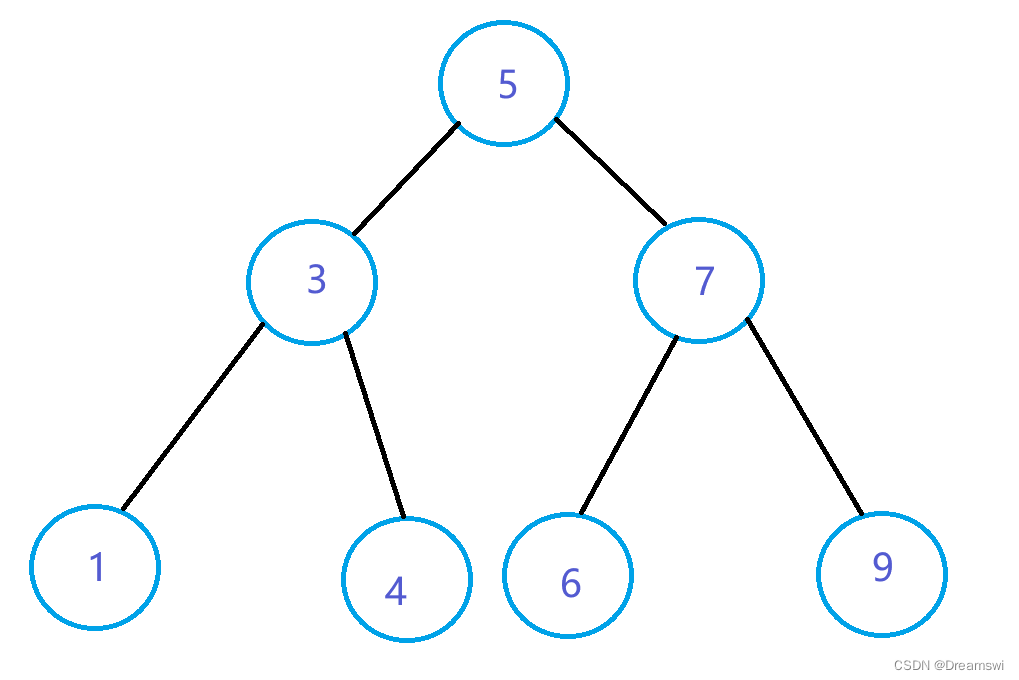
在搜索时,若大于根,则去右子树寻找;若小于根,则去左子树寻找。直到找到或为空结束。在理想状态下只需查找树的高度次。
代码实现
cpp
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//key版本
namespace key
{
template<class T>
struct BSTreeNode
{
BSTreeNode<T>* _left;
BSTreeNode<T>* _right;
T _key;
BSTreeNode(const T& key)
:_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_key(key)
{}
};
template<class T>
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<T> Node;
public:
bool Insert(const T& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(key);
if (parent->_key > key)
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
return true;
}
Node* find(const T& key)
{
Node* cur = root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return cur;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
bool Erase(const T& key)
{
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
if (cur->_left == nullptr)
{
if (cur == root)
{
root = cur->_right;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
}
delete cur;
}
else if (cur->_right == nullptr)
{
if (cur == root)
{
root = cur->_left;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
}
delete cur;
}
else
{
Node* rightMinParent = cur;
Node* rightMin = cur -> _right;
while (rightMin->_left)
{
rightMinParent = rightMin;
rightMin = rightMin->_left;
}
swap(cur->_key, rightMin->_key);
//假设没有进循环,那么rightMin = cur->_right,所以要判断一下。
if (rightMin == rightMinParent->_left)
rightMinParent->_left = rightMin->_right;
else
rightMinParent->_right = rightMin->_right;
delete rightMin;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(root);
cout << endl;
}
private:
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << " ";
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
Node* root = nullptr;
};
}
//key_value版本
namespace key_value
{
template<class T, class V>
struct BSTreeNode
{
BSTreeNode<T,V>* _left;
BSTreeNode<T,V>* _right;
T _key;
V _value;
BSTreeNode(const T& key,const V& value = V())
:_left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _key(key)
,_value(value)
{}
};
template<class T, class V>
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<T,V> Node;
public:
bool Insert(const T& key, const V& value)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
root = new Node(key,value);
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(key, value);;
if (parent->_key > key)
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
return true;
}
Node* find(const T& key)
{
Node* cur = root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return cur;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
bool Erase(const T& key)
{
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
if (cur->_left == nullptr)
{
if (cur == root)
{
root = cur->_right;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
}
delete cur;
}
else if (cur->_right == nullptr)
{
if (cur == root)
{
root = cur->_left;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
}
delete cur;
}
else
{
Node* rightMinParent = cur;
Node* rightMin = cur->_right;
//找cur右子树最小的值
while (rightMin->_left)
{
rightMinParent = rightMin;
rightMin = rightMin->_left;
}
swap(cur->_key, rightMin->_key);
swap(cur->_value, rightMin->_value);
//假设没有进循环,那么rightMin = cur->_right,所以要判断一下。
if (rightMin == rightMinParent->_left)
rightMinParent->_left = rightMin->_right;
else
rightMinParent->_right = rightMin->_right;
delete rightMin;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(root);
cout << endl;
}
private:
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << " " << root->_value << endl;
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
Node* root = nullptr;
};
}Insert函数详解
cpp
bool Insert(const T& key)
{
//假设根节点为空
if (root == nullptr)
{
root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
//根节点不为空
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else//等于
{
//出现重复,不插入
return false;
}
}
//将新节点连接入树
cur = new Node(key);
if (parent->_key > key)
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
return true;
}(1)若根节点为空,为其新建(new)一个节点。
(2)若根节点不为空,则根据二叉树定义(大于当前根的键值进右子树,小于当前根的键值进左子树)去寻找合适的位置新建节点。出现等于即重复的情况不插入。
(3)新节点连接入树时,要检查他是parent的左节点还是右节点,判断完毕后再连接。
Erase函数详解
cpp
bool Erase(const T& key)
{
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else//找到删除目标
{
//假设目标左子树为空
if (cur->_left == nullptr)
{
if (cur == root)
{
root = cur->_right;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
}
delete cur;
}
//假设目标右子树为空
else if (cur->_right == nullptr)
{
if (cur == root)
{
root = cur->_left;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
}
delete cur;
}
else//左右子树都不为空
{
Node* rightMinParent = cur;
Node* rightMin = cur -> _right;
while (rightMin->_left)
{
rightMinParent = rightMin;
rightMin = rightMin->_left;
}
swap(cur->_key, rightMin->_key);
//假设没有进循环,那么rightMin = cur->_right,所以要判断一下。
if (rightMin == rightMinParent->_left)
rightMinParent->_left = rightMin->_right;
else
rightMinParent->_right = rightMin->_right;
delete rightMin;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}(1)第一步寻找删除目标(有可能是根节点),找不到返回false,表示删除失败。
(2)删除
- 目标左子树为空
- 目标右子树为空
- 目标左右子树都不为空
左子树为空
删除目标不是根节点时,让目标的父节点指向他的右子树。当然也要判断目标是他的父节点的左子树还是右子树。
为父节点的左子树:
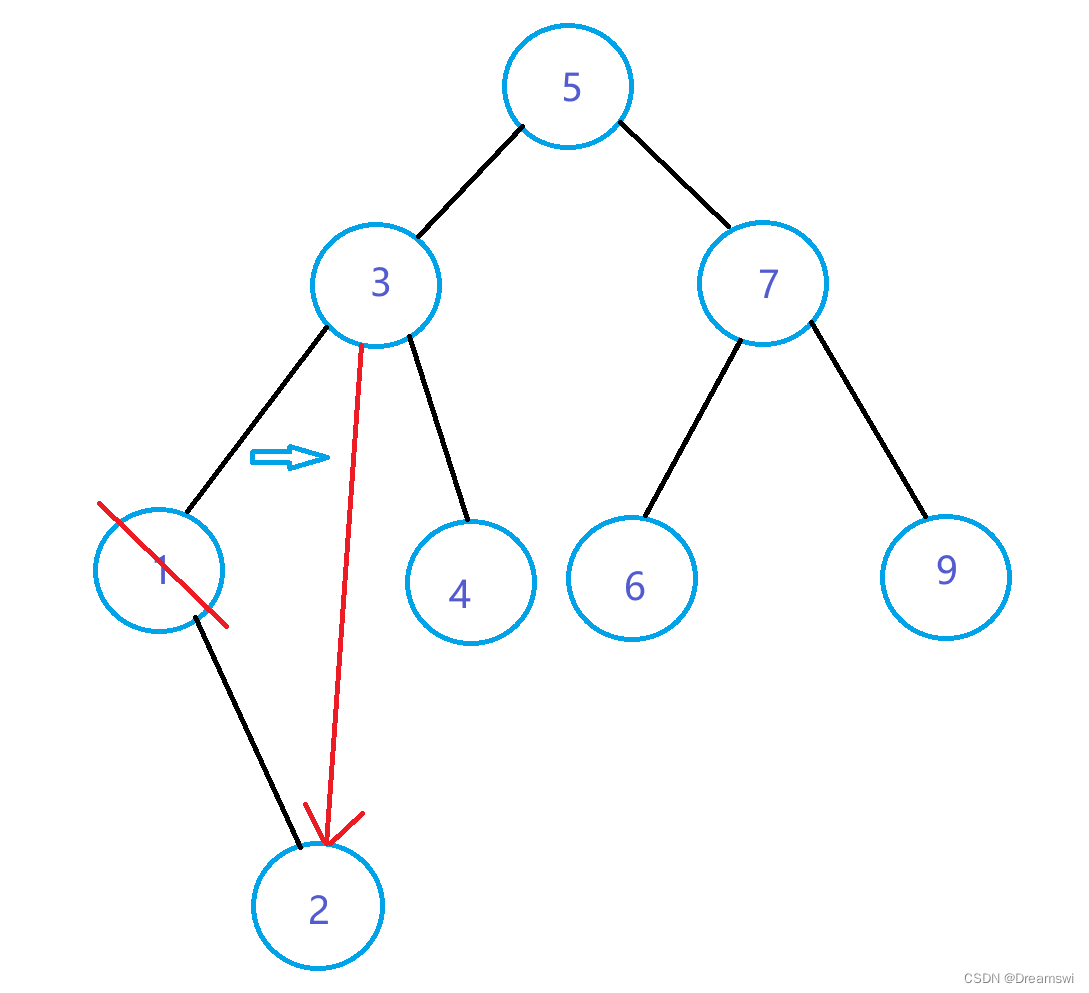
为父节点的右子树:

目标为根节点:
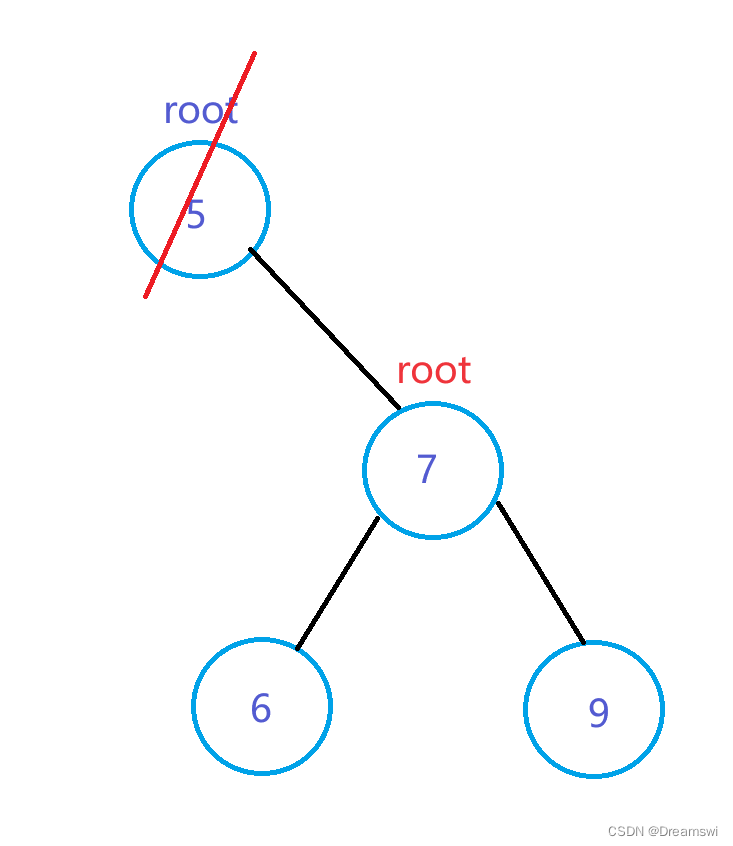
(右子树为空的情况只是与左子树为空方向相反,不过多赘述)
左右子树都不为空时
交换 目标的键值 和 目标的右子树中的最左节点的键值 ,然后让最左节点的父节点指向最左节点的右子树(因为是最左节点,所以左子树一定为空,右子树可能为空可能不为空),最后将这个最左节点删除。
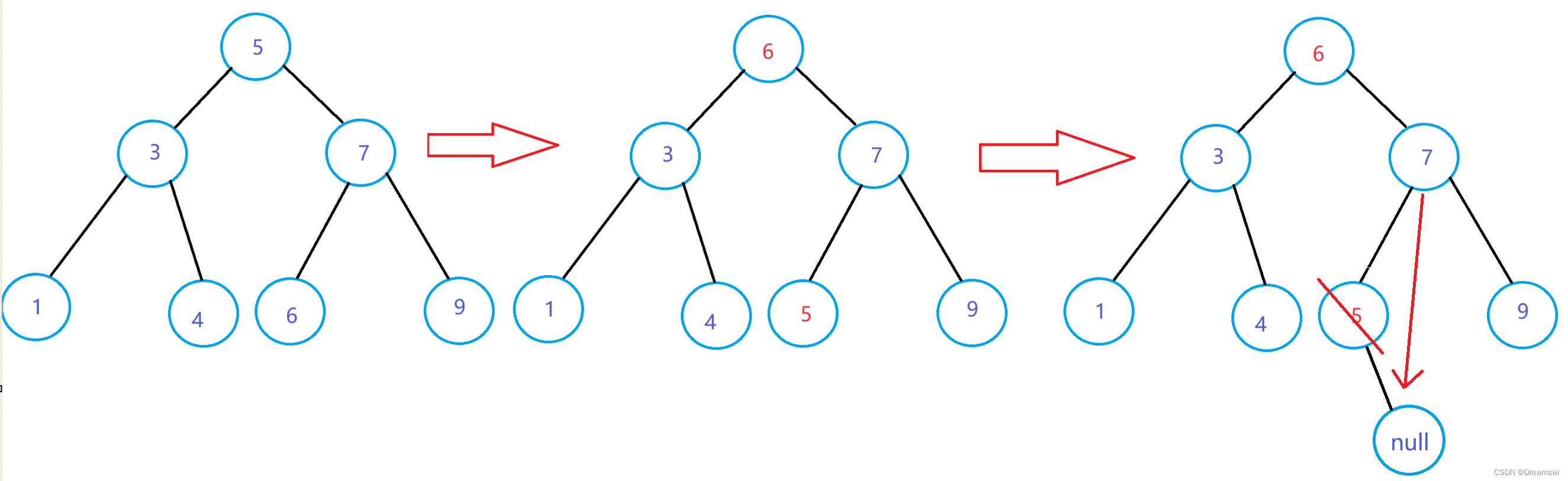
让最左节点的父节点指向最左节点的右子树前,也要判断该最左节点是否是其父节点的左子树,因为有可能出现图中的情况。
此时右子树最左节点是7,但他却是父节点的右子树。此时是父节点的右指向最左节点的右子树,而不是父节点的左去指向。
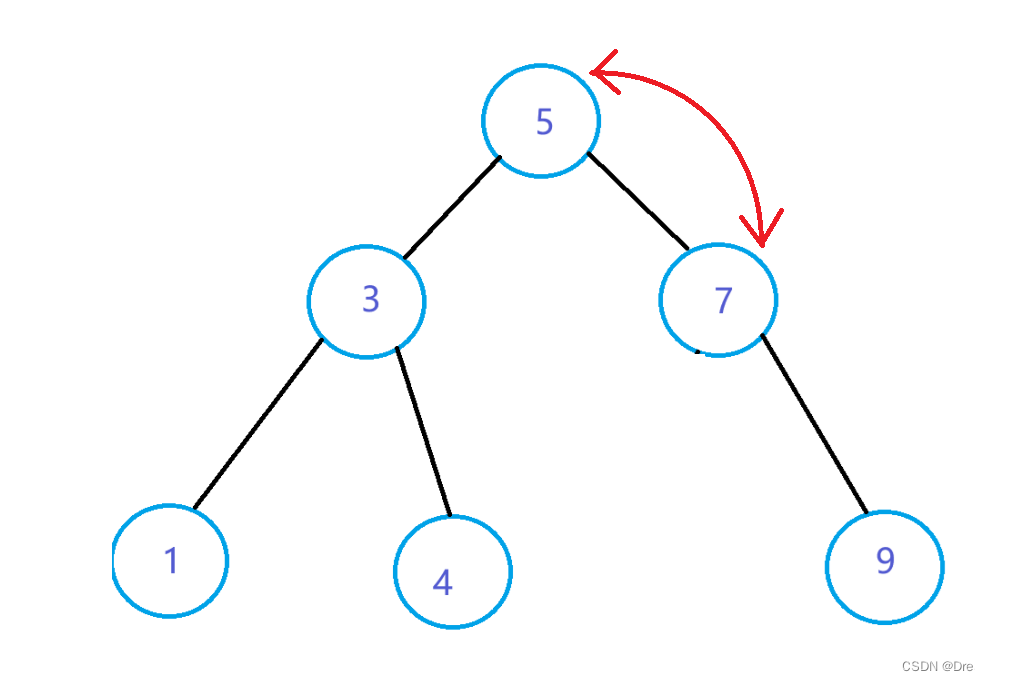
原理
删除后要保持树还是搜索二叉树。那么首先先理清一下节点键值的关系。
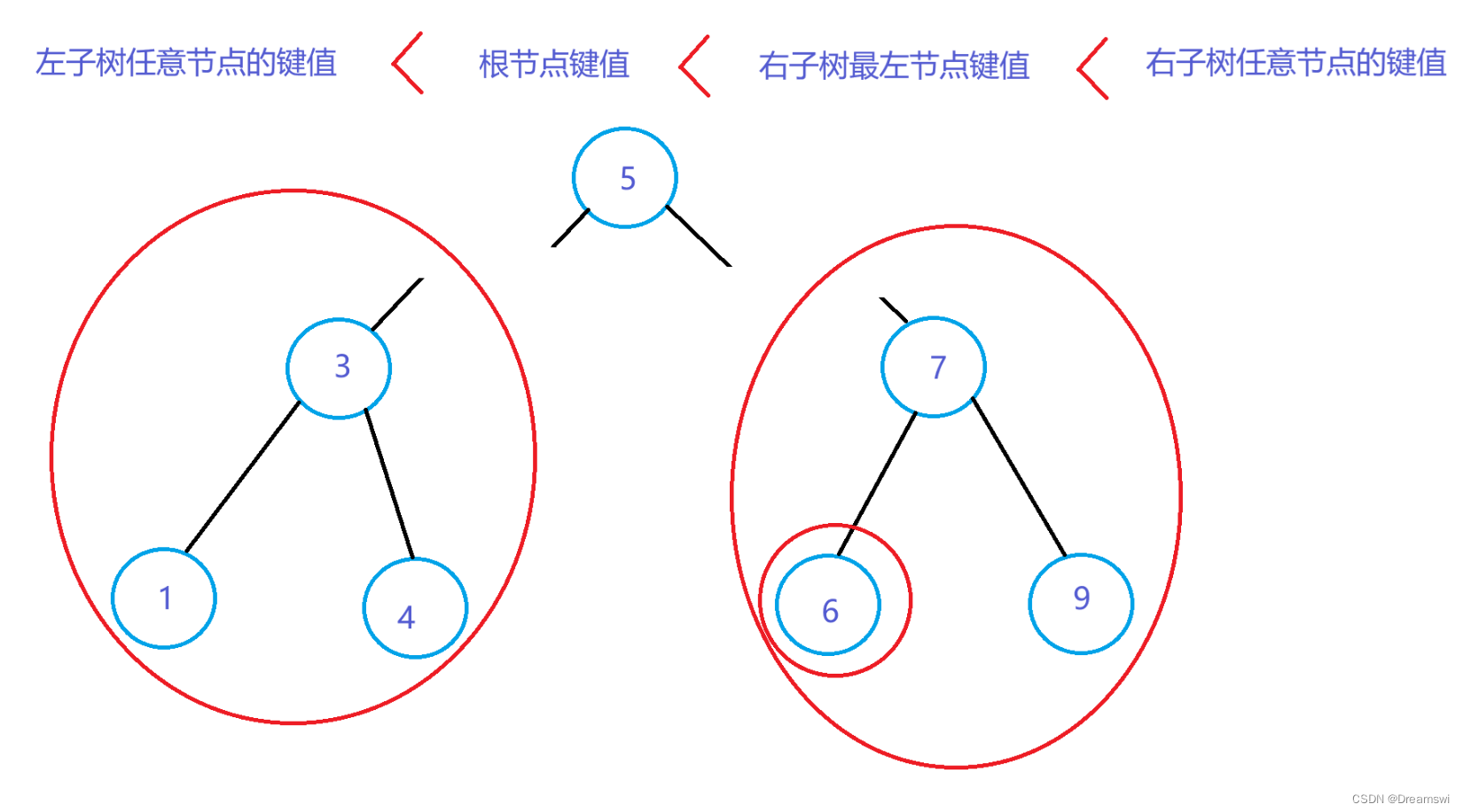
所以我们是希望保持如图的节点关系,那么右子树的最左节点满足做根节点条件。
因为在任意树中都有 右大于根大于左 ,所以该树最左节点存储最小键值。
特殊存储情况
当出现顺序插入时,会呈现出这样的情况,这个时候遍历的时间复杂度就退化到了O(n),此时搜索二叉树就失去了意义。不过平衡二叉树和红黑树解决了高度不平衡导致搜索效率下降的问题。