欢迎大家关注全网生信学习者系列:
- WX公zhong号:生信学习者
- Xiao hong书:生信学习者
- 知hu:生信学习者
- CDSN:生信学习者2
介绍
本教程使用基于R的函数来估计微生物群落的香农指数和丰富度,使用MetaPhlAn profile数据。估计结果进一步进行了可视化,并与元数据关联,以测试统计显著性。
数据
大家通过以下链接下载数据:
- 百度网盘链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1f1SyyvRfpNVO3sLYEblz1A
- 提取码: 请关注WX公zhong号_生信学习者_后台发送 复现msm 获取提取码
R 包
Alpha diversity estimation and visualization
使用alpha_diversity_funcs.R计算alpha多样性和可视化。
- 代码
r
SE_converter <- function(md_rows, tax_starting_row, mpa_md) {
# SE_converter function is to convery metadata-wedged mpa table into SummarisedExperiment structure.
# md_rows: a vector specifying the range of rows indicating metadata.
# tax_starting_row: an interger corresponding to the row where taxonomic abundances start.
# mpa_md: a metaphlan table wedged with metadata, in the form of dataframe.
md_df <- mpa_md[md_rows,] # extract metadata part from mpa_md table
tax_df <- mpa_md[tax_starting_row: nrow(mpa_md),] # extract taxonomic abundances part from mpa_md table
### convert md_df to a form compatible with SummarisedExperiment ###
SE_md_df <- md_df[, -1]
rownames(SE_md_df) <- md_df[, 1]
SE_md_df <- t(SE_md_df)
### convert md_df to a form compatible with SummarisedExperiment ###
### prep relab values in a form compatible with SummarisedExperiment ###
SE_relab_df <- tax_df[, -1]
rownames(SE_relab_df) <- tax_df[, 1]
col_names <- colnames(SE_relab_df)
SE_relab_df[, col_names] <- apply(SE_relab_df[, col_names], 2, function(x) as.numeric(as.character(x)))
### prep relab values in a form compatible with SummarisedExperiment ###
SE_tax_df <- tax_df[, 1:2]
rownames(SE_tax_df) <- tax_df[, 1]
SE_tax_df <- SE_tax_df[-2]
colnames(SE_tax_df) <- c("species")
SE_data <- SummarizedExperiment::SummarizedExperiment(assays = list(relative_abundance = SE_relab_df),
colData = SE_md_df,
rowData = SE_tax_df)
SE_data
}
est_alpha_diversity <- function(se_data) {
# This function is to estimate alpha diversity (shannon index and richness) of a microbiome and output results in dataframe.
# se_data: the SummarizedExperiment data structure containing metadata and abundance values.
se_data <- se_data |>
mia::estimateRichness(abund_values = "relative_abundance", index = "observed")
se_data <- se_data |>
mia::estimateDiversity(abund_values = "relative_abundance", index = "shannon")
se_alpha_div <- data.frame(SummarizedExperiment::colData(se_data))
se_alpha_div
}
make_boxplot <- function(df, xlabel, ylabel, font_size = 11,
jitter_width = 0.2, dot_size = 1,
font_style = "Arial", stats = TRUE, pal = NULL) {
# This function is to create a boxplot using categorical data.
# df: The dataframe containing microbiome alpha diversities, e.g. `shannon` and `observed` with categorical metadata.
# xlabel: the column name one will put along x-axis.
# ylabel: the index estimate one will put along y-axis.
# font_size: the font size, default: [11]
# jitter_width: the jitter width, default: [0.2]
# dot_size: the dot size inside the boxplot, default: [1]
# font_style: the font style, default: `Arial`
# pal: a list of color codes for pallete, e.g. c(#888888, #eb2525). The order corresponds the column order of boxplot.
# stats: wilcox rank-sum test. default: TRUE
if (stats) {
nr_group = length(unique(df[, xlabel])) # get the number of groups
if (nr_group == 2) {
group_pair = list(unique(df[, xlabel]))
ggpubr::ggboxplot(data = df, x = xlabel, y = ylabel, color = xlabel,
palette = pal, ylab = ylabel, xlab = xlabel,
add = "jitter", add.params = list(size = dot_size, jitter = jitter_width)) +
ggpubr::stat_compare_means(comparisons = group_pair, exact = T, alternative = "less") +
ggplot2::stat_summary(fun.data = function(x) data.frame(y = max(df[, ylabel]),
label = paste("Mean=",mean(x))), geom="text") +
ggplot2::theme(text = ggplot2::element_text(size = font_size, family = font_style))
} else {
group_pairs = my_combn(unique((df[, xlabel])))
ggpubr::ggboxplot(data = df, x = xlabel, y = ylabel, color = xlabel,
palette = pal, ylab = ylabel, xlab = xlabel,
add = "jitter", add.params = list(size = dot_size, jitter = jitter_width)) +
ggpubr::stat_compare_means() +
ggpubr::stat_compare_means(comparisons = group_pairs, exact = T, alternative = "greater") +
ggplot2::stat_summary(fun.data = function(x) data.frame(y= max(df[, ylabel]),
label = paste("Mean=",mean(x))), geom="text") +
ggplot2::theme(text = ggplot2::element_text(size = font_size, family = font_style))
}
} else {
ggpubr::ggboxplot(data = df, x = xlabel, y = ylabel, color = xlabel,
palette = pal, ylab = ylabel, xlab = xlabel,
add = "jitter", add.params = list(size = dot_size, jitter = jitter_width)) +
ggplot2::theme(text = ggplot2::element_text(size = font_size, family = font_style))
}
}
my_combn <- function(x) {
combs <- list()
comb_matrix <- combn(x, 2)
for (i in 1: ncol(comb_matrix)) {
combs[[i]] <- comb_matrix[,i]
}
combs
}
felm_fixed <- function(data_frame, f_factors, t_factor, measure) {
# This function is to perform fixed effect linear modeling
# data_frame: a dataframe containing measures and corresponding effects
# f_factors: a vector of header names in the dataframe which represent fixed effects
# t_factors: test factor name in the form of string
# measure: the measured values in column, e.g., shannon or richness
# all_factors <- c(t_factor, f_factors)
# for (i in all_factors) {
# vars <- unique(data_frame[, i])
# lookup <- setNames(seq_along(vars) -1, vars)
# data_frame[, i] <- lookup[data_frame[, i]]
# }
# View(data_frame)
str1 <- paste0(c(t_factor, paste0(f_factors, collapse = " + ")), collapse = " + ")
str2 <- paste0(c(measure, str1), collapse = " ~ ")
felm_stats <- lfe::felm(eval(parse(text = str2)), data = data_frame)
felm_stats
}加载一个包含元数据和分类群丰度的合并MetaPhlAn profile文件
r
mpa_df <- data.frame(read.csv("./data/merged_abundance_table_species_sgb_md.tsv", header = TRUE, sep = "\t"))| sample | P057 | P054 | P052 | ... | P049 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sexual_orientation | MSM | MSM | MSM | ... | Non-MSM |
| HIV_status | negative | positive | positive | ... | negative |
| ethnicity | Caucasian | Caucasian | Caucasian | ... | Caucasian |
| antibiotics_6month | Yes | No | No | ... | No |
| BMI_kg_m2_WHO | ObeseClassI | Overweight | Normal | ... | Overweight |
| Methanomassiliicoccales_archaeon | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ... | 0.01322 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| Methanobrevibacter_smithii | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ... | 0.19154 |
接下来,我们将数据框转换为SummarizedExperiment数据结构,以便使用SE_converter函数继续分析,该函数需要指定三个参数:
md_rows: a vector specifying the range of rows indicating metadata. Note: 1-based.tax_starting_row: an interger corresponding to the row where taxonomic abundances start.mpa_md: a metaphlan table wedged with metadata, in the form of dataframe.
r
SE <- SE_converter(md_rows = 1:5,
tax_starting_row = 6,
mpa_md = mpa_df)
SE
class: SummarizedExperiment
dim: 1676 139
metadata(0):
assays(1): relative_abundance
rownames(1676): Methanomassiliicoccales_archaeon|t__SGB376
GGB1567_SGB2154|t__SGB2154 ... Entamoeba_dispar|t__EUK46681
Blastocystis_sp_subtype_1|t__EUK944036
rowData names(1): species
colnames(139): P057 P054 ... KHK16 KHK11
colData names(5): sexual_orientation HIV_status ethnicity
antibiotics_6month BMI_kg_m2_WHO接下来,我们可以使用est_alpha_diversity函数来估计每个宏基因组样本的香农指数和丰富度。
r
alpha_df <- est_alpha_diversity(se_data = SE)
alpha_df| sexual_orientation | HIV_status | ethnicity | antibiotics_6month | BMI_kg_m2_WHO | observed | shannon | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P057 | MSM | negative | Caucasian | Yes | ObeseClassI | 134 | 3.1847 |
| P054 | MSM | positive | Caucasian | No | Overweight | 141 | 2.1197 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| P052 | MSM | positive | Caucasian | No | Normal | 152 | 2.5273 |
为了比较不同组之间的alpha多样性差异,我们可以使用make_boxplot函数,并使用参数:
df: The dataframe containing microbiome alpha diversities, e.g.shannonandobservedwith categorical metadata.xlabel: the column name one will put along x-axis.ylabel: the index estimate one will put along y-axis.font_size: the font size, default: [11]jitter_width: the jitter width, default: [0.2]dot_size: the dot size inside the boxplot, default: [1]font_style: the font style, default:Arialpal: a list of color codes for pallete, e.g. c(#888888, #eb2525). The order corresponds the column order of boxplot.stats: wilcox rank-sum test. default:TRUE
r
shannon <- make_boxplot(df = alpha_df,
xlabel = "sexual_orientation",
ylabel = "shannon",
stats = TRUE,
pal = c("#888888", "#eb2525"))
richness <- make_boxplot(df = alpha_df,
xlabel = "sexual_orientation",
ylabel = "observed",
stats = TRUE,
pal = c("#888888", "#eb2525"))
multi_plot <- ggpubr::ggarrange(shannon, richness, ncol = 2)
ggplot2::ggsave(file = "shannon_richness.svg", plot = multi_plot, width = 4, height = 5)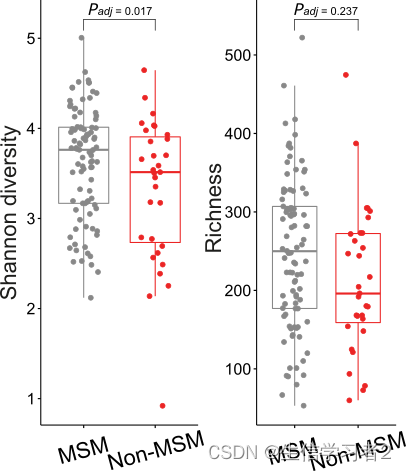
通过固定效应线性模型估计关联的显著性
在宏基因组分析中,除了感兴趣的变量(例如性取向)之外,通常还需要处理多个变量(例如HIV感染和抗生素使用)。因此,在测试微生物群落矩阵(例如香农指数或丰富度)与感兴趣的变量(例如性取向)之间的关联时,控制这些混杂效应非常重要。在这里,我们使用基于固定效应线性模型的felm_fixed函数,该函数实现在R包lfe 中,以估计微生物群落与感兴趣变量之间的关联显著性,同时控制其他变量的混杂效应。
data_frame: The dataframe containing microbiome alpha diversities, e.g.shannonandobservedwith multiple variables.f_factors: A vector of variables representing fixed effects.t_factor: The variable of interest for testing.measure: The header indicating microbiome measure, e.g.shannonorrichness
r
lfe_stats <- felm_fixed(data_frame = alpha_df,
f_factors = c(c("HIV_status", "antibiotics_6month")),
t_factor = "sexual_orientation",
measure = "shannon")
summary(lfe_stats)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-2.3112 -0.4666 0.1412 0.5200 1.4137
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 3.62027 0.70476 5.137 9.64e-07 ***
sexual_orientationMSM 0.29175 0.13733 2.125 0.0355 *
HIV_statuspositive -0.28400 0.14658 -1.937 0.0548 .
antibiotics_6monthNo -0.10405 0.67931 -0.153 0.8785
antibiotics_6monthYes 0.01197 0.68483 0.017 0.9861
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
Residual standard error: 0.6745 on 134 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared(full model): 0.07784 Adjusted R-squared: 0.05032
Multiple R-squared(proj model): 0.07784 Adjusted R-squared: 0.05032
F-statistic(full model):2.828 on 4 and 134 DF, p-value: 0.02725
F-statistic(proj model): 2.828 on 4 and 134 DF, p-value: 0.02725