pg_control为什么会存在?
为啥会有pg_control这么个文件呢? pg_control是PostgreSQL中一个很重要的文件,我们之前讲到过PostgreSQL的启动过程,启动过程中很重要的一项工作就是故障恢复,启动startup进程,回放WAL日志进行故障恢复,而从哪里开始进行回放呢?我怎么知道起点在哪里呢?这个位置的保存一定是在磁盘中,而不是在内存中,假设数据库因故障崩溃,内存中的数据会丢失,所以,只有checkpointer进程在做checkpoint操作时不断的更新pg_control文件,使之持久化保存,数据库启动进行故障恢复时,读取该文件,获得故障恢复的起始位置。
除了保存检查点信息,还保存一些其他的状态等信息,用于数据库启动等。比如数据库状态信息,系统表版本号等。
看下面的代码,数据库启动时会检查pg_control文件,如果文件被损坏,数据库就会启动失败。
c++
main()
--> MemoryContextInit() // 初始化内存上下文: TopMemoryContext、ErrorContext
--> PostmasterMain(argc, argv); // Postmaster main entry point
--> pqsignal_pm(SIGCHLD, reaper); /* handle child termination */ // 注册信号处理函数
--> checkDataDir(); // 检查数据目录
--> ValidatePgVersion(DataDir); // 检查PG_VERSION文件,PG实例版本是否与程序兼容
--> checkControlFile(); // 检查pg_control文件
--> CreateDataDirLockFile(true); // 创建postmaster.pid文件
--> LocalProcessControlFile(false); // 读pg_control,到ControlFileData中
--> ReadControlFile();startup进程从pg_control中获取故障恢复起点:
c++
StartupProcessMain(void)
--> StartupXLOG();
--> ValidateXLOGDirectoryStructure(); // 检查pg_wal是否存在
--> readRecoverySignalFile(); // 依据standby.signal和recovery.signal是否存在,判断进入何种状态
--> validateRecoveryParameters();
if (read_backup_label(&checkPointLoc, &backupEndRequired, &backupFromStandby))
{
// 如果backup_label文件存在,则表示从备份文件中进行恢复(例如使用pg_basebackup进行备份)
// 此种情况,设置backup_label,而不是用pg_control,为啥呢?下面就是解释
/*
* If we see a backup_label during recovery, we assume that we are recovering
* from a backup dump file, and we therefore roll forward from the checkpoint
* identified by the label file, NOT what pg_control says. This avoids the
* problem that pg_control might have been archived one or more checkpoints
* later than the start of the dump, and so if we rely on it as the start
* point, we will fail to restore a consistent database state.
*/
}
else
{
/* Get the last valid checkpoint record. */
checkPointLoc = ControlFile->checkPoint; // 从pg_control中获取检查点信息
RedoStartLSN = ControlFile->checkPointCopy.redo;
record = ReadCheckpointRecord(xlogreader, checkPointLoc, 1, true);
--> XLogBeginRead(xlogreader, RecPtr); // Begin reading WAL at 'RecPtr'.
--> ReadRecord(xlogreader, LOG, true); // Attempt to read the next XLOG record.
for (;;)
{
XLogReadRecord(xlogreader, &errormsg); // Attempt to read an XLOG record.
}
}pg_control文件的内容
pg_control保存在PGDATA/global/pg_control中,我们通过pg_controldata查看其具体内容:
其中有2个是非常重要的,
shell
Latest checkpoint location: 0/D04FD00 -- 最后一次的checkpoint位置
Latest checkpoint's REDO location: 0/D04FCC8 -- 重做点位置,非常重要,崩溃恢复时回放的起点怎么解释呢?
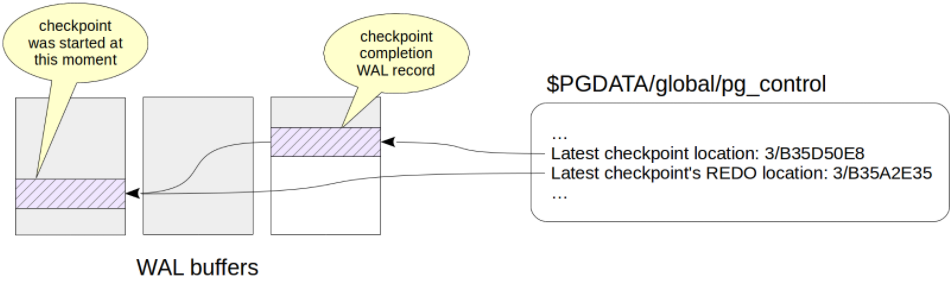
就是说checkpoint操作是需要一定时间的,在开始进行checkpoint时,先记录当前点为Latest checkpoint REDO location,作为重做点。当完成刷盘操作后,把checkpoint相关信息也生成一条WAL记录,再把这个WAL记录也写入WAL日志文件中,位置就是Latest checkpoint location。
如果checkpoint的过程中,节点故障挂掉了?这种情况,如果checkpoint没有完成,那么其pg_control文件就没有被更新,也就是说pg_control还是上次的pg_control文件,再次启动时,尽管已经做了部分checkpoint操作,但是仍然从老的重做点开始回放,回放具有幂等性,仍能进行正常的恢复操作。
shell
postgres@slpc:~/pgsql$ ./bin/pg_controldata -D masternode/
pg_control version number: 1300
Catalog version number: 202107181 -- 系统表版本号
Database system identifier: 7242131451622390647 -- 数据库系统标识符,用于标识一套数据库系统,物理复制的主备库拥有相同的数据库唯一标识串,initdb时生成
Database cluster state: in production
pg_control last modified: 2023年08月03日 星期四 18时17分24秒
Latest checkpoint location: 0/D04FD00 -- 最后一次的checkpoint位置
Latest checkpoint's REDO location: 0/D04FCC8 -- 重做点
Latest checkpoint's REDO WAL file: 00000001000000000000000D
Latest checkpoint's TimeLineID: 1
Latest checkpoint's PrevTimeLineID: 1
Latest checkpoint's full_page_writes: on
Latest checkpoint's NextXID: 0:25998
Latest checkpoint's NextOID: 24641
Latest checkpoint's NextMultiXactId: 1
Latest checkpoint's NextMultiOffset: 0
Latest checkpoint's oldestXID: 726
Latest checkpoint's oldestXID's DB: 1
Latest checkpoint's oldestActiveXID: 25998
Latest checkpoint's oldestMultiXid: 1
Latest checkpoint's oldestMulti's DB: 1
Latest checkpoint's oldestCommitTsXid:0
Latest checkpoint's newestCommitTsXid:0
Time of latest checkpoint: 2023年08月03日 星期四 18时17分18秒
Fake LSN counter for unlogged rels: 0/3E8
Minimum recovery ending location: 0/0 -- 备机用,用于指定当备考异常终止再启动时,只有应用WAL日志过指定点后才能对外提供只读服务,否则,用户读到的数据可能会不一致。
Min recovery ending loc's timeline: 0
Backup start location: 0/0
Backup end location: 0/0
End-of-backup record required: no
wal_level setting: replica
wal_log_hints setting: off
max_connections setting: 100
max_worker_processes setting: 8
max_wal_senders setting: 10
max_prepared_xacts setting: 0
max_locks_per_xact setting: 64
track_commit_timestamp setting: off
Maximum data alignment: 8
Database block size: 8192
Blocks per segment of large relation: 131072
WAL block size: 8192
Bytes per WAL segment: 16777216
Maximum length of identifiers: 64
Maximum columns in an index: 32
Maximum size of a TOAST chunk: 1996
Size of a large-object chunk: 2048
Date/time type storage: 64-bit integers
Float8 argument passing: by value
Data page checksum version: 0
Mock authentication nonce: 5faa9a77552e9f84e1dadd05fabcc97d121cc211905bd02386eb881dd347c198关于其具体含义,可以看下面的定义,更多可参考src/include/catalog/pg_control.h的定义。
c++
/* Contents of pg_control. */
typedef struct ControlFileData
{
/* Unique system identifier --- to ensure we match up xlog files with the installation that produced them. */
uint64 system_identifier;
uint32 pg_control_version; /* PG_CONTROL_VERSION */
uint32 catalog_version_no; /* see catversion.h */
/* System status data */
DBState state; /* see enum above */
pg_time_t time; /* time stamp of last pg_control update */
XLogRecPtr checkPoint; /* last check point record ptr */
CheckPoint checkPointCopy; /* copy of last check point record */
XLogRecPtr unloggedLSN; /* current fake LSN value, for unlogged rels */
/*
* These two values determine the minimum point we must recover up to
* before starting up:
*
* minRecoveryPoint is updated to the latest replayed LSN whenever we
* flush a data change during archive recovery. That guards against
* starting archive recovery, aborting it, and restarting with an earlier
* stop location. If we've already flushed data changes from WAL record X
* to disk, we mustn't start up until we reach X again. Zero when not
* doing archive recovery.
*
* backupStartPoint is the redo pointer of the backup start checkpoint, if
* we are recovering from an online backup and haven't reached the end of
* backup yet. It is reset to zero when the end of backup is reached, and
* we mustn't start up before that. A boolean would suffice otherwise, but
* we use the redo pointer as a cross-check when we see an end-of-backup
* record, to make sure the end-of-backup record corresponds the base
* backup we're recovering from.
*
* backupEndPoint is the backup end location, if we are recovering from an
* online backup which was taken from the standby and haven't reached the
* end of backup yet. It is initialized to the minimum recovery point in
* pg_control which was backed up last. It is reset to zero when the end
* of backup is reached, and we mustn't start up before that.
*
* If backupEndRequired is true, we know for sure that we're restoring
* from a backup, and must see a backup-end record before we can safely
* start up. If it's false, but backupStartPoint is set, a backup_label
* file was found at startup but it may have been a leftover from a stray
* pg_start_backup() call, not accompanied by pg_stop_backup().
*/
XLogRecPtr minRecoveryPoint;
TimeLineID minRecoveryPointTLI;
XLogRecPtr backupStartPoint;
XLogRecPtr backupEndPoint;
bool backupEndRequired;
/* Parameter settings that determine if the WAL can be used for archival or hot standby. */
int wal_level;
bool wal_log_hints;
int MaxConnections;
int max_worker_processes;
int max_wal_senders;
int max_prepared_xacts;
int max_locks_per_xact;
bool track_commit_timestamp;
/*
* This data is used to check for hardware-architecture compatibility of
* the database and the backend executable. We need not check endianness
* explicitly, since the pg_control version will surely look wrong to a
* machine of different endianness, but we do need to worry about MAXALIGN
* and floating-point format. (Note: storage layout nominally also
* depends on SHORTALIGN and INTALIGN, but in practice these are the same
* on all architectures of interest.)
*
* Testing just one double value is not a very bulletproof test for
* floating-point compatibility, but it will catch most cases.
*/
uint32 maxAlign; /* alignment requirement for tuples */
double floatFormat; /* constant 1234567.0 */
#define FLOATFORMAT_VALUE 1234567.0
/* This data is used to make sure that configuration of this database is compatible with the backend executable.*/
uint32 blcksz; /* data block size for this DB */
uint32 relseg_size; /* blocks per segment of large relation */
uint32 xlog_blcksz; /* block size within WAL files */
uint32 xlog_seg_size; /* size of each WAL segment */
uint32 nameDataLen; /* catalog name field width */
uint32 indexMaxKeys; /* max number of columns in an index */
uint32 toast_max_chunk_size; /* chunk size in TOAST tables */
uint32 loblksize; /* chunk size in pg_largeobject */
bool float8ByVal; /* float8, int8, etc pass-by-value? */
/* Are data pages protected by checksums? Zero if no checksum version */
uint32 data_checksum_version;
/* Random nonce, used in authentication requests that need to proceed
* based on values that are cluster-unique, like a SASL exchange that
* failed at an early stage. */
char mock_authentication_nonce[MOCK_AUTH_NONCE_LEN];
pg_crc32c crc; /* CRC of all above ... MUST BE LAST! */
} ControlFileData;pg_controldata
可通过pg_controldata -D masternode/这种形式查看pg_control文件的内容,我们看一下其主流程,就是读pg_control文件,然后将内容进行解析。
c++
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
ControlFileData *ControlFile;
/* get a copy of the control file */
ControlFile = get_controlfile(DataDir, &crc_ok);
printf(_("pg_control version number: %u\n"), ControlFile->pg_control_version);
printf(_("Catalog version number: %u\n"), ControlFile->catalog_version_no);
printf(_("Database system identifier: %llu\n"), (unsigned long long) ControlFile->system_identifier);
printf(_("Database cluster state: %s\n"), dbState(ControlFile->state));
printf(_("pg_control last modified: %s\n"), pgctime_str);
printf(_("Latest checkpoint location: %X/%X\n"), LSN_FORMAT_ARGS(ControlFile->checkPoint));
printf(_("Latest checkpoint's REDO location: %X/%X\n"), LSN_FORMAT_ARGS(ControlFile->checkPointCopy.redo));
printf(_("Latest checkpoint's REDO WAL file: %s\n"), xlogfilename);
// 其他信息...
}
// 读pg_control文件到ControlFileData中
ControlFileData *get_controlfile(const char *DataDir, bool *crc_ok_p)
{
ControlFileData *ControlFile;
ControlFile = palloc(sizeof(ControlFileData));
fd = open(ControlFilePath, O_RDONLY | PG_BINARY, 0);
r = read(fd, ControlFile, sizeof(ControlFileData));
close(fd);
return ControlFile;
}