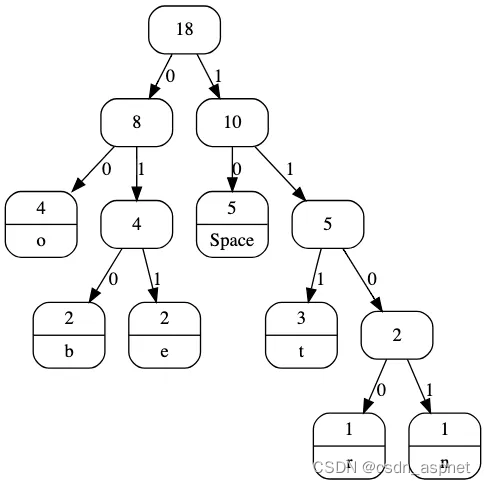
Huffman Tree 进行解码 示例图
c语言:c语言 霍夫曼编码 | 贪婪算法(Huffman Coding | Greedy Algo)_霍夫曼的贪婪c语言-CSDN博客
c++:c++ 霍夫曼编码 | 贪婪算法(Huffman Coding | Greedy Algo)_霍夫曼的贪婪算法设计核心代码-CSDN博客
c#:C# 霍夫曼编码 | 贪婪算法(Huffman Coding | Greedy Algo)-CSDN博客
c++ STL:c++ STL 霍夫曼编码 | 贪婪算法(Huffman Coding | Greedy Algo)-CSDN博客
java:java 霍夫曼编码 | 贪婪算法(Huffman Coding | Greedy Algo)-CSDN博客
python:python 霍夫曼编码 | 贪婪算法(Huffman Coding | Greedy Algo)-CSDN博客
javascript:JavaScript 霍夫曼编码 | 贪婪算法(Huffman Coding | Greedy Algo)-CSDN博客
我们在之前的文章中 讨论了霍夫曼编码。在这篇文章中,我们将讨论解码。
例子:
输入数据: AAAAAABCCCCCCDDEEEEE
频率: A:6,B:1,C:6,D:2,E:5
编码数据: 00000000000011001010101010111111110101010
哈夫曼树: "#"是用于内部节点的特殊字符,因为
内部节点不需要字符字段。
#(20)
/ \
#(12) #(8)
/ \ / \
A(6) C(6) E(5) #(3)
/ \
B(1) D(2)
'A' 的代码是 '00','C' 的代码是 '01',..
解码数据: AAAAAAABCCCCCCDDEEEEE
输入数据: GeeksforGeeks
字符 频率为
e 10, f 1100, g 011, k 00, o 010, r 1101, s 111
编码的哈夫曼数据: 01110100011111000101101011101000111
解码的哈夫曼数据: geeksforgeeks
请按照以下步骤解决问题:
**注意:**要解码编码数据,我们需要霍夫曼树。我们遍历二进制编码数据。要找到与当前位对应的字符,我们使用以下简单步骤:
1、我们从根开始,依次进行,直到找到叶子。
2、如果当前位为 0,我们就移动到树的左节点。
3、如果该位为 1,我们移动到树的右节点。
4、如果在遍历过程中遇到叶节点,我们会打印该特定叶节点的字符,然后再次从步骤 1 开始继续迭代编码数据。
下面的代码将一个字符串作为输入,对其进行编码,并将其保存在变量编码字符串中。然后对其进行解码并打印原始字符串。
下面是上述方法的实现:
// C++ program to encode and decode a string using
// Huffman Coding.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define MAX_TREE_HT 256
using namespace std;
// to map each character its huffman value
map<char, string> codes;
// To store the frequency of character of the input data
map<char, int> freq;
// A Huffman tree node
struct MinHeapNode {
char data; // One of the input characters
int freq; // Frequency of the character
MinHeapNode *left, *right; // Left and right child
MinHeapNode(char data, int freq)
{
left = right = NULL;
this->data = data;
this->freq = freq;
}
};
// utility function for the priority queue
struct compare {
bool operator()(MinHeapNode* l, MinHeapNode* r)
{
return (l->freq > r->freq);
}
};
// utility function to print characters along with
// there huffman value
void printCodes(struct MinHeapNode* root, string str)
{
if (!root)
return;
if (root->data != '$')
cout << root->data << ": " << str << "\n";
printCodes(root->left, str + "0");
printCodes(root->right, str + "1");
}
// utility function to store characters along with
// there huffman value in a hash table, here we
// have C++ STL map
void storeCodes(struct MinHeapNode* root, string str)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
if (root->data != '$')
codes[root->data] = str;
storeCodes(root->left, str + "0");
storeCodes(root->right, str + "1");
}
// STL priority queue to store heap tree, with respect
// to their heap root node value
priority_queue<MinHeapNode*, vector<MinHeapNode*>, compare>
minHeap;
// function to build the Huffman tree and store it
// in minHeap
void HuffmanCodes(int size)
{
struct MinHeapNode *left, *right, *top;
for (map<char, int>::iterator v = freq.begin();
v != freq.end(); v++)
minHeap.push(new MinHeapNode(v->first, v->second));
while (minHeap.size() != 1) {
left = minHeap.top();
minHeap.pop();
right = minHeap.top();
minHeap.pop();
top = new MinHeapNode('$',
left->freq + right->freq);
top->left = left;
top->right = right;
minHeap.push(top);
}
storeCodes(minHeap.top(), "");
}
// utility function to store map each character with its
// frequency in input string
void calcFreq(string str, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++)
freq[str[i]]++;
}
// function iterates through the encoded string s
// if s[i]=='1' then move to node->right
// if s[i]=='0' then move to node->left
// if leaf node append the node->data to our output string
string decode_file(struct MinHeapNode* root, string s)
{
string ans = "";
struct MinHeapNode* curr = root;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {
if (s[i] == '0')
curr = curr->left;
else
curr = curr->right;
// reached leaf node
if (curr->left == NULL and curr->right == NULL) {
ans += curr->data;
curr = root;
}
}
// cout<<ans<<endl;
return ans + '\0';
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
string str = "geeksforgeeks";
string encodedString, decodedString;
calcFreq(str, str.length());
HuffmanCodes(str.length());
cout << "Character With there Frequencies:\n";
for (auto v = codes.begin(); v != codes.end(); v++)
cout << v->first << ' ' << v->second << endl;
for (auto i : str)
encodedString += codes[i];
cout << "\nEncoded Huffman data:\n"
<< encodedString << endl;
// Function call
decodedString
= decode_file(minHeap.top(), encodedString);
cout << "\nDecoded Huffman Data:\n"
<< decodedString << endl;
return 0;
}
输出:
具有以下频率的字符:
e 10
f 1100
g 011
k 00
o 010
r 1101
s 111
编码的哈夫曼数据:
01110100011111000101101011101000111
解码的哈夫曼数据:
geeksforgeeks
时间复杂度:
霍夫曼编码算法的时间复杂度为O(n log n),其中n为输入字符串的字符个数。辅助空间复杂度也是O(n),其中n为输入字符串的字符个数。
在给定的 C++ 实现中,时间复杂度主要由使用优先级队列创建 Huffman 树决定,这需要 O(n log n) 时间。空间复杂度主要由用于存储字符频率和代码的映射决定,这需要 O(n) 空间。用于打印代码和存储代码的递归函数也增加了空间复杂度。
比较输入文件大小和输出文件大小:
比较输入文件大小和霍夫曼编码的输出文件。我们可以用一种简单的方法计算输出数据的大小。假设我们的输入是一个字符串"geeksforgeeks",存储在文件 input.txt 中。
输入文件大小:
输入: "geeksforgeeks"
字符总数即输入长度:13
大小: 13 个字符出现次数 * 8 位 = 104 位或 13 个字节。
输出文件大小:
输入: "geeksforgeeks"
字符 | 频率 | 二进制哈夫曼值 |
e | 4 | 10 |
f | 1 | 1100 |
g | 2 | 011 |
k | 2 | 00 |
o | 1 | 010 |
r | 1 | 1101 |
s | 2 | 111 |
因此要计算输出大小:
e:出现 4 次 * 2 位 = 8 位
f:出现 1 次 * 4 位 = 4 位
g:出现 2 次 * 3 位 = 6 位
k:出现 2 次 * 2 位 = 4 位
o:出现 1 次 * 3 位 = 3 位
r:出现 1 次 * 4 位 = 4 位
s:出现 2 次 * 3 位 = 6 位
总和: 35 位,约 5 字节
由此可见,编码后的数据量是比较大的,上面的方法也可以帮我们确定N的值,也就是编码后数据的长度。