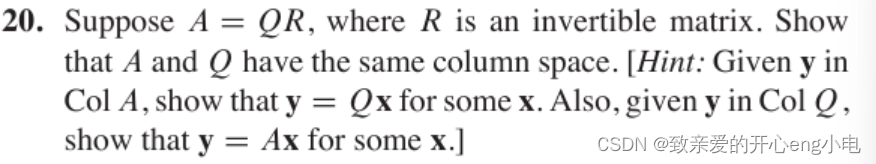 answer
answer
To show that \( A \) and \( Q \) have the same column space, we'll use the given hints:
Step 1: Show that \( \text{Col } A \subseteq \text{Col } Q \)
Given \( y \in \text{Col } A \), we can write \( y = Ax \) for some vector \( x \).
Since \( A = QR \) and \( R \) is invertible, we have:
\[ y = Ax = QRx \]
Let \( x' = Rx \). Since \( R \) is invertible, \( x' \) can be any vector in \(\mathbb{R}^n\). Thus:
\[ y = Qx' \]
This shows that \( y \) is also in the column space of \( Q \), i.e., \( \text{Col } A \subseteq \text{Col } Q \).
Step 2: Show that \( \text{Col } Q \subseteq \text{Col } A \)
Given \( y \in \text{Col } Q \), we can write \( y = Qx \) for some vector \( x \).
Since \( A = QR \) and \( R \) is invertible, we can multiply both sides by \( R^{-1} \):
\[ Q = AR^{-1} \]
Thus:
\[ y = Qx = AR^{-1}x \]
Let \( x' = R^{-1}x \). Since \( R \) is invertible, \( x' \) can be any vector in \(\mathbb{R}^n\). Thus:
\[ y = Ax' \]
This shows that \( y \) is also in the column space of \( A \), i.e., \( \text{Col } Q \subseteq \text{Col } A \).
Conclusion
Since we've shown that \( \text{Col } A \subseteq \text{Col } Q \) and \( \text{Col } Q \subseteq \text{Col } A \), we conclude that \( \text{Col } A = \text{Col } Q \).
Therefore, \( A \) and \( Q \) have the same column space.
details
To understand why \( x' \) can be any vector in \(\mathbb{R}^n\), let's break it down step by step.
Understanding the Concept
Given that \( R \) is an invertible matrix:
- **Invertibility of \( R \)**: Since \( R \) is invertible, there exists a matrix \( R^{-1} \) such that:
\[ R R^{-1} = I \]
where \( I \) is the identity matrix.
- **Transformation by \( R \)**: Any vector \( x \in \mathbb{R}^n \) can be transformed by multiplying it by \( R \), resulting in a new vector \( x' \). We write:
\[ x' = Rx \]
- **Invertible Transformation**: Because \( R \) is invertible, we can always find \( x \) given \( x' \) by multiplying \( x' \) by \( R^{-1} \):
\[ x = R^{-1} x' \]
Why \( x' \) Can Be Any Vector in \(\mathbb{R}^n\)
Let's see why \( x' \) can be any vector in \(\mathbb{R}^n\):
-
**Surjectivity**: The function \( f: \mathbb{R}^n \to \mathbb{R}^n \) defined by \( f(x) = Rx \) is surjective because for any vector \( x' \) in the output space (the codomain), there exists an \( x \) in the input space (the domain) such that \( Rx = x' \). This is because \( R \) has full rank (since it's invertible).
-
**Vector Space Mapping**: Since \( R \) maps \( \mathbb{R}^n \) to itself in a bijective manner (one-to-one and onto), for every vector \( x' \in \mathbb{R}^n \), there exists a vector \( x \in \mathbb{R}^n \) such that \( x' = Rx \).
-
**Existence of \( x \)**: Given any vector \( x' \in \mathbb{R}^n \), we can always find a corresponding vector \( x \) using \( x = R^{-1} x' \). Therefore, \( x' \) can be any vector in \(\mathbb{R}^n\).
Example
Let's consider a concrete example with \( R \):
- Suppose \( R \) is a 2x2 invertible matrix:
\[ R = \begin{pmatrix} 2 & 1 \\ 1 & 3 \end{pmatrix} \]
- We can find \( R^{-1} \):
\[ R^{-1} = \frac{1}{5} \begin{pmatrix} 3 & -1 \\ -1 & 2 \end{pmatrix} \]
- Now, given any vector \( x' \in \mathbb{R}^2 \), say \( x' = \begin{pmatrix} 4 \\ 5 \end{pmatrix} \):
\[ x = R^{-1} x' = \frac{1}{5} \begin{pmatrix} 3 & -1 \\ -1 & 2 \end{pmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} 4 \\ 5 \end{pmatrix} = \frac{1}{5} \begin{pmatrix} 3 \cdot 4 + (-1) \cdot 5 \\ (-1) \cdot 4 + 2 \cdot 5 \end{pmatrix} = \frac{1}{5} \begin{pmatrix} 12 - 5 \\ -4 + 10 \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} 1.4 \\ 1.2 \end{pmatrix} \]
This shows that for any \( x' \), we can find an \( x \) such that \( x' = Rx \), thus demonstrating that \( x' \) can indeed be any vector in \(\mathbb{R}^n\).
By understanding this property of invertible matrices, we can see why \( x' \) can be any vector in \(\mathbb{R}^n\).