NARF 全称 normal aligned radial feature(法线对齐的径向特征) ,是一种为从深度图像中识别物体而提出的3D关键点检测和描述的算法,该算法由Bastian Steder和 Radu Bogdan Rusu等人于2010年在他们的文章《Point Feature Extraction on 3D Range Scans Taking into Account Object Boundaries》中首次提出。
NARF是基于深度图像的关键点提取算法,与普通的灰度图像不一样,深度图像中深度值发生跳变的地方往往就是图像中物体的边缘部分。因此NARF算法会首先进行边缘检测,然后再从中选出表面稳定但领域变化较大的边缘点作为关键点。
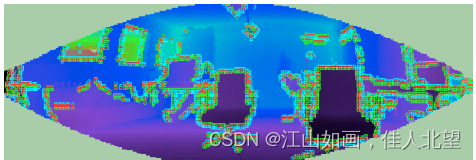
深度图像
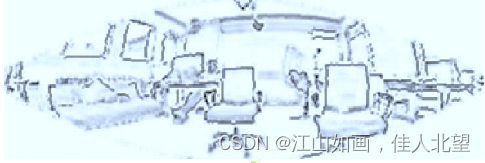
边缘检测的结果
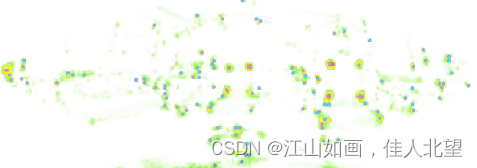
关键点提取的结果
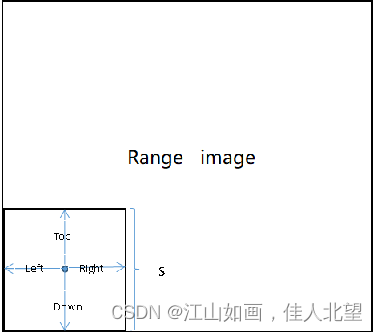
为了找到边缘,在每个深度图(range image)上,给定查询点p,在以p为中心,s为边长的矩形窗格内,计算每个点到p的距离,并对距离的集合升序排列,得到集合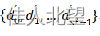
然后计算点p与上、下、左、右四个方向的邻域的距离
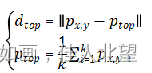
然后对点p在上、下、左、右四个方向打分,判断点p是否为边缘点
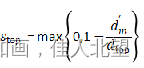
将分数值与阈值T(原文文给的参考值为0.8),对评分大于T的点进行非极大值抑制,就区分出了物体的边缘点和非边缘点
 边缘提取示意图
边缘提取示意图
接着,就可以借用边缘点信息进行NARF关键点探测了,探测的步骤如下: 首先遍历深度图像中的每一个点,计算每个点的主方向v,再计算根据领域信息确定点的强度因子I1和方向因子I2:
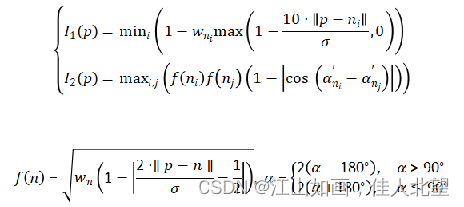
然后将强度因子和方向因子相乘便得到兴趣值I。 然后利用高斯核来平滑每个点的兴趣值。 最后设定阈值T2,当兴趣值I大于阈值时,即为NARF关键点。T2的参考值可以为0.5。
配准结果示意图
深度图像示意图

边缘点提取结果示意图
