常用注解
常见的注解解析方法有两种:
- 编译期直接扫描:编译器在编译 Java 代码的时候扫描对应的注解并处理,比如某个方法使用@Override 注解,编译器在编译的时候就会检测当前的方法是否重写了父类对应的方法。
- 运行期通过反射处理:像框架中自带的注解(比如 Spring 框架的 @Value、@Component)都是通过反射来进行处理的
这个博客对常用注解讲的很详细且有例子 SpringBoot常用的50个注解
以下是根据苍穹外卖来整理的注解和使用实例。
1.@ResponseBody
的作用其实是将java对象转为json格式的数据 ,然后直接写入HTTP response 的body中;
@RequestMapping后,返回值通常解析为跳转路径,但是加上 @ResponseBody 后返回结果不会被解析为跳转路径,而是直接写入 HTTP response body 中。
2.@RestController=@ReponseBody+@Controller
在类上用@RestController,其内的所有方法都会默认加上@ResponseBody,也就是默认返回JSON格式。将控制器方法的返回值转换为JSON格式,并以HTTP响应的方式返回给客户端。
@RestController和@Controller的共同点是都用来表示Spring某个类是否可以接收HTTP请求,二者区别: @RestController无法返回指定页面,而@Controller可以;前者可以直接返回数据,后者需要@ResponseBody辅助。
在@RestController中指定Bean的名称。
java
@RestController("adminShopController")//为了避免两个Bean都叫shopController的冲突,所以用为了区分他俩
@RequestMapping("/admin/shop")
@Slf4j
@Api(tags = "店铺相关接口")
public class ShopController {
}
java
@RestController("UserShopController")
@RequestMapping("/user/shop")
@Api(tags = "店铺相关接口")
@Slf4j
public class ShopController {
}3.@RequestBody是作用在形参列表上 ,用于将前台发送过来固定格式的数据【xml格式 或者 json等】封装为对应的 JavaBean 对象,封装时使用到的一个对象是系统默认配置的 HttpMessageConverter进行解析,然后封装到形参上。
就是将JSON格式的数据封装到实体类中
4.@Transactional是Spring框架中用于声明式事务管理的关键注解。通过使用@Transactional注解,我们可以更加方便地管理事务,保障数据的一致性和可靠性。用于声明式事务管理**,保证方法或类中的操作在同一个事务中执行**。
5.@RequestMapping映射请求URL和处理方法。跳转路径
6.@GetMapping用于映射HTTP GET请求。
7.@PostMapping用于映射HTTP POST请求。
@RequestParam用于获取请求参数的值。
java
@DeleteMapping
@ApiOperation("菜品批量删除")
public Result delete(@RequestParam List<Long> ids){//注解@RequestParam,可以将地址栏中多个数字参数提取出来然后变成List集合。
log.info("菜品批量删除:{}",ids);
dishService.deleteBatch(ids);
return Result.success();
}
@ConfigurationProperties注解代表当前类是一个配置属性类,作用是:封装配置文件中的一些配置项。
原理就是:通过配置属性类,将配置文件中的配置项,封装成一个类,然后通过@Autowired注解注入到要使用的地方。
10.取的是路径参数,加注解@PathVariable,如果和路径参数不同名,就要加括号双引号指明取的是哪个路径参数@PathVariable("status") ;如果同名,就不用加。
java
@PostMapping("/status/{status}")
@ApiOperation("启用禁用员工账号")
public Result startOrStop(@PathVariable Integer status,Long id){
log.info("启用禁用员工账号:{},{}",status,id);
employeeService.startOrStop(status,id);
return Result.success();
}- AOP相关注解
切入点 :@Pointcut里面写的是对哪些方法进行拦截,要满足2点:
①必须是mapper下的所有类的方法,
②还要有AutoFill这个注解。
在对切面的定义中共使用@Pointcut("execution(* com.sky.mapper.*.*(..)) && @annotation(com.sky.annotation.AutoFill)")这里指定使用的包范围和在有注解标注的方法上。
mapper中使用的示例:
java
@AutoFill(OperationType.UPDATE)
void update(Employee employee);(1)创建自定义注解
annotation.AutoFill.java 注解类
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)//指定注解只能加载方法上,@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)运行时
Target注解指定加上什么上面,Retention注解指定什么时候用,
java
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)//指定注解只能加载方法上
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface AutoFill {
//通过枚举-指定当前属性OperationType
//数据库操作类型OperationType:就两种 Update 和 Insert
OperationType value();
}(2)切面类 aspect.AutoFillAspect.java 自动填充的切片类
java
@Aspect
@Component
@Slf4j
public class AutoFillAspect {
//这个包里的类和方法和加上@AutoFill注解的
@Pointcut("execution(* com.sky.mapper.*.*(..)) && @annotation(com.sky.annotation.AutoFill)")
public void autoFillPointCut() {
}
//前置通知,在sql执行前加上即(公共字段赋值)
@Before("autoFillPointCut()")//当匹配上切点表达式的执行这个
public void autoFill(JoinPoint joinPoint) {//插入链接点的参数值
//1.获取到当前被栏截的方法上的数据库操作类型
//2.获取到当前被拦截的方法的参数--实体对象
//3.准备赋值的数据
//4.根据当前不同的操作类型,为对应的属性通过反射来赋值
}
}12.Swagger使用注解
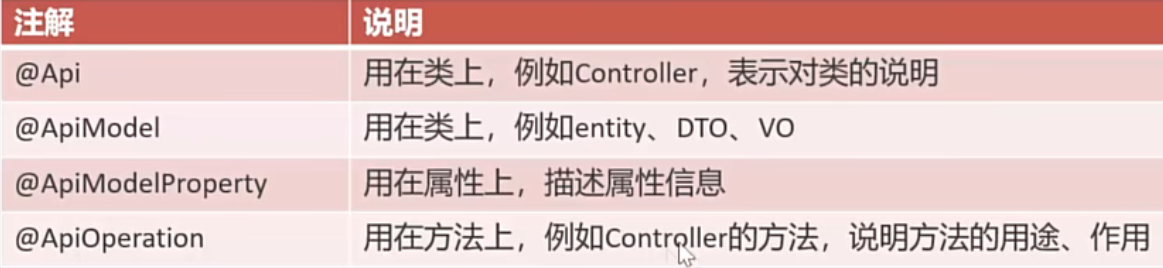
@Api(tags = "员工相关接口")
java
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/admin/employee")
@Slf4j
@Api(tags = "员工相关接口")//tags用来描述类的作用
public class EmployeeController {@ApiOperation("员工登录")
java
@PostMapping("/login")
@ApiOperation("员工登录")
public Result<EmployeeLoginVO> login(@RequestBody EmployeeLoginDTO employeeLoginDTO) {@ApiModel(description = "员工登录时传递的数据模型")
@ApiModelProperty("用户名")
java
@Data
@ApiModel(description = "员工登录时传递的数据模型")
public class EmployeeLoginDTO implements Serializable {
@ApiModelProperty("用户名")
private String username;
@ApiModelProperty("密码")
private String password;
}13.@Bean //项目启动时就会调用方法创建对象
@ConditionalOnMissingBean//保证Spring容器里只有一个Util对象,条件对象当没Bean时再创建
注意要return的是这个新创建的对象,不然后面自动注入会失败,这里的主要目的就是创建Bean对象
java
@Bean //项目启动时就会调用方法创建对象
@ConditionalOnMissingBean//保证Spring容器里只有一个Util对象,条件对象当没Bean时再创建
public AliOssUtil aliOssUtil(AliOssProperties aliOssProperties) {
return new AliOssUtil(aliOssProperties.getEndpoint(),
aliOssProperties.getAccessKeyId(),
aliOssProperties.getAccessKeySecret(),
aliOssProperties.getBucketName());
}因为涉及到多个表,所以添加@Transactional的注解
(需要在启动类上添加@EnableTransactionManagement注解):开启注解方式的事务管理
java
@Transactional//涉及几多个数据表,需要保证数据一致性,需要事务注解--保证原子性,全成功或全失败
@Override
public void saveWithFlavor(DishDTO dishDTO) {
//开始新增菜品
}15.Spring Cache框架,实现了基于注解的缓存功能。
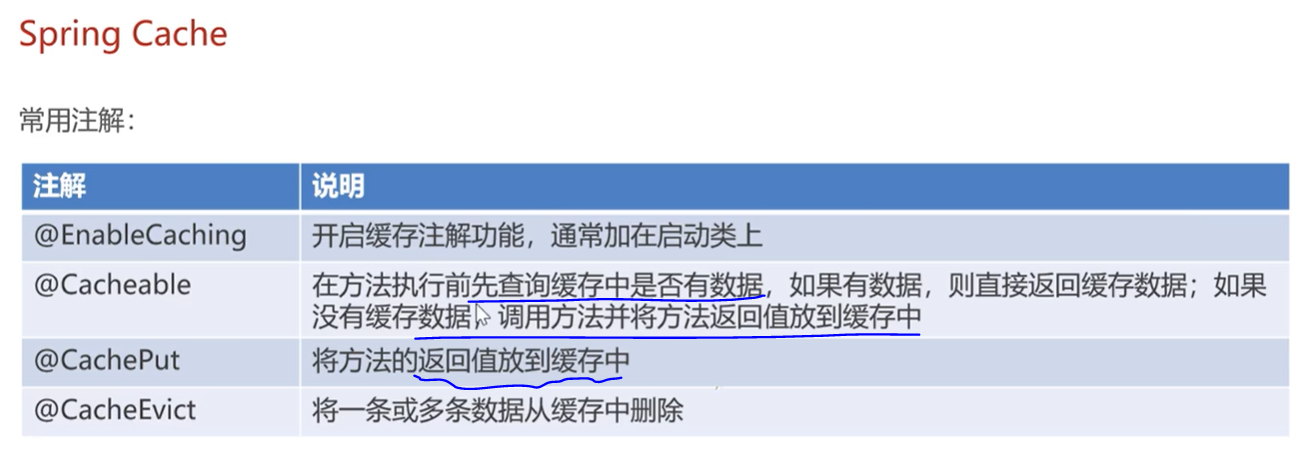
都是在Controller层:
(1)@CachePut这个注释将方法的返回结果,user对象保存到Redis中,同时生成动态的key,userCache::user.id
java
@CachePut(cacheNames="userCache",key="abs")//Spring Cache缓存数据,key的生成:userCache:abc
@CachePut(cacheNames="userCache",key="#user.id")//与形参保持一致,或者
@CachePut(cacheNames="userCache",key="#result.id")//返回值result,或者
@CachePut(cacheNames="userCache",key="#p0.id")//获得当前方法的第一个参数user,或者
@CachePut(cacheNames="userCache",key="#a0.id")//获得当前方法的第一个参数user,或者
@CachePut(cacheNames="userCache",key="#root.args[0].id")//获得当前方法的第一个参数user
public User save(@RequestBody User user){
userMapper.insert(user);
return result;
}插入完数据后,数据库生成的主键值会自动赋给user对象
Redis可以形成树形结构
(2)@Cacheable注解
java
@Cacheable(cahceNames="userCache"),key="#id")//key的生成,userCache::10
public User getById(Long id){
User user = userMapper.getById(id);
return user;
}(3)@CacheEvict一次清理一条数据
java
@CacheEvict(cahceNames="userCache"),key="#id")//key的生成,userCache::10
public void deleteById(Long id){
userMapper.deleteById(id);
}清除所有数据
java
@CacheEvict(cahceNames="userCache"),allEntries=true)//userCache下的所有键值对
public void deleteAlld(){
userMapper.deleteAll();
}动态sql
insert 返回生成的主键值
xml
<insert id="insert" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id"><!-- 产生的主键值会赋给id属性-->
insert into dish (name, category_id, price, image, description, create_time, update_time, create_user, update_user, status)
values (#{name}, #{categoryId}, #{price}, #{image}, #{description}, #{createTime}, #{updateTime}, #{createUser}, #{updateUser}, #{status})
</insert>mapper:
不用注解,动态sql使用映射文件
在resource文件夹里都是xml文件
select
<select>标签的id是mapper中的对应方法名,resultType是返回的参数类型。
java
<select id="selectByPage" resultType="com.sky.entity.Employee">
select * from employee
<where>
<if test="name!=null and name !='' ">
and name like concat('%',#{name},'%') <!--模糊查询 like -->
</if>
</where>
order by create_time desc <!--创建时间降序-->
</select>稍复杂一点的select
动态sql
sql语句:左外链接 :将左边的表的所有项与右边的表作连接
将菜和种类两个表按照种类id链接起来,以此获得种类名称
sql
select d.*,c.name as categoryName from dish d left outer join category c on d.category_id=c.id由于种类名称查出来也叫name,所以给字段起别名
xml
<select id="pageQuery" resultType="com.sky.vo.DishVO">
select d.*,c.name categoryName from dish d left join category c on d.category_id = c.id
<where><!--毕竟动态sql。给它用where动态拼上DTO的3个属性 -->
<if test="categoryId! =null">d.category_id=#{categoryId}</if>
<if test="status!=null">d.status=#{status}</if>
<if test="name!=null">d.name like concat('%',#{name},'%')</if>
</where>
order by d.create_time desc<!--根据创建时间降序 -->
</select>delete
(1)sql
按照菜id查全部信息,以此得到是否在售卖
sql
@Select("select * from dish where id=#{id}")
Dish getById(Long id);(2)sql
是否有套餐关联
// select setmeal id from setmeal dish where dish_id in (1,2,3,4)
List queryUnsale(List ids);传入菜品List列表,用动态sql查每个菜品是否有套餐
SetMealDishMapper.xml
xml
<select id="getSetmealIdsByDishIds" resultType="java.lang.Long">
select setmeal_id from setmeal_dish where dish_id in
<foreach collection="dishIds" separator="," item="id" open="(" close=")">
#{id}
</foreach>
</select>foreach循环,collection是集合,item是一个个项,separator是分割符号,open是开始符号,close是结束符号。每个元素用逗号分割,然后用大括号括起来。
(3)删除菜---传入为列表
xml
<delete id="deleteBatch">
delete from dish where id in
<foreach collection="ids" item="id" separator="," open="(" close=")">
#{id}
</foreach>
</delete>(4)删除口味---传入为列表
xml
<delete id="deleteBatchByDishIds">
delete from dish_flavor where dish_id in
<foreach collection="ids" item="id" open="(" close=")" separator=",">
#{id}
</foreach>
</delete>update
xml
<update id="update">
update dish
<set>
<if test="name!=null">name=#{name},</if>
<if test="categoryId!=null">category_id=#{categoryId},</if>
<if test="price!=null">price=#{price},</if>
<if test="image!=null">image=#{image},</if>
<if test="description!=null">description=#{description},</if>
<if test="status!=null">status=#{status},</if>
<if test="updateTime!=null">update_time=#{updateTime},</if>
<if test="updateUser!=null">update_user=#{updateUser},</if>
</set>
where id=#{id}
</update>