Reading the Username & Password
Spring Security 为从 HttpServletRequest 读取用户名和密码提供了以下内置机制:
Form Login
SpringSecurity 支持通过 HTML 表单提供用户名和密码。本节详细介绍 Spring Security 中基于表单的身份验证是如何工作的。
本节讨论 SpringSecurity 中基于表单的登录是如何工作的。首先,我们看看用户是如何被重定向到登录表单的:

*Figure 1. Redirecting to the Login Page*
- 首先,用户向未授权的资源(/private)发出未经身份验证的请求。
- Spring Security 的 AuthorizationFilter 指示通过引发 AccessDeniedException 拒绝未经身份验证的请求。
- 由于用户未通过身份验证,ExceptionTranslationFilter 会启动身份验证,并通过配置的 AuthenticationEntryPoint 将请求重定向到登录页面。在大多数情况下,AuthenticationEntryPoint 是 LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint 的一个实例。
- 浏览器请求它被重定向到的登录页面。
- 应用程序中的某些内容必须呈现登录页面。
当用户名和密码提交时,UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 会对用户名和密码进行身份验证。UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 扩展了 AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter,所以下图应该看起来非常相似:

该图基于我们的 SecurityFilterChain 图构建。
- 当用户提交他们的用户名和密码时,UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 通过从 HttpServletRequest 实例中提取用户名和密码来创建一个 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken,这是一种身份验证类型。
- 接下来,将 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 传递到 AuthenticationManager 实例以进行身份验证。AuthenticationManager 的细节取决于用户信息的存储方式。
- 如果身份验证失败,则为"失败"。
- SecurityContextHolder 被清除。
- LoginFail 被调用。如果没有配置 me,这是一个 no-op。请参见 Javadoc 中的 RememberMeServices 接口。
- 将调用验证失败处理AuthenticationFailureHandler程序。请参见 Javadoc 中的验证失败处理程序
AuthenticationFailureHandler类
- 如果身份验证成功,则为"成功"。
- SessionAuthenticationStrategy 会在新登录时收到通知。请参阅 Javadoc 中的 SessionAuthenticationStrategy 接口。
- Authentication 会被设置在 SecurityContextHolder 中。请参阅 Javadoc 中的 SecurityContextPersistenceFilter 类。
- RememberMeServices.loginSuccess 会被调用。如果没有配置记住我功能,这将是一个无操作。请参阅 Javadoc 中的 RememberMeServices 接口。
- ApplicationEventPublisher 会发布一个 InteractiveAuthenticationSuccessEvent。
- AuthenticationSuccessHandler 会被调用。通常,这个处理程序是 SimpleUrlAuthenticationSuccessHandler,它会重定向到我们重定向到登录页面时由 ExceptionTranslationFilter 保存的请求。
默认情况下,启用了 SpringSecurity 表单登录。但是,一旦提供了任何基于 servlet 的配置,就必须显式提供基于表单的登录。下面的示例显示了一个最小的、显式的 Java 配置:
Form Login
java
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) {
http
.formLogin(withDefaults());
// ...
}在前面的配置中,SpringSecurity 呈现默认登录页面。大多数生产应用程序需要自定义登录表单。
Custom Login Form Configuration
java
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) {
http
.formLogin(form -> form
.loginPage("/login")
.permitAll()
);
// ...
}当在 SpringSecurity 配置中指定登录页时,您负责呈现该页。下面的 Thymeleaf 模板生成一个符合/login 登录页面的 HTML 登录表单:
Login Form - src/main/resources/templates/login.html
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:th="https://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>Please Log In</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Please Log In</h1>
<div th:if="${param.error}">
Invalid username and password.</div>
<div th:if="${param.logout}">
You have been logged out.</div>
<form th:action="@{/login}" method="post">
<div>
<input type="text" name="username" placeholder="Username"/>
</div>
<div>
<input type="password" name="password" placeholder="Password"/>
</div>
<input type="submit" value="Log in" />
</form>
</body>
</html>关于默认的 HTML 表单有几个关键点:
- 表单应该发送post请求到/login。
- 该表单需要包含一个 CSRF 令牌,Thymeleaf 会自动包含该令牌。
- 表单应该在名为 username 的参数中指定用户名。
- 表单应该在名为 password 的参数中指定密码。
- 如果找到名为 error 的 HTTP 参数,则表示用户未能提供有效的用户名或密码。
- 如果找到名为 logout 的 HTTP 参数,则表示用户已成功注销。
许多用户只需要定制登录页面即可。但是,如果需要,您可以使用附加配置自定义前端显示的所有内容。
如果使用 Spring MVC,则需要一个将 GET/login 映射到我们创建的登录模板的控制器。下面的示例显示了最小的 LoginController:
java
@Controller
class LoginController {
@GetMapping("/login")
String login() {
return "login";
}
}Basic Authentication
本节详细介绍 Spring Security 如何为基于 servlet 的应用程序提供对Basic HTTP Authentication 的支持。
本节描述在 SpringSecurity 中 HTTP Basic身份验证是如何工作的。首先,我们看到 WWW-Authenticate 头被发送回未经身份验证的客户端:

*Figure 1. Sending WWW-Authenticate Header*
前面的图是基于我们的 SecurityFilterChain 图构建的。
- 首先,用户向未经授权的资源/私有资源发出未经身份验证的请求。
- Spring Security 的 AuthorizationFilter 指示通过引发 AccessDeniedException 拒绝未经身份验证的请求。
- 由于用户没有经过身份验证,ExceptionTransationFilter 将启动"启动身份验证"。配置的 AuthenticationEntryPoint 是 BasicAuthenticationEntryPoint 的一个实例,它发送一个 WWW-Authenticate 头。RequestCache 通常是一个 NullRequestCache,它不保存请求,因为客户端能够重播它最初请求的请求。
当客户端收到 WWW-Authenticate 头时,它知道应该使用用户名和密码重试。下图显示了正在处理的用户名和密码的流程:
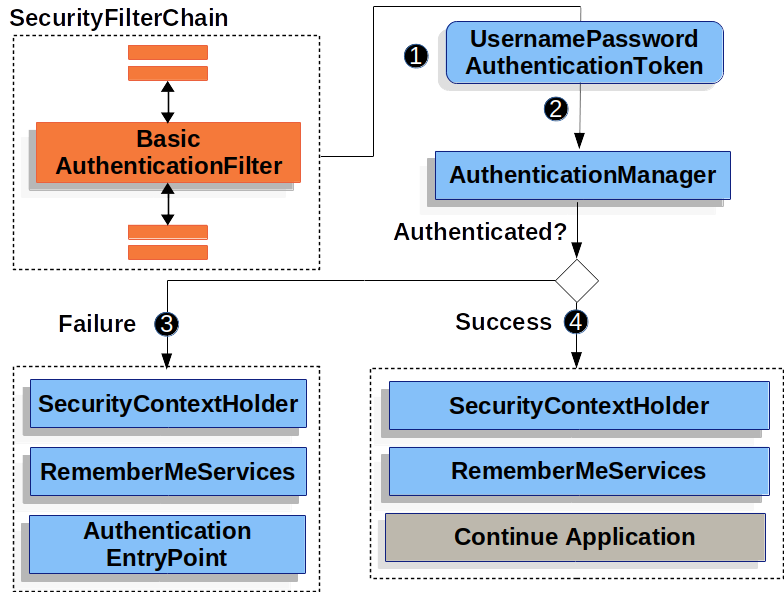
*Figure 2. Authenticating Username and Password*
前面的图是基于我们的 SecurityFilterChain 图构建的。
- 当用户提交他们的用户名和密码时,BasicAuthenticationFilter 会创建一个 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken,这是一种从 HttpServletRequest 中提取用户名和密码的验证类型。
- 接下来,将 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 传递到 AuthenticationManager 以进行身份验证。AuthenticationManager 的细节取决于用户信息的存储方式。
- 如果身份验证失败,则为"失败"。
- SecurityContextHolder 被清除。
- LoginFail 被调用。如果没有配置"记住我",这是一个禁用操作。请参见 Javadoc 中的 RememberMeServices 接口。
- AuthenticationEntryPoint 被调用来触发要再次发送的 WWW-Authenticate。
- 如果身份验证成功,则"成功"。
- 身份验证在 SecurityContextHolder 上设置。
- 已调用 RememberMeServices.loginSuccess。如果未配置"记住我",则此操作为禁用。请参见 Javadoc 中的 RememberMeServices 接口。
- BasicAuthenticationFilter 调用 FilterChain.doFilter (request,response)来继续其余的应用程序逻辑。请参见 Javadoc 中的 BasicAuthenticationFilter 类
默认情况下,将启用 SpringSecurity 的 HTTPBasic 身份验证支持。但是,一旦提供了任何基于 servlet 的配置,就必须显式提供 HTTPBasic。
下面的示例显示了一个最小的、显式的配置:
Explicit HTTP Basic Configuration
java
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) {
http
// ...
.httpBasic(withDefaults());
return http.build();
}Digest Authentication
本节提供有关 Spring Security 如何提供对 DigestAuthenticationFilter 的支持的详细信息。
在现代应用程序中不应使用摘要身份验证,因为它不被认为是安全的。最明显的问题是,必须以明文、加密或 MD5格式存储密码。所有这些存储格式都被认为是不安全的。相反,您应该使用单向自适应密码散列(bCrypt、 PBKDF2、 SCrypt 等)来存储凭据,而这是摘要身份验证所不支持的。
摘要身份验证试图解决基本身份验证的许多弱点,特别是通过确保凭据永远不会以明文形式通过网络发送。许多浏览器支持摘要身份验证。
控制 HTTP 摘要身份验证的标准由 RFC 2617定义,它更新了 RFC 2069规定的摘要身份验证标准的早期版本。大多数用户代理实现 RFC2617。Spring Security 的摘要认证支持与 rfc2617规定的" auth"质量保护(qop)兼容,后者也提供 rfc2069向下兼容。如果需要使用未加密的 HTTP (不使用 TLS 或 HTTPS)并希望最大限度地提高身份验证过程的安全性,则摘要身份验证被视为一种更具吸引力的选择。但是,每个人都应该使用 HTTPS。
中央到摘要身份验证是一个" nonce"。这是服务器生成的值。Spring Security 现在采用以下格式:
Digest Syntax
txt
base64(expirationTime + ":" + md5Hex(expirationTime + ":" + key))
expirationTime: The date and time when the nonce expires, expressed in milliseconds
key: A private key to prevent modification of the nonce token您需要确保使用 NoOpPasswordEncoder 配置不安全的纯文本密码存储。(请参见 Javadoc 中的 NoOpPasswordEncoder 类。)下面提供了使用 Java 配置配置摘要身份验证的示例:
Digest Authentication
java
@Autowired
UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
DigestAuthenticationEntryPoint authenticationEntryPoint() {
DigestAuthenticationEntryPoint result = new DigestAuthenticationEntryPoint();
result.setRealmName("My App Realm");
result.setKey("3028472b-da34-4501-bfd8-a355c42bdf92");
return result;
}
DigestAuthenticationFilter digestAuthenticationFilter() {
DigestAuthenticationFilter result = new DigestAuthenticationFilter();
result.setUserDetailsService(userDetailsService);
result.setAuthenticationEntryPoint(authenticationEntryPoint());
return result;
}
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
// ...
.exceptionHandling(e -> e.authenticationEntryPoint(authenticationEntryPoint()))
.addFilter(digestAuthenticationFilter());
return http.build();
}