分析Profiler Timeline中的算子序列,通过寻找频繁项集的办法,得到TOPK可融合的算子序列
- 1.相关链接
- 2.代码【仅分析带通信算子的Pattern】
- [3.在实际工程中发现 ['all_gather', 'matrix_mm_out']频率最高](#3.在实际工程中发现 ['all_gather', 'matrix_mm_out']频率最高)
- [4.[Ascend MC2](https://gitee.com/ascend/MindSpeed/blob/master/docs/features/mc2.md)](#4.Ascend MC2)
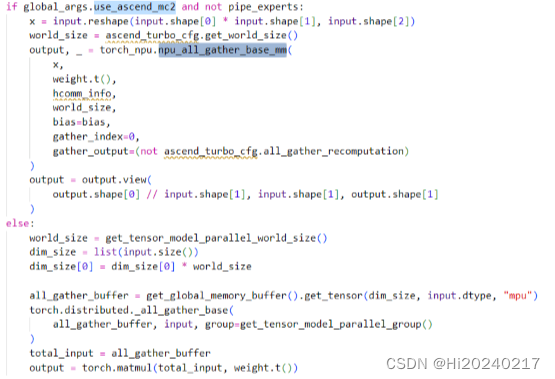
- 5.torch_npu.npu_all_gather_base_mm
本文尝试分析Profiler Timeline中的算子序列,通过寻找频繁项集的办法,得到TOPK可融合的算子序列
1.相关链接
2.代码【仅分析带通信算子的Pattern】
python
from collections import defaultdict, deque
def rolling_hash(s, base=257, mod=10**9 + 7):
h = 0
for ch in s:
h = (h * base + ord(ch)) % mod
return h
def find_top_n_fixed_length_sequences(arr, length, top_n):
# 创建一个字典来存储子序列及其出现次数和偏移位置
sequence_data = defaultdict(lambda: {"count": 0, "positions": []})
base, mod = 257, 10**9 + 7
# 滑动窗口计算固定长度子序列
for i in range(len(arr) - length + 1):
window = arr[i:i + length]
if "all_gather" in window or "reduce_scatter" in window: #只处理函通信算子的pattern
flat_window = ''.join(window)
h = rolling_hash(flat_window, base, mod)
sequence_data[h]['count'] += 1
sequence_data[h]['positions'].append(i)
# 按照出现频率排序,并获取前N个子序列
sorted_sequences = sorted(sequence_data.items(), key=lambda item: item[1]['count'], reverse=True)
top_sequences = sorted_sequences[:top_n]
return top_sequences, sequence_data
# 加载profiler生成的timeline,提取出算子名列表及偏移未知,这里构造了一个简单的数据
operators=["mm","all_gather","binary_add","dropout_backward","fill","eltwise_silu","mm","all_gather","fill"]
offsets=range(0,len(operators))
# 要求最少两个元素的子序列,且取前3个出现频率最高的长度为2的子序列
length = 2
top_n = 1
# 获取前N个频繁的长度为固定长度的子序列
top_sequences, sequence_data = find_top_n_fixed_length_sequences(operators, length, top_n)
# 反向查找实际的序列值
reverse_lookup = {}
for i in range(len(operators) - length + 1):
window = operators[i:i + length]
flat_window = ''.join(window)
h = rolling_hash(flat_window)
if h not in reverse_lookup:
reverse_lookup[h] = window
# 输出结果并去重
unique_sequences = set() # 用来跟踪已经输出的序列
for seq_hash, data in top_sequences:
seq = reverse_lookup[seq_hash]
seq_tuple = tuple(seq)
if seq_tuple not in unique_sequences:
unique_sequences.add(seq_tuple)
positions = sequence_data[seq_hash]['positions']
print(f'序列: {seq}, 出现频率: {data["count"]}')
for pos in positions:
beg=pos
end=pos+length
ts_beg=offsets[beg]
ts_end=offsets[end]
print(ts_beg,ts_end,operators[ts_beg:ts_end])DEMO 输出
bash
序列: ['mm', 'all_gather'], 出现频率: 2
0 2 ['mm', 'all_gather']
6 8 ['mm', 'all_gather']3.在实际工程中发现 ['all_gather', 'matrix_mm_out']频率最高
4.Ascend MC2

5.torch_npu.npu_all_gather_base_mm