ReID 算法,全称是"行人再识别(Person Re-Identification)"算法,可应用于智能驾驶或智能机器人陪伴等领域。它的目标是在不同摄像头或不同时间拍摄的多张图像中,准确识别出是否为同一个人。本文以 ReID 中比较有名的 OSNet 模型为例,讲解如何在地平线计算平台量化该模型。
OSNet(Omni-Scale Network)是 行人再识别 任务中非常流行的一种深度学习架构,旨在高效提取行人图像中不同尺度的判别特征。
核心思想:Omni-Scale Feature Learning
OSNet 的核心思想是:在一个卷积块中同时捕捉多种尺度的信息,而不是像传统方法那样堆叠多个尺度层。
传统 ReID 网络可能在不同层捕捉不同尺度(如局部细节 vs 整体结构),但 OSNet 尝试在每一层同时捕捉小尺度和大尺度的信息。
osnet_ain_x1_0 是 OSNet 系列中性能较强的一个变体,其全称是:
OSNet-AIN-x1.0 :Omni-Scale Network with Adaptive Instance Normalization(自适应实例归一化)
特点解析
- 多尺度特征学习(OSNet 核心)
OSBlock模块引入多个不同感受野的卷积分支。- 实现:局部细节与全局上下文同时建模。
- 相比传统 ResNet,有更强的判别性和更少的参数。
- AIN:自适应实例****归一化
-
Adaptive Instance Normalization 是一种可以调节风格的归一化方法,常用于领域自适应。
-
在 ReID 中,行人图像来自不同摄像头或环境,AIN 可以自适应不同图像风格,减轻 域偏移(domain shift) 的影响。
-
提升跨摄像头、跨数据集的识别能力。
一、源码导出 ONNX
1.1 克隆代码仓库
克隆代码仓库的 master 分支。
Plain
git clone https://github.com/KaiyangZhou/deep-person-reid.git之后按照官方指导搭建好环境。
1.2 下载预训练权重
使用 Multi-source domain generalization 章节 osnet_ain_x1_0 的 MS+D+C->M 权重 osnet_ain_ms_d_c.pth.tar。
Plain
https://kaiyangzhou.github.io/deep-person-reid/MODEL_ZOO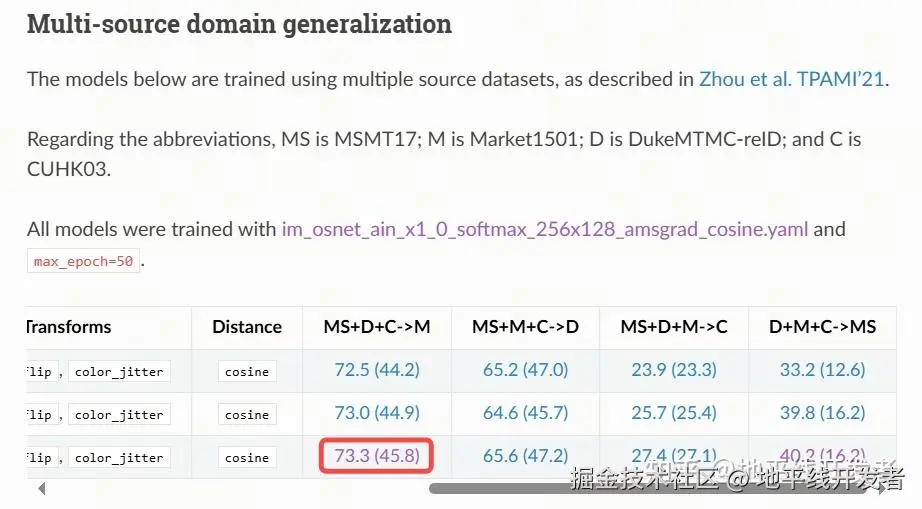
1.3 导出 onnx
将 osnet_ain_ms_d_c.pth.tar 权重文件存放到项目根目录,编写并运行 onnx 导出脚本。
Plain
import torch
from torchreid.utils.feature_extractor import FeatureExtractor
def export_onnx(model, im):
f = 'osnet_ain_x1_0.onnx'
torch.onnx.export(
model.cpu(),
im.cpu(),
f,
opset_version=11,
do_constant_folding=True,
input_names=['input'],
output_names=['output']
)
return 0
if __name__ == "__main__":
extractor = FeatureExtractor(
model_name="osnet_ain_x1_0",
model_path="./osnet_ain_ms_d_c.pth.tar",
device=str('cpu')
)
im = torch.zeros(1, 3, 256, 128).to('cpu')
export_onnx(extractor.model.eval(), im)1.4 检查 onnx 和 pytorch 一致性
Plain
import onnx
import torch
import onnxruntime as ort
import numpy as np
from pathlib import Path
from torchreid.utils.feature_extractor import FeatureExtractor
def cosine_similarity(a, b):
a = np.array(a)
b = np.array(b)
return np.dot(a, b) / (np.linalg.norm(a) * np.linalg.norm(b))
def max_difference(a, b):
a = np.array(a).ravel()
b = np.array(b).ravel()
diff = np.abs(a - b)
max_diff = np.max(diff)
max_idx = np.argmax(diff)
print(f"最大差值: {max_diff},位置索引: {max_idx}")
return max_diff, max_idx
if __name__ == "__main__":
extractor = FeatureExtractor(
model_name="osnet_ain_x1_0",
model_path="./osnet_ain_ms_d_c.pth.tar",
device=str('cpu')
)
im = torch.randn(1, 3, 256, 128).to('cpu')
with torch.no_grad():
pt_model = extractor.model.eval()
output = pt_model(im)
onnx_path = 'osnet_ain_x1_0.onnx'
session = ort.InferenceSession(onnx_path, providers=['CPUExecutionProvider'])
input_tensor =im.numpy()
input_name = session.get_inputs()[0].name
outputs = session.run(None, {input_name: input_tensor})
output_tensor = outputs[0]
print(cosine_similarity(output.numpy().reshape(-1), output_tensor.reshape(-1)))
max_difference(output.numpy().reshape(-1), output_tensor.reshape(-1))如果多次运行,相似度打印均为 1,且最大差值均在 e-5 以内,则可认为 onnx 和 pytorch 的输出保持一致。
二、PTQ 量化
2.1 生成校准数据
可以从官方数据集(Market-1501-v15.09.15)中选择数百张 jpg 图片用来生成校准数据。
在生成校准数据前,需要明确预处理参数,在源码 deep-person-reid-master/torchreid/data/transforms.py 中,可以得知训练时会将图片直接 resize 成模型输入尺寸,并使用 imagenet 数据集的标准归一化参数,即:
Plain
norm_mean = [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
norm_std = [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]且由归一化参数可知,模型训练时使用的色彩通道顺序是 rgb。
此时可以基于 horizon_model_convert_sample 提供的脚本生成校准数据,只需基于 02_preprocess.sh 和 preprocess.py 脚本做如下改动:
Plain
python3 ../../../data_preprocess.py \
--src_dir ./market_1501_jpg \ # 从Market-1501-v15.09.15数据集挑选的jpg图片
--dst_dir ./calib_data_rgb_f32 \ # 生成的校准数据文件夹
--pic_ext .rgb \ # 色彩通道顺序
--read_mode opencv \ # 读图方式使用opencv
--saved_data_type float32 \ # 校准数据的数据类型使用float32
--cal_img_num 300 # 生成300份校准数据
from horizon_tc_ui.data.transformer import (
BGR2RGBTransformer, HWC2CHWTransformer, ResizeTransformer)
def calibration_transformers():
transformers = [
ResizeTransformer(target_size=(256, 128)), # 直接对图像做resize
HWC2CHWTransformer(), # 从HWC更改为CHW
BGR2RGBTransformer(data_format="CHW"), # 将色彩通道顺序更改为RGB
]
return transformers由于归一化计算会集成到 PTQ 生成模型的预处理节点中,因此校准数据无需做归一化处理。
2.2 量化编译
推荐使用如下 YAML 配置:
Plain
calibration_parameters:
cal_data_dir: calib_data_rgb_f32
cal_data_type: float32
calibration_type: max
max_percentile: 0.99999
optimization: set_all_nodes_int16
run_on_cpu: "/conv1/bn/InstanceNormalization_mean1;/conv1/bn/InstanceNormalization_sub1;/conv1/bn/InstanceNormalization_mul1;/conv1/bn/InstanceNormalization_mean2;/conv1/bn/InstanceNormalization_reciprocal;/conv1/bn/InstanceNormalization_mul2;/conv1/bn/InstanceNormalization_mul3;/conv2/conv2.0/IN/InstanceNormalization_mean1;/conv2/conv2.0/IN/InstanceNormalization_sub1;/conv2/conv2.0/IN/InstanceNormalization_mul1;/conv2/conv2.0/IN/InstanceNormalization_mean2;/conv2/conv2.0/IN/InstanceNormalization_reciprocal;/conv2/conv2.0/IN/InstanceNormalization_mul2;/conv2/conv2.0/IN/InstanceNormalization_mul3"
compiler_parameters:
jobs: 32
optimize_level: O3
input_parameters:
input_name: input
input_shape: 1x3x256x128
input_type_rt: nv12
input_type_train: rgb
input_layout_train: NCHW
norm_type: 'data_mean_and_scale'
mean_value: 123.675 116.28 103.53
scale_value: 0.01712475383 0.0175070028 0.0174291938998
model_parameters:
march: bayes-e
onnx_model: osnet_ain_x1_0.onnx
output_model_file_prefix: reid
working_dir: model_output这里使用 nv12 作为板端模型的输入,mean_value 和 scale_value 由归一化参数计算得到。同时,考虑到 InstanceNormalization 算子的量化风险较高,因此为模型中的前两个 InstanceNormalization 配置浮点计算精度,YAML 中 run_on_cpu 配置的算子较多是因为 InstanceNormalization 会被 PTQ 拆分成多个算子。
可以使用以下命令编译:
Plain
hb_mapper makertbin --config osnet_config.yaml --model-type onnx编译完成后,日志打印的相似度如下(quantized.onnx 对比 optimized.onnx):
Plain
=========================================================================
Output Cosine Similarity L1 Distance L2 Distance Chebyshev Distance
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
output 0.995540 0.057718 0.008716 0.482978余弦相似度>0.99,可初步认为量化精度满足需求。
2.3 验证 PTQ 生成 onnx 的输出相似度
在编译流程结束后,可以手动验证各 PTQ 生成物和原始 onnx 的输出相似度,及时发现可能的精度问题。
*请根据不同的计算平台修改代码。
Plain
import cv2
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
from horizon_tc_ui import HB_ONNXRuntime
def cosine_similarity(a, b):
a = np.array(a)
b = np.array(b)
return np.dot(a, b) / (np.linalg.norm(a) * np.linalg.norm(b))
def bgr2nv12(image):
image = image.astype(np.uint8)
height, width = image.shape[0], image.shape[1]
yuv420p = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2YUV_I420).reshape((height * width * 3 // 2, ))
y = yuv420p[:height * width]
uv_planar = yuv420p[height * width:].reshape((2, height * width // 4))
uv_packed = uv_planar.transpose((1, 0)).reshape((height * width // 2, ))
nv12 = np.zeros_like(yuv420p)
nv12[:height * width] = y
nv12[height * width:] = uv_packed
return nv12
def nv12Toyuv444(nv12, target_size):
height = target_size[0]
width = target_size[1]
nv12_data = nv12.flatten()
yuv444 = np.empty([height, width, 3], dtype=np.uint8)
yuv444[:, :, 0] = nv12_data[:width * height].reshape(height, width)
u = nv12_data[width * height::2].reshape(height // 2, width // 2)
yuv444[:, :, 1] = Image.fromarray(u).resize((width, height),resample=0)
v = nv12_data[width * height + 1::2].reshape(height // 2, width // 2)
yuv444[:, :, 2] = Image.fromarray(v).resize((width, height),resample=0)
return yuv444
def rgb_preprocess(img_path):
bgr_input = cv2.imread(img_path)
bgr_input = cv2.resize(bgr_input, (128,256), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
rgb_input = cv2.cvtColor(bgr_input, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
mean = np.array([123.675, 116.28, 103.53], dtype=np.float32)
scale = np.array([0.01712475383, 0.0175070028, 0.0174291938998], dtype=np.float32)
rgb_input = (rgb_input - mean) * scale
rgb_input = rgb_input[np.newaxis,:,:,:]
rgb_input = np.transpose(rgb_input, (0, 3, 1, 2))
return rgb_input
def yuv444_preprocess(img_path):
bgr_input = cv2.imread(img_path)
bgr_input = cv2.resize(bgr_input, (128,256), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
nv12_input = bgr2nv12(bgr_input)
yuv444 = nv12Toyuv444(nv12_input, (256,128))
yuv444_nhwc = yuv444[np.newaxis,:,:,:]
yuv444_nchw = np.transpose(yuv444_nhwc, (0, 3, 1, 2))
return yuv444_nhwc, yuv444_nchw
def main():
rgb_input = rgb_preprocess("test_img.jpg")
yuv444_nhwc, yuv444_nchw = yuv444_preprocess("test_img.jpg")
sess = HB_ONNXRuntime(model_file="./osnet_ain_x1_0.onnx")
input_names = sess.input_names
output_names = sess.output_names
input_info = {input_names[0]: rgb_input}
onnx_output = sess.run(output_names, input_info)
sess = HB_ONNXRuntime(model_file="./model_output/reid_original_float_model.onnx")
input_info = {input_names[0]: yuv444_nchw}
ori_output = sess.run(output_names, input_info)
sess = HB_ONNXRuntime(model_file="./model_output/reid_optimized_float_model.onnx")
input_info = {input_names[0]: yuv444_nchw}
opt_output = sess.run(output_names, input_info)
sess = HB_ONNXRuntime(model_file="./model_output/reid_calibrated_model.onnx")
input_info = {input_names[0]: yuv444_nchw}
calib_output = sess.run(output_names, input_info)
sess = HB_ONNXRuntime(model_file="./model_output/reid_quantized_model.onnx")
input_info = {input_names[0]: yuv444_nhwc}
quant_output = sess.run(output_names, input_info)
print("onnx_ori ", cosine_similarity(onnx_output[0].reshape(-1), ori_output[0].reshape(-1)))
print("onnx_opt ", cosine_similarity(onnx_output[0].reshape(-1), opt_output[0].reshape(-1)))
print("onnx_calib ", cosine_similarity(onnx_output[0].reshape(-1), calib_output[0].reshape(-1)))
print("onnx_quant ", cosine_similarity(onnx_output[0].reshape(-1), quant_output[0].reshape(-1)))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()PTQ 各阶段生成的 onnx 和原始 onnx 的相似度打印结果如下:
Plain
onnx_ori 0.99779123
onnx_opt 0.9977911
onnx_calib 0.99509
onnx_quant 0.9942628余弦相似度均>0.99,可进一步认为量化精度满足需求。
三、精度评测
3.1 评测结果
测试数据集:Market-1501-v15.09.15
1.距离度量方式:cosine
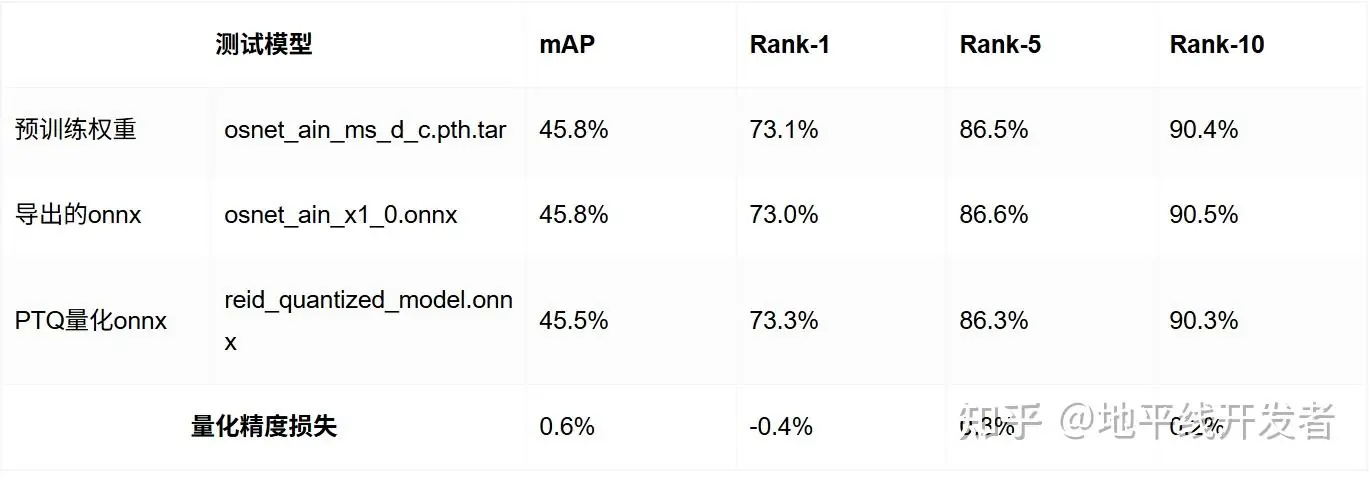
2.距离度量方式:euclidean
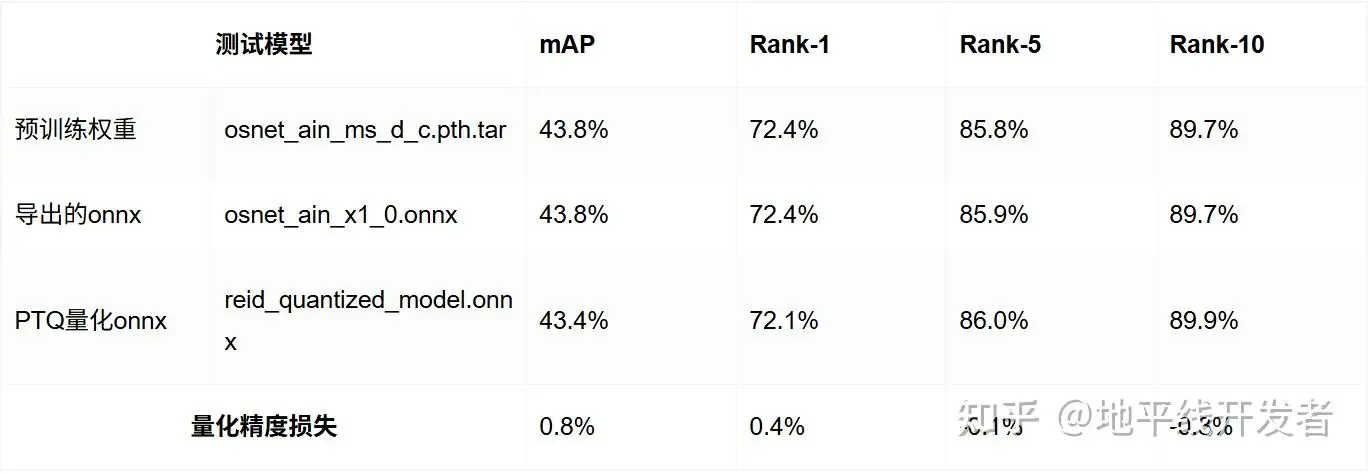
3.2 评测方法
3.2.1 预训练权重
在第一章配置好的官方运行环境中,使用代码仓库的现有方法对预训练权重做精度评测。
Plain
PYTHONPATH=. python3 scripts/main.py \
--config-file configs/im_osnet_ain_x1_0_softmax_256x128_amsgrad_cosine.yaml \
--root ./ \
model.load_weights ./osnet_ain_ms_d_c.pth.tar \
test.evaluate True3.2.2 导出的 onnx
需要基于第一章配置好的官方运行环境,额外安装 onnxruntime 和 tqdm 模块。
Plain
pip install onnxruntime
pip install tqdm测试时,datamanager 参数需要和 configs/im_osnet_ain_x1_0_softmax_256x128_amsgrad_cosine.yaml 对齐。
Plain
import cv2
import torch
import numpy as np
import onnxruntime as ort
from PIL import Image
from tqdm import tqdm
from torchreid.data import ImageDataManager
from torchreid.metrics import compute_distance_matrix, evaluate_rank
def extract_feature(img_path):
img = cv2.imread(img_path)
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
img = Image.fromarray(img)
img = transform(img)
img = img.unsqueeze(0).numpy()
feat = session.run(None, {input_name: img})[0]
return feat[0]
def extract_features(dataset):
features, pids, camids = [], [], []
for img_path, pid, camid, _ in tqdm(dataset, desc="Extracting features"):
feat = extract_feature(img_path)
features.append(feat)
pids.append(pid)
camids.append(camid)
return np.stack(features), np.array(pids), np.array(camids)
datamanager = ImageDataManager(
use_gpu=False,
root="./",
sources=['market1501'],
height=256,
width=128,
batch_size_train=64,
batch_size_test=1,
transforms=['random_flip', 'color_jitter']
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
query_loader = datamanager.test_loader['market1501']['query']
gallery_loader = datamanager.test_loader['market1501']['gallery']
query = query_loader.dataset.query
gallery = gallery_loader.dataset.gallery
transform = query_loader.dataset.transform
session = ort.InferenceSession('osnet_ain_x1_0.onnx', providers=['CPUExecutionProvider'])
input_name = session.get_inputs()[0].name
query_features, query_pids, query_camids = extract_features(query)
gallery_features, gallery_pids, gallery_camids = extract_features(gallery)
distmat = compute_distance_matrix(
torch.tensor(query_features),
torch.tensor(gallery_features),
metric='cosine'
).numpy()
cmc, mAP = evaluate_rank(
distmat, query_pids, gallery_pids, query_camids, gallery_camids, use_cython=False
)
print("\n=== Market1501 Evaluation Results (ONNX model) ===")
print(f"mAP : {mAP:.2%}")
print(f"Rank-1 : {cmc[0]:.2%}")
print(f"Rank-5 : {cmc[4]:.2%}")
print(f"Rank-10 : {cmc[9]:.2%}")3.2.3 PTQ 量化 onnx
需要基于第一章配置好的官方运行环境,额外安装 onnxruntime 和 tqdm 模块,并安装 horizon-nn/hmct 和 horizon-tc-ui。
Plain
pip install onnxruntime
pip install tqdm
pip install horizon_nn-1.1.0.post0.dev202506060002+840a0a685d053923c1a577c5032b7e0cfc84e6ac-cp310-cp310-linux_x86_64.whl --no-deps
pip install horizon_tc_ui-1.24.4-cp310-cp310-linux_x86_64.whl --no-deps测试时,datamanager 参数需要和 configs/im_osnet_ain_x1_0_softmax_256x128_amsgrad_cosine.yaml 对齐,且需要把输入数据处理成 yuv444 类型。
Plain
import cv2
import torch
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
from tqdm import tqdm
from horizon_tc_ui import HB_ONNXRuntime
from torchreid.data import ImageDataManager
from torchreid.metrics import compute_distance_matrix, evaluate_rank
def bgr2nv12(image):
image = image.astype(np.uint8)
height, width = image.shape[0], image.shape[1]
yuv420p = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2YUV_I420).reshape((height * width * 3 // 2, ))
y = yuv420p[:height * width]
uv_planar = yuv420p[height * width:].reshape((2, height * width // 4))
uv_packed = uv_planar.transpose((1, 0)).reshape((height * width // 2, ))
nv12 = np.zeros_like(yuv420p)
nv12[:height * width] = y
nv12[height * width:] = uv_packed
return nv12
def nv12Toyuv444(nv12, target_size):
height = target_size[0]
width = target_size[1]
nv12_data = nv12.flatten()
yuv444 = np.empty([height, width, 3], dtype=np.uint8)
yuv444[:, :, 0] = nv12_data[:width * height].reshape(height, width)
u = nv12_data[width * height::2].reshape(height // 2, width // 2)
yuv444[:, :, 1] = Image.fromarray(u).resize((width, height),resample=0)
v = nv12_data[width * height + 1::2].reshape(height // 2, width // 2)
yuv444[:, :, 2] = Image.fromarray(v).resize((width, height),resample=0)
return yuv444
def preprocess_nhwc(img_path):
bgr_input = cv2.imread(img_path)
bgr_input = cv2.resize(bgr_input, (128,256), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
nv12_input = bgr2nv12(bgr_input)
yuv444 = nv12Toyuv444(nv12_input, (256,128))
yuv444 = yuv444[np.newaxis,:,:,:]
return yuv444
def extract_feature(img_path):
for input_name in input_names:
feed_dict[input_name] = preprocess_nhwc(img_path)
feat = sess.run(output_names, feed_dict)
return feat[0]
def extract_features(dataset):
features, pids, camids = [], [], []
for img_path, pid, camid, _ in tqdm(dataset, desc="Extracting features"):
feat = extract_feature(img_path)
features.append(feat)
pids.append(pid)
camids.append(camid)
return np.stack(features), np.array(pids), np.array(camids)
if __name__ == "__main__":
datamanager = ImageDataManager(
use_gpu=False,
root="./",
sources=['market1501'],
height=256,
width=128,
batch_size_train=64,
batch_size_test=1,
transforms=['random_flip', 'color_jitter']
)
query_loader = datamanager.test_loader['market1501']['query']
gallery_loader = datamanager.test_loader['market1501']['gallery']
query = query_loader.dataset.query
gallery = gallery_loader.dataset.gallery
transform = query_loader.dataset.transform
sess = HB_ONNXRuntime(model_file='./model_output_inx2_cpu/reid_quantized_model.onnx')
input_names = [input.name for input in sess.get_inputs()]
output_names = [output.name for output in sess.get_outputs()]
feed_dict = dict()
query_features, query_pids, query_camids = extract_features(query)
gallery_features, gallery_pids, gallery_camids = extract_features(gallery)
distmat = compute_distance_matrix(
torch.tensor(query_features.squeeze(1)),
torch.tensor(gallery_features.squeeze(1)),
metric='cosine'
).numpy()
cmc, mAP = evaluate_rank(
distmat, query_pids, gallery_pids, query_camids, gallery_camids, use_cython=False
)
print("\n=== Market1501 Evaluation Results (ONNX model) ===")
print(f"mAP : {mAP:.2%}")
print(f"Rank-1 : {cmc[0]:.2%}")
print(f"Rank-5 : {cmc[4]:.2%}")
print(f"Rank-10 : {cmc[9]:.2%}")四、性能评测
4.1 评测结果
Plain
Running condition:
Thread number is: 1
Frame count is: 1000
Program run time: 51433.128000 ms
Perf result:
Frame totally latency is: 51417.804688 ms
Average latency is: 51.417805 ms
Frame rate is: 19.442722 FPS以 X5 为例,该模型的单线程推理延时为 51.4ms,对应 FPS 为 19.4
Latency 是指单流程推理模型所耗费的平均时间,重在表示在资源充足的情况下推理一帧的平均耗时,体现在上板运行是单核单线程统计。
FPS 是指多流程同时进行模型推理平均一秒推理的帧数,重在表示充分使用资源情况下模型的吞吐,体现在上板运行为单核多线程;统计方法是同时起多个线程进行模型推理,计算平均 1s 推理的总帧数。
Latency 与 FPS 的统计情景不同,Latency 为单流程(单核单线程)推理,FPS 为多流程(单核多线程)推理,因此推算不一致;若统计 FPS 时将流程(线程)数量设置为 1 ,则通过 Latency 推算 FPS 和测出的一致。
4.2 评测方法
可板端使用 hrt_model_exec 工具获取模型的实测性能数据,测试命令如下:
Plain
hrt_model_exec perf --model-file reid.bin --frame-count 1000 --thread-num 1