一、赛事背景
在当今科技日新月异的时代,人工智能(AI)技术正以前所未有的深度和广度渗透到科研领域,特别是在化学及药物研发中展现出了巨大潜力。精准预测分子性质有助于高效筛选出具有优异性能的候选药物。以PROTACs为例,它是一种三元复合物由目标蛋白配体、linker、E3连接酶配体组成,靶向降解目标蛋白质。本次大赛聚焦于运用先进的人工智能算法预测其降解效能,旨在激发参赛者创新思维,推动AI技术与化学生物学的深度融合,进一步提升药物研发效率与成功率,为人类健康事业贡献智慧力量。通过此次大赛,我们期待见证并孵化出更多精准、高效的分子性质预测模型,共同开启药物发现的新纪元。
二、赛事任务
选手根据提供的demo数据集,可以基于demo数据集进行数据增强、自行搜集数据等方式扩充数据集,并自行划分数据。运用深度学习、强化学习或更加优秀人工智能的方法预测PROTACs的降解能力,若DC50>100nM且Dmax<80% ,则视为降解能力较差(demo数据集中Label=0);若DC50<=100nM或Dmax>=80%,则视为降解能力好(demo数据集中Label=1)。
下面给出代码流程:
- 数据加载 :
- 使用
pandas库从Excel文件中加载训练和测试数据集。
- 使用
- 数据预处理 :
- 删除训练集中不需要的列('DC50 (nM)'和'Dmax (%)')。
- 检查测试集中的列,如果某列的非空值少于10个,则将该列从训练和测试集中删除。
- 将训练和测试集合并为一个数据集,以便进行统一处理。
- SMILES转换 :
- 使用
rdkit库将SMILES字符串转换为isomeric SMILES,并将其连接成一个字符串。
- 使用
- TF-IDF计算 :
- 使用
TfidfVectorizer计算SMILES字符串的TF-IDF值,并将其添加到数据集中。
- 使用
- 自然数编码 :
- 对所有对象类型的列进行自然数编码,即将每个唯一值映射到一个整数。
- 数据分割 :
- 将带有标签的数据分割为训练集和验证集,测试集保持不变(包含NaN标签)。
- 特征筛选 :
- 选择除'uuid'、'Label'和'smiles_list'之外的所有列作为特征。
- 网格搜索优化参数 :
- 使用
GridSearchCV进行参数优化,找到最佳的CatBoost分类器参数。
- 使用
- 模型训练和验证 :
- 使用最佳参数训练CatBoost分类器,并使用验证集进行早停,以防止过拟合。
- 预测和保存结果 :
- 使用训练好的模型对测试集进行预测,并将预测结果保存为CSV文件。
下面是具体代码的分享
python
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from catboost import CatBoostClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import f1_score
from rdkit import Chem
from rdkit.Chem import Descriptors
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
import os, gc, warnings
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV, KFold
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
# 数据加载
train_full = pd.read_excel(r'C:\\Users\\admin\\Desktop\\dataset-new\\dataset-new\\traindata-new.xlsx')
test = pd.read_excel(r'C:\\Users\\admin\\Desktop\\dataset-new\\dataset-new\\testdata-new.xlsx')
# 数据预处理
train_full = train_full.drop(['DC50 (nM)', 'Dmax (%)'], axis=1)
drop_cols = []
for f in test.columns:
if test[f].notnull().sum() < 10:
drop_cols.append(f)
train_full = train_full.drop(drop_cols, axis=1)
test = test.drop(drop_cols, axis=1)
data = pd.concat([train_full, test], axis=0, ignore_index=True)
cols = data.columns[2:] # 假设前两列是uuid和Label(或类似的列),这里需要根据实际情况调整
# SMILES转换
data['smiles_list'] = data['Smiles'].apply(lambda x: [Chem.MolToSmiles(mol, isomericSmiles=True) for mol in [Chem.MolFromSmiles(x)]])
data['smiles_list'] = data['smiles_list'].map(lambda x: ' '.join(x))
# TF-IDF计算
tfidf = TfidfVectorizer(max_df=0.9, min_df=1, sublinear_tf=True)
res = tfidf.fit_transform(data['smiles_list'])
tfidf_df = pd.DataFrame(res.toarray())
tfidf_df.columns = [f'smiles_tfidf_{i}' for i in range(tfidf_df.shape[1])]
data = pd.concat([data, tfidf_df], axis=1)
# 自然数编码
def label_encode(series):
unique = list(series.unique())
return series.map(dict(zip(unique, range(series.nunique()))))
for col in cols:
if data[col].dtype == 'object':
data[col] = label_encode(data[col])
labeled_data = data[data.Label.notnull()]
train, val = train_test_split(labeled_data, test_size=0.01, random_state=42, stratify=labeled_data['Label'])
# 外部验证集仍然是原始测试集,它包含NaN标签
test = data[data.Label.isnull()]
# 特征筛选
features = [f for f in train.columns if f not in ['uuid', 'Label', 'smiles_list']]
# 构建训练集和验证集
x_train = train[features]
y_train = train['Label'].astype(int)
x_val = val[features]
y_val = val['Label'].astype(int)
# 网格搜索优化参数
params = {
'learning_rate': [0.1],
'depth': [ 6],
'l2_leaf_reg': [1],
'bootstrap_type': ['Bernoulli'],
'od_type': ['Iter'],
'random_seed': [42]
}
model = CatBoostClassifier(iterations=20, eval_metric='AUC', verbose=1)
grid_search = GridSearchCV(model, params, cv=5, scoring='f1', verbose=1, n_jobs=-1)
grid_search.fit(x_train, y_train)
# 输出最佳参数
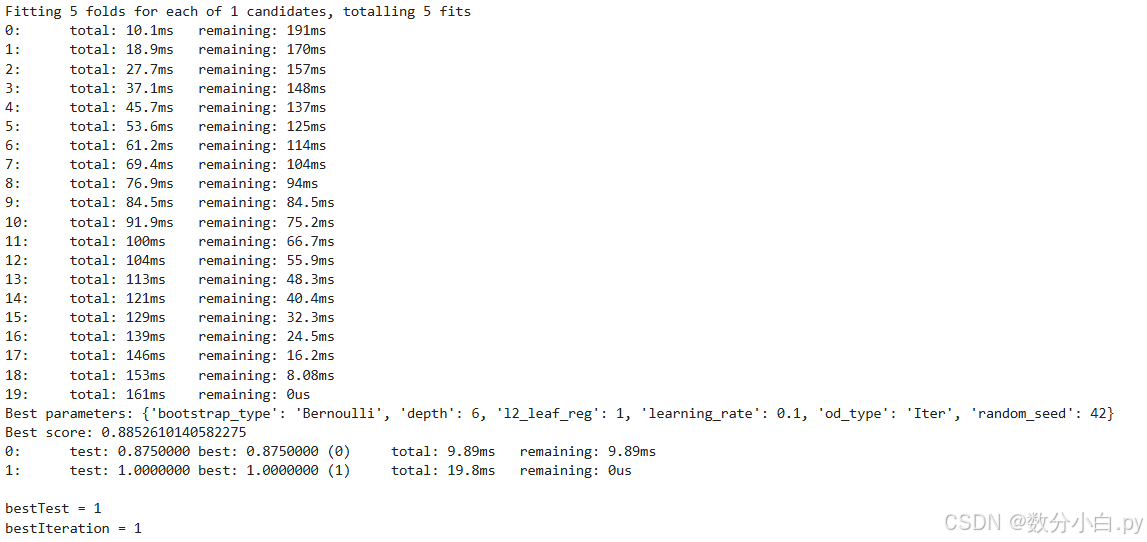
print("Best parameters:", grid_search.best_params_)
print("Best score:", grid_search.best_score_)
# 使用最佳参数训练模型,并使用验证集进行早停
best_model = CatBoostClassifier(**grid_search.best_params_, iterations=2, eval_metric='AUC', use_best_model=True, verbose=1)
best_model.fit(x_train, y_train, eval_set=[(x_val, y_val)])
# 预测
test_pred = best_model.predict_proba(test[features])[:, 1]
# 保存结果
pd.DataFrame({
'uuid': test['uuid'],
'Label': np.where(test_pred > 0.5, 1, 0)
}).to_csv('submit.csv', index=None)最后是运行结果: