项目简介:
小李哥将继续每天介绍一个基于亚马逊云科技AWS云计算平台的全球前沿AI技术解决方案,帮助大家快速了解国际上最热门的云计算平台亚马逊云科技AWS AI最佳实践,并应用到自己的日常工作里。
本次介绍的是如何在亚马逊云科技上利用SageMaker机器学习服务部署开源大模型,使用LangChain框架调用大模型生成回复,并利用RAG技术增强内容生成,再通过Streamlit框架开发用户界面回答用于关于用户关于特定文档的问题。本架构设计全部采用了云原生Serverless架构,提供可扩展和安全的AI解决方案。本方案的解决方案架构图如下:

方案所需基础知识
什么是 Amazon SageMaker?
Amazon SageMaker 是亚马逊云科技提供的一站式机器学习服务,旨在帮助开发者和数据科学家轻松构建、训练和部署机器学习模型。SageMaker 提供了从数据准备、模型训练到模型部署的全流程工具,使用户能够高效地在云端实现机器学习项目。
为什么利用 LangChain 框架调用大模型 API 生成回复?
LangChain 是一个强大的框架,旨在简化调用大型语言模型(如 GPT-3、Amazon Bedrock 上的模型等)API 的过程。通过 LangChain,开发者可以轻松地构建和管理复杂的对话逻辑,将多个 API 调用和自然语言处理(NLP)任务无缝集成到一起,从而实现智能、上下文丰富的对话体验。

利用 RAG 开发AI问答服务的好处
RAG(检索增强生成,Retrieval-Augmented Generation)是一种结合文档检索与生成式 AI 模型的技术,用于构建强大的问答系统。通过将文档检索与生成模型结合,RAG 可以在提供实时、准确的回答时,确保回复的内容基于最新的文档信息。
提高回答准确性:
RAG 结合检索和生成模型,使系统能够从大量文档中提取相关信息,并生成符合上下文的准确答案,确保回答内容的可靠性和权威性。
支持实时更新:
RAG 系统可以动态检索和生成答案,确保用户获得基于最新信息的回复,特别适用于内容频繁更新的领域。
增强用户体验:
通过使用 LangChain 调用大模型 API 和 RAG 技术,问答服务不仅能提供流畅的自然语言交互,还能回答复杂、多样的问题,显著提升用户体验。
降低开发复杂性:
LangChain 框架简化了与大模型的集成,RAG 技术则优化了信息检索和答案生成过程,二者结合有效降低了开发智能问答系统的复杂性。
本方案包括的内容
1. 利用Amazon SageMaker部署一个Flan-T5大语言模型
2. 通过LangChain框架调用大语言模型
3. 在SageMaker Studio上利用RAG技术开发一个基于文档内容回答问题的GenAI应用
4. 开发和部署Streamlit框架开发的网页应用
项目搭建具体步骤:
- 登录亚马逊云科技控制台,进入Studio功能,点击Open Studio进入Studio,用于在Jupyter Notebook中运行大模型代码。

2.点击Studio Classic,再点击Open进入Jupyter Notebook

- 点击主页中的JumpStart功能快速创建大语言模型

- 搜索并选择"Falcon 7B Instruct BF16"大模型

- 选择部署大模型的计算资源类型为"ml.g5.4xlarge",再点击开始部署

- 我们创建一个requirements.txt文件,复制以下内容用于安装必要依赖。
XML
boto3==1.34.37
langchain==0.0.276
numpy==1.23.5
pandas==1.5.3
scikit_learn==1.2.1
seaborn==0.12.2
sentence-transformers
faiss-gpu-cu11- 创建一个Jupyter Notebook ipynb文件,首先运行以下代码指定模型id,并安装必要依赖。
XML
endpoint_name = "jumpstart-dft-hf-llm-falcon-7b-instruct-bf16"
!pip install --upgrade pip
!pip install --upgrade --no-cache --force-reinstall -r requirements.txt- 运行以下代码,导入必要依赖
python
import boto3, json
import pandas as pd
import langchain
from langchain.embeddings import SagemakerEndpointEmbeddings
from langchain.llms.sagemaker_endpoint import ContentHandlerBase
from langchain.chains import RetrievalQA
from langchain.document_loaders import TextLoader
from langchain.indexes import VectorstoreIndexCreator
from langchain.vectorstores import Chroma, AtlasDB, FAISS
from langchain.text_splitter import CharacterTextSplitter
from langchain import PromptTemplate
from langchain.chains.question_answering import load_qa_chain
from langchain.document_loaders.csv_loader import CSVLoader
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
from langchain.embeddings import HuggingFaceEmbeddings- 接下来我们定义两个函数"query_endpoint_with_json_payload"和"parse_response_model",用于调用大模型和提取生成回复中的内容,并配置模型区域、节点名、回复提取函数、提示词。
python
def query_endpoint_with_json_payload(encoded_json, endpoint_name, content_type="application/json"):
client = boto3.client("runtime.sagemaker")
response = client.invoke_endpoint(
EndpointName=endpoint_name, ContentType=content_type, Body=encoded_json
)
return response
# parse the Sagemaker Endpoint response to the user query
def parse_response_model(query_response):
model_predictions = json.loads(query_response["Body"].read())
return [gen["generated_text"] for gen in model_predictions]
_MODEL_CONFIG_ = {
"jumpstart-dft-hf-llm-falcon-7b-instruct-bf16" : {
"aws_region": "us-east-1",
"endpoint_name": endpoint_name,
"parse_function": parse_response_model,
"prompt": """{context}\n\nGiven the above context, answer the following question:\n{question}\nAnswer: """,
},
}- 定义模型参数,定义模型输入、输出请求格式,并按该格式调用SageMaker上部署的Falcon模型。
python
import json
from langchain.llms.sagemaker_endpoint import LLMContentHandler, SagemakerEndpoint
parameters ={
"max_new_tokens": 100,
"num_return_sequences": 1,
"top_k": 50,
"top_p": 0.95,
"do_sample": False,
"return_full_text": False,
"temperature": 0.2
}
class ContentHandler(LLMContentHandler):
content_type = "application/json"
accepts = "application/json"
def transform_input(self, prompt: str, model_kwargs={}) -> bytes:
input_str = json.dumps({"inputs": prompt, "parameters": model_kwargs})
return input_str.encode("utf-8")
def transform_output(self, output: bytes) -> str:
response_json = json.loads(output.read().decode("utf-8"))
return response_json[0]["generated_text"]
content_handler = ContentHandler()
sm_llm_falcon_instruct = SagemakerEndpoint(
endpoint_name=_MODEL_CONFIG_["jumpstart-dft-hf-llm-falcon-7b-instruct-bf16"]["endpoint_name"],
region_name=_MODEL_CONFIG_["jumpstart-dft-hf-llm-falcon-7b-instruct-bf16"]["aws_region"],
model_kwargs=parameters,
content_handler=content_handler,
)- 向大模型提问示例问题,可以得到常规回复。
python
sm_llm_falcon_instruct("Which day comes after Friday?")
- 初始化一个HuggingFace向量模型
python
sm_llm_embeddings = HuggingFaceEmbeddings()- 创建一个关于Amazon SageMaker产品问题与回复的csv文件,再将该csv文件导入Pandas DataFrame,只提取答案后再存入到processd.csv文件中。
python
s3_path = "s3://jumpstart-cache-prod-us-east-2/training-datasets/Amazon_SageMaker_FAQs/Amazon_SageMaker_FAQs.csv"
!mkdir -p rag_data
!aws s3 cp $s3_path rag_data/Amazon_SageMaker_FAQs.csv
df_knowledge = pd.read_csv("rag_data/Amazon_SageMaker_FAQs.csv", header=None, usecols=[1], names=["Answer"])
df_knowledge.to_csv("rag_data/processed.csv", header=False, index=False)- 利用LangChain读取csv文件
python
loader = CSVLoader(file_path="rag_data/processed.csv")
documents = loader.load()- 设置llm大模型模型回复参数
python
sm_llm_falcon_instruct.model_kwargs = {
"max_new_tokens": 50,
"num_return_sequences": 1,
"top_k": 50,
"top_p": 0.95,
"do_sample": False,
"return_full_text": False,
"temperature": 0.1
}- 利用LangChain将文档进行分割,再使用
FAISS(Facebook AI Similarity Search)通过HuggingFace向量模型将文档转为向量并创建索引。
python
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=100, chunk_overlap=5)
texts = text_splitter.split_documents(documents)
sm_llm_embeddings
docsearch = FAISS.from_documents(texts, sm_llm_embeddings)- 通过问题对文档内容进行语义搜索得到回复,问题为:"如何为Amazon SageMaker上的托管临时训练选择实例类型"。
python
question = "Which instances can I use with managed spot training in Amazon SageMaker?"
docs = docsearch.similarity_search(question, k=3)
docs得到相关回复和所在文档元数据信息

- 下面我们通过提示词模板构建问答链,再基于问题调用知识库进行语义搜索得到回复
python
prompt_template = """{context}\n\nGiven the above context, answer the following question:\n{question}\n\nAnswer:"""
PROMPT = PromptTemplate(template=prompt_template, input_variables=["context", "question"])
sm_llm_falcon_instruct.model_kwargs = {
"max_new_tokens": 50,
"num_return_sequences": 1,
"top_k": 50,
"top_p": 0.95,
"do_sample": False,
"return_full_text": True,
"temperature": 0.1,
}
chain = load_qa_chain(llm=sm_llm_falcon_instruct, prompt=PROMPT)
result = chain({"input_documents": docs, "question": question}, return_only_outputs=True)["output_text"]
print(result)我们可以看到LangChain问答链根据我们定义的提示词中的格式得到了正确回复。

- 我们再创建一个新的Python函数"main.py",复制以下代码。这个文件包括了我们刚刚通过LangChain文本向量化、利用RAG与大模型与知识库API交互全部完整代码。同时创建了一个streamlit服务器与用户在UI进行交互。
python
# From Cell 2 with small modifications
import os
import streamlit as st
import json
import boto3
import logging
from langchain.chains import RetrievalQA
from langchain.indexes import VectorstoreIndexCreator
from langchain_community.vectorstores import Chroma, FAISS
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain_community.embeddings import SagemakerEndpointEmbeddings
from langchain_community.embeddings.sagemaker_endpoint import EmbeddingsContentHandler
from langchain_community.llms.sagemaker_endpoint import LLMContentHandler, SagemakerEndpoint
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter, CharacterTextSplitter
from langchain_community.embeddings import HuggingFaceEmbeddings
# Set up logging
logger = logging.getLogger()
logger.setLevel(logging.INFO)
# From Cell 5
sm_llm_embeddings = HuggingFaceEmbeddings()
# From Cell 4 and 6
class ContentHandler(LLMContentHandler):
content_type = "application/json"
accepts = "application/json"
def transform_input(self, prompt: str, model_kwargs={}) -> bytes:
input_str = json.dumps({"inputs": prompt, "parameters": model_kwargs})
return input_str.encode("utf-8")
def transform_output(self, output: bytes) -> str:
response_json = json.loads(output.read().decode("utf-8"))
return response_json[0]["generated_text"]
def query_endpoint_with_json_payload(encoded_json, endpoint_name, content_type="application/json"):
client = boto3.client("runtime.sagemaker")
response = client.invoke_endpoint(
EndpointName=endpoint_name, ContentType=content_type, Body=encoded_json
)
return response
def parse_response_model(query_response):
model_predictions = json.loads(query_response["Body"].read())
return [gen["generated_text"] for gen in model_predictions]
# The following replaces cells 8 and 9
# loading PDF, DOCX and TXT files as LangChain Documents
def load_document(file):
import os
name, extension = os.path.splitext(file)
if extension == '.pdf':
from langchain.document_loaders import PyPDFLoader
print(f'Loading {file}')
loader = PyPDFLoader(file)
elif extension == '.docx':
from langchain.document_loaders import Docx2txtLoader
print(f'Loading {file}')
loader = Docx2txtLoader(file)
elif extension == '.txt':
from langchain.document_loaders import TextLoader
loader = TextLoader(file)
elif extension == '.csv':
from langchain_community.document_loaders.csv_loader import CSVLoader
loader = CSVLoader(file)
else:
print('Document format is not supported!')
return None
document = loader.load()
return document
# From Cell 11
def split_text(document):
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=100, chunk_overlap=5)
texts = text_splitter.split_documents(document)
return texts
# Cell 11
def create_embeddings(texts):
docsearch = FAISS.from_documents(texts, sm_llm_embeddings)
return docsearch
# Not in notebook but needed for streamlite application
def clear_history():
if 'history' in st.session_state:
del st.session_state['history']
# Application build from notebook - see individual parts
def ask_and_get_answer(question, documents):
from langchain_community.llms.sagemaker_endpoint import LLMContentHandler, SagemakerEndpoint
from langchain.chains.question_answering import load_qa_chain
# From Cell 13
docs = documents.similarity_search(question, k=3)
# From Cell 14
prompt_template = """You are an AI assistant for answering questions.
Refrane from providing any information that is not in the provide context.
If there is not an answer in the provided context respond with "I don't know."
{context}
Question: {question}
Answer:"""
parameters ={
"max_new_tokens": 100,
"num_return_sequences": 1,
"top_k": 50,
"top_p": 0.95,
"do_sample": False,
"return_full_text": False,
"temperature": 0.2
}
# From Cell 4
_MODEL_CONFIG_ = {
"jumpstart-dft-hf-llm-falcon-7b-instruct-bf16" : {
"aws_region": "us-east-1",
"endpoint_name": "jumpstart-dft-hf-llm-falcon-7b-instruct-bf16",
"parse_function": parse_response_model,
"prompt": prompt_template,
},
}
# From Cell 6
content_handler = ContentHandler()
sm_llm_falcon_instruct = SagemakerEndpoint(
endpoint_name=_MODEL_CONFIG_["jumpstart-dft-hf-llm-falcon-7b-instruct-bf16"]["endpoint_name"],
region_name=_MODEL_CONFIG_["jumpstart-dft-hf-llm-falcon-7b-instruct-bf16"]["aws_region"],
model_kwargs=parameters,
content_handler=content_handler,
)
# From Cell 10
sm_llm_falcon_instruct.model_kwargs = {
"max_new_tokens": 50,
"num_return_sequences": 1,
"top_k": 50,
"top_p": 0.95,
"do_sample": False,
"return_full_text": True,
"temperature": 0.1,
}
# From Cell 14 and 15
PROMPT = PromptTemplate(template=prompt_template, input_variables=["context", "question"])
chain = load_qa_chain(llm=sm_llm_falcon_instruct, prompt=PROMPT)
answer = chain({"input_documents": docs, "question": question}, return_only_outputs=True)["output_text"]
return answer
# Code required for the Streamlite app
if __name__ == "__main__":
import os
st.subheader('Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)')
with st.sidebar:
# file uploader widget
uploaded_file = st.file_uploader('Upload context file:', type=['pdf', 'docx', 'txt', 'csv'])
# add data button widget
add_data = st.button('Process Context File', on_click=clear_history)
if uploaded_file and add_data: # if the user browsed a file
with st.spinner('Reading, chunking and embedding file ... Please Wait'):
# writing the file from RAM to the current directory on disk
bytes_data = uploaded_file.read()
file_name = os.path.join('./', uploaded_file.name)
with open(file_name, 'wb') as f:
f.write(bytes_data)
document = load_document(file_name)
texts = split_text(document)
# creating the embeddings and returning FAISS vector store.
vector_store = create_embeddings(texts)
# saving the vector store in the streamlit session state (to be persistent between reruns)
st.session_state.vs = vector_store
st.success('File processing completed successfully! You can now ask questions.')
# user's question text input widget
question = st.text_input('Ask a question about the content of your file:')
if question: # if the user entered a question and hit enter
question = f"{question}"
if 'vs' in st.session_state: # if there's the vector store (user uploaded, split and embedded a file)
vector_store = st.session_state.vs
# st.write(f'k: {k}')
response = ask_and_get_answer(question, vector_store)
answer = response.partition("Answer:")[2]
# text area widget for the LLM answer
st.text_area('LLM Answer: ', value=answer, height=400)
st.divider()
# if there's no chat history in the session state, create it
if 'history' not in st.session_state:
st.session_state.history = ''
# the current question and answer
value = f'Q: {question} \nA: {answer}'
st.session_state.history = f'{value} \n {"-" * 100} \n {st.session_state.history}'
h = st.session_state.history
# text area widget for the chat history
st.text_area(label='Chat History', value=h, key='history')- 我们通过以下命令启动streamlit服务器。启动后会返回服务器的URL地址,复制该地址在浏览器中打开。
bash
streamlit run main.py --server.enableXsrfProtection false- 浏览器中打开后,我们进入了UI界面,点击"Browse files"上传文档,上传刚刚我们从Amazon Sagemaker产品常见问题csv文件中提取的问题csv文件,"processed.csv"。

- 上传成功后,我们再问题界面提问"什么是SageMaker",就可以得到利用RAG基于知识库中文档得到的相关回答。
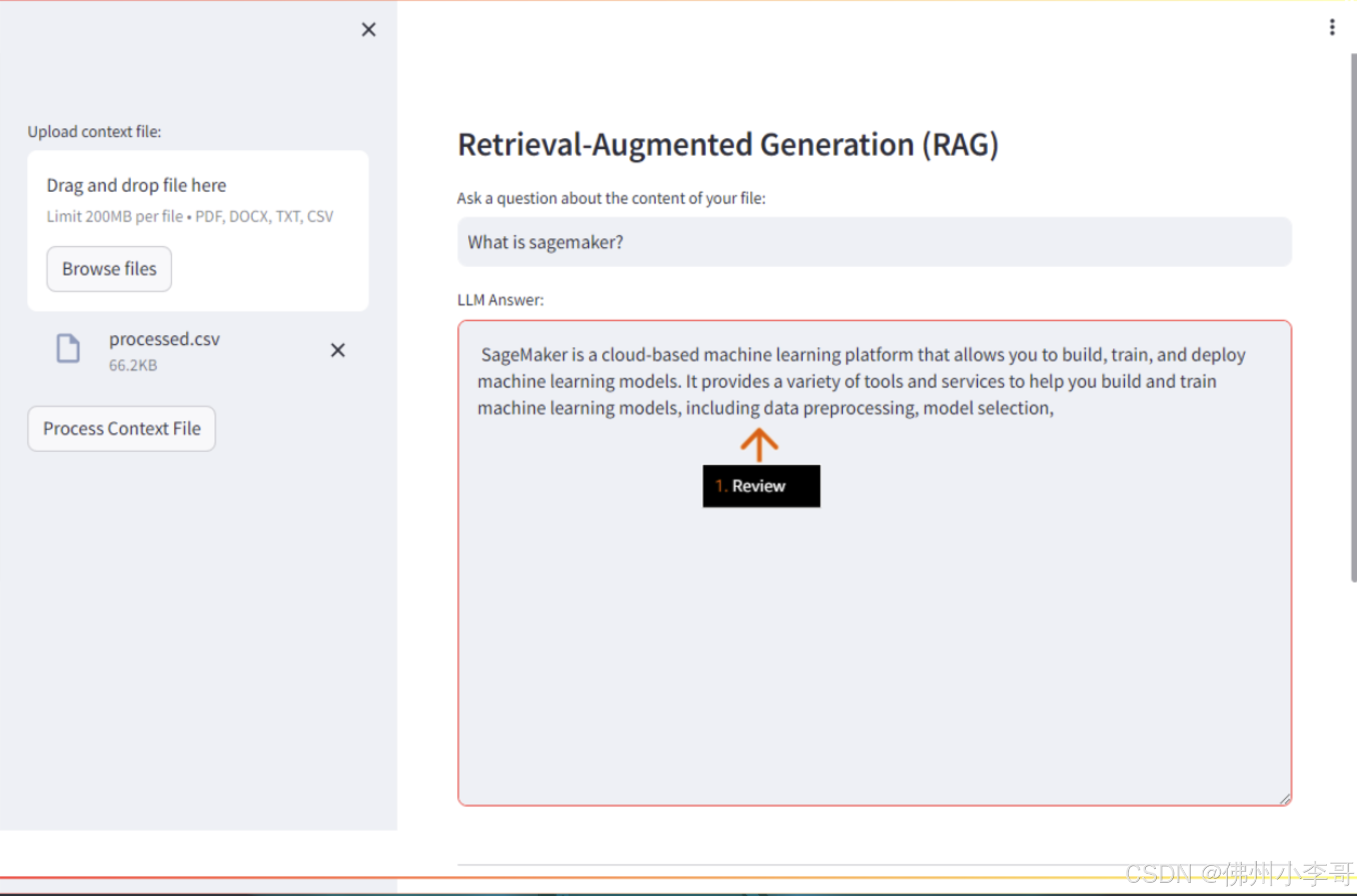
以上就是在亚马逊云科技上利用亚马逊云科技上利用部署开源大模型,并利用RAG技术和Streamlit开发GenAI文档问答服务的全部步骤。欢迎大家未来与我一起,未来获取更多国际前沿的生成式AI开发方案。